Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D02OZE
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000744
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Digoxin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
digoxin; 20830-75-5; 12beta-Hydroxydigitoxin; Digoxine; Lanoxin; Lanoxicaps; Digossina; Digoxina; Digoxinum; Digosin; Lanicor; Digacin; Dilanacin; CHEBI:4551; MLS000069819; Lanacordin; Cardiogoxin; Eudigox; Davoxin; SMR000059217; Rougoxin; Mapluxin; Lenoxin; Lanacrist; Dynamos; Vanoxin; Neo-Lanicor; Lanoxin PG; Digoxin Pediatric; Digoxin Nativelle; SK-Digoxin; UNII-73K4184T59; Homolle's digitalin; Hemigoxine Nativelle; MFCD00003674; Digitek (TN); Lanoxicaps (TN); Lanoxin (TN); Digoxin (JP15/USP); (3beta,5beta,12beta)-3-{[2,6-dideoxy-beta-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1->4)-2,6-dideoxy-beta-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1->4)-2,6-dideoxy-beta-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-12,14-dihydroxycard-20(22)-enolide; 4-[(1S,2S,5S,7R,10R,11S,14R,15S,16R)-5-{[(2R,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-11,16-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8700^{2,7}; [3H]digoxin
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Arrhythmia [ICD-11: BC9Z] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Congestive cardiac insufficiency [ICD-11: BD1Z; ICD-10: I50, I50.9] | Approved | [1], [2] | ||
| Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10-BD13] | Approved | [1], [2] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiarrhythmic Agents
|
|||
| Company |
GlaxoSmithKline
|
|||
| Structure |
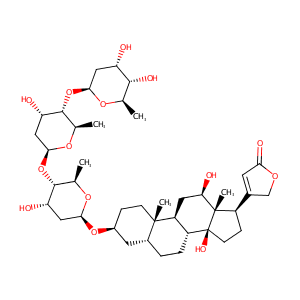 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C41H64O14
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2C(OC(CC2O)OC3C(OC(CC3O)OC4CCC5(C(C4)CCC6C5CC(C7(C6(CCC7C8=CC(=O)OC8)O)C)O)C)C)C)O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C41H64O14/c1-19-36(47)28(42)15-34(50-19)54-38-21(3)52-35(17-30(38)44)55-37-20(2)51-33(16-29(37)43)53-24-8-10-39(4)23(13-24)6-7-26-27(39)14-31(45)40(5)25(9-11-41(26,40)48)22-12-32(46)49-18-22/h12,19-21,23-31,33-38,42-45,47-48H,6-11,13-18H2,1-5H3/t19-,20-,21-,23-,24+,25-,26-,27+,28+,29+,30+,31-,33+,34+,35+,36-,37-,38-,39+,40+,41+/m1/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
LTMHDMANZUZIPE-PUGKRICDSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 20830-75-5
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9171, 3139699, 7847364, 7979083, 8787891, 10321270, 11466465, 11467585, 11486129, 11533002, 14840467, 16531631, 17389540, 24893992, 24894045, 25664046, 26752810, 29204039, 30082596, 46508524, 47277036, 47350829, 47500941, 47871144, 48415894, 48425070, 48493824, 49698492, 49718191, 50105460, 50105461, 56313674, 56422204, 57287890, 57409429, 57654114, 79412392, 85788562, 87568294, 90481132, 92125420, 92298240, 92729949, 93167166, 99431517, 103707689, 103913751, 111366106, 117393920, 121363091
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:4551
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00668 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
C01AA05
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=005355486
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides coprophilus DSM 18228
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides coprophilus DSM 18228 (log2FC = -0.333; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -0.594; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697 (log2FC = -0.43; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859 (log2FC = -0.907; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.783; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.68; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10 (log2FC = -0.593; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.605; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208 (log2FC = -0.631; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483 (log2FC = -0.339; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183 (log2FC = -0.369; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.393; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 (log2FC = -0.448; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.607; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 (log2FC = -0.663; p = 0.0). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.468; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.472; p = 0.0). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides johnsonii DSM 18315
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Parabacteroides johnsonii DSM 18315 (log2FC = -0.488; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184 (log2FC = -0.367; p = 0.005). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eggerthellales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eggerthella lenta
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4], [5], [6], [7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Cardiac glycoside reductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | C=C reduction and deglycosylation | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Dihydrodigoxigenin; dihydrodigoxin | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Decrease activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized to Dihydrodigoxigenin and dihydrodigoxin by the cardiac glycoside reductase of Eggerthella lenta through C = C reduction and deglycosylation, which results in the decrease of drug's activity and the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.383; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.396; p = 0.003). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [6], [8], [9], [10], [11] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Lactone ring reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Dihydrodigoxin; dihydrodigoxigenin | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Decrease activity | |||
| Description | Digoxin can be metabolized to Dihydrodigoxin and dihydrodigoxigenin by gut microbiota through lactone ring reduction, which results in the decrease of the drug's activity. | |||
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Coriobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Collinsella aerofaciens
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Collinsella aerofaciens was decreased by Digoxin (adjusted p-values: 6.95E-03). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Organic anion transporter M1 (SLCO4C1) | Target Info | Modulator | [13] |
| Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase (SPT ATPase) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [14] | |
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4726). | |||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 021648. | |||
| REF 3 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 4 | Mechanistic insight into digoxin inactivation by Eggerthella lenta augments our understanding of its pharmacokinetics. Gut Microbes. 2014 Mar-Apr;5(2):233-8. | |||
| REF 5 | The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(1):31-40. | |||
| REF 6 | Gut Microbiota-Mediated Drug-Antibiotic Interactions. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Oct;43(10):1581-9. | |||
| REF 7 | Gut Reactions: Breaking Down Xenobiotic-Microbiome Interactions. Pharmacol Rev. 2019 Apr;71(2):198-224. | |||
| REF 8 | Predicting and Understanding the Human Microbiome's Impact on Pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jul;40(7):495-505. | |||
| REF 9 | Inactivation of digoxin by the gut flora: reversal by antibiotic therapy. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 1;305(14):789-94. | |||
| REF 10 | Cometabolism of microbes and host: implications for drug metabolism and drug-induced toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;94(5):574-81. | |||
| REF 11 | The metabolic effect of gut microbiota on drugs. Drug Metab Rev. 2020 Feb;52(1):139-156. | |||
| REF 12 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 13 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1227). | |||
| REF 14 | Fab antibody fragments: some applications in clinical toxicology. Drug Saf. 2004;27(14):1115-33. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

