COVID-19 Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D03KAY
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Darunavir + ritonavir + oseltamivir + hydroxychloroquine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Prezista + norvir + rseltamivir + oxichloroquine
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Combination drug
|
|||
| Indication | Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) | Phase 3 | [1] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiviral Agents
|
|||
| Structure |
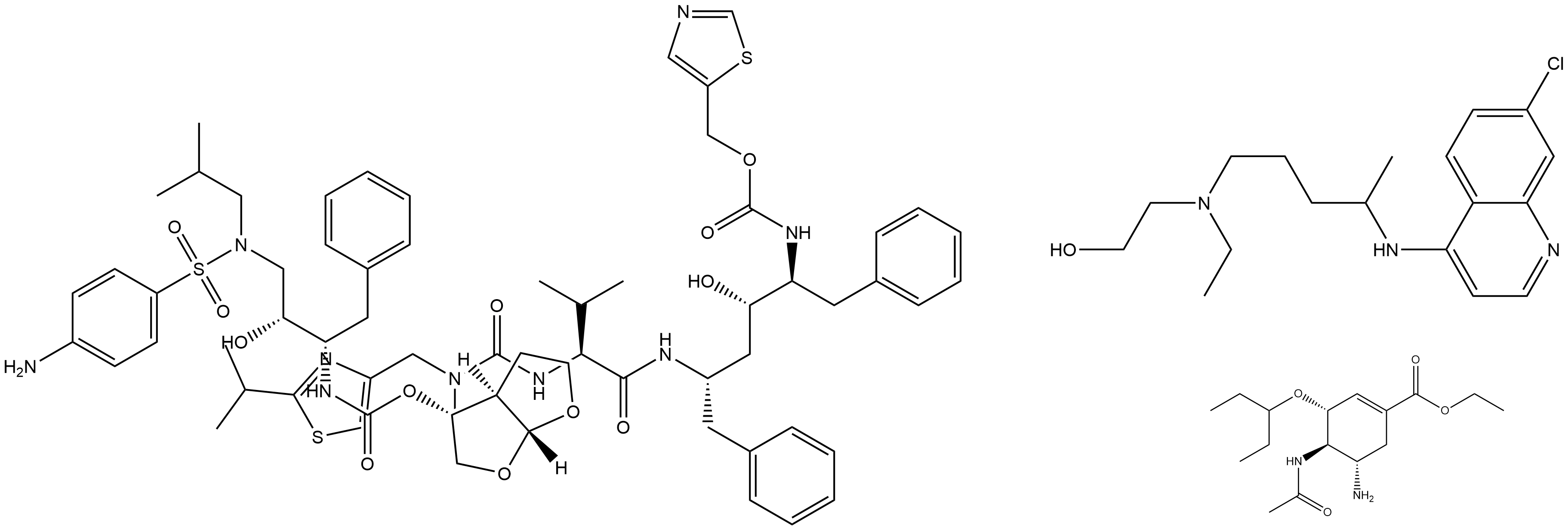 |
Download2D MOL
|
||
| Target | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | HUMAN glycosylation of host receptor (GHR) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [2], [3] |
| The mechanisms of hydroxychloroquine-induced anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects include inhibition of pH-dependent viral fusion/replication and prevention of viral envelope glycoprotein as well as host receptor protein glycosylation. | ||||
| HUMAN pH-dependent viral fusion/replication (pH-DVF/R) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [2], [3] | |
| The mechanisms of hydroxychloroquine-induced anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects include inhibition of pH-dependent viral fusion/replication and prevention of viral envelope glycoprotein as well as host receptor protein glycosylation. | ||||
| HUMAN toll-like receptor 7/9 signalling pathway (TLR7/9 pathway) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [4], [5] | |
| Hydroxychloroquine interferes with TLR7 and TLR9 ligand binding and TLR signalling (through lysosomal inhibition and reduced MyD88 signalling), which inhibits TLR-mediated cell activation and cytokine production. Evidence demonstrates that hydroxychloroquine has antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndromecoronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2) in vitro and in small, poorly controlled or uncontrolled clinical studies. | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04303299) Various Combination of Protease Inhibitors, Oseltamivir, Favipiravir, and Hydroxychloroquine for Treatment of COVID-19 : A Randomized Control Trial | |||
| 2 | Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020 Mar;30(3):269-271. | |||
| 3 | Insights from nanomedicine into chloroquine efficacy against COVID-19. Nat Nanotechnol. 2020 Apr;15(4):247-249. | |||
| 4 | Mechanisms of action of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: implications for rheumatology. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;16(3):155-166. | |||
| 5 | Use of Hydroxychloroquine and Chloroquine During the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Every Clinician Should Know. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 31. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

