Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0R1RS
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000617
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Indomethacin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Aconip; Amuno; Arthrexin; Artracin; Artrinovo; Artrivia; Bonidin; Bonidon; Catlep; Confortid; Dolcidium; Dolovin; Durametacin; Elmetacin; Hicin; IMN; Idomethine; Imbrilon; Inacid; Indacin; Indameth; Indmethacine; Indocid; Indocin; Indomecol; Indomed; Indomee; Indometacin; Indometacina; Indometacine; Indometacinum; Indometacyna; Indomethacine; Indomethacinum; Indomethancin; Indomethazine; Indomethegan; Indomethine; Indometicina; Indomo; Indomod; Indoptic; Indoptol; Indorektal; Indoxen; Inflazon; Infrocin; Lausit; Liometacen; Metacen; Metartril; Methazine; Metindol; Mezolin; Miametan; Mikametan; Mobilan; Novomethacin; Reumacide; Sadoreum; Tannex; Vonum; Bonidon Gel; DESMETHYL INDOMETHACIN; Dolcidium PL;Flexin continus; Indocid Pda; Indocid Sr; Indocin Sr; Indolar SR; Indometacyna [Polish]; Indometicina [Spanish]; Inteban sp; Rhemacin LA; Rheumacin LA; I 7378; IN1454; Indomet 140; Aconip (TN); Apo-Indomethacin; Chibro-amuno; Chrono-indicid; Chrono-indocid; Indo-Lemmon; Indo-Spray; Indo-phlogont; Indo-rectolmin; Indo-tablinen; Indocid (TN); Indocid (pharmaceutical); Indocin (TN); Indocin I.V; Indometacina [INN-Spanish]; Indometacine [INN-French]; Indometacinum [INN-Latin]; Indomethacin (USP); Indomethacin [USAN:BAN]; Novo-Methacin; Indochron E-R (TN); Indocin I.V.; Indocin-SR (TN); Indometacin (JP15/INN); Indomethacin & MAP-30; Indomethacin, Indochron E-R, Indocin-SR, Indocid, Indocin, Indomethacin
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20; ICD-9: 714] | Approved | [1] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Recordati Rare Diseases Inc
|
|||
| Structure |
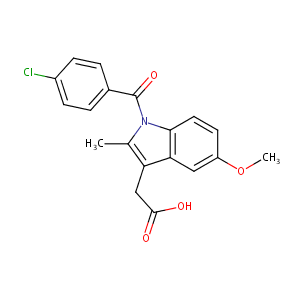 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C19H16ClNO4
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C2=C(N1C(=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl)C=CC(=C2)OC)CC(=O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C19H16ClNO4/c1-11-15(10-18(22)23)16-9-14(25-2)7-8-17(16)21(11)19(24)12-3-5-13(20)6-4-12/h3-9H,10H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 53-86-1
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
5032, 611045, 612102, 832223, 841055, 856012, 3225554, 5208606, 6435989, 7847209, 7888379, 7979604, 8027945, 8027950, 8027958, 8149387, 8152346, 10321568, 10525985, 11111328, 11111329, 11113361, 11121750, 11122230, 11335446, 11360685, 11362903, 11363813, 11365465, 11366375, 11368027, 11368937, 11370997, 11370998, 11371496, 11373534, 11373628, 11376189, 11377099, 11404374, 11446060, 11461657, 11466300, 11467420, 11484715, 11486099, 11488786, 11490284, 11491833, 11494733
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:49662
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01156 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
C01EB03; M01AB01; M02AA23; S01BC01
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000053861
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Beta glucuronidase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Hydrolysis | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by the beta glucuronidase of Bacteroides through hydrolysis, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859 (log2FC = -0.78; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.645; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.614; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10 (log2FC = -0.569; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.677; p = 0.009). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208 (log2FC = -0.565; p = 0.015). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183 (log2FC = -0.446; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731 (log2FC = -0.493; p = 0.019). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.498; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 (log2FC = -0.39; p = 0.033). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.716; p = 0.004). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.688; p = 0.022). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.658; p = 0.015). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184 (log2FC = -0.357; p = 0.044). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Beta glucuronidase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Hydrolysis | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by the beta glucuronidase of Bifidobacterium through hydrolysis, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Beta glucuronidase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Hydrolysis | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by the beta glucuronidase of Clostridium through hydrolysis, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [4], [5] | |||
| Microbial Enzyme | Beta glucuronidase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Deconjugation | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Decrease activity; Increase side effect (diarrhea | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by the beta glucuronidase of gut microbiota through deconjugation, which results in the decrease of drug's activity and the increase of the drug's side effect (diarrhea; anorexia; weight loss). | |||
| Studied Microbe: Luminal bacteria | [6] | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase side effect | |||
| Description | Indomethacin can be metabolized by Luminal bacteria, which results in the increase of the drug's side effect. | |||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 2 | Gut microbiota modulates drug pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Rev. 2018 Aug;50(3):357-368. | |||
| REF 3 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 4 | The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(1):31-40. | |||
| REF 5 | The intestinal microbiota modulates the anticancer immune effects of cyclophosphamide. Science. 2013 Nov 22;342(6161):971-6. | |||
| REF 6 | Toxicomicrobiomics: The Human Microbiome vs. Pharmaceutical, Dietary, and Environmental Xenobiotics. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 16;11:390. | |||
| REF 7 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

