Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D06OMK
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000162
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Tacrolimus
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Advagraf; Fujimycin; Graceptor; Modigraf; Prograf; Protopic; Protopy; Tacarolimus; Tsukubaenolide; Tacrolimus anhydrous; FK 506; FK5; FK506; FR 900506; FR900506; K506; L 679934; Advagraf (TN); FR-900506; Fk-506; L-679934; LCP-Tacro; Prograf (TN); Protopic (TN); Tacrolimus (INN); Tacrolimus (Prograf); Tacrolimus (anhydrous); (-)-FK 506; 15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(23H)-tetrone; 8-DEETHYL-8-[BUT-3-ENYL]-ASCOMYCIN
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Organ transplant rejection [ICD-11: NE84; ICD-9: 279.5, 996] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Ocular allergy [ICD-11: 4A81] | Phase 3 | [1], [2] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Immunosuppressive Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Fujisawa; Sucampo
|
|||
| Structure |
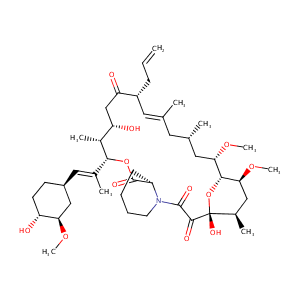 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C44H69NO12
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1CC(C2C(CC(C(O2)(C(=O)C(=O)N3CCCCC3C(=O)OC(C(C(CC(=O)C(C=C(C1)C)CC=C)O)C)C(=CC4CCC(C(C4)OC)O)C)O)C)OC)OC
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C44H69NO12/c1-10-13-31-19-25(2)18-26(3)20-37(54-8)40-38(55-9)22-28(5)44(52,57-40)41(49)42(50)45-17-12-11-14-32(45)43(51)56-39(29(6)34(47)24-35(31)48)27(4)21-30-15-16-33(46)36(23-30)53-7/h10,19,21,26,28-34,36-40,46-47,52H,1,11-18,20,22-24H2,2-9H3/b25-19+,27-21+/t26-,28+,29+,30-,31+,32-,33+,34-,36+,37-,38-,39+,40+,44+/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
QJJXYPPXXYFBGM-LFZNUXCKSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 104987-11-3
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
4572, 832905, 842004, 7887491, 7980719, 8150098, 10299743, 12013904, 14815954, 14889261, 24841759, 26703416, 26705532, 26705535, 26713140, 26715494, 26756858, 29216422, 36888289, 46506004, 47574395, 48020022, 50111459, 50111460, 53788265, 57404698, 74380484, 76558282, 85788970, 91011629, 92308089, 92310166, 92711966, 96025241, 99301078, 99302128, 99436940, 103164549, 103939344, 104178757, 104222107, 104634734, 109693101, 118048657, 119525750, 124757870, 124766122, 124892446, 124892447, 124892448
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:61049
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D02105 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
D11AH01; L04AD02
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=109581933
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Alistipes indistinctus DSM22520
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Alistipes indistinctus DSM22520 (log2FC = -0.808; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697 (log2FC = -0.841; p = 0.004). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 (log2FC = -0.82; p = 0.046). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.753; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.398; p = 0.016). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.765; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.463; p = 0.011). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.774; p = 0.012). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503 (log2FC = -0.372; p = 0.009). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184 (log2FC = -0.357; p = 0.039). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eggerthellales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eggerthella lenta ATCC 25559
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Eggerthella lenta ATCC 25559 (log2FC = -0.827; p = 0.026). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli BW25113
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Escherichia coli BW25113 (log2FC = -0.971; p = 0.004). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Providencia alcalifaciens DSM 30120
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Providencia alcalifaciens DSM 30120 (log2FC = -1.051; p = 0.034). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Erysipelotrichales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium ramosum DSM 1402
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Clostridium ramosum DSM 1402 (log2FC = -0.822; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989 (log2FC = -0.964; p = 0.045). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -1.928; p = 0.007). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia luti DSM 14534
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Blautia luti DSM 14534 (log2FC = -0.643; p = 0.03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium difficile 120
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Clostridium difficile 120 (log2FC = -0.901; p = 0.033). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -2.801; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sporogenes ATCC 15579
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Clostridium sporogenes ATCC 15579 (log2FC = -1.451; p = 0.022). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | M1 (demethylbutyryl metabolite) | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Decrease activity | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized to M1 (demethylbutyryl metabolite) by Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which results in the decrease of the drug's activity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia intestinalis L1-82
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Roseburia intestinalis L1-82 (log2FC = -1.211; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149 (log2FC = -0.504; p = 0.038). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Verrucomicrobiales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835 (log2FC = -1.672; p = 0.004). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Victivallales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Victivallis vadensis ATCC BAA-548
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Tacrolimus can be metabolized by Victivallis vadensis ATCC BAA-548 (log2FC = -1.019; p = 0.005). | |||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6784). | |||
| REF 2 | New developments in immunosuppressive therapy for heart transplantation. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):1-21. | |||
| REF 3 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 4 | Commensal Gut Bacteria Convert the Immunosuppressant Tacrolimus to Less Potent Metabolites. Drug Metab Dispos. 2019 Mar;47(3):194-202. | |||
| REF 5 | Emerging drugs for ocular allergy. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2005 Aug;10(3):505-20. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

