Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0D2VS
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000625
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Exemestane
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Aromasil; Aromasin; Aromasine; EXE; Exemestance; Exemestano; Exemestanum; Nikidess; Pfizer brand of exemestane; Curator_000009; Fce 24304; Aromasin (TN); Aromasin, Exemestane; Exemestano [INN-Spanish]; Exemestanum [INN-Latin]; FCE-24304; PNU-155971; Exemestane [USAN:INN:BAN]; Exemestane (JAN/USP/INN); (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S)-10,13-dimethyl-6-methylidene-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-dione; 6-Methylenandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione; 6-Methyleneandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione; 6-methylideneandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Hormonally-responsive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C65] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
|||
| Structure |
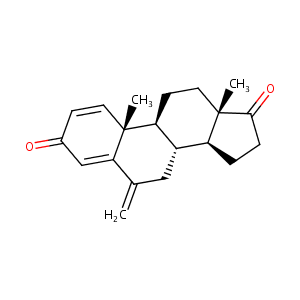 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C20H24O2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC12CCC3C(C1CCC2=O)CC(=C)C4=CC(=O)C=CC34C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C20H24O2/c1-12-10-14-15-4-5-18(22)20(15,3)9-7-16(14)19(2)8-6-13(21)11-17(12)19/h6,8,11,14-16H,1,4-5,7,9-10H2,2-3H3/t14-,15-,16-,19+,20-/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
BFYIZQONLCFLEV-DAELLWKTSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 107868-30-4
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
10362, 532118, 7848026, 7978495, 8186720, 11528610, 12014009, 14898201, 14922734, 26719821, 43117629, 46386592, 46508243, 47734117, 48415996, 49681613, 53787997, 57313998, 71825450, 76229105, 92308414, 92712532, 99436932, 99437373, 103770357, 104320132, 117585772, 118043418, 119525530, 124658984, 124757072, 125163876, 126608810, 126630089, 126666059, 127510064, 134337915, 135260226, 135724569, 136367947, 136903807, 136946607, 137005560, 137230761, 141857635, 144115969, 144205052, 151979532, 152034580, 152164568
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:4953
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00861 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
L02BG06
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=107868304
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [3] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Double reduction | |||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Exemestane can be metabolized by gut microbiota through double reduction. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Aromatase (CYP19A1) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [4] |
| BioCyc | Superpathway of steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||
| Estradiol biosynthesis II | ||||
| Estradiol biosynthesis I | ||||
| KEGG Pathway | Steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | FSH Signaling Pathway | |||
| Panther Pathway | Androgen/estrogene/progesterone biosynthesis | |||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Androgen and Estrogen Metabolism | |||
| Reactome | Endogenous sterols | |||
| WikiPathways | Metapathway biotransformation | |||
| Tryptophan metabolism | ||||
| Oxidation by Cytochrome P450 | ||||
| Ovarian Infertility Genes | ||||
| Metabolism of steroid hormones and vitamin D | ||||
| FSH signaling pathway | ||||
| Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway | ||||
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7073). | |||
| REF 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||
| REF 3 | Personalized Mapping of Drug Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome. Cell. 2020 Jun 25;181(7):1661-1679.e22. | |||
| REF 4 | Aromatase inhibitors--theoretical concept and present experiences in the treatment of endometriosis. Zentralbl Gynakol. 2003 Jul-Aug;125(7-8):247-51. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

