Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T16042
(Former ID: TTDR00234)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
LOG15; Arachidonate omega-6 lipoxygenase; Arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, leukocyte-type; 15-Lipoxygenase; 15-LOX-1; 12/15-lipoxygenase; 12-LOX
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ALOX15
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Converts arachidonic acid into 12-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid/12-HPETE and 15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid/15-HPETE. Also converts linoleic acid to 13-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoic acid. May also act on (12S)-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid/(12S)-HPETE to produce hepoxilin A3. Probably plays an important role in the immune and inflammatory responses. Through the oxygenation of membrane-bound phosphatidylethanolamine in macrophages may favor clearance of apoptotic cells during inflammation by resident macrophages and prevent an autoimmune response associated with the clearance of apoptotic cells by inflammatory monocytes. In parallel, may regulate actin polymerization which is crucial for several biological processes, including macrophage function. May also regulate macrophage function through regulation of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway. Finally, it is also involved in the cellular response to IL13/interleukin-13. In addition to its role in the immune and inflammatory responses, may play a role in epithelial wound healing in the cornea maybe through production of lipoxin A4. May also play a role in endoplasmic reticulum stress response and the regulation of bone mass. Non-heme iron-containing dioxygenase that catalyzes the stereo-specific peroxidation of free and esterified polyunsaturated fatty acids generating a spectrum of bioactive lipid mediators.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Oxygenase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.13.11.33
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MGLYRIRVSTGASLYAGSNNQVQLWLVGQHGEAALGKRLWPARGKETELKVEVPEYLGPL
LFVKLRKRHLLKDDAWFCNWISVQGPGAGDEVRFPCYRWVEGNGVLSLPEGTGRTVGEDP QGLFQKHREEELEERRKLYRWGNWKDGLILNMAGAKLYDLPVDERFLEDKRVDFEVSLAK GLADLAIKDSLNVLTCWKDLDDFNRIFWCGQSKLAERVRDSWKEDALFGYQFLNGANPVV LRRSAHLPARLVFPPGMEELQAQLEKELEGGTLFEADFSLLDGIKANVILCSQQHLAAPL VMLKLQPDGKLLPMVIQLQLPRTGSPPPPLFLPTDPPMAWLLAKCWVRSSDFQLHELQSH LLRGHLMAEVIVVATMRCLPSIHPIFKLIIPHLRYTLEINVRARTGLVSDMGIFDQIMST GGGGHVQLLKQAGAFLTYSSFCPPDDLADRGLLGVKSSFYAQDALRLWEIIYRYVEGIVS LHYKTDVAVKDDPELQTWCREITEIGLQGAQDRGFPVSLQARDQVCHFVTMCIFTCTGQH ASVHLGQLDWYSWVPNAPCTMRLPPPTTKDATLETVMATLPNFHQASLQMSITWQLGRRQ PVMVAVGQHEEEYFSGPEPKAVLKKFREELAALDKEIEIRNAKLDMPYEYLRPSVVENSV AI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T86D6K | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
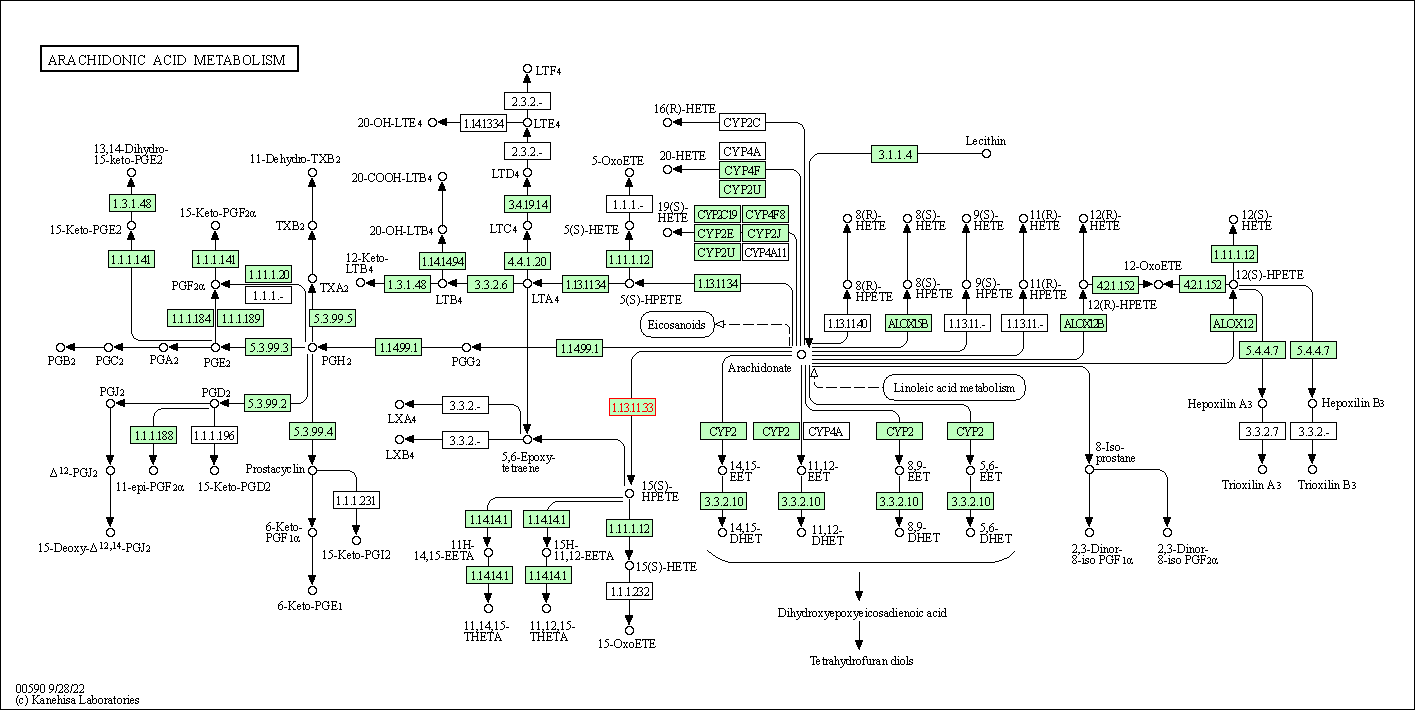
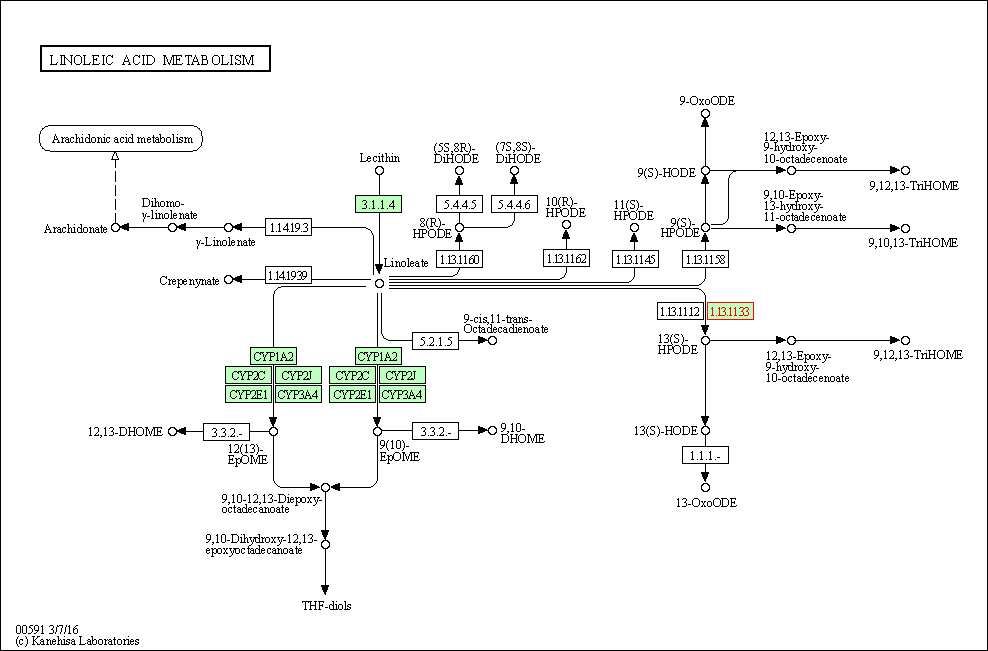
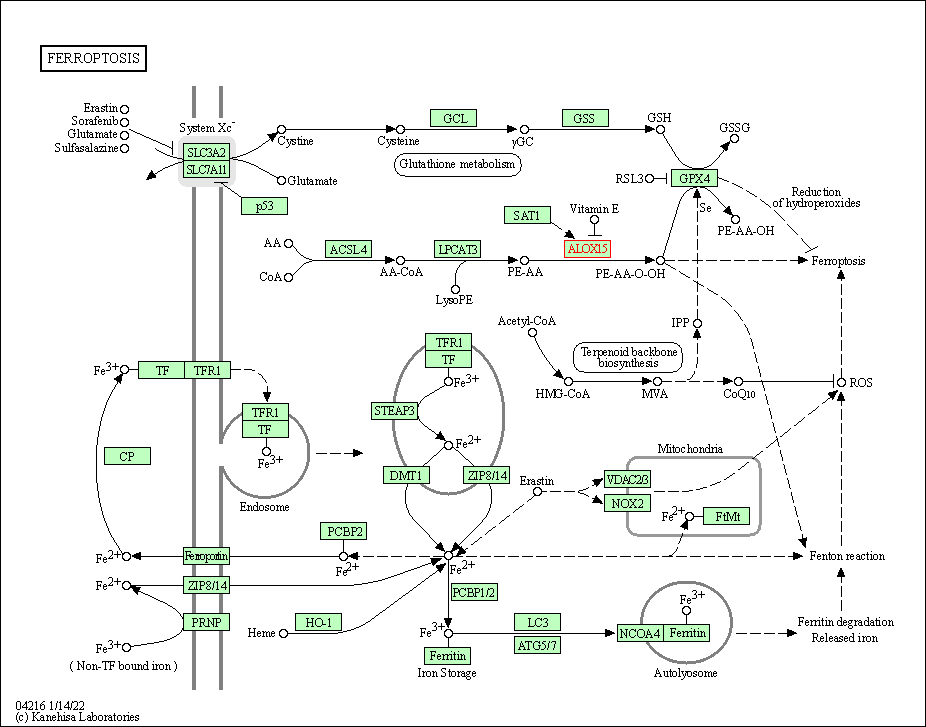
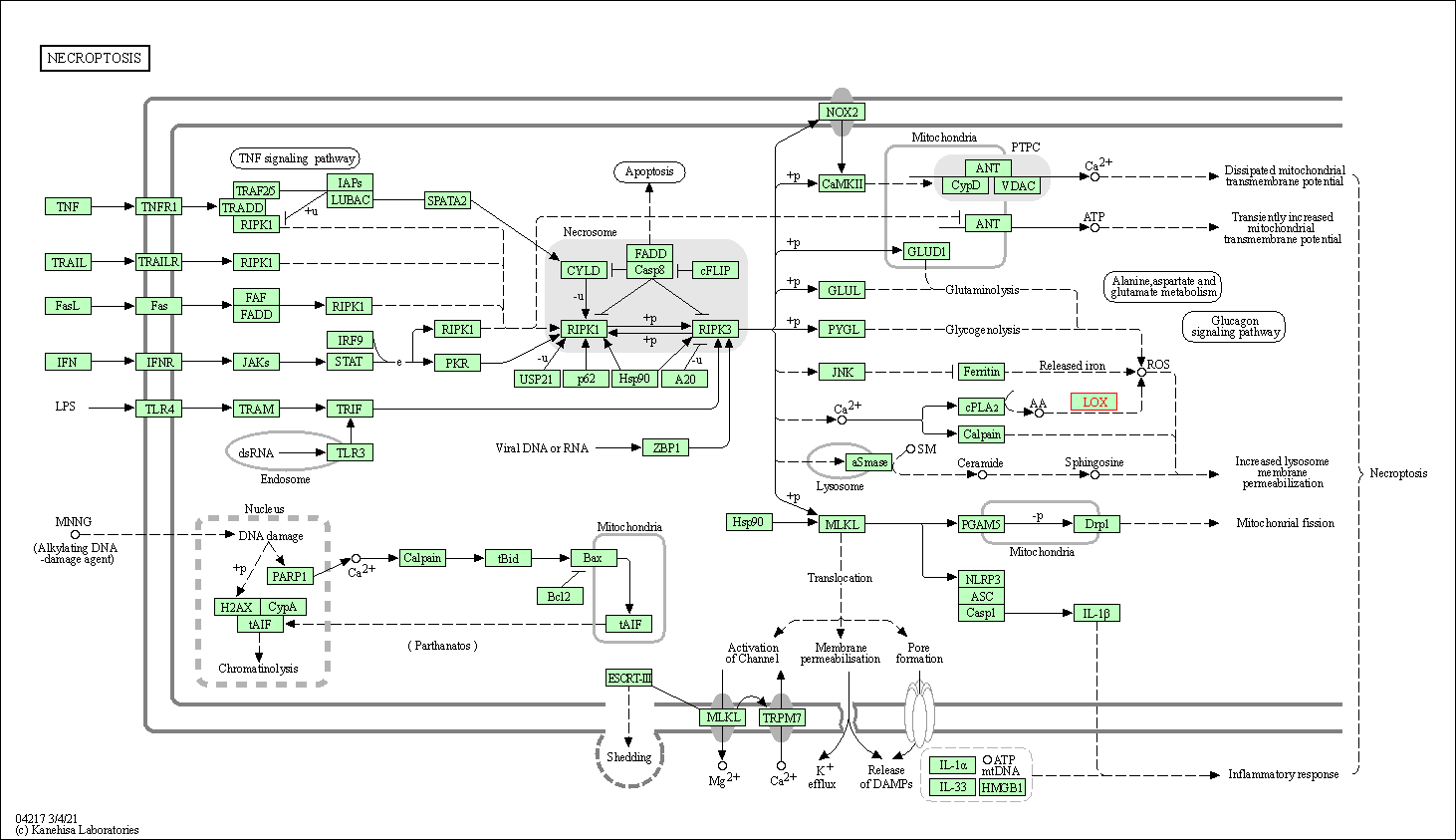
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | hsa00590 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Linoleic acid metabolism | hsa00591 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 4.93E-06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.94E-01 | Radiality | 1.33E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 8.33E+00 | Topological coefficient | 4.89E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 2 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Resolvin D biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Lipoxin biosynthesis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Linoleic acid metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 4 | Serotonergic synapse | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL4 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Arachidonic Acid Metabolism | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL4-mediated signaling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Eicosanoid Synthesis | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | 15-Lipoxygenase inhibitors: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016;26(1):65-88. | |||||
| REF 2 | Inhibitors of phospholipase A2 and their therapeutic potential: an update on patents (2012-2016).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Feb;27(2):217-225. | |||||
| REF 3 | Discovery of platelet-type 12-human lipoxygenase selective inhibitors by high-throughput screening of structurally diverse libraries. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Nov 15;15(22):6900-8. | |||||
| REF 4 | Exploring sponge-derived terpenoids for their potency and selectivity against 12-human, 15-human, and 15-soybean lipoxygenases. J Nat Prod. 2003 Feb;66(2):230-5. | |||||
| REF 5 | Lipoxygenase inhibitory constituents of the fruits of noni (Morinda citrifolia) collected in Tahiti. J Nat Prod. 2007 May;70(5):859-62. | |||||
| REF 6 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 7 | Probing the activity differences of simple and complex brominated aryl compounds against 15-soybean, 15-human, and 12-human lipoxygenase. J Med Chem. 2004 Jul 29;47(16):4060-5. | |||||
| REF 8 | Using enzyme assays to evaluate the structure and bioactivity of sponge-derived meroterpenes. J Nat Prod. 2009 Oct;72(10):1857-63. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

