Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T40192
(Former ID: TTDI01966)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
DNA-binding factor KBF1 (p105)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in Bcells 1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1; Nuclear factor NFkappaB p50 subunit; Nuclear factor NFkappaB p105 subunit; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit; EBP1; EBP-1; DNAbinding factor KBF1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
NFKB1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Muscular dystrophy [ICD-11: 8C70] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 3 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||||
| Function |
NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105. NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAEDDPYLGRPEQMFHLDPSLTHTIFNPEVFQPQMALPTDGPYLQILEQPKQRGFRFRYV
CEGPSHGGLPGASSEKNKKSYPQVKICNYVGPAKVIVQLVTNGKNIHLHAHSLVGKHCED GICTVTAGPKDMVVGFANLGILHVTKKKVFETLEARMTEACIRGYNPGLLVHPDLAYLQA EGGGDRQLGDREKELIRQAALQQTKEMDLSVVRLMFTAFLPDSTGSFTRRLEPVVSDAIY DSKAPNASNLKIVRMDRTAGCVTGGEEIYLLCDKVQKDDIQIRFYEEEENGGVWEGFGDF SPTDVHRQFAIVFKTPKYKDINITKPASVFVQLRRKSDLETSEPKPFLYYPEIKDKEEVQ RKRQKLMPNFSDSFGGGSGAGAGGGGMFGSGGGGGGTGSTGPGYSFPHYGFPTYGGITFH PGTTKSNAGMKHGTMDTESKKDPEGCDKSDDKNTVNLFGKVIETTEQDQEPSEATVGNGE VTLTYATGTKEESAGVQDNLFLEKAMQLAKRHANALFDYAVTGDVKMLLAVQRHLTAVQD ENGDSVLHLAIIHLHSQLVRDLLEVTSGLISDDIINMRNDLYQTPLHLAVITKQEDVVED LLRAGADLSLLDRLGNSVLHLAAKEGHDKVLSILLKHKKAALLLDHPNGDGLNAIHLAMM SNSLPCLLLLVAAGADVNAQEQKSGRTALHLAVEHDNISLAGCLLLEGDAHVDSTTYDGT TPLHIAAGRGSTRLAALLKAAGADPLVENFEPLYDLDDSWENAGEDEGVVPGTTPLDMAT SWQVFDILNGKPYEPEFTSDDLLAQGDMKQLAEDVKLQLYKLLEIPDPDKNWATLAQKLG LGILNNAFRLSPAPSKTLMDNYEVSGGTVRELVEALRQMGYTEAIEVIQAASSPVKTTSQ AHSLPLSPASTRQQIDELRDSDSVCDSGVETSFRKLSFTESLTSGASLLTLNKMPHDYGQ EGPLEGKI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A03065 ; BADD_A03470 ; BADD_A05675 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T06RMZ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CAT 1004 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Duchenne dystrophy | [2] | |
| 2 | P54 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CAT 1004 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | P54 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|



| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
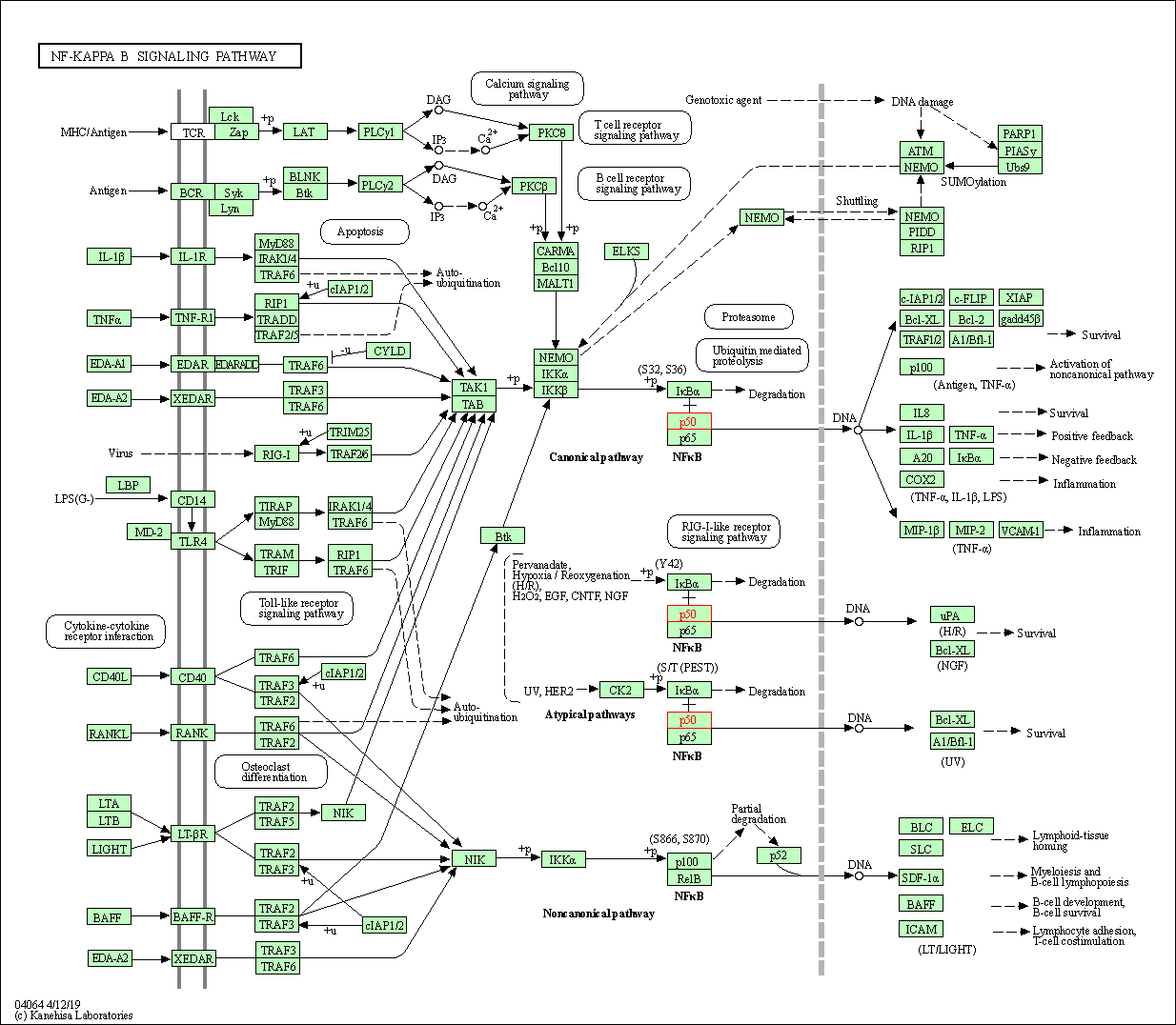
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
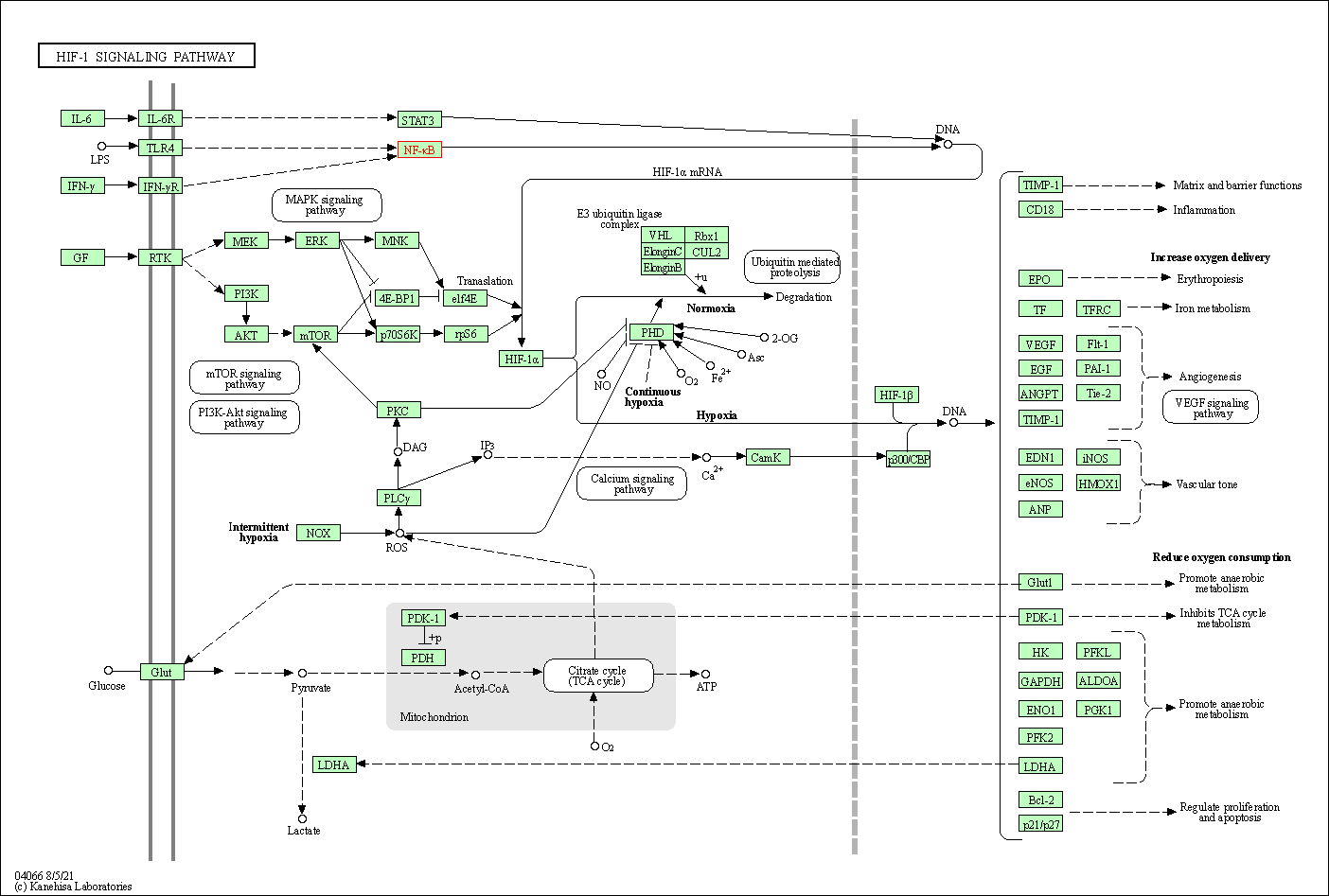
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
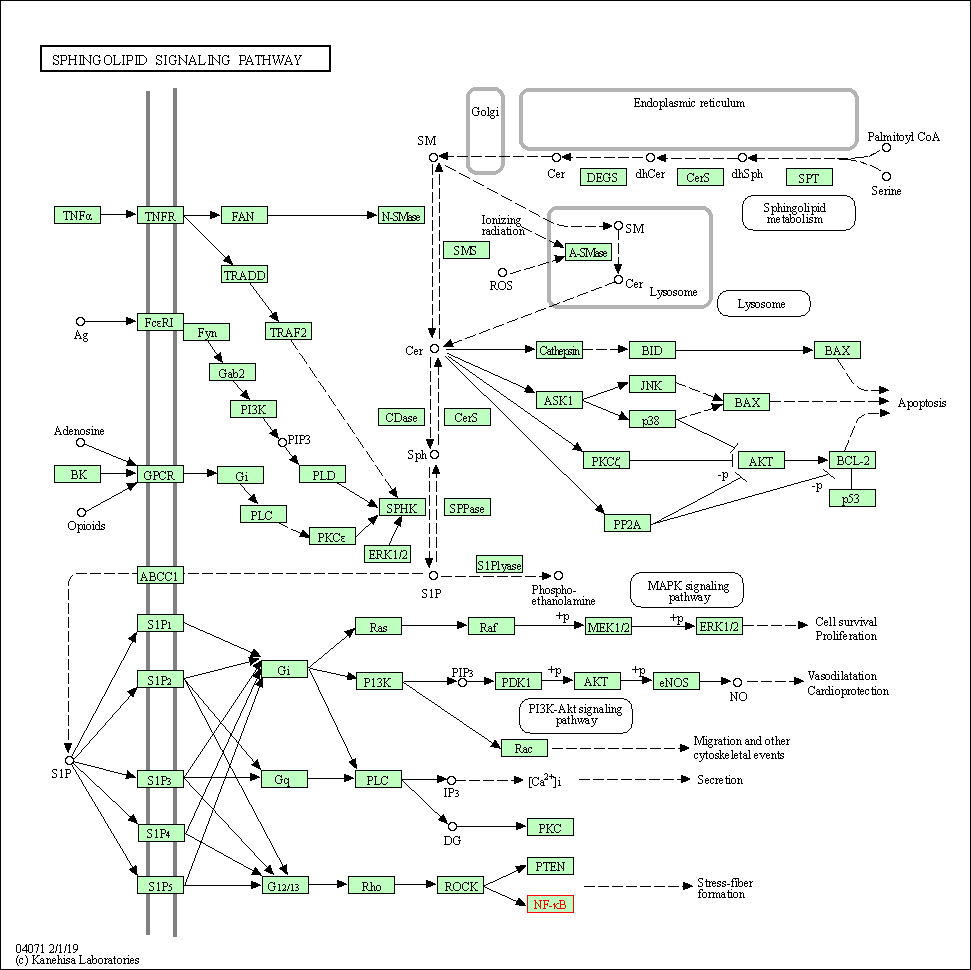
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
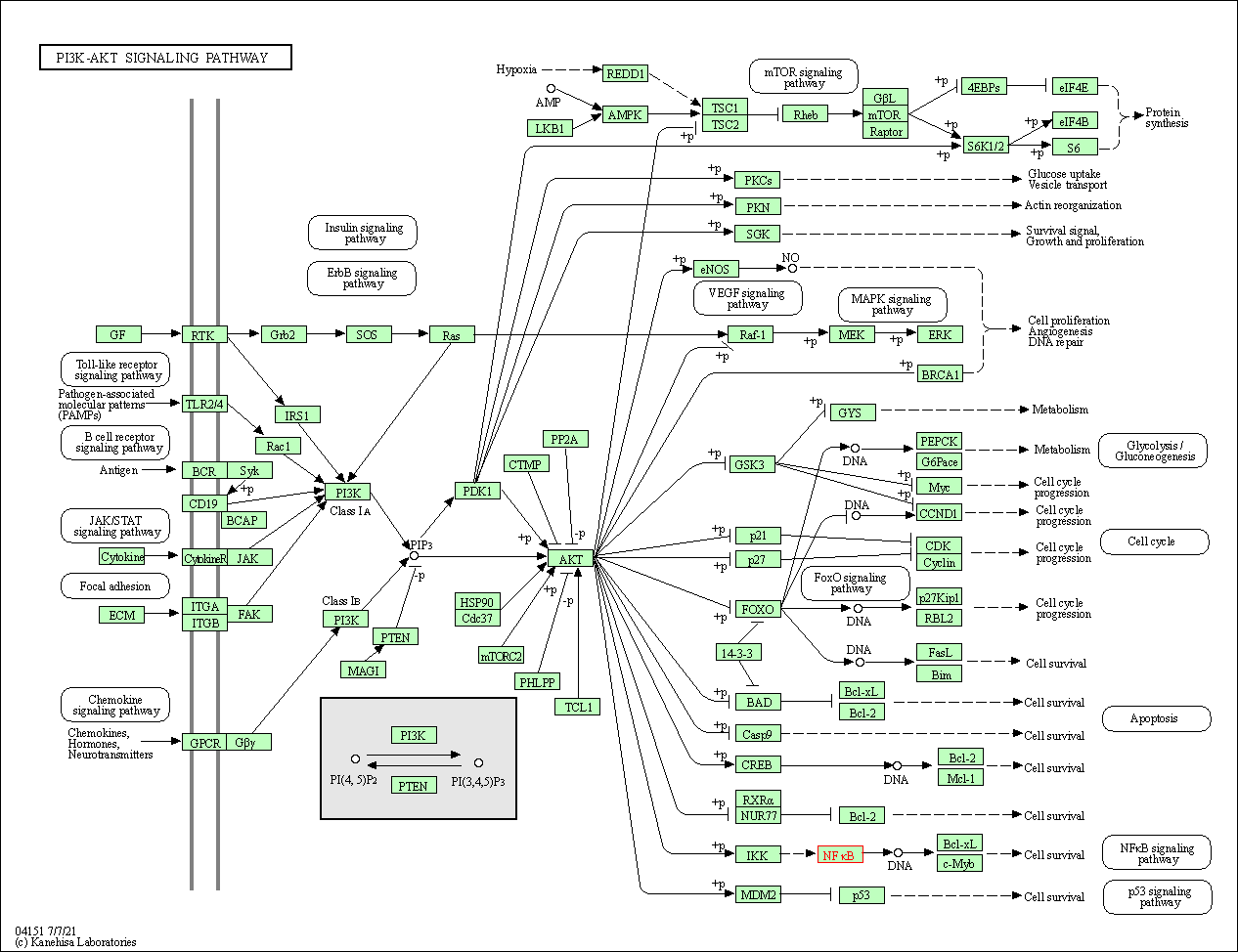
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
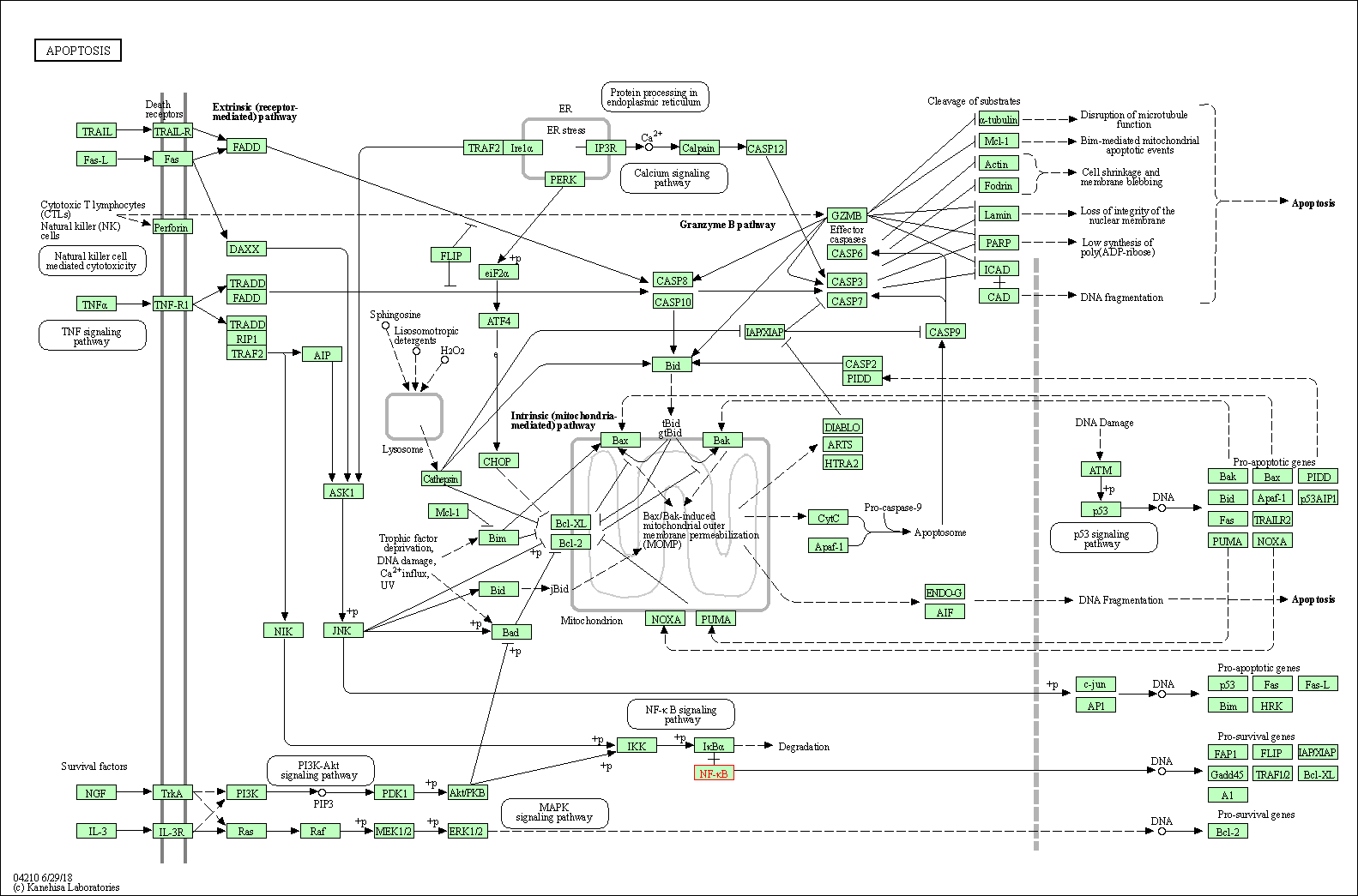
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
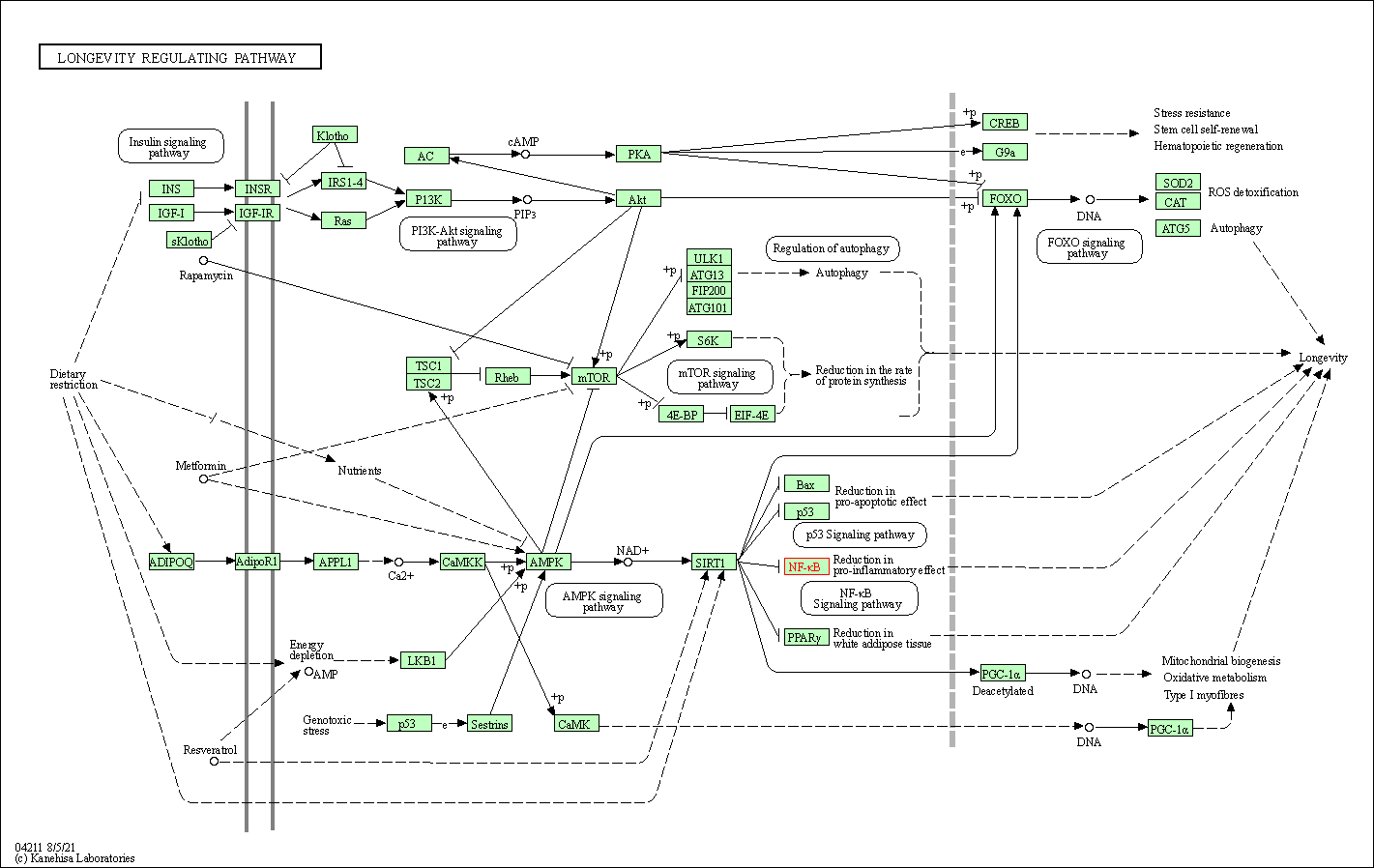
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
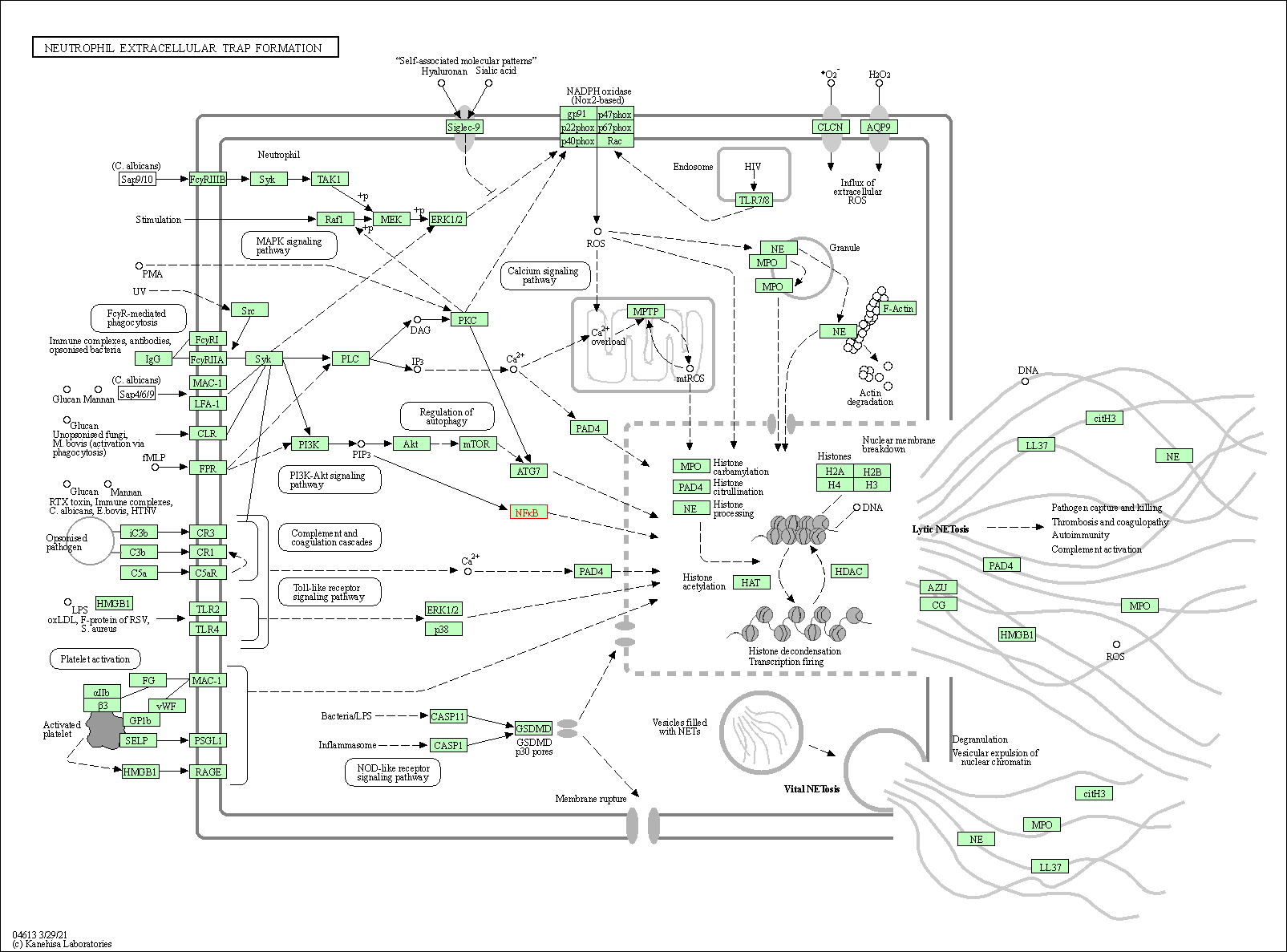
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
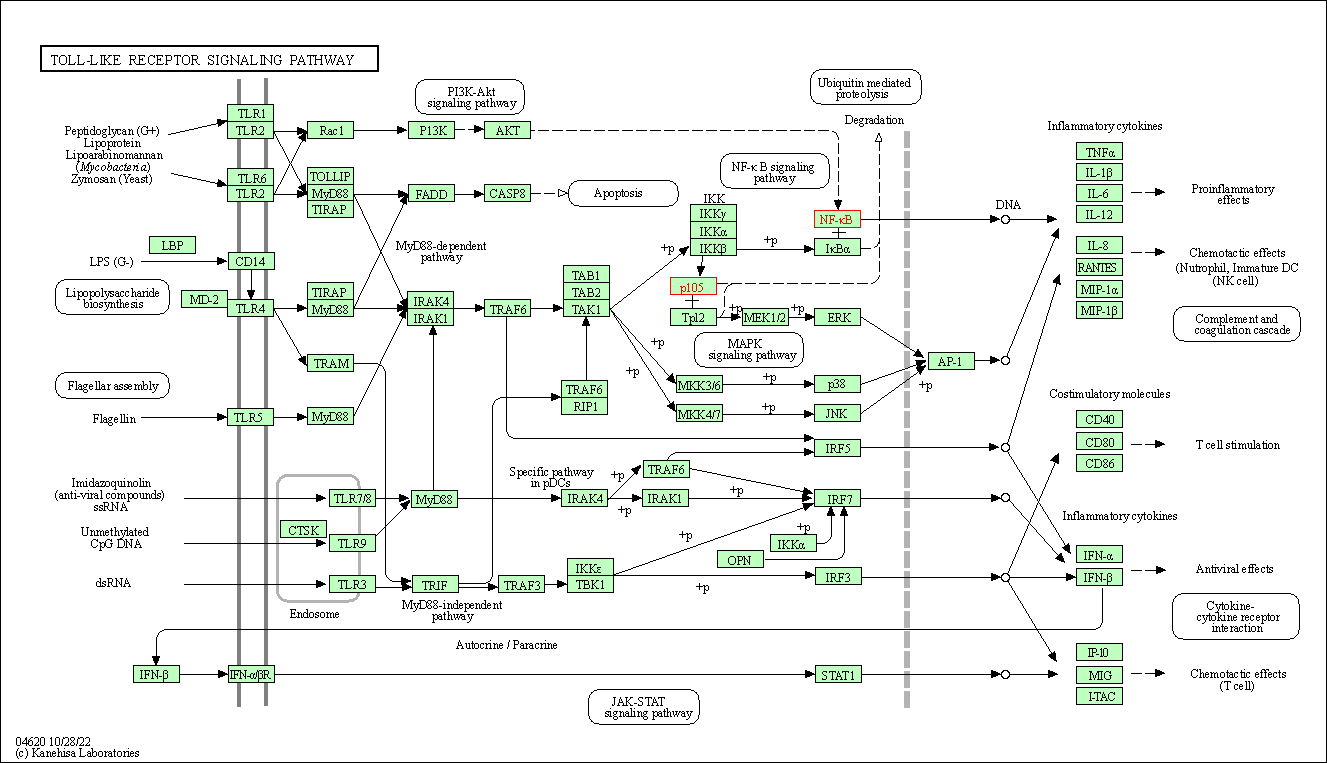
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | hsa04623 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
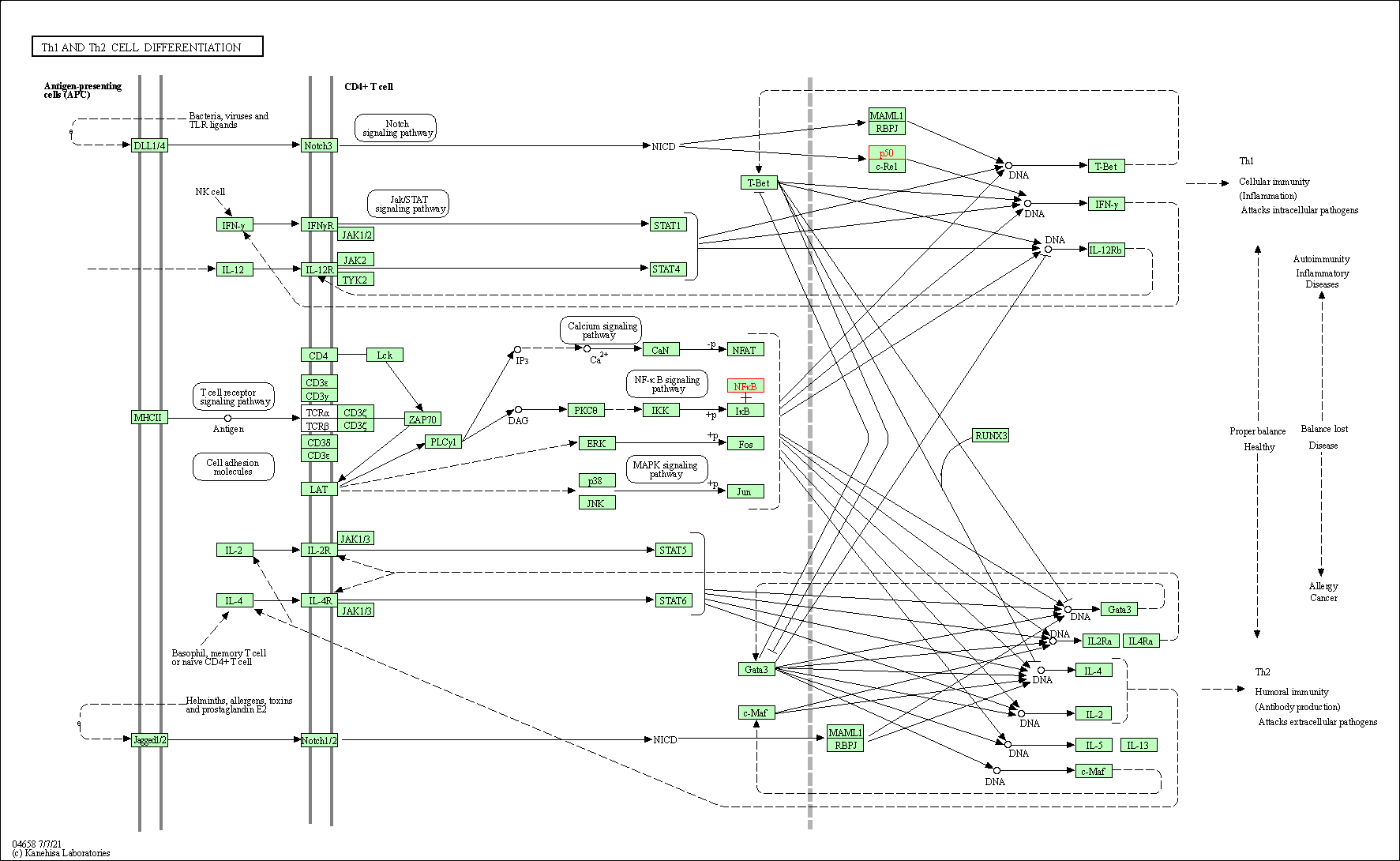
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
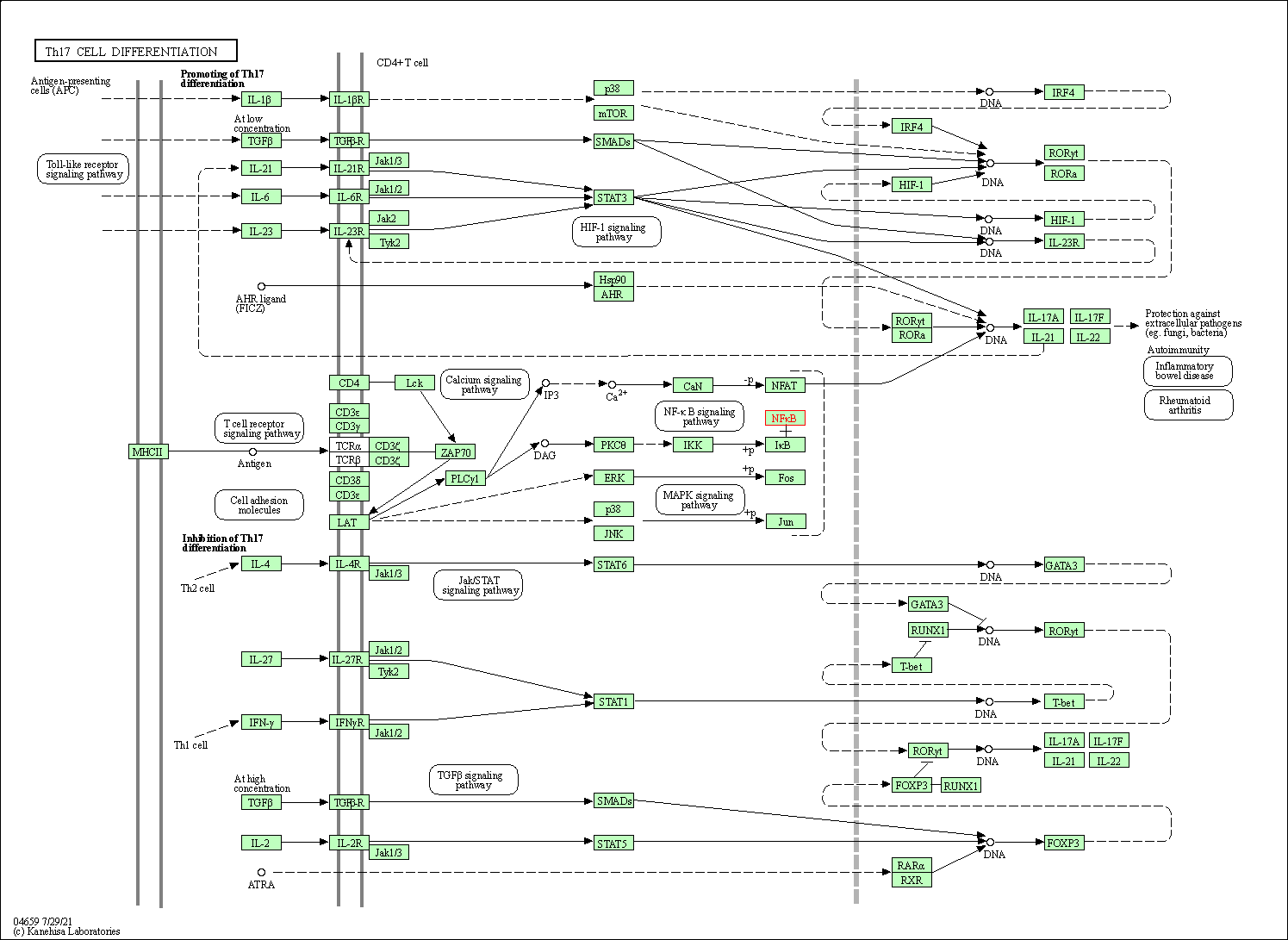
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
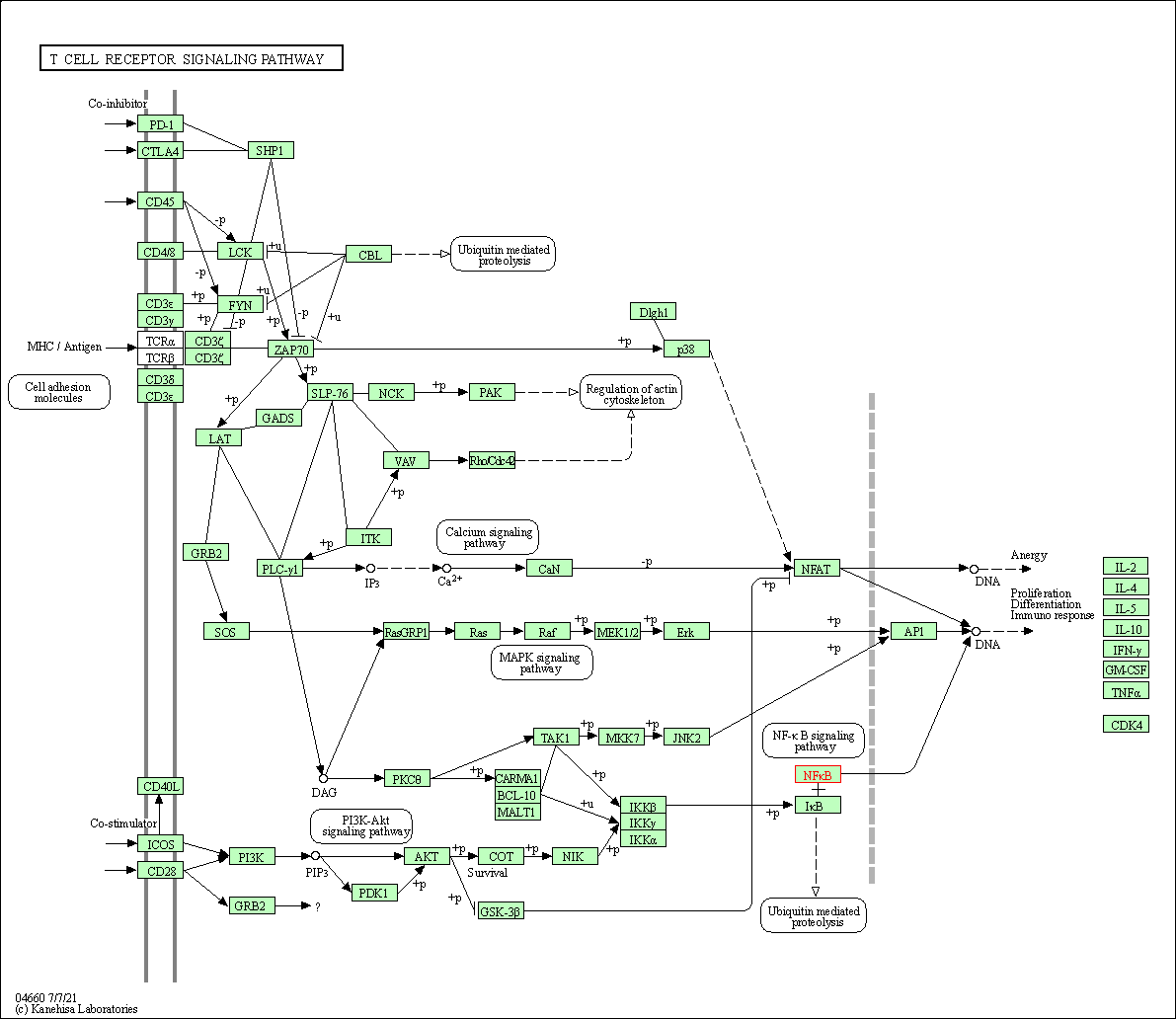
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
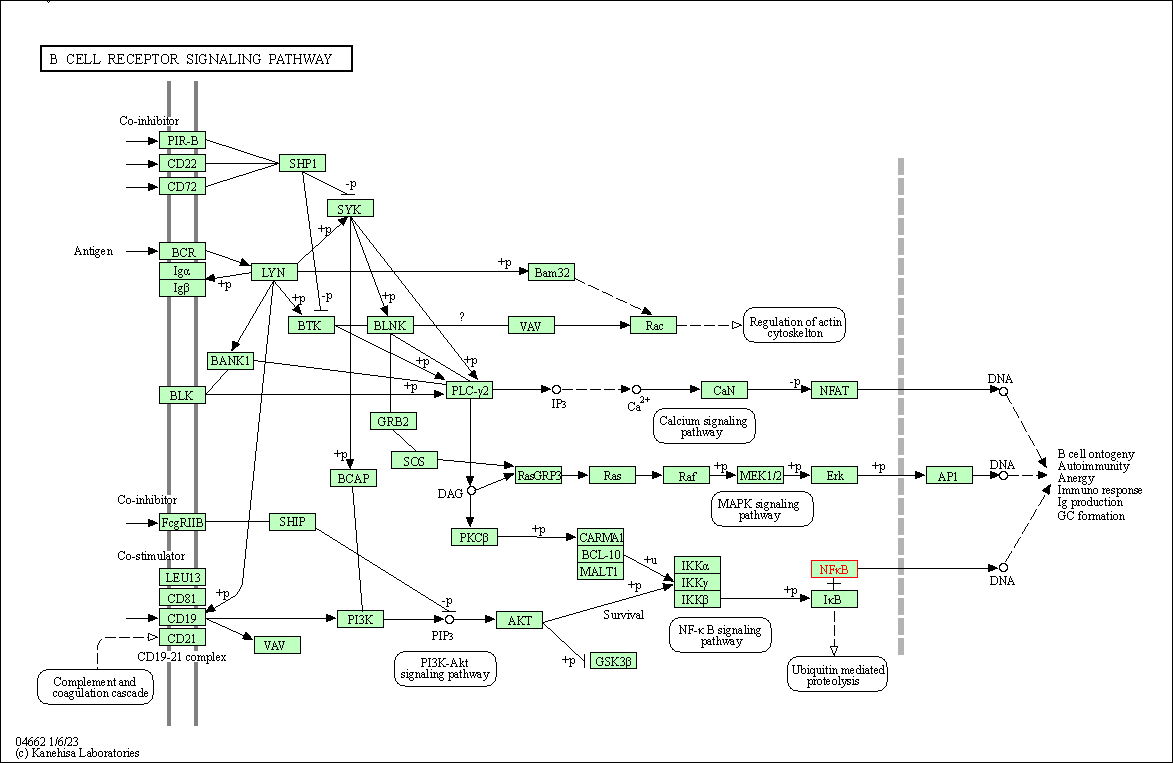
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 33 | Degree centrality | 3.55E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 8.28E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.54E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.30E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.73E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Identification of p54(nrb) and the 14-3-3 Protein HS1 as TNF-alpha-inducible genes related to cell cycle control and apoptosis in human arterial endothelial cells. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Jul 31;38(4):447-56. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | Biotechnology in Comparative Perspective, Gerhard Fuchs. Page(82). | |||||
| REF 4 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Catabasis Pharmaceuticals Inc. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

