Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0WN0U
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000487
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Felodipine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Agon; Felobeta; Felocor; Feloday; Felodipina; Felodipinum; Felodur; Felogamma; Felogard; Fensel; Flodil; Hydac; Lexxel; Logimax; Modip; Munobal; Penedil; Perfudal; Plandil; Plendil; Preslow; Prevex; Renedil; Splendil; AGON SR; AbZ Brand of Felodipine; Aliud Brand of Felodipine; Alphapharm Brand of Felodipine; Alpharma Brand of Felodipine; Astra Brand of Felodipine; AstraZeneca Brand of Felodipine; Aventis Brand of Felodipine; Azupharma Brand of Felodipine; BC Brand of Felodipine; Betapharm Brand of Felodipine; Ct Arzneimittel Brand of Felodipine; Felo Biochemie; Felo Puren; Felodipin AL; Felodipin AZU; Felodipin AbZ; Felodipin Heumann; Felodipin Stada; Felodipin dura; Felodipin ratiopharm; Felodipin von ct; FelodurER; Heumann Brand of Felodipine; Hexal Brand of Felodipine; Hoechst Brand of Felodipine; Merck dura Brand of Felodipine; Munobal Retard; Pharmaceutica Astra Brand of Felodipine; Pharmacia Spain Brandof Felodipine; Plendil Depottab; Plendil ER; Plendil Retard; Promed Brand of Felodipine; Ratiopharm Brand of Felodipine; Stadapharm Brand of Felodipine; TheraPharm Brand of Felodipine; Worwag Brand of Felodipine; F 9677; Felodipin 1A Pharma; H 154 82; H 15482; CGH-869; Ct-Arzneimittel Brand of Felodipine; Dl-Felodipine; Felo-Puren; Felodipin-ratiopharm; Felodipina [INN-Spanish]; Felodipinum [INN-Latin]; H 154-82; H 154/82; Heumann, Felodipin; Plendil (TN); AE-641/11429675; Felodipine [USAN:BAN:INN]; Felodipine [USAN:INN:BAN]; H-154/82; Felodipine (JAN/USP/INN); Plendil, Renedil, Feloday, Felodipine; Ethyl methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate; (+-)-Ethyl methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate; (+/-)-ethylmethyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate; 1A Brand of Felodipine; 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-, ethyl methylester; 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-,ethyl methyl ester; 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-, ethyl methyl ester; 3-Ethyl 5-methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate; 3-ethyl 5-methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate; 4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinecarboxylic acid ethyl methyl ester; 4-(2,3-dichloro-phenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydro-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid 3-ethyl ester 5-methyl ester; 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid ethyl methyl ester; 5-O-ethyl 3-O-methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00-BA04; ICD-9: 401] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
|||
| Company |
AstraZeneca
|
|||
| Structure |
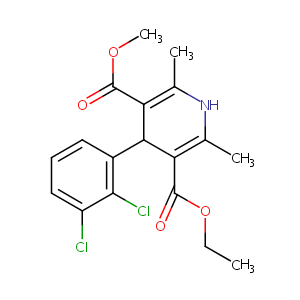 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C18H19Cl2NO4
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCOC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C2=C(C(=CC=C2)Cl)Cl)C(=O)OC)C)C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C18H19Cl2NO4/c1-5-25-18(23)14-10(3)21-9(2)13(17(22)24-4)15(14)11-7-6-8-12(19)16(11)20/h6-8,15,21H,5H2,1-4H3
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RZTAMFZIAATZDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 72509-76-3
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
856004, 5309057, 7847385, 7979219, 8152117, 10321744, 11466506, 11467626, 11486291, 11528719, 12012613, 14927301, 16960569, 17405071, 24278449, 29222468, 46506968, 47509540, 47656605, 47879634, 48179244, 48328566, 48416001, 49698512, 50106289, 50106290, 53777614, 53788382, 56423042, 56424130, 56463217, 56463516, 57321731, 78292296, 85231057, 85788575, 87351806, 90340828, 92125582, 92303867, 92308861, 92711325, 93166891, 99453448, 103024636, 103543150, 103856247, 103914230, 104170219, 104253409
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:585948
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00872 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
C08CA02
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=072509763
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides caccae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides caccae was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 1.13E-04). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxigenic
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxigenic was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 3.25E-04). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis nontoxigenic
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides fragilis nontoxigenic was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 1.68E-05). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 8.43E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides uniformis was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 8.28E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides vulgatus was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 4.42E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Parabacteroides distasonis was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 3.70E-06). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides merdae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Parabacteroides merdae was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 4.97E-05). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Prevotella copri
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Prevotella copri was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 2.74E-04). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridioides difficile
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Clostridioides difficile was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 2.03E-04). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium perfringens
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Clostridium perfringens was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 5.46E-05). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Coprococcus comes
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Coprococcus comes was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 1.14E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia intestinalis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Roseburia intestinalis was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 2.29E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus bromii
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Ruminococcus bromii was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 4.08E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus torques
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Ruminococcus torques was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 9.03E-03). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Lactobacillales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Streptococcus parasanguinis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Streptococcus parasanguinis was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 8.36E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Streptococcus salivarius
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Streptococcus salivarius was decreased by Felodipine (adjusted p-values: 4.63E-03). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Calcium channel unspecific (CaC) | Target Info | Blocker | [4] |
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4190). | |||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 075896. | |||
| REF 3 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 4 | Molecular pharmacology of human Cav3.2 T-type Ca2+ channels: block by antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics, and their analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Feb;328(2):621-7. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

