Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T53270
(Former ID: TTDI00061)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF-4)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
cAMPresponsive elementbinding protein 2; cAMPdependent transcription factor ATF4; cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 2; cAMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4; Taxresponsive enhancer elementbinding protein 67; TaxREB67; Tax-responsive enhancer element-binding protein 67; TXREB; DNAbinding protein TAXREB67; DNA-binding protein TAXREB67; Cyclic AMPresponsive elementbinding protein 2; Cyclic AMPdependent transcription factor ATF4; Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 2; Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-4; CREB2; CREB-2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ATF4
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Binds the cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AC][AG]-3'), a sequence present in many viral and cellular promoters. Cooperates with FOXO1 in osteoblasts to regulate glucose homeostasis through suppression of beta-cell production and decrease in insulin production. It binds to a Tax-responsive enhancer element in the long terminal repeat of HTLV-I. Regulates the induction of DDIT3/CHOP and asparagine synthetase (ASNS) in response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In concert with DDIT3/CHOP, activates the transcription of TRIB3 and promotes ER stress-induced neuronal apoptosis by regulating the transcriptional induction of BBC3/PUMA. Activates transcription of SIRT4. Regulates the circadian expression of the core clock component PER2 and the serotonin transporter SLC6A4. Binds in a circadian time-dependent manner to the cAMP response elements (CRE) in the SLC6A4 and PER2 promoters and periodically activates the transcription of these genes. During ER stress response, activates the transcription of NLRP1, possibly in concert with other factors. Transcriptional activator.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Basic leucine zipper bZIP
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MTEMSFLSSEVLVGDLMSPFDQSGLGAEESLGLLDDYLEVAKHFKPHGFSSDKAKAGSSE
WLAVDGLVSPSNNSKEDAFSGTDWMLEKMDLKEFDLDALLGIDDLETMPDDLLTTLDDTC DLFAPLVQETNKQPPQTVNPIGHLPESLTKPDQVAPFTFLQPLPLSPGVLSSTPDHSFSL ELGSEVDITEGDRKPDYTAYVAMIPQCIKEEDTPSDNDSGICMSPESYLGSPQHSPSTRG SPNRSLPSPGVLCGSARPKPYDPPGEKMVAAKVKGEKLDKKLKKMEQNKTAATRYRQKKR AEQEALTGECKELEKKNEALKERADSLAKEIQYLKDLIEEVRKARGKKRVP Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T23KDW | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|







| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
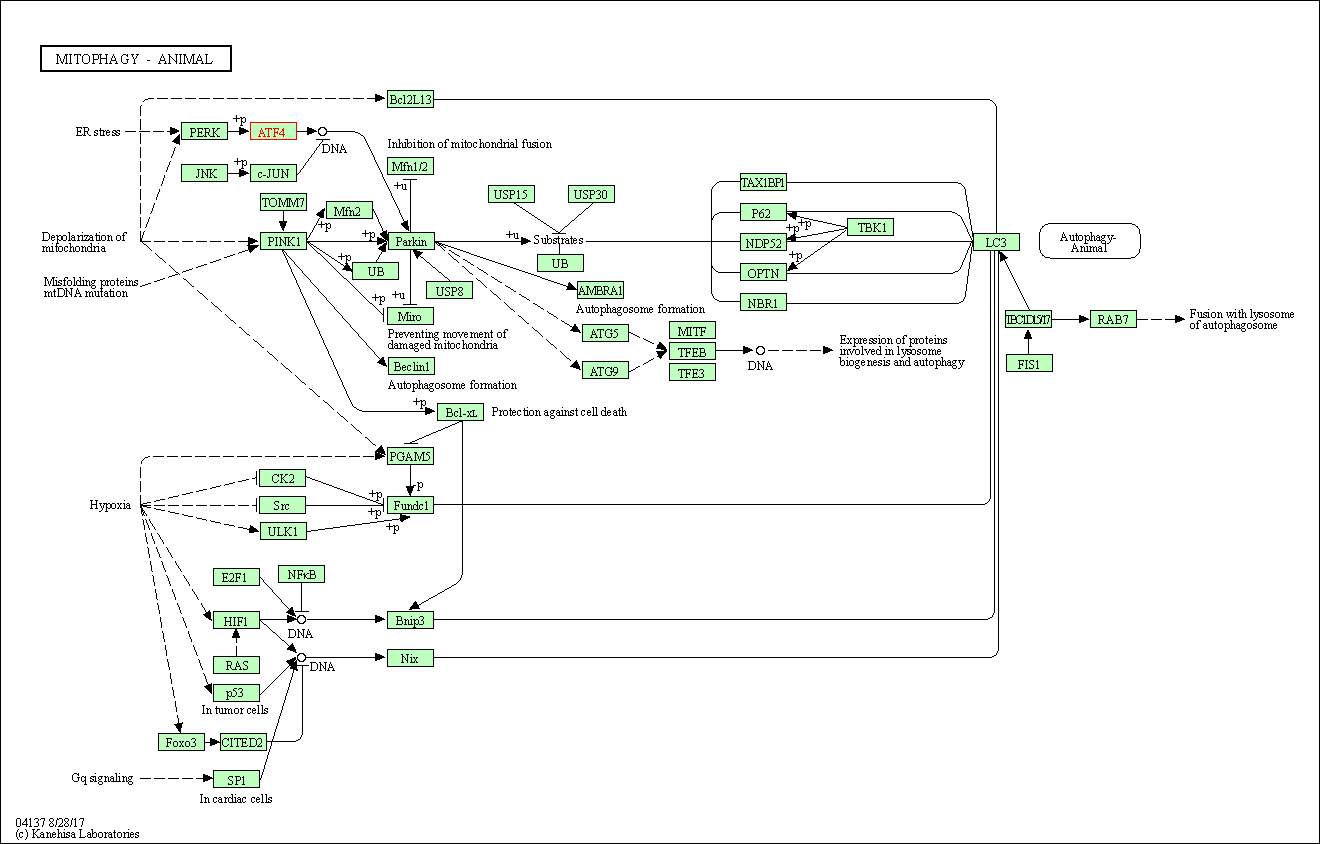
| Mitophagy - animal | hsa04137 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
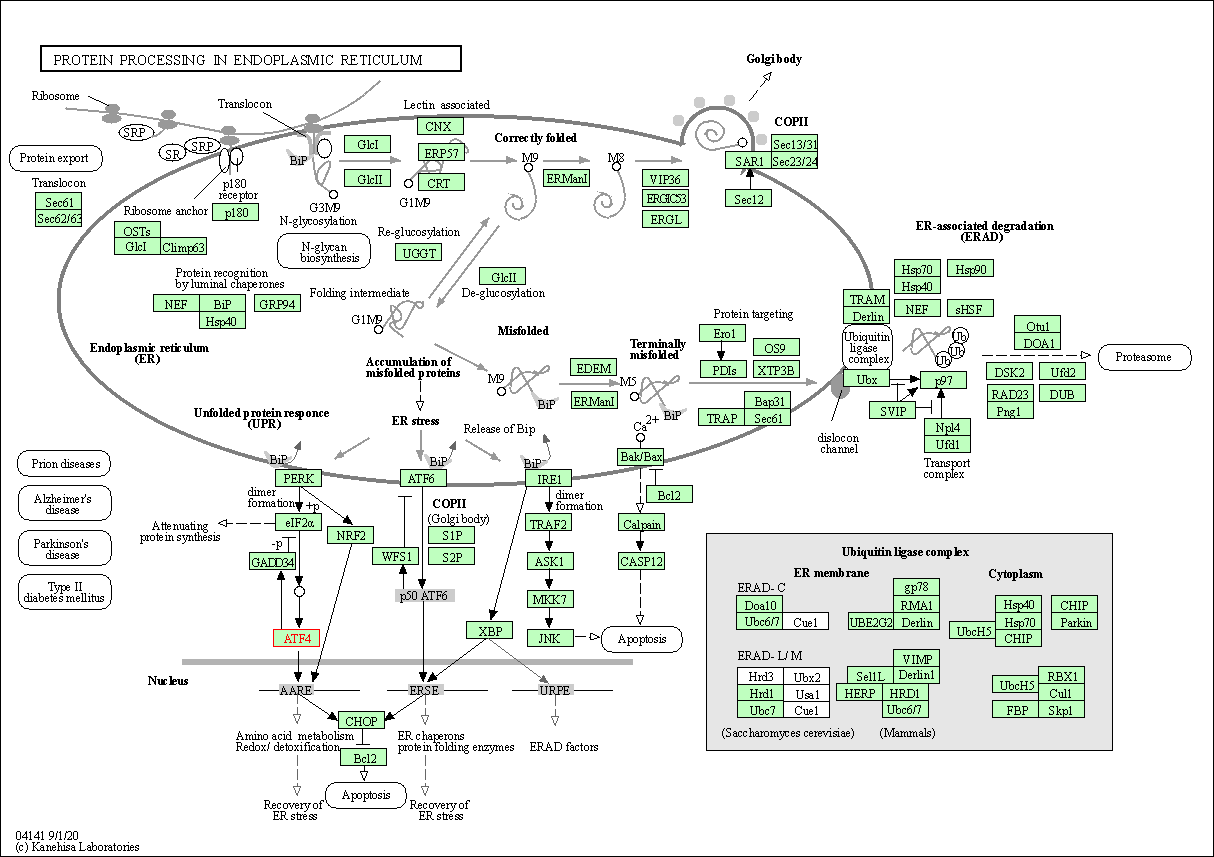
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
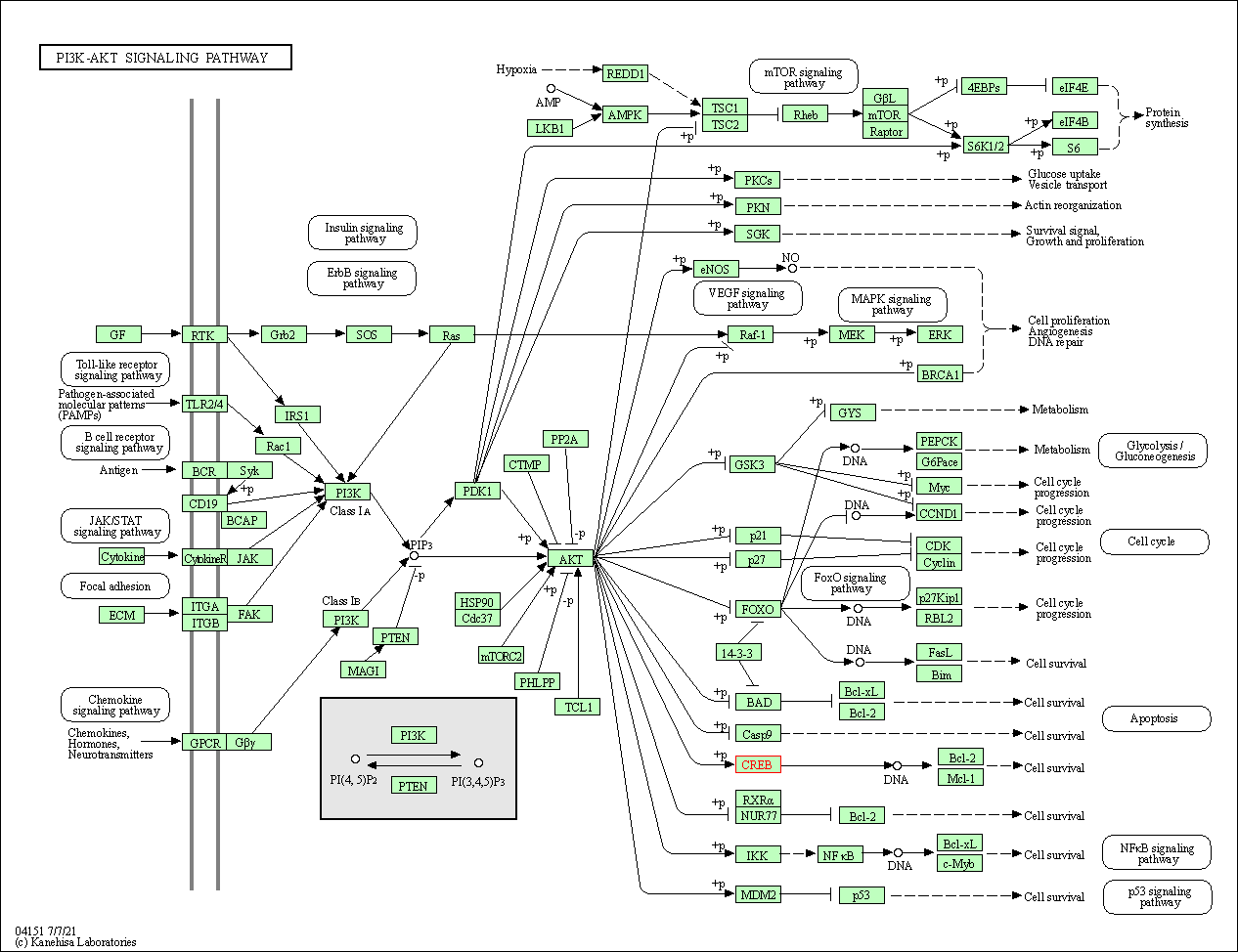
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
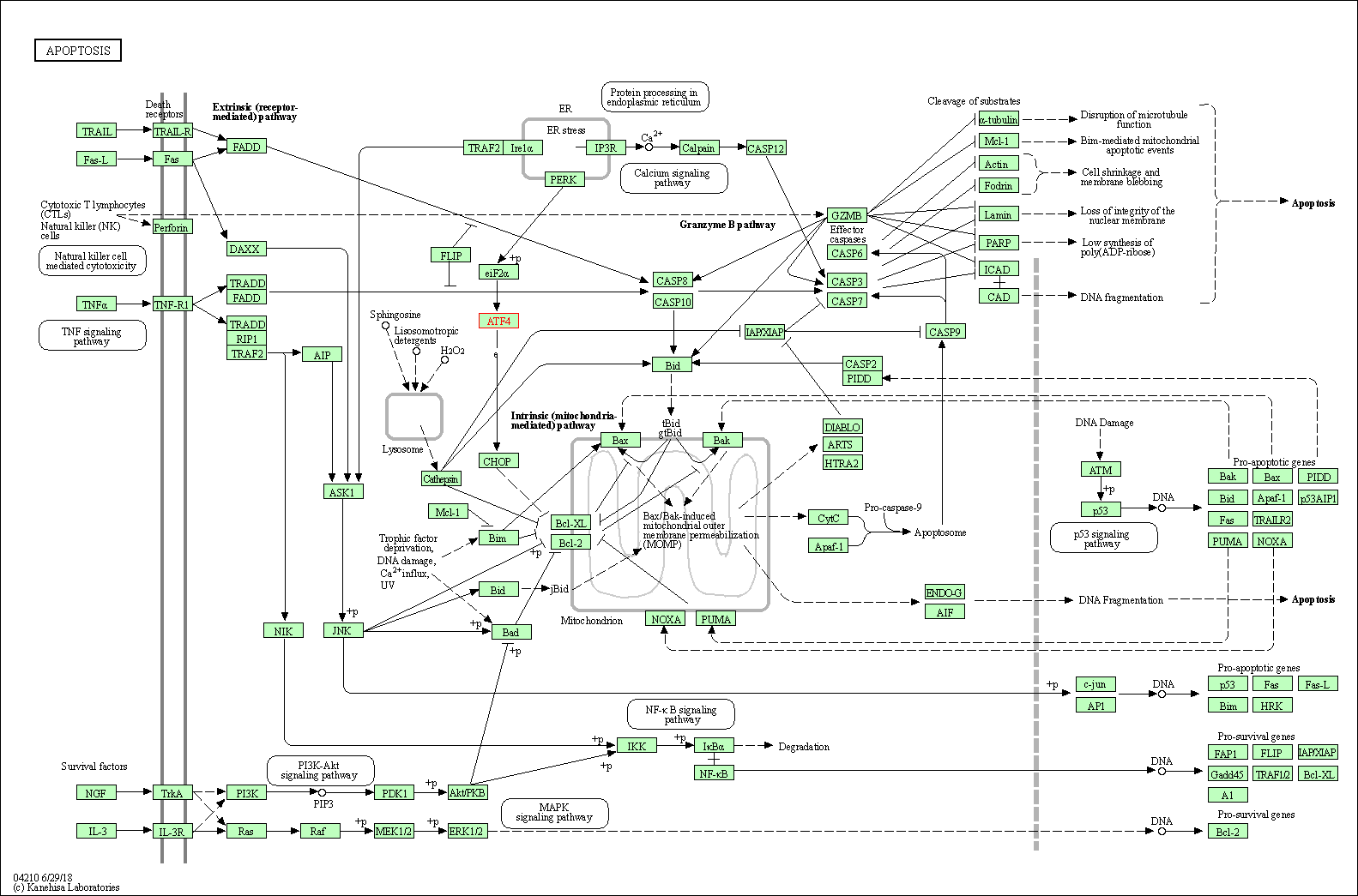
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
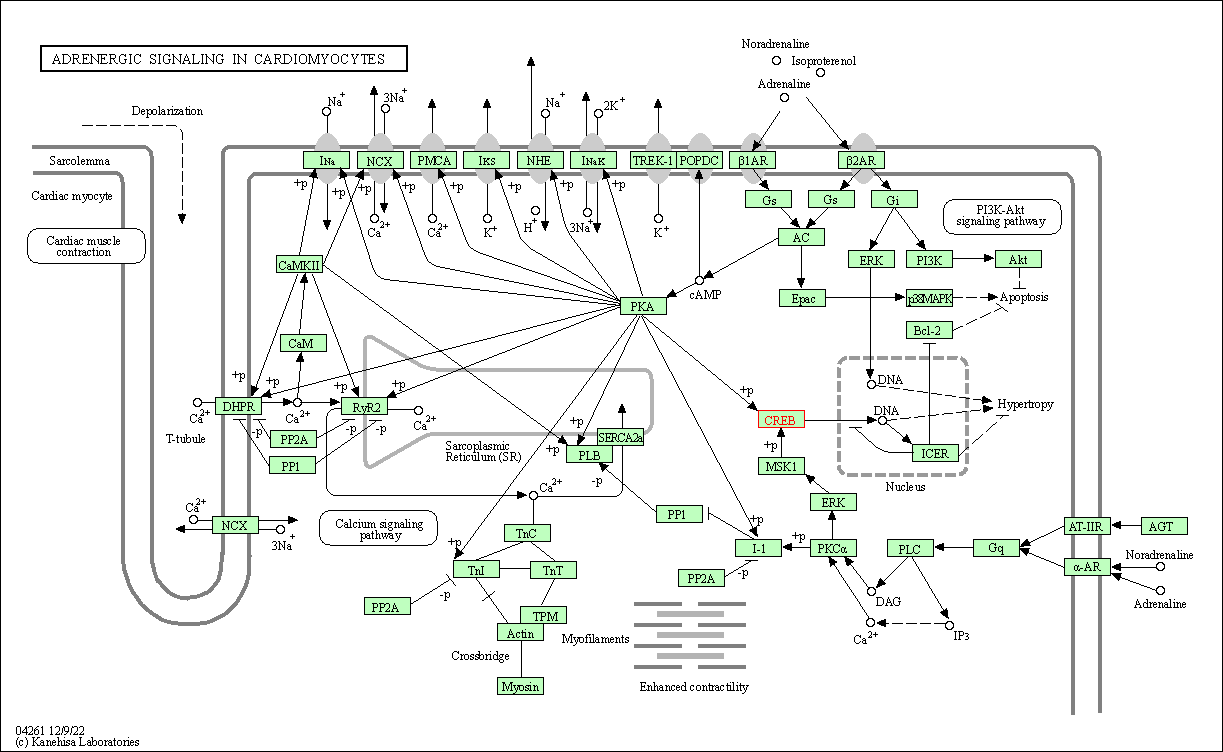
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
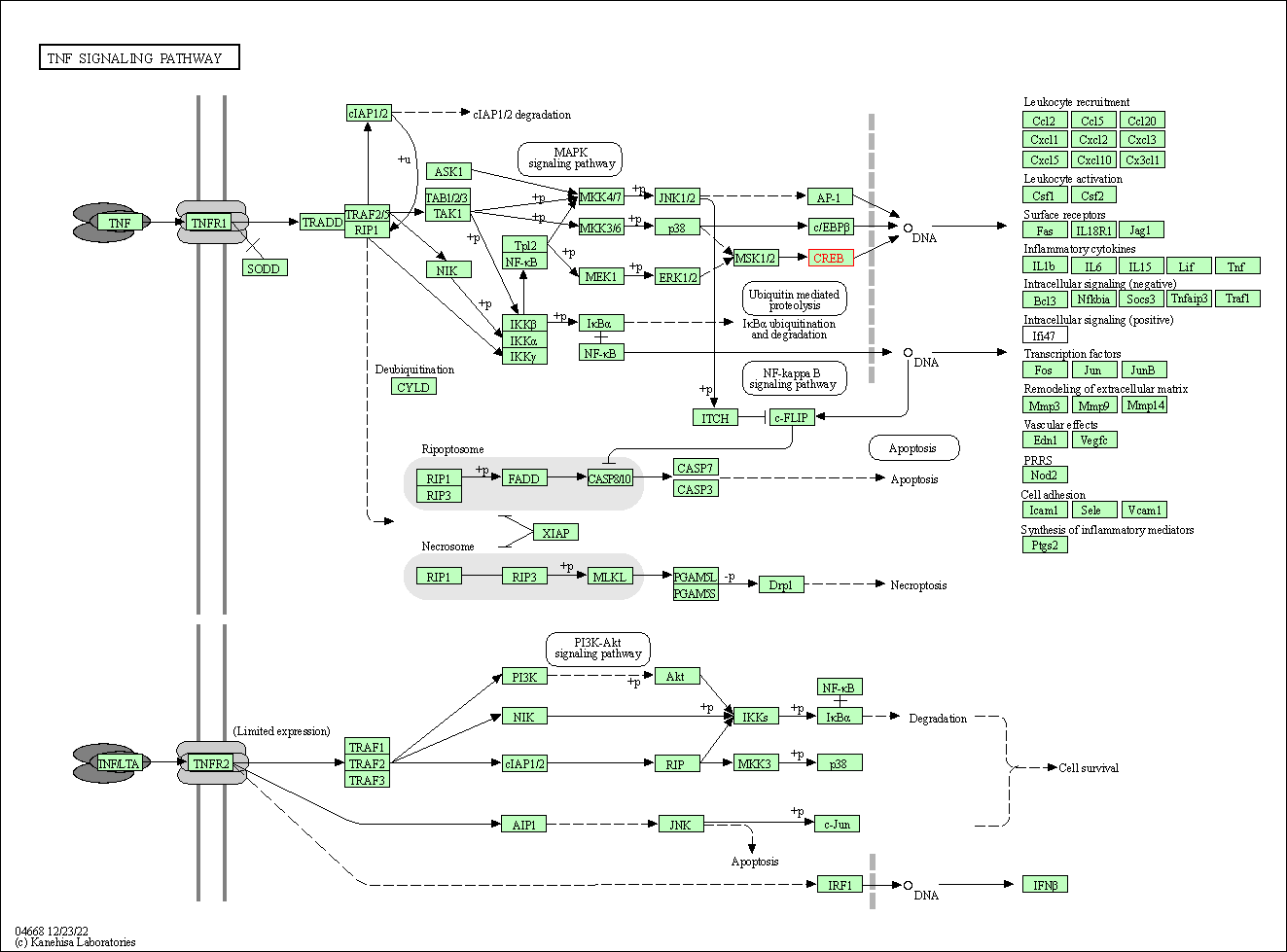
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
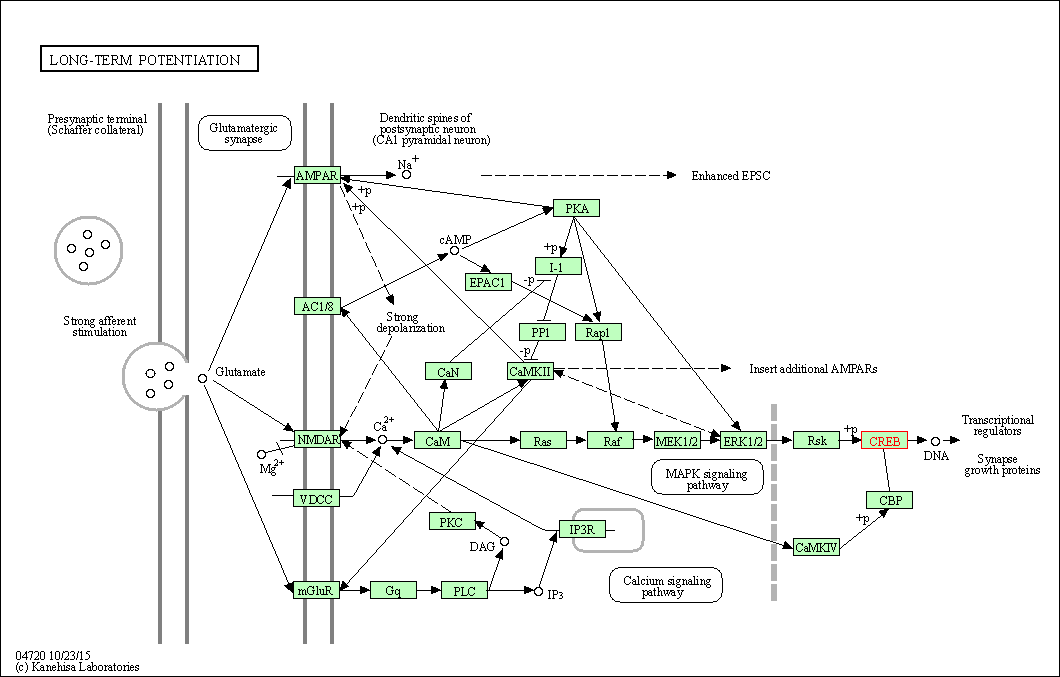
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
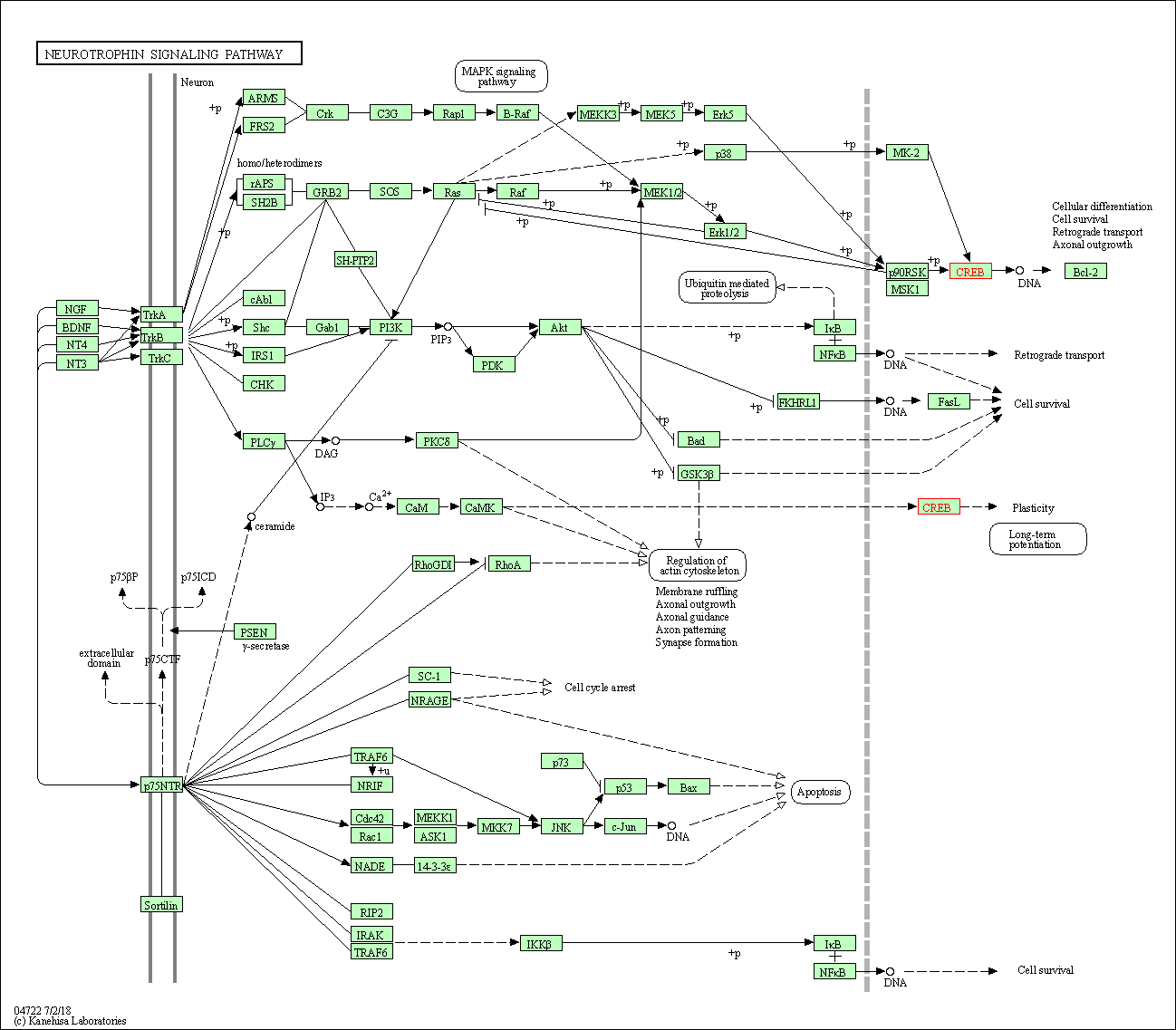
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
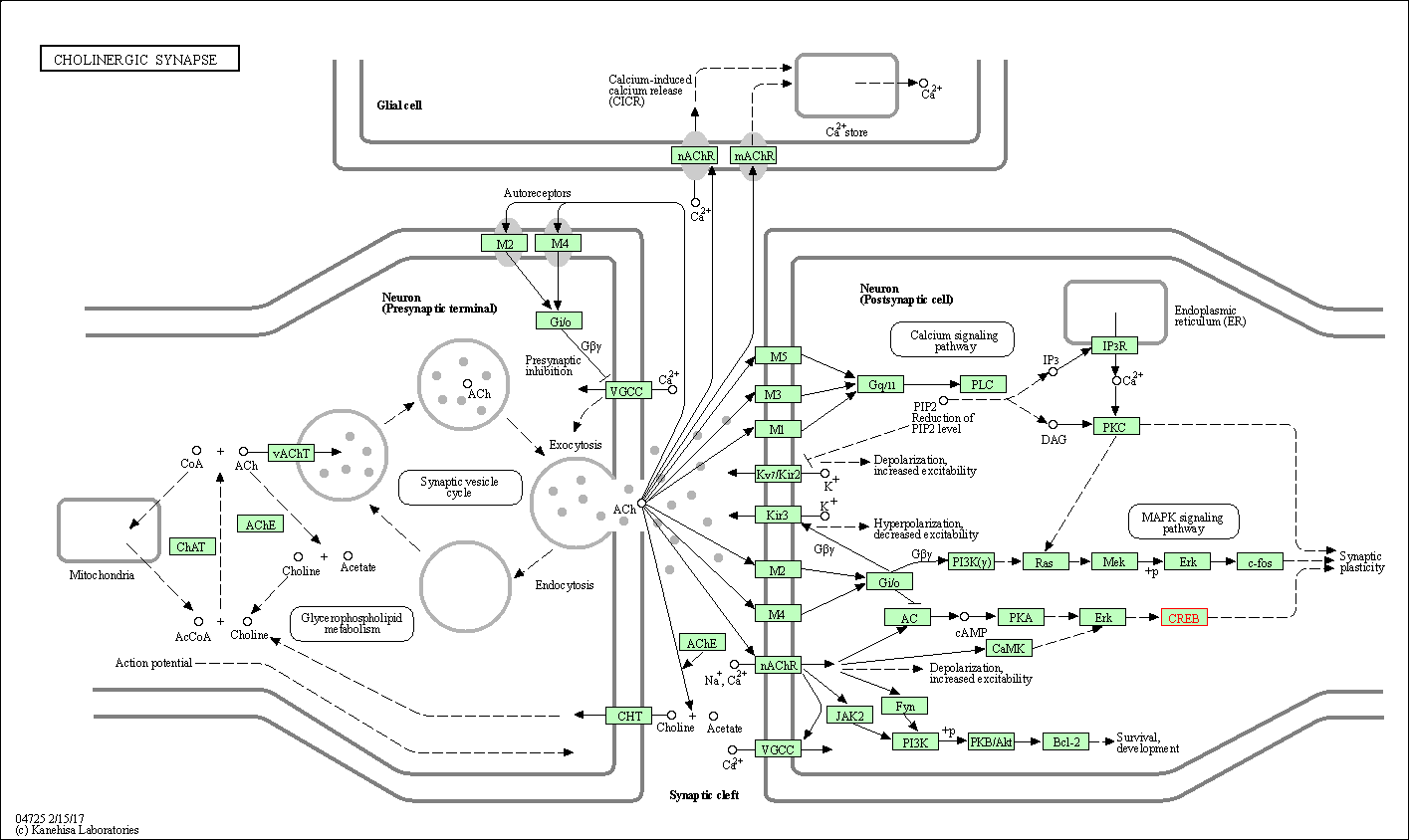
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
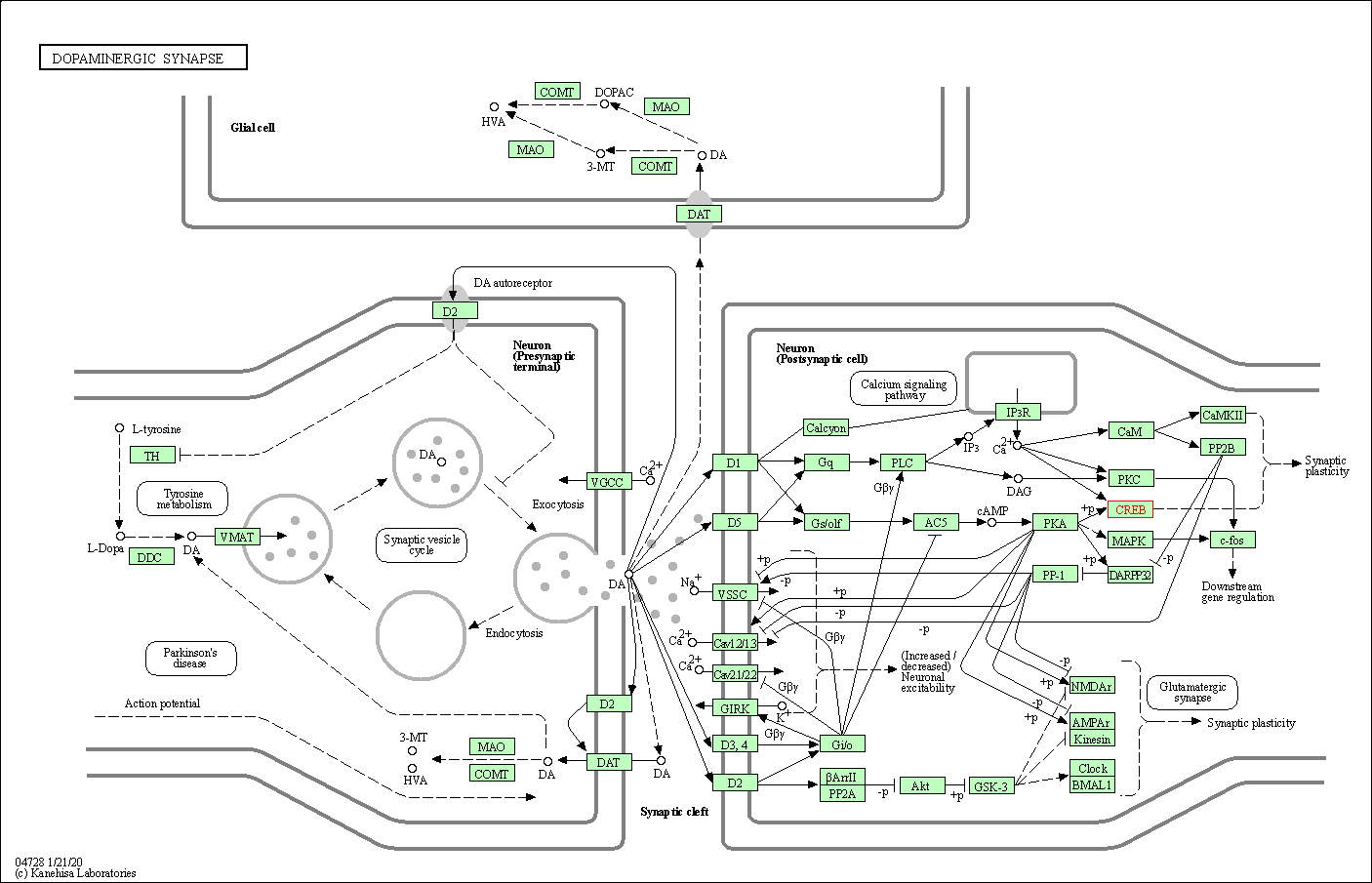
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
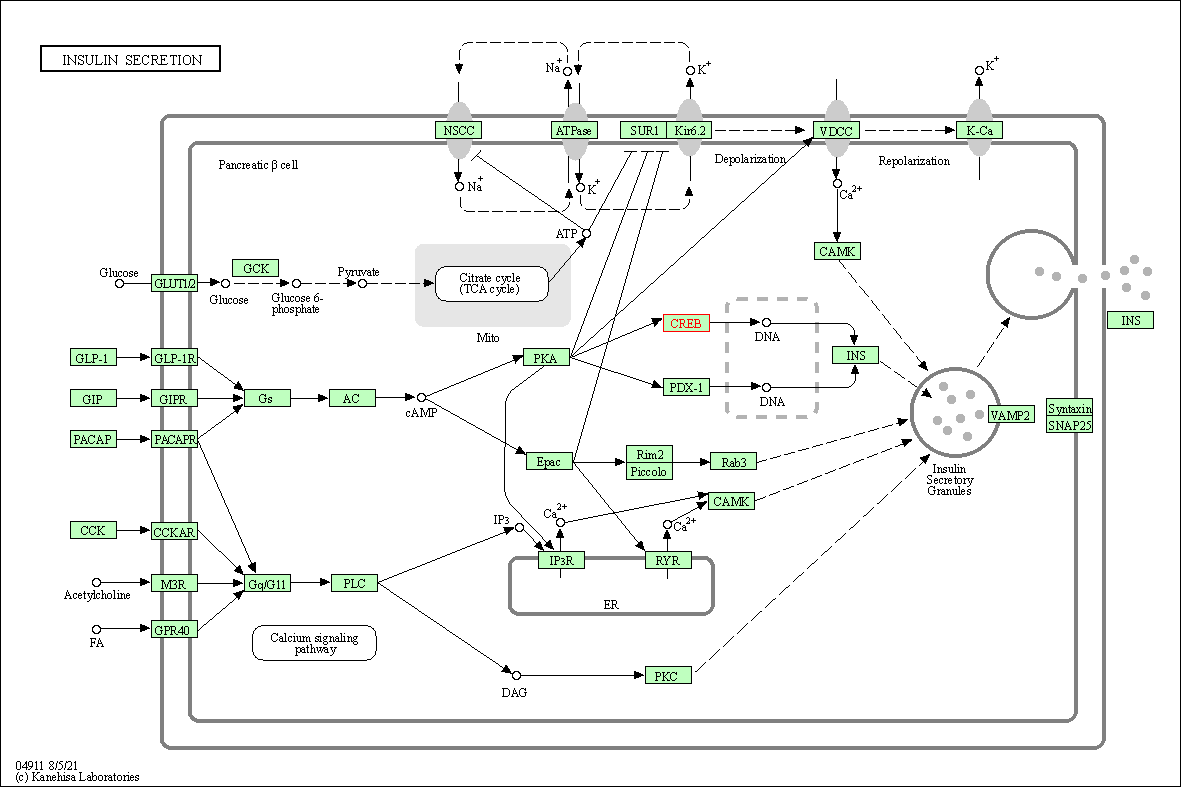
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
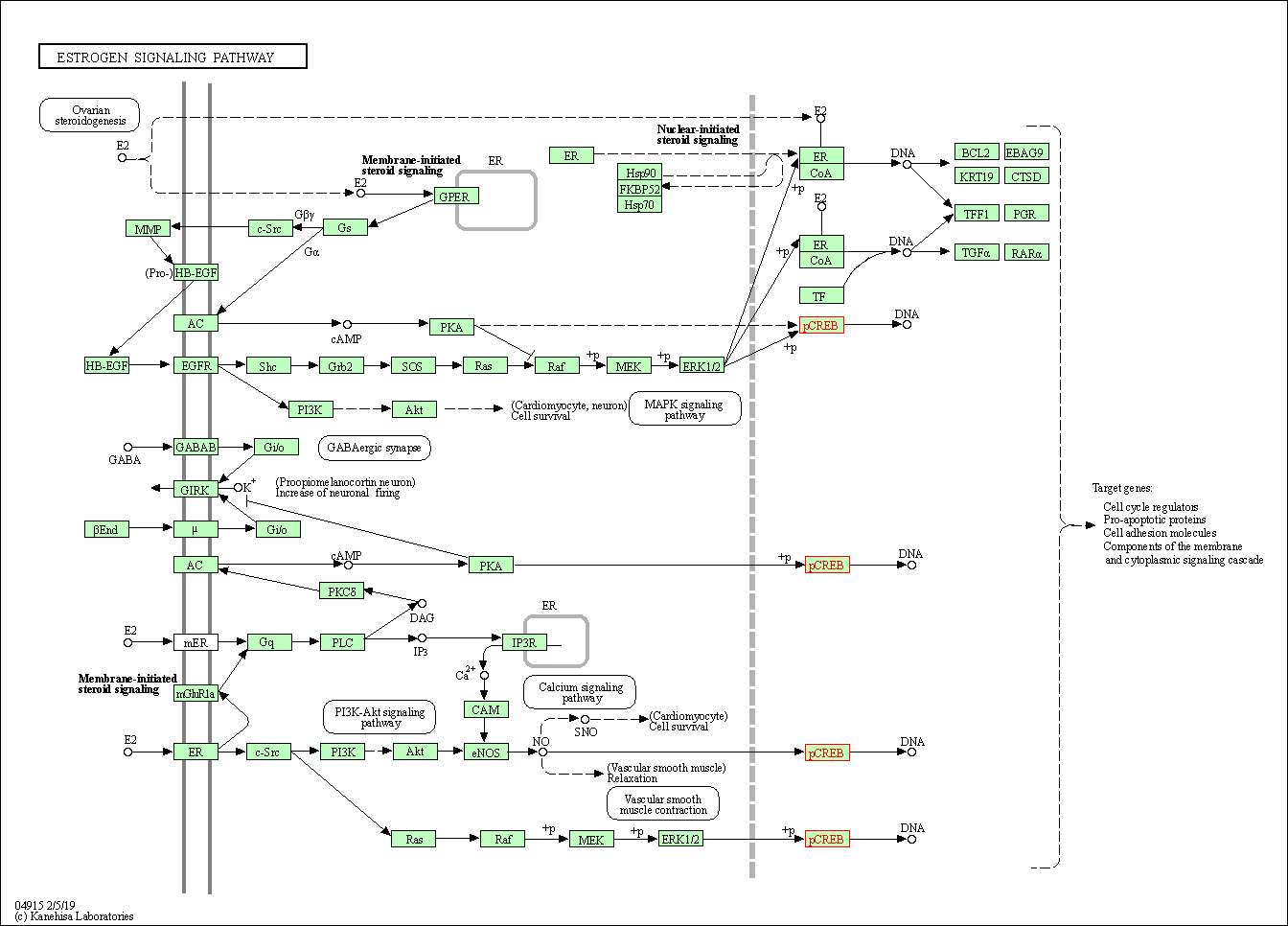
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone synthesis | hsa04918 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
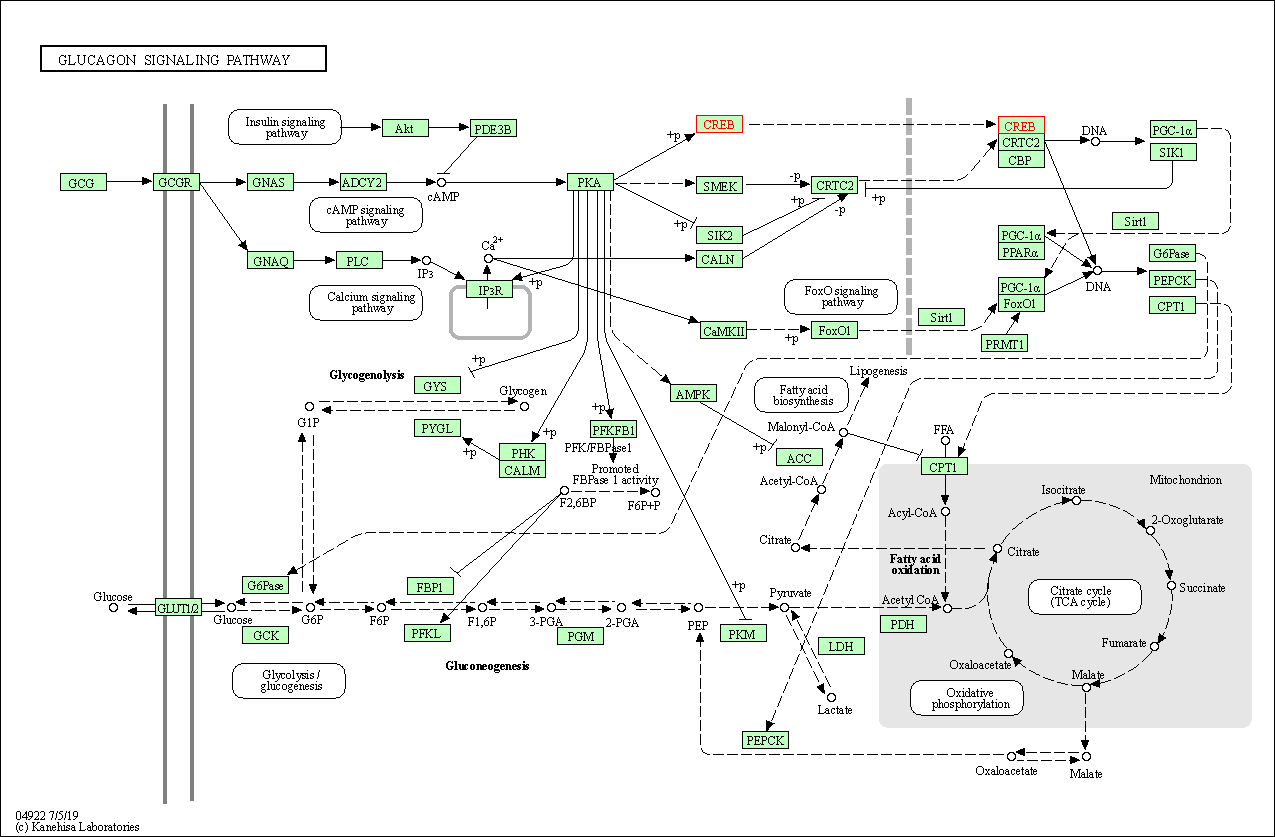
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
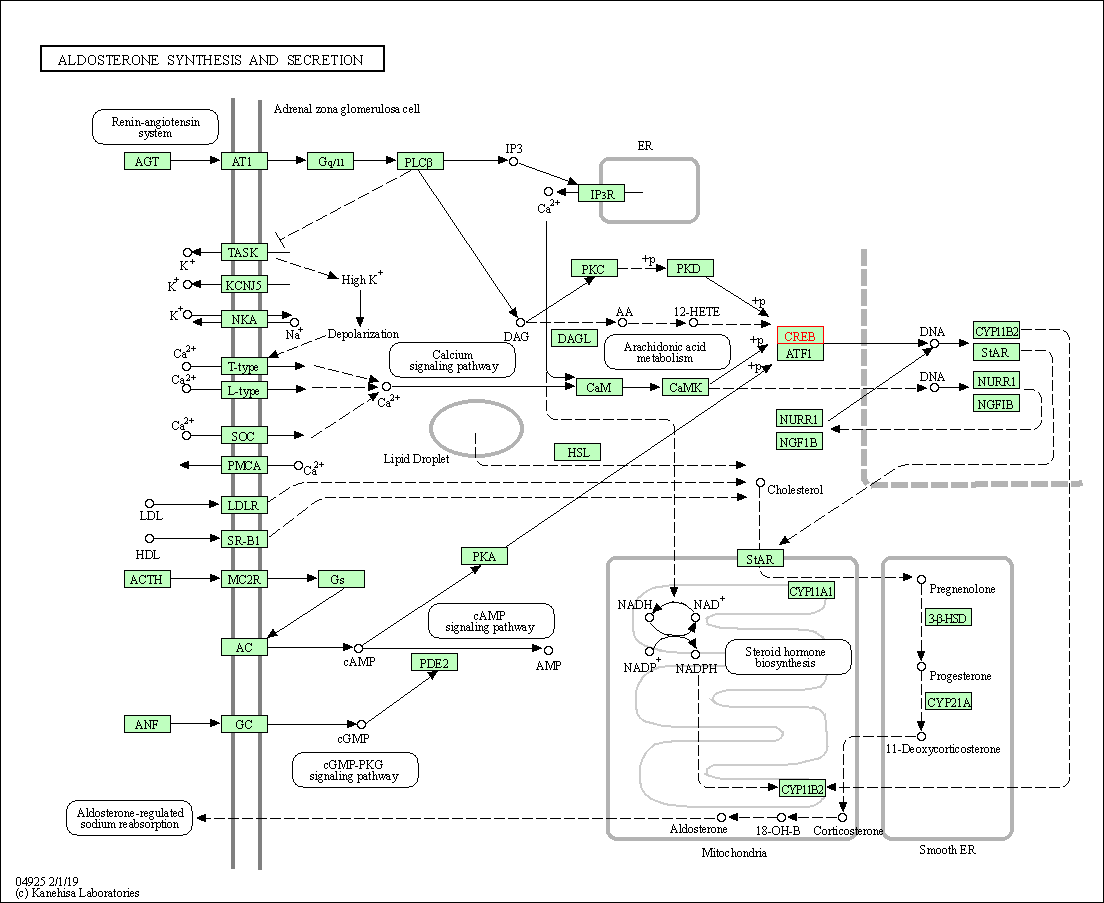
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
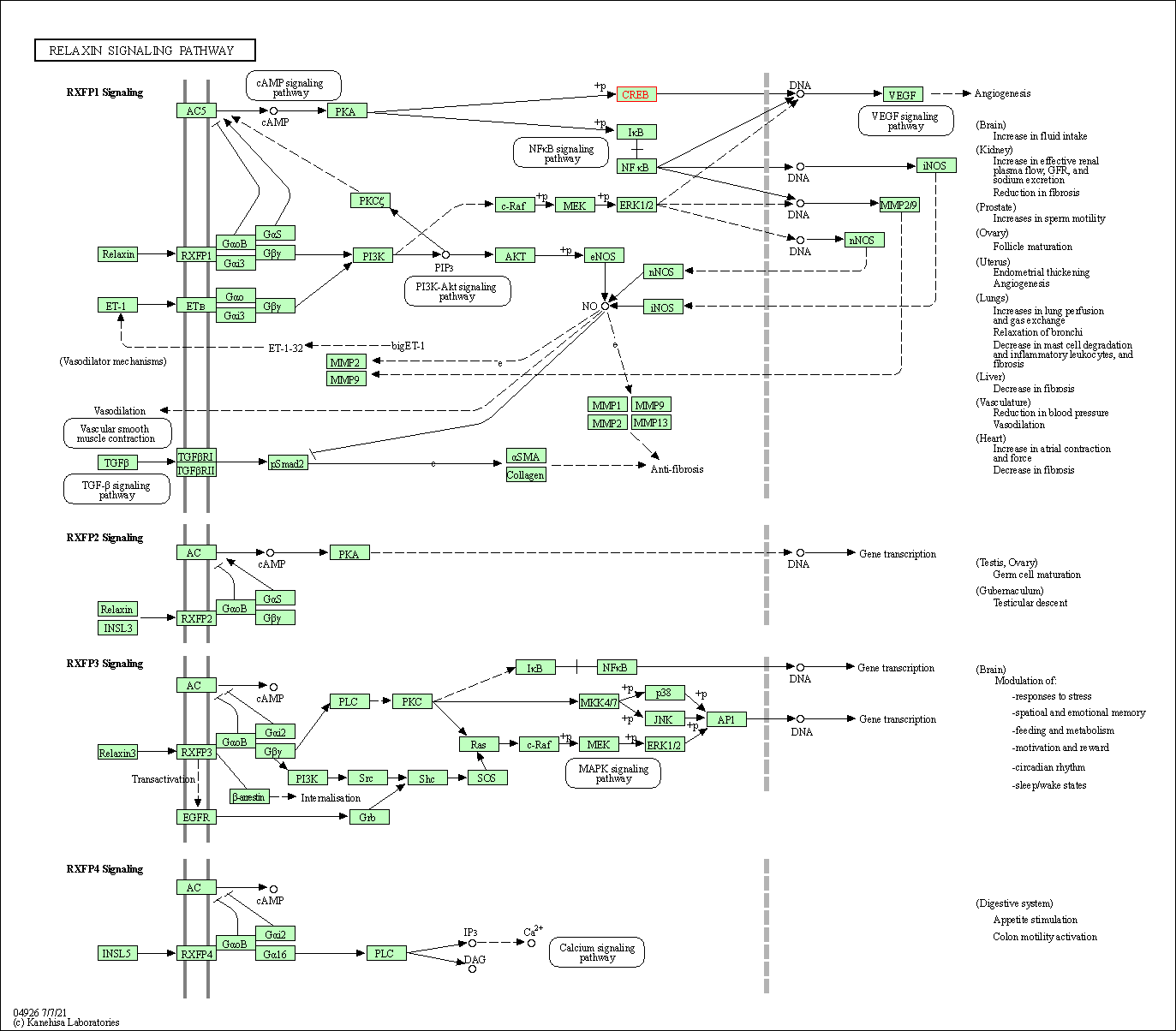
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cortisol synthesis and secretion | hsa04927 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
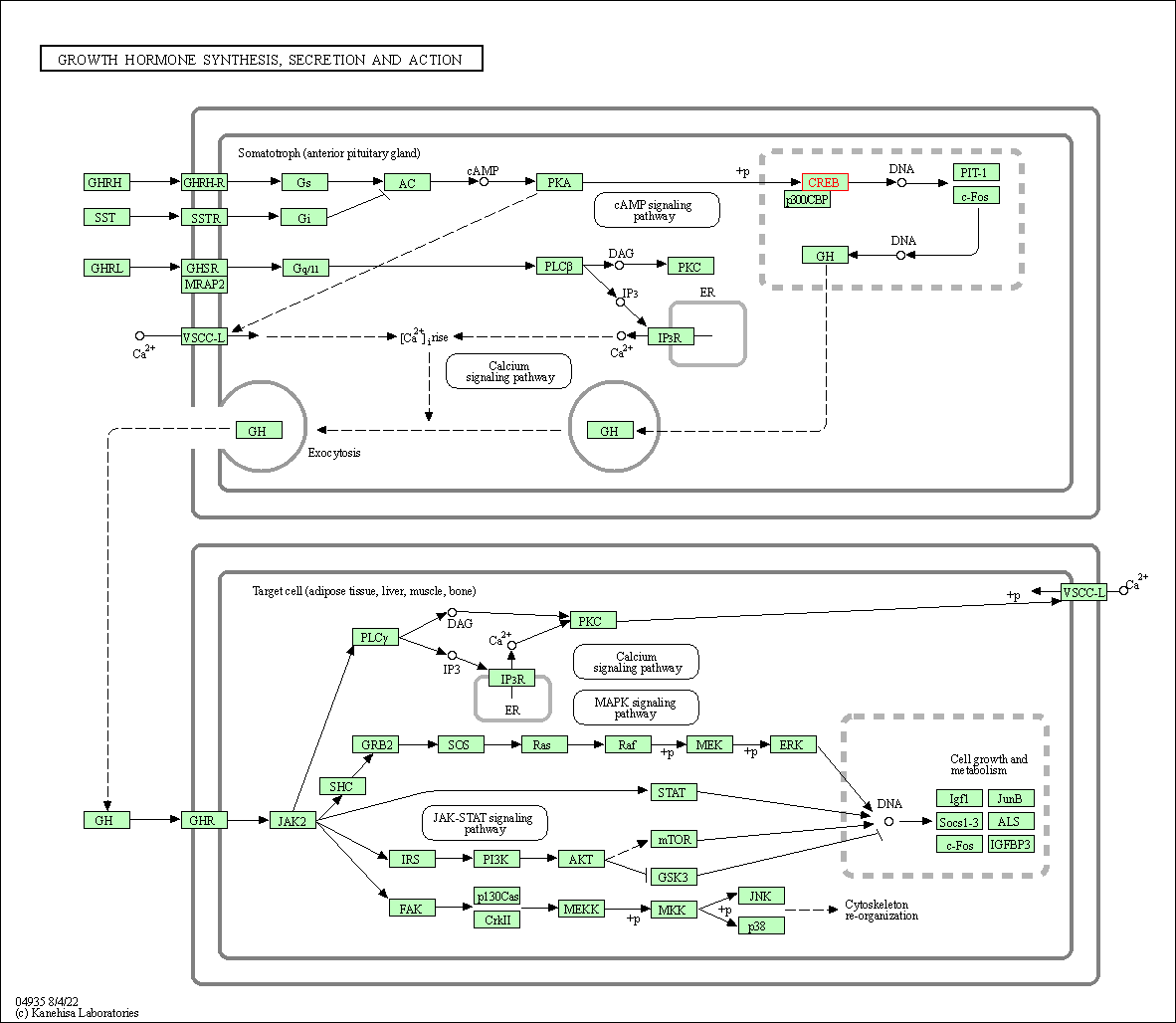
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 15 | Degree centrality | 1.61E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.76E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.36E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.43E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.20E+01 | Topological coefficient | 9.24E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Role of ATF4 in skeletal muscle atrophy. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017 May;20(3):164-168. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

