Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0E6XR
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000004
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Dasatinib
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Sprycel (TN); BMS 354825; BMS-354825; BMS-354825, Sprycel, BMS354825, Dasatinib; BMS354825; Dasatinib (USAN); Dasatinib [USAN]; Dasatinib anhydrous; Dasatinib, BMS 354825; Dasatinibum; Sprycel; Spyrcel
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Chronic myelogenous leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0; ICD-10: C92.1; ICD-9: 205.1] | Approved | [1], [2], [3], [4] | |
| Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83; ICD-10: C90.0] | Phase 2 | [1], [5] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Bristol Myers Squibb
|
|||
| Structure |
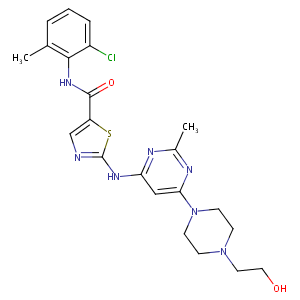 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C22H26ClN7O2S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C(=CC=C1)Cl)NC(=O)C2=CN=C(S2)NC3=CC(=NC(=N3)C)N4CCN(CC4)CCO
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C22H26ClN7O2S/c1-14-4-3-5-16(23)20(14)28-21(32)17-13-24-22(33-17)27-18-12-19(26-15(2)25-18)30-8-6-29(7-9-30)10-11-31/h3-5,12-13,31H,6-11H2,1-2H3,(H,28,32)(H,24,25,26,27)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
ZBNZXTGUTAYRHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 302962-49-8
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
10061134, 12015788, 14859389, 17397755, 17422520, 36127155, 46505143, 46513626, 47883136, 48429642, 49742622, 50070229, 50070567, 50071309, 50100097, 50125840, 52995488, 53799228, 56312240, 56312839, 56313127, 56373968, 56459420, 57288451, 57354110, 57551950, 74374210, 85246174, 87235888, 87357382, 93581026, 99381604, 99437986, 103501621, 103905543, 111644212, 117418208, 117695728, 118050493, 119503515, 124361516, 124756940, 124893650, 124893651, 124893652, 125001912, 125163747, 125264620, 125347447, 126624063
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:49375
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00589 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
L01XE06
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.482; p = 0.004). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium ruminantium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Bifidobacterium ruminantium (log2FC = -0.533; p = 0.007). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium ruminantium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Bifidobacterium ruminantium. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.38; p = 0.016). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium bolteae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Clostridium bolteae. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.485; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterocloster bolteae ATCC BAA-613
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Enterocloster bolteae ATCC BAA-613 (log2FC = -2.327; p = 0.005). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Lactobacillales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Lactobacillus reuteri CF48-3A
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Dasatinib can be metabolized by Lactobacillus reuteri CF48-3A (log2FC = -0.961; p = 0.0). | |||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRM | DRM Info | |||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5678). | |||
| REF 2 | 2006 drug approvals: finding the niche. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007 Feb;6(2):99-101. | |||
| REF 3 | Dasatinib: a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia and philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Ther. 2007 Nov;29(11):2289-308. | |||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 5 | Current and future treatments of bone metastases. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Dec;13(4):609-27. | |||
| REF 6 | Emerging Insights on the Interaction Between Anticancer and Immunosuppressant Drugs and Intestinal Microbiota in Pediatric Patients. Clin Transl Sci. 2020 Mar;13(2):238-259. | |||
| REF 7 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 8 | A comparison of physicochemical property profiles of marketed oral drugs and orally bioavailable anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors in clinical development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(14):1408-22. | |||
| REF 9 | In vitro and clinical investigation of the relationship between CCR5 receptor occupancy and anti-HIV activity of Aplaviroc. J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;48(10):1179-88. | |||
| REF 10 | Multi-target therapeutics: when the whole is greater than the sum of the parts. Drug Discov Today. 2007 Jan;12(1-2):34-42. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

