Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D03KXY
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNAP001503
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Doxifluridine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Furtulon (TN)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z; ICD-10: C76-C80; ICD-9: 140-229] | Approved | [1] | |
| Structure |
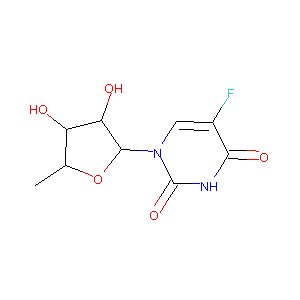 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C9H11FN2O5
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1C(C(C(O1)N2C=C(C(=O)NC2=O)F)O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C9H11FN2O5/c1-3-5(13)6(14)8(17-3)12-2-4(10)7(15)11-9(12)16/h2-3,5-6,8,13-14H,1H3,(H,11,15,16)/t3-,5-,6-,8-/m1/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
ZWAOHEXOSAUJHY-ZIYNGMLESA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 3094-09-5
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
583128, 811761, 7848372, 8163712, 12013031, 15196585, 15221079, 17405100, 24278444, 24878211, 29215154, 29286008, 47275540, 48415926, 50061740, 50106323, 50106324, 50296037, 53777643, 56312499, 56312502, 56320807, 56322615, 56463254, 57330035, 66571155, 76715693, 91699170, 92303781, 92309058, 93576659, 103321248, 104023314, 104179036, 104344868, 117393919, 118855339, 121361359, 124749791, 124799815, 127301313, 127301314, 127301315, 127301316, 127301317, 127301318, 127301319, 127301320, 127301321, 127301322
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:31521
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-fluorouracil | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity (intestinal tract toxicity) | |||
| Description | Doxifluridine can be metabolized to 5-fluorouracil by Escherichia coli, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity (intestinal tract toxicity). | |||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 2 | Personalized Mapping of Drug Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome. Cell. 2020 Jun 25;181(7):1661-1679.e22. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

