Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0B1CM
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC014545
|
|||
| Drug Name |
2-Methoxy-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-benzyl)-phenol
|
|||
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL10121; 2-methoxy-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)phenol; NSC648581; Neuro_000355; AC1Q56F6; AC1L85N6; CTK6J6605; ZINC1630963; BDBM50212289; NSC-648581; NCI60_016862
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Discovery agent [ICD-11: N.A.] | Investigative | [1] | |
| Structure |
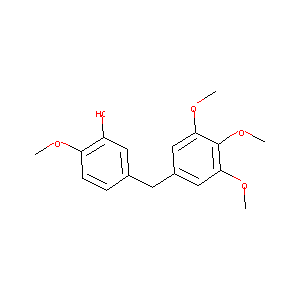 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C17H20O5
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)CC2=CC(=C(C(=C2)OC)OC)OC)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C17H20O5/c1-19-14-6-5-11(8-13(14)18)7-12-9-15(20-2)17(22-4)16(10-12)21-3/h5-6,8-10,18H,7H2,1-4H3
|
|||
| InChIKey |
JFZDWXGLUXEEAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Tubulin (TUB) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] |
| Tubulin beta (TUBB) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Phagosome | |||
| Gap junction | ||||
| Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | FSH Signaling Pathway | |||
| TCR Signaling Pathway | ||||
| EGFR1 Signaling Pathway | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Cytoskeletal regulation by Rho GTPase | |||
| Huntington disease | ||||
| Reactome | Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition | |||
| Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes | ||||
| Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes | ||||
| Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization?from the centrosome | ||||
| Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane | ||||
| WikiPathways | Parkin-Ubiquitin Proteasomal System pathway | |||
| Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | ||||
| Mitotic G2-G2/M phases | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Synthesis of alkoxy-substituted diaryl compounds and correlation of ring separation with inhibition of tubulin polymerization: differential enhance... J Med Chem. 1992 Mar 20;35(6):1058-67. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

