Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D05NOS
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000294
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Triflupromazine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Adazine; Fluopromazine; Fluorofen; Neoprin; Nivoman; Psyquil; Siquil; Trifluopromazine; Triflupromazina; Triflupromazinum;Vesprin; Vetame; Fluopromazine monohydrochloride; Trifluopromazine hydrochloride; Triflupromazine [INN]; Triflupromazina [INN-Spanish]; Triflupromazinum [INN-Latin]; Vesprin (TN); Triflupromazine (USP/INN)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Psychotic disorder [ICD-11: 6A20-6A25] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antipsychotic Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Bristol-Myers Squibb
|
|||
| Structure |
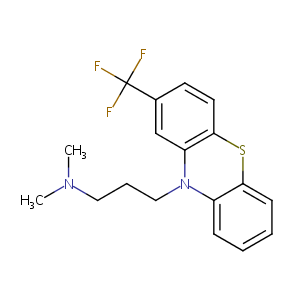 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C18H19F3N2S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)CCCN1C2=CC=CC=C2SC3=C1C=C(C=C3)C(F)(F)F
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C18H19F3N2S/c1-22(2)10-5-11-23-14-6-3-4-7-16(14)24-17-9-8-13(12-15(17)23)18(19,20)21/h3-4,6-9,12H,5,10-11H2,1-2H3
|
|||
| InChIKey |
XSCGXQMFQXDFCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 146-54-3
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
5664289, 7847456, 8153424, 10508360, 11111873, 11111874, 11335983, 11361222, 11362929, 11365491, 11368053, 11374201, 11376215, 11405424, 11405821, 11462194, 11466081, 11467201, 11485862, 11492556, 11493909, 14925496, 24263033, 29224607, 46507344, 47365232, 47440302, 47440303, 47662324, 47662325, 47736524, 48035163, 48259273, 48259274, 48334534, 48416663, 49698933, 50006493, 50100355, 50104262, 50839748, 56394865, 57322847, 85209834, 90341005, 103024193, 103179080, 103841663, 103957782, 104309608
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:9711
|
|||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N05AA05
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000146543
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium rectale
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Eubacterium rectale was decreased by Triflupromazine hydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 8.01E-03). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Verrucomicrobiales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Akkermansia muciniphila
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila was decreased by Triflupromazine hydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 6.85E-04). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | 5-HT 2B receptor (HTR2B) | Target Info | Antagonist | [4] |
| KEGG Pathway | Calcium signaling pathway | |||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| Gap junction | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | ||||
| Panther Pathway | 5HT2 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | |||
| Reactome | Serotonin receptors | |||
| G alpha (q) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | Serotonin Receptor 2 and ELK-SRF/GATA4 signaling | |||
| Monoamine GPCRs | ||||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | ||||
| Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4330). | |||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 011123. | |||
| REF 3 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 4 | Some properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the hindquarters of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;67(1):79-85. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

