Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T94324
(Former ID: TTDR01338)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Histone deacetylase 10 (HDAC10)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Polyamine deacetylase HDAC10; HD10
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HDAC10
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Exhibits attenuated catalytic activity toward N(1),N(8)-diacetylspermidine and very low activity, if any, toward N(1)-acetylspermidine. Histone deacetylase activity has been observed in vitro. Has also been shown to be involved in MSH2 deacetylation. The physiological relevance of protein/histone deacetylase activity is unclear and could be very weak. May play a role in the promotion of late stages of autophagy, possibly autophagosome-lysosome fusion and/or lysosomal exocytosis in neuroblastoma cells. May play a role in homologous recombination. May promote DNA mismatch repair. Polyamine deacetylase (PDAC), which acts preferentially on N(8)-acetylspermidine, and also on acetylcadaverine and acetylputrescine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Carbon-nitrogen hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.5.1.48
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MGTALVYHEDMTATRLLWDDPECEIERPERLTAALDRLRQRGLEQRCLRLSAREASEEEL
GLVHSPEYVSLVRETQVLGKEELQALSGQFDAIYFHPSTFHCARLAAGAGLQLVDAVLTG AVQNGLALVRPPGHHGQRAAANGFCVFNNVAIAAAHAKQKHGLHRILVVDWDVHHGQGIQ YLFEDDPSVLYFSWHRYEHGRFWPFLRESDADAVGRGQGLGFTVNLPWNQVGMGNADYVA AFLHLLLPLAFEFDPELVLVSAGFDSAIGDPEGQMQATPECFAHLTQLLQVLAGGRVCAV LEGGYHLESLAESVCMTVQTLLGDPAPPLSGPMAPCQSALESIQSARAAQAPHWKSLQQQ DVTAVPMSPSSHSPEGRPPPLLPGGPVCKAAASAPSSLLDQPCLCPAPSVRTAVALTTPD ITLVLPPDVIQQEASALREETEAWARPHESLAREEALTALGKLLYLLDGMLDGQVNSGIA ATPASAAAATLDVAVRRGLSHGAQRLLCVALGQLDRPPDLAHDGRSLWLNIRGKEAAALS MFHVSTPLPVMTGGFLSCILGLVLPLAYGFQPDLVLVALGPGHGLQGPHAALLAAMLRGL AGGRVLALLEENSTPQLAGILARVLNGEAPPSLGPSSVASPEDVQALMYLRGQLEPQWKM LQCHPHLVA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
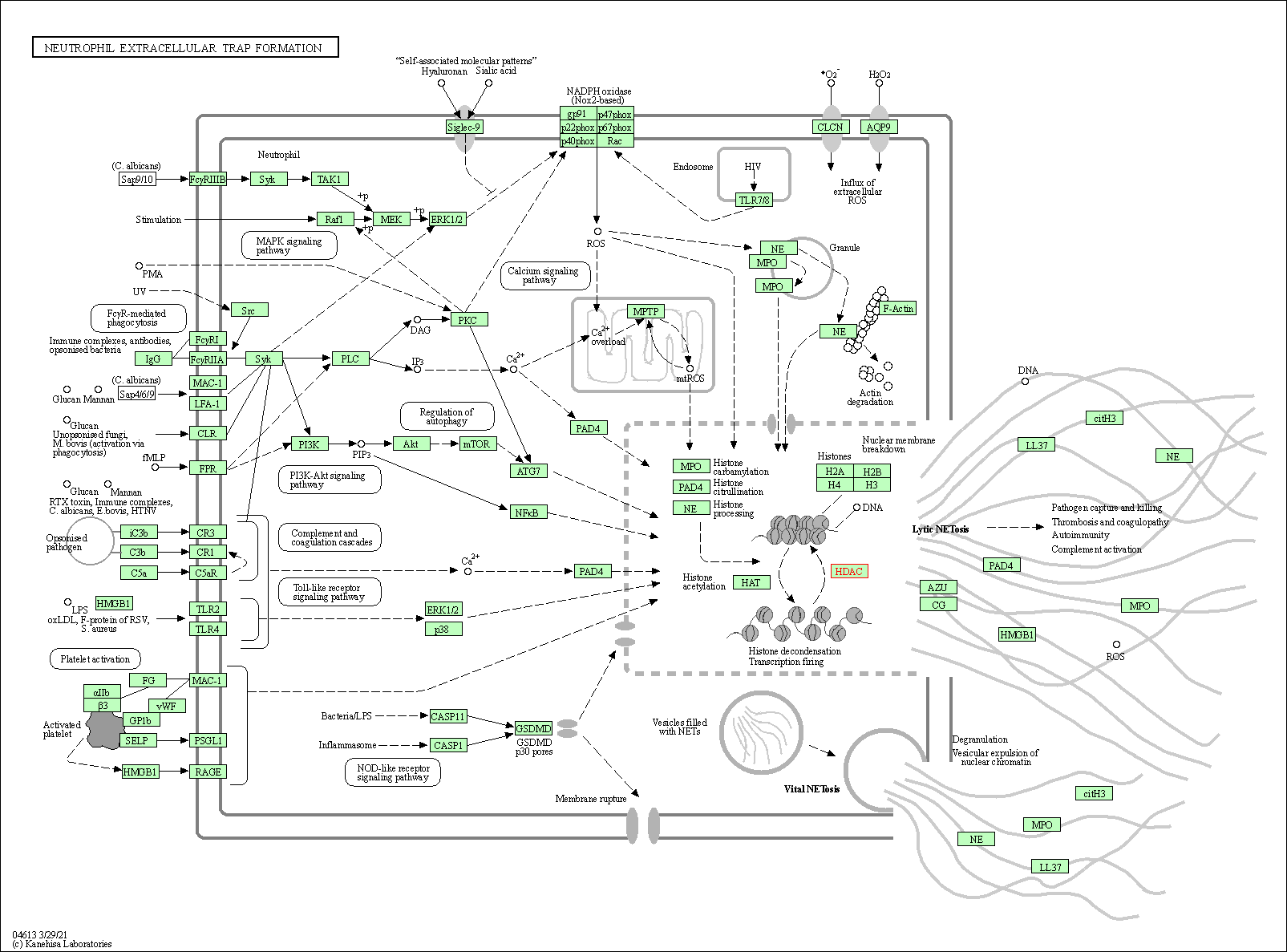
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID Pathway | [+] 2 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Signaling events mediated by HDAC Class II | |||||
| 2 | Signaling events mediated by HDAC Class I | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | HDAC inhibitors: a 2013-2017 patent survey.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Apr 19:1-17. | |||||
| REF 2 | Heterocyclic ketones as inhibitors of histone deacetylase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Nov 17;13(22):3909-13. | |||||
| REF 3 | New sulfurated derivatives of valproic acid with enhanced histone deacetylase inhibitory activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Mar 15;18(6):1893-7. | |||||
| REF 4 | Structure-based optimization of phenylbutyrate-derived histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2005 Aug 25;48(17):5530-5. | |||||
| REF 5 | Zn2+-chelating motif-tethered short-chain fatty acids as a novel class of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2004 Jan 15;47(2):467-74. | |||||
| REF 6 | Inhibitors of human histone deacetylase: synthesis and enzyme and cellular activity of straight chain hydroxamates. J Med Chem. 2002 Feb 14;45(4):753-7. | |||||
| REF 7 | Novel inhibitors of human histone deacetylases: design, synthesis, enzyme inhibition, and cancer cell growth inhibition of SAHA-based non-hydroxama... J Med Chem. 2005 Feb 24;48(4):1019-32. | |||||
| REF 8 | Stereodefined and polyunsaturated inhibitors of histone deacetylase based on (2E,4E)-5-arylpenta-2,4-dienoic acid hydroxyamides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 May 17;14(10):2477-81. | |||||
| REF 9 | Aromatic sulfide inhibitors of histone deacetylase based on arylsulfinyl-2,4-hexadienoic acid hydroxyamides. J Med Chem. 2006 Jan 26;49(2):800-5. | |||||
| REF 10 | Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2003 Nov 20;46(24):5097-116. | |||||
| REF 11 | Three new cyclostellettamines, which inhibit histone deacetylase, from a marine sponge of the genus Xestospongia. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 May 17;14(10):2617-20. | |||||
| REF 12 | Mercaptoamide-based non-hydroxamic acid type histone deacetylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Apr 15;15(8):1969-72. | |||||
| REF 13 | N-Hydroxy-(4-oxime)-cinnamide: a versatile scaffold for the synthesis of novel histone deacetylase [correction of deacetilase] (HDAC) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Apr 15;19(8):2346-9. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

