Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0A6KR
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000733
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Balsalazide
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Balsalazida; Balsalazido; Balsalazidum; Colazal; Balsalazida [Spanish]; Balsalazide Disodium; Balsalazido [Spanish]; Balsalazidum [Latin]; Balsalazide (INN); Balsalazide [INN:BAN]; Colazal (TN); Colazide (TN); (3Z)-3-[[4-(2-carboxyethylcarbamoyl)phenyl]hydrazinylidene]-6-oxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1-carboxylic acid; (E)-5-((4-(((2-Carboxyethyl)amino)carbonyl)phenyl)azo)-2-hydroxybenzoic acid; (E)-5-({p-[(2-carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}azo)-2-salicylic acid; 3-(2-{4-[(2-carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}hydrazinylidene)-6-oxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1-carboxylic acid; 5-[(E)-{4-[(2-carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}diazenyl]-2-hydroxybenzoic acid; 5-[4-(2-carboxy-ethylcarbamoyl)-phenylazo]-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Inflammatory bowel disease [ICD-11: DD72; ICD-10: K50-K52] | Approved | [1] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
|||
| Structure |
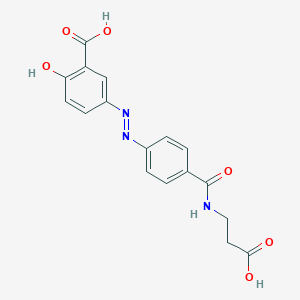 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C17H15N3O6
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1C(=O)NCCC(=O)O)N=NC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)C(=O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C17H15N3O6/c21-14-6-5-12(9-13(14)17(25)26)20-19-11-3-1-10(2-4-11)16(24)18-8-7-15(22)23/h1-6,9,21H,7-8H2,(H,18,24)(H,22,23)(H,25,26)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
IPOKCKJONYRRHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 80573-04-2
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
14852312, 42980434, 46386828, 46505592, 49681625, 49886313, 50411239, 51091813, 56313727, 85460328, 92308641, 93166930, 114465198, 119526088, 124659117, 124800401, 126664722, 134223177, 134338020, 135013543, 137005615, 137248705, 142971157, 144205805, 152031987, 160964350, 162255240, 164788084, 170465305, 172080513, 179151210, 179296041, 184675317, 187072705, 189017810, 223682076, 225236812, 226490226, 226505668, 226509403, 240771437, 241161229, 242114841, 251916812, 251918051, 252218186
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:267413
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00210 ; BADD_D00211 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
A07EC04
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=080573042
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Azoreductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-aminosalicylic acid | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Balsalazide can be metabolized to 5-aminosalicylic acid by the azoreductase of Clostridium sp. through reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and toxicity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Azoreductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-aminosalicylic acid | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Balsalazide can be metabolized to 5-aminosalicylic acid by the azoreductase of Eubacterium sp. through reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and toxicity. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridia
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-aminosalicylic acid | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity | |||
| Description | Balsalazide can be metabolized to 5-aminosalicylic acid by Clostridia, which results in the increase of the drug's activity. | |||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [4], [5], [6], [7] | |||
| Microbial Enzyme | Azoreductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Azo bond reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 6-aminosalicylic acid; sulfapyridine | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase side effect | |||
| Description | Balsalazide can be metabolized to 6-aminosalicyclic acid and sulfapyridine by the azoreductase of gut microbiota through azo bond reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and side effect. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 (COX-1) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [8] |
| BioCyc | C20 prostanoid biosynthesis | |||
| KEGG Pathway | Arachidonic acid metabolism | |||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Platelet activation | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||
| Panther Pathway | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | |||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Arachidonic Acid Metabolism | |||
| WikiPathways | Prostaglandin Synthesis and Regulation | |||
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | ||||
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | ||||
| Eicosanoid Synthesis | ||||
| Selenium Micronutrient Network | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 077806. | |||
| REF 2 | Gut microbiota modulates drug pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Rev. 2018 Aug;50(3):357-368. | |||
| REF 3 | Studies of two novel sulfasalazine analogs, ipsalazide and balsalazide. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Jul;28(7):609-15. | |||
| REF 4 | Cometabolism of microbes and host: implications for drug metabolism and drug-induced toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;94(5):574-81. | |||
| REF 5 | Gut microbiome interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl Res. 2017 Jan;179:204-222. | |||
| REF 6 | Predicting and Understanding the Human Microbiome's Impact on Pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jul;40(7):495-505. | |||
| REF 7 | The metabolic effect of gut microbiota on drugs. Drug Metab Rev. 2020 Feb;52(1):139-156. | |||
| REF 8 | Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

