Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D09ANG
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000358
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Misoprostol
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Cytotec; GyMiso; Isprelor; Misopess; Misoprostolum; Misotol; SC 29333; Cytotec (TN); Misoprostolum [INN-Latin]; SC-29333; XP-16J; Misoprostol (JAN/USAN/INN); Methyl (11alpha,13E)-11,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprost-13-en-1-oate; Methyl (+-)-11-alpha,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprost-13-en-1-oate; Methyl 7-[(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(E)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-enyl]-5-oxocyclopentyl]heptanoate; (+/-)-15-Deoxy-(16RS)-16-hydroxy-16-methylprostaglandin E1 methyl ester; (11-alpha,13E)-(+-)-11,16-Dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprost-13-en-1-oic acid methyl ester
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Medical abortion [ICD-11: JA00.1Z; ICD-10: O04; ICD-9: 779.6] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Abortifacient Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Pfizer Pharmaceuticals
|
|||
| Structure |
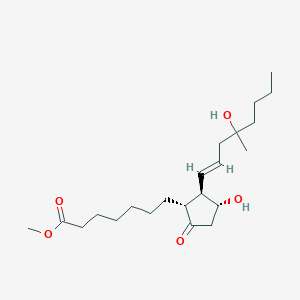 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C22H38O5
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCCCC(C)(CC=CC1C(CC(=O)C1CCCCCCC(=O)OC)O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C22H38O5/c1-4-5-14-22(2,26)15-10-12-18-17(19(23)16-20(18)24)11-8-6-7-9-13-21(25)27-3/h10,12,17-18,20,24,26H,4-9,11,13-16H2,1-3H3/b12-10+/t17-,18-,20-,22?/m1/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
OJLOPKGSLYJEMD-URPKTTJQSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 59122-46-2
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:94387
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01477 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
A02BB01; G02AD06
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=059122462
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [3] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Ester hydrolysis | |||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Misoprostol can be metabolized by gut microbiota through ester hydrolysis. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Prostacyclin receptor (PTGIR) | Target Info | Antagonist | [4], [5], [6] |
| KEGG Pathway | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | ||||
| Platelet activation | ||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Intracellular Signalling Through Prostacyclin Receptor and Prostacyclin | |||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Thromboxane A2 receptor signaling | |||
| Reactome | Prostanoid ligand receptors | |||
| G alpha (s) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | Prostaglandin Synthesis and Regulation | |||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | ||||
| Small Ligand GPCRs | ||||
| Endothelin Pathways | ||||
| Platelet homeostasis | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1936). | |||
| REF 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||
| REF 3 | Personalized Mapping of Drug Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome. Cell. 2020 Jun 25;181(7):1661-1679.e22. | |||
| REF 4 | Palmitoylation of the human prostacyclin receptor. Functional implications of palmitoylation and isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 28;278(9):6947-58. | |||
| REF 5 | The future potential of eicosanoids and their inhibitors in paediatric practice. Drugs. 1998 Aug;56(2):169-76. | |||
| REF 6 | Structural organization and chromosomal assignment of the human prostacyclin receptor gene. Genomics. 1995 May 1;27(1):142-8. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

