Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T16868
(Former ID: TTDC00137)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Neural cadherin (CDH2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
NCAD; N-cadherin; Cadherin-2; CDw325; CDHN; CD325
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CDH2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. Acts as a regulator of neural stem cells quiescence by mediating anchorage of neural stem cells to ependymocytes in the adult subependymal zone: upon cleavage by MMP24, CDH2-mediated anchorage is affected, leading to modulate neural stem cell quiescence. CDH2 may be involved in neuronal recognition mechanism. In hippocampal neurons, may regulate dendritic spine density. Calcium-dependent cell adhesion protein; preferentially mediates homotypic cell-cell adhesion by dimerization with a CDH2 chain from another cell.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cadherin protein
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MCRIAGALRTLLPLLAALLQASVEASGEIALCKTGFPEDVYSAVLSKDVHEGQPLLNVKF
SNCNGKRKVQYESSEPADFKVDEDGMVYAVRSFPLSSEHAKFLIYAQDKETQEKWQVAVK LSLKPTLTEESVKESAEVEEIVFPRQFSKHSGHLQRQKRDWVIPPINLPENSRGPFPQEL VRIRSDRDKNLSLRYSVTGPGADQPPTGIFIINPISGQLSVTKPLDREQIARFHLRAHAV DINGNQVENPIDIVINVIDMNDNRPEFLHQVWNGTVPEGSKPGTYVMTVTAIDADDPNAL NGMLRYRIVSQAPSTPSPNMFTINNETGDIITVAAGLDREKVQQYTLIIQATDMEGNPTY GLSNTATAVITVTDVNDNPPEFTAMTFYGEVPENRVDIIVANLTVTDKDQPHTPAWNAVY RISGGDPTGRFAIQTDPNSNDGLVTVVKPIDFETNRMFVLTVAAENQVPLAKGIQHPPQS TATVSVTVIDVNENPYFAPNPKIIRQEEGLHAGTMLTTFTAQDPDRYMQQNIRYTKLSDP ANWLKIDPVNGQITTIAVLDRESPNVKNNIYNATFLASDNGIPPMSGTGTLQIYLLDIND NAPQVLPQEAETCETPDPNSINITALDYDIDPNAGPFAFDLPLSPVTIKRNWTITRLNGD FAQLNLKIKFLEAGIYEVPIIITDSGNPPKSNISILRVKVCQCDSNGDCTDVDRIVGAGL GTGAIIAILLCIIILLILVLMFVVWMKRRDKERQAKQLLIDPEDDVRDNILKYDEEGGGE EDQDYDLSQLQQPDTVEPDAIKPVGIRRMDERPIHAEPQYPVRSAAPHPGDIGDFINEGL KAADNDPTAPPYDSLLVFDYEGSGSTAGSLSSLNSSSSGGEQDYDYLNDWGPRFKKLADM YGGGDD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T12IEI | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Exherin | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Exherin | Drug Info | [1], [3] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cadherin-related family member 5 (CDHR5) | 25.664 (29/113) | 3.00E-03 | |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
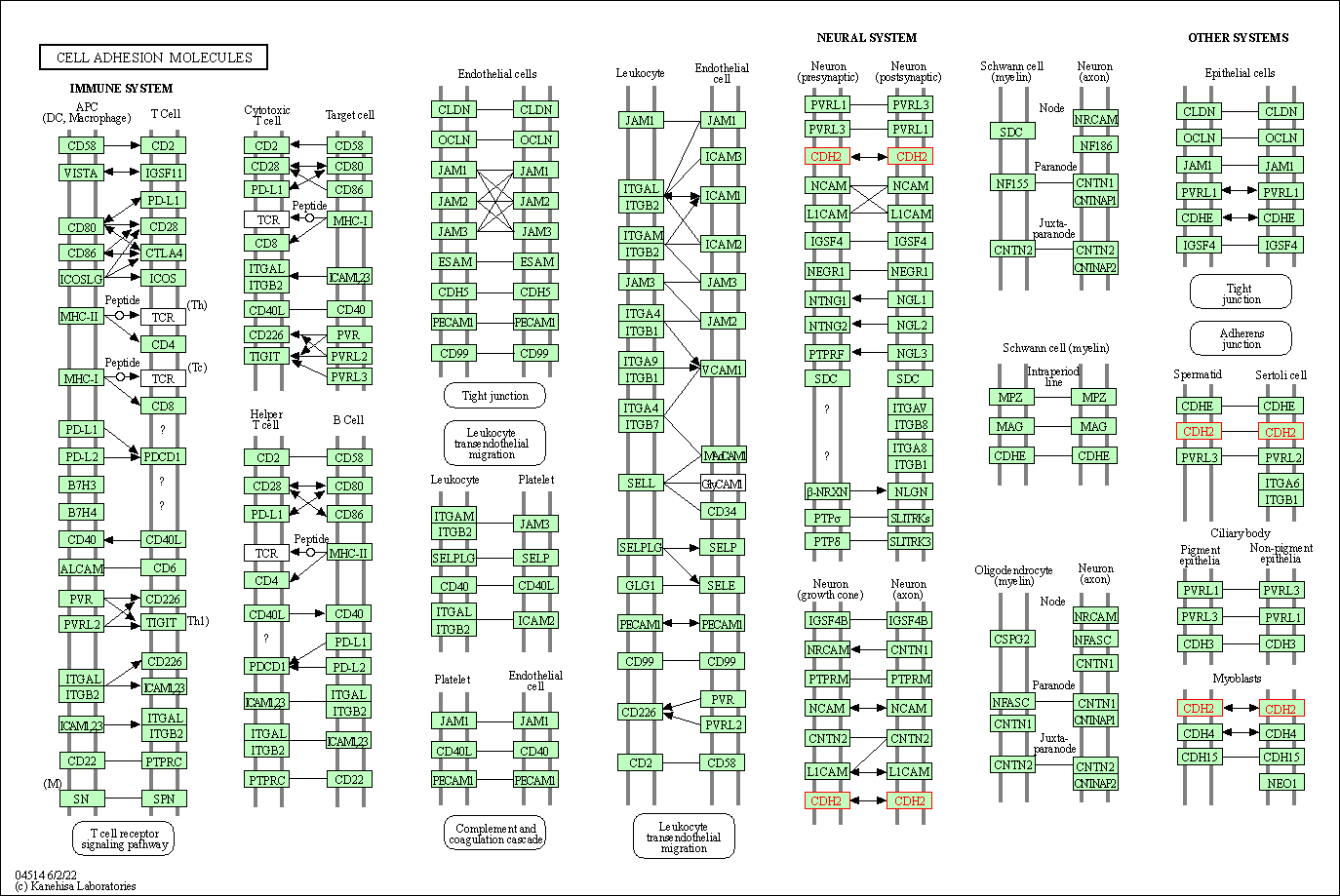
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 7.88E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.45E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.93E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.92E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.80E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | |||||
| 2 | Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 2 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cadherin signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Wnt signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 4 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Signaling events mediated by PTP1B | |||||
| 2 | Posttranslational regulation of adherens junction stability and dissassembly | |||||
| 3 | N-cadherin signaling events | |||||
| 4 | FGF signaling pathway | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | CDO in myogenesis | |||||
| 2 | Adherens junctions interactions | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 5 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis FSGS | |||||
| 2 | BDNF signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy | |||||
| 4 | Neural Crest Differentiation | |||||
| 5 | Cell junction organization | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical and pharmacological phase I evaluation of Exherin (ADH-1), a selective anti-N-cadherin peptide in patients with N-cadherin-expressing soli... Ann Oncol. 2009 Apr;20(4):741-5. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00264433) A Study of the Safety and Effects of ADH-1 Given Intravenously as a Single Agent. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Gateways to clinical trials. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Sep;26(7):587-612. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

