COVID-19 Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0D5FU
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Baricitinib
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050); Baricitinib [USAN:INN]; C16H17N7O2S; INCB 028050; INCB-028050; INCB028050; ISP4442I3Y; J-503551; LY-3009104; LY3009104; Olumiant (TN); UNII-ISP4442I3Y; olumiant
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) | Phase 3 | [1] | |
| Other Indication | Rheumatoid arthritis | Approved | [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiviral Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Incyte/Eli Lilly
|
|||
| Structure |
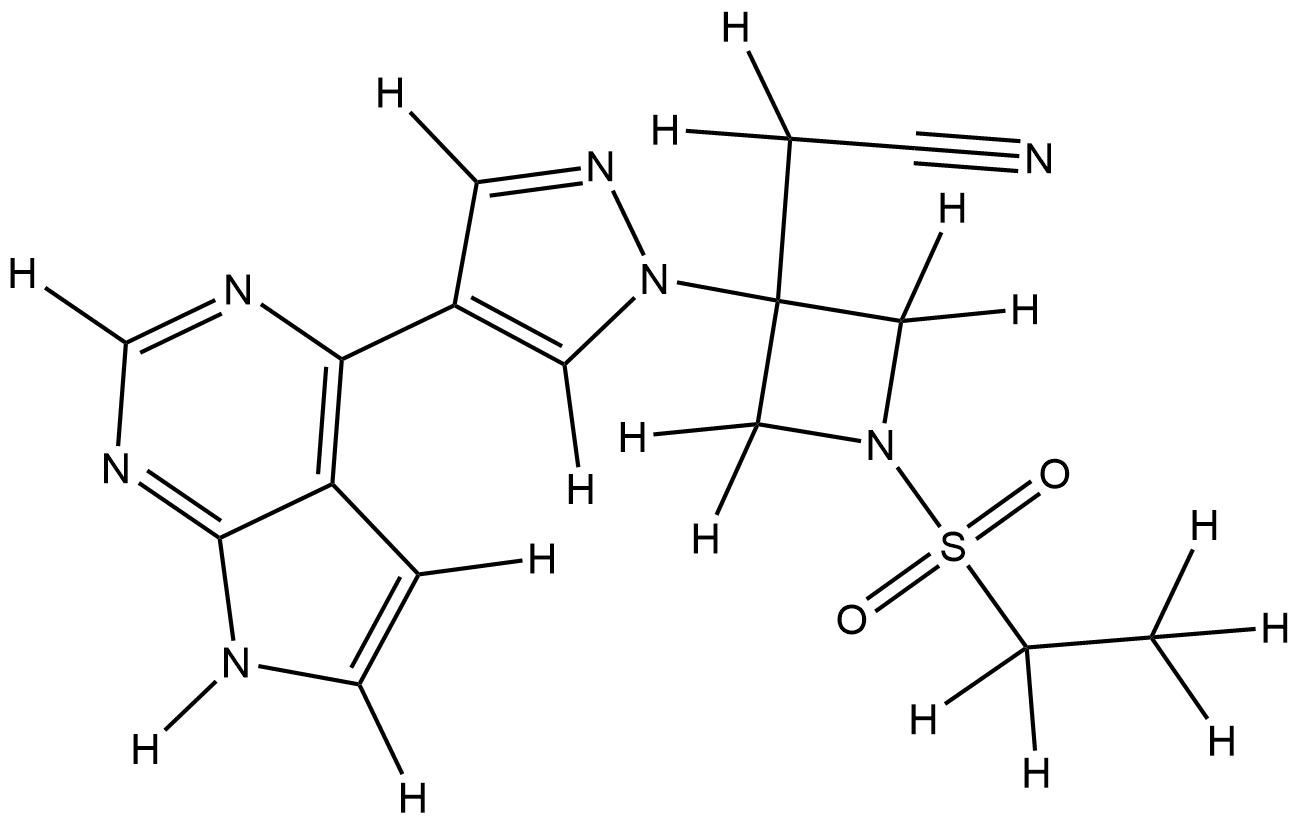 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C16H17N7O2S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCS(=O)(=O)N1CC(C1)(CC#N)N2C=C(C=N2)C3=C4C=CNC4=NC=N3
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C16H17N7O2S/c1-2-26(24,25)22-9-16(10-22,4-5-17)23-8-12(7-21-23)14-13-3-6-18-15(13)20-11-19-14/h3,6-8,11H,2,4,9-10H2,1H3,(H,18,19,20)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
XUZMWHLSFXCVMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 1187594-09-7
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
85205106, 89960290, 103932354, 135313591, 136946415, 137856279, 144115683, 152258684, 160647521, 160703522, 162009736, 162011992, 162108950, 163312339, 164045123, 164194014, 170501894, 172087008, 172918187, 174006690, 174526483, 176250838, 185979207, 189561494, 198946894, 203105586, 208265518, 215785530, 223366123, 223375538, 223630418, 223705259, 224310310, 227140190, 244162815, 249733389, 249814474, 249816401, 252110203, 252160600, 252214958, 252443897, 252451786, 252553656
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:95341
|
|||
| Target | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | HUMAN adaptor-associated kinase 1 (AAK1) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [3], [4] |
| Baricitinib was found to inhibit the AP2-associated kinase 1 (AAK1) and the cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK), members of the numb-associated kinase (NAK) family involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Therefore, baricitinib can impair SARS-CoV-2 endocytosis and the early stages of virus spread, while also inhibiting the signaling of several cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of viral pneumonia and the emergence of cytokine storm. | ||||
| HUMAN cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [3], [4] | |
| Baricitinib was found to inhibit the AP2-associated kinase 1 (AAK1) and the cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK), members of the numb-associated kinase (NAK) family involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Therefore, baricitinib can impair SARS-CoV-2 endocytosis and the early stages of virus spread, while also inhibiting the signaling of several cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of viral pneumonia and the emergence of cytokine storm. | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04345289) Efficacy and Safety of Novel Treatment Options for Adults With COVID-19 Pneumonia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||
| 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| 3 | Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease. Lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395(10223):e30-e31. | |||
| 4 | COVID-19: combining antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatments. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;20(4):400-402. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

