Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T61227
(Former ID: TTDI03294)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
IP3 receptor isoform 1 (ITPR1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor; Type 1 InsP3 receptor; InsP3R1; Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1; IP3R 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ITPR1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Involved in the regulation of epithelial secretion of electrolytes and fluid through the interaction with AHCYL1. Plays a role in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Cytoplasmic calcium released from the ER triggers apoptosis by the activation of CaM kinase II, eventually leading to the activation of downstream apoptosis pathways. Intracellular channel that mediates calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum following stimulation by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Ryanodine-inositol triphosphate calcium channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MSDKMSSFLHIGDICSLYAEGSTNGFISTLGLVDDRCVVQPETGDLNNPPKKFRDCLFKL
CPMNRYSAQKQFWKAAKPGANSTTDAVLLNKLHHAADLEKKQNETENRKLLGTVIQYGNV IQLLHLKSNKYLTVNKRLPALLEKNAMRVTLDEAGNEGSWFYIQPFYKLRSIGDSVVIGD KVVLNPVNAGQPLHASSHQLVDNPGCNEVNSVNCNTSWKIVLFMKWSDNKDDILKGGDVV RLFHAEQEKFLTCDEHRKKQHVFLRTTGRQSATSATSSKALWEVEVVQHDPCRGGAGYWN SLFRFKHLATGHYLAAEVDPDFEEECLEFQPSVDPDQDASRSRLRNAQEKMVYSLVSVPE GNDISSIFELDPTTLRGGDSLVPRNSYVRLRHLCTNTWVHSTNIPIDKEEEKPVMLKIGT SPVKEDKEAFAIVPVSPAEVRDLDFANDASKVLGSIAGKLEKGTITQNERRSVTKLLEDL VYFVTGGTNSGQDVLEVVFSKPNRERQKLMREQNILKQIFKLLQAPFTDCGDGPMLRLEE LGDQRHAPFRHICRLCYRVLRHSQQDYRKNQEYIAKQFGFMQKQIGYDVLAEDTITALLH NNRKLLEKHITAAEIDTFVSLVRKNREPRFLDYLSDLCVSMNKSIPVTQELICKAVLNPT NADILIETKLVLSRFEFEGVSSTGENALEAGEDEEEVWLFWRDSNKEIRSKSVRELAQDA KEGQKEDRDVLSYYRYQLNLFARMCLDRQYLAINEISGQLDVDLILRCMSDENLPYDLRA SFCRLMLHMHVDRDPQEQVTPVKYARLWSEIPSEIAIDDYDSSGASKDEIKERFAQTMEF VEEYLRDVVCQRFPFSDKEKNKLTFEVVNLARNLIYFGFYNFSDLLRLTKILLAILDCVH VTTIFPISKMAKGEENKGNNDVEKLKSSNVMRSIHGVGELMTQVVLRGGGFLPMTPMAAA PEGNVKQAEPEKEDIMVMDTKLKIIEILQFILNVRLDYRISCLLCIFKREFDESNSQTSE TSSGNSSQEGPSNVPGALDFEHIEEQAEGIFGGSEENTPLDLDDHGGRTFLRVLLHLTMH DYPPLVSGALQLLFRHFSQRQEVLQAFKQVQLLVTSQDVDNYKQIKQDLDQLRSIVEKSE LWVYKGQGPDETMDGASGENEHKKTEEGNNKPQKHESTSSYNYRVVKEILIRLSKLCVQE SASVRKSRKQQQRLLRNMGAHAVVLELLQIPYEKAEDTKMQEIMRLAHEFLQNFCAGNQQ NQALLHKHINLFLNPGILEAVTMQHIFMNNFQLCSEINERVVQHFVHCIETHGRNVQYIK FLQTIVKAEGKFIKKCQDMVMAELVNSGEDVLVFYNDRASFQTLIQMMRSERDRMDENSP LMYHIHLVELLAVCTEGKNVYTEIKCNSLLPLDDIVRVVTHEDCIPEVKIAYINFLNHCY VDTEVEMKEIYTSNHMWKLFENFLVDICRACNNTSDRKHADSILEKYVTEIVMSIVTTFF SSPFSDQSTTLQTRQPVFVQLLQGVFRVYHCNWLMPSQKASVESCIRVLSDVAKSRAIAI PVDLDSQVNNLFLKSHSIVQKTAMNWRLSARNAARRDSVLAASRDYRNIIERLQDIVSAL EDRLRPLVQAELSVLVDVLHRPELLFPENTDARRKCESGGFICKLIKHTKQLLEENEEKL CIKVLQTLREMMTKDRGYGEKLISIDELDNAELPPAPDSENATEELEPSPPLRQLEDHKR GEALRQVLVNRYYGNVRPSGRRESLTSFGNGPLSAGGPGKPGGGGGGSGSSSMSRGEMSL AEVQCHLDKEGASNLVIDLIMNASSDRVFHESILLAIALLEGGNTTIQHSFFCRLTEDKK SEKFFKVFYDRMKVAQQEIKATVTVNTSDLGNKKKDDEVDRDAPSRKKAKEPTTQITEEV RDQLLEASAATRKAFTTFRREADPDDHYQPGEGTQATADKAKDDLEMSAVITIMQPILRF LQLLCENHNRDLQNFLRCQNNKTNYNLVCETLQFLDCICGSTTGGLGLLGLYINEKNVAL INQTLESLTEYCQGPCHENQNCIATHESNGIDIITALILNDINPLGKKRMDLVLELKNNA SKLLLAIMESRHDSENAERILYNMRPKELVEVIKKAYMQGEVEFEDGENGEDGAASPRNV GHNIYILAHQLARHNKELQSMLKPGGQVDGDEALEFYAKHTAQIEIVRLDRTMEQIVFPV PSICEFLTKESKLRIYYTTERDEQGSKINDFFLRSEDLFNEMNWQKKLRAQPVLYWCARN MSFWSSISFNLAVLMNLLVAFFYPFKGVRGGTLEPHWSGLLWTAMLISLAIVIALPKPHG IRALIASTILRLIFSVGLQPTLFLLGAFNVCNKIIFLMSFVGNCGTFTRGYRAMVLDVEF LYHLLYLVICAMGLFVHEFFYSLLLFDLVYREETLLNVIKSVTRNGRSIILTAVLALILV YLFSIVGYLFFKDDFILEVDRLPNETAVPETGESLASEFLFSDVCRVESGENCSSPAPRE ELVPAEETEQDKEHTCETLLMCIVTVLSHGLRSGGGVGDVLRKPSKEEPLFAARVIYDLL FFFMVIIIVLNLIFGVIIDTFADLRSEKQKKEEILKTTCFICGLERDKFDNKTVTFEEHI KEEHNMWHYLCFIVLVKVKDSTEYTGPESYVAEMIKERNLDWFPRMRAMSLVSSDSEGEQ NELRNLQEKLESTMKLVTNLSGQLSELKDQMTEQRKQKQRIGLLGHPPHMNVNPQQPA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T74RBE | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
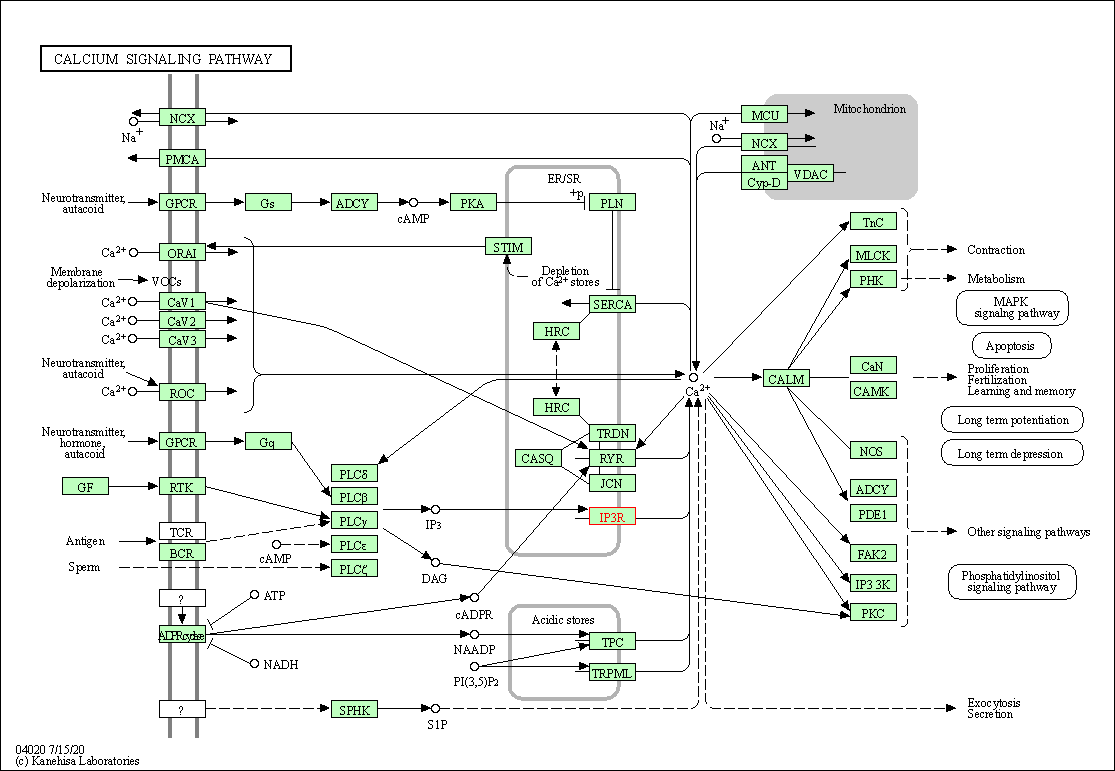
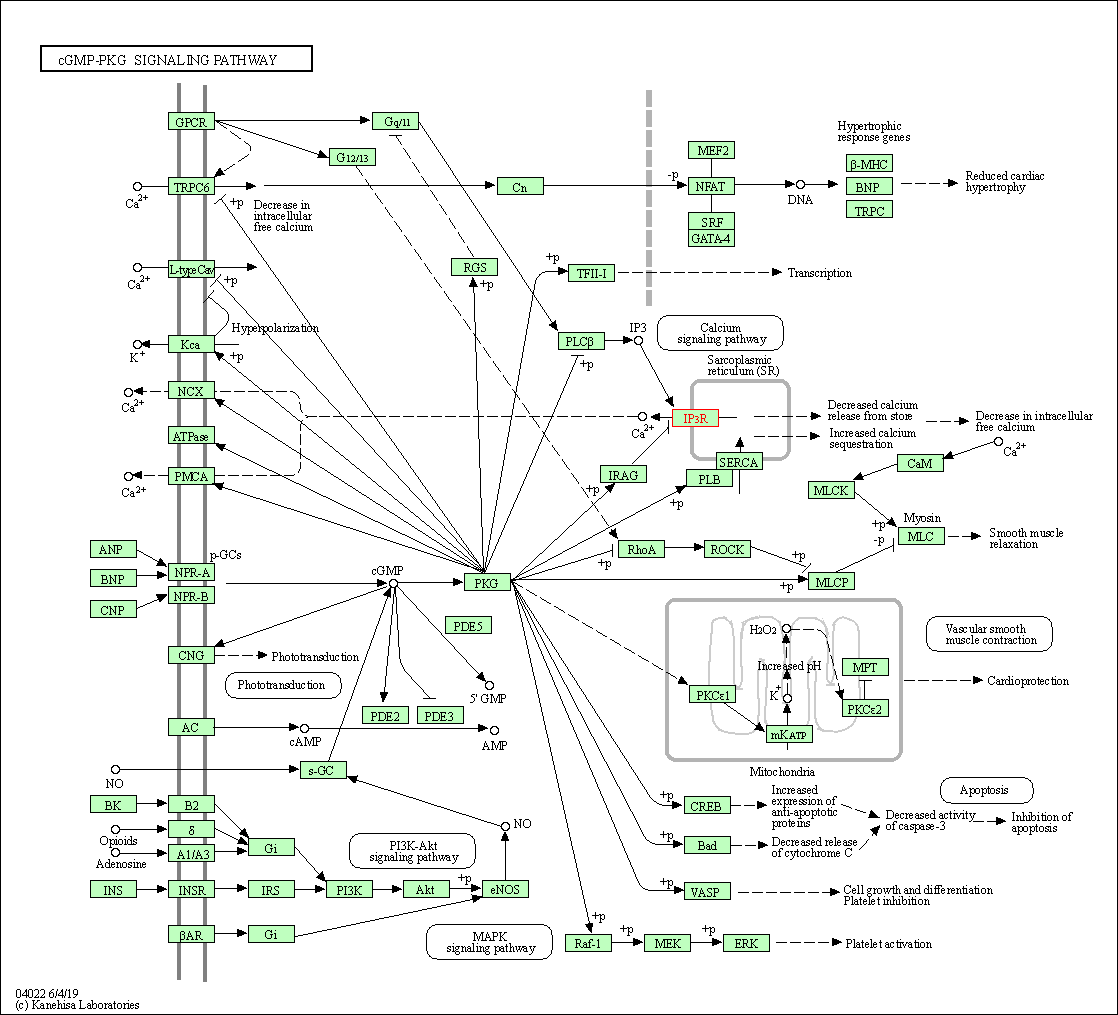
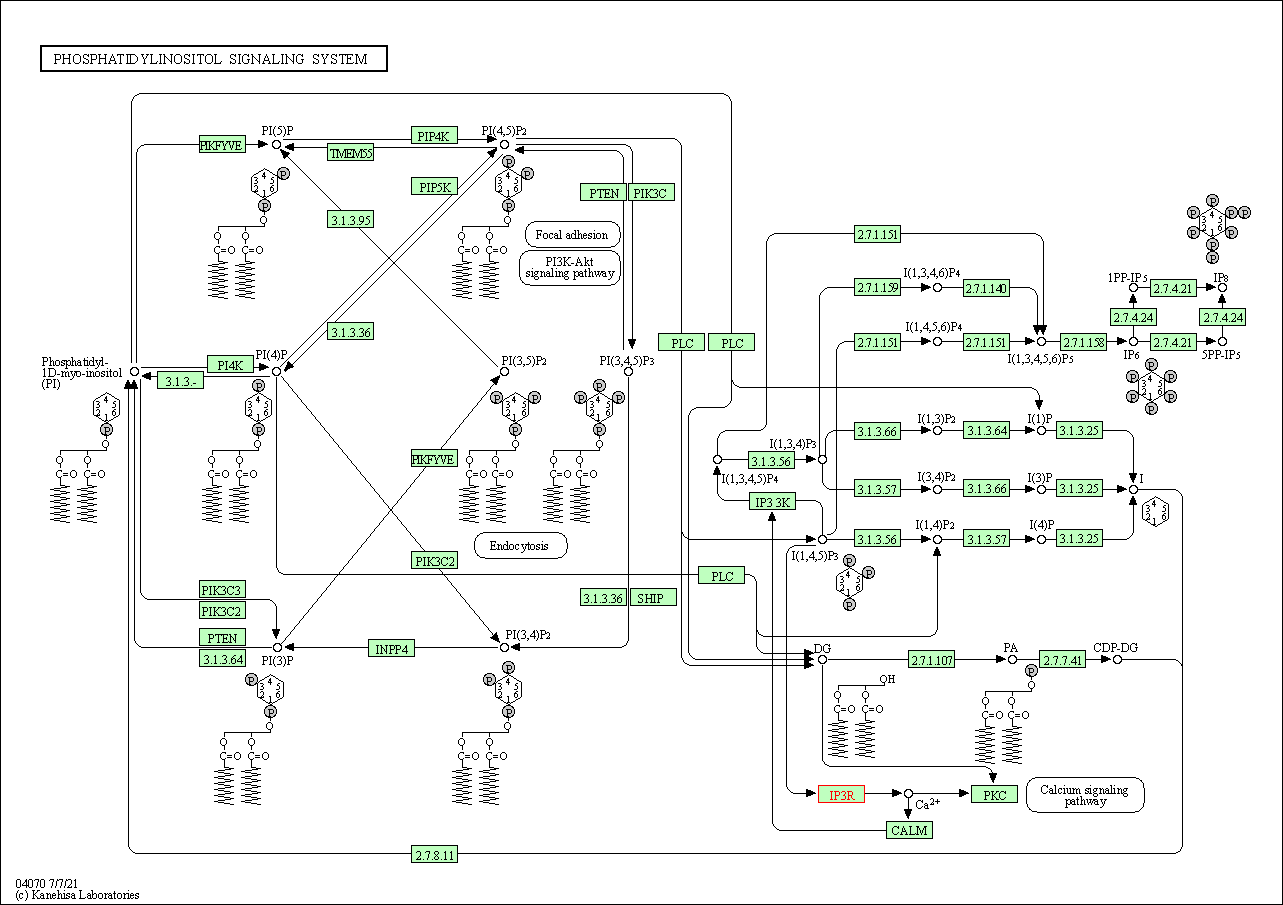
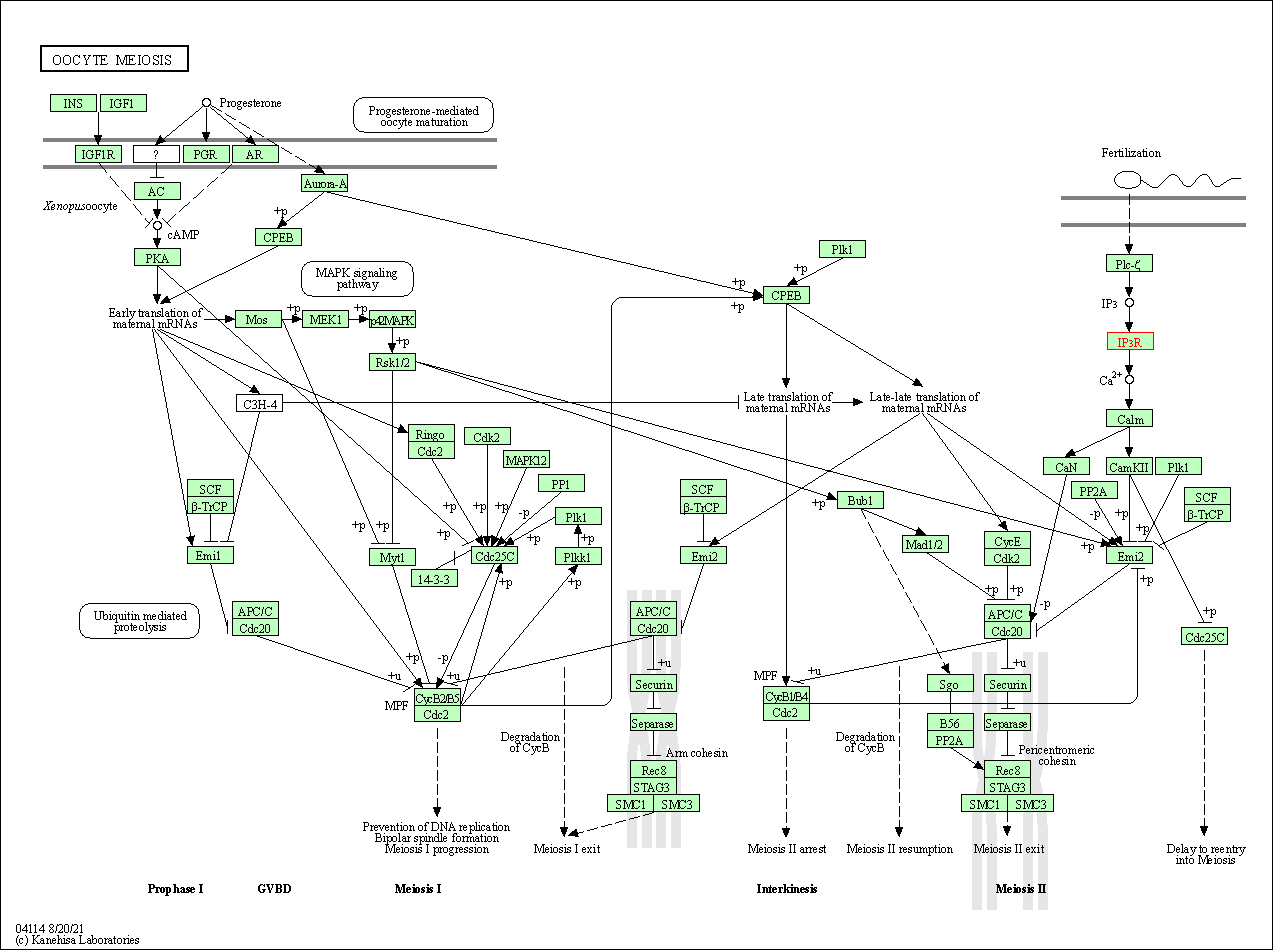

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | hsa04070 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oocyte meiosis | hsa04114 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
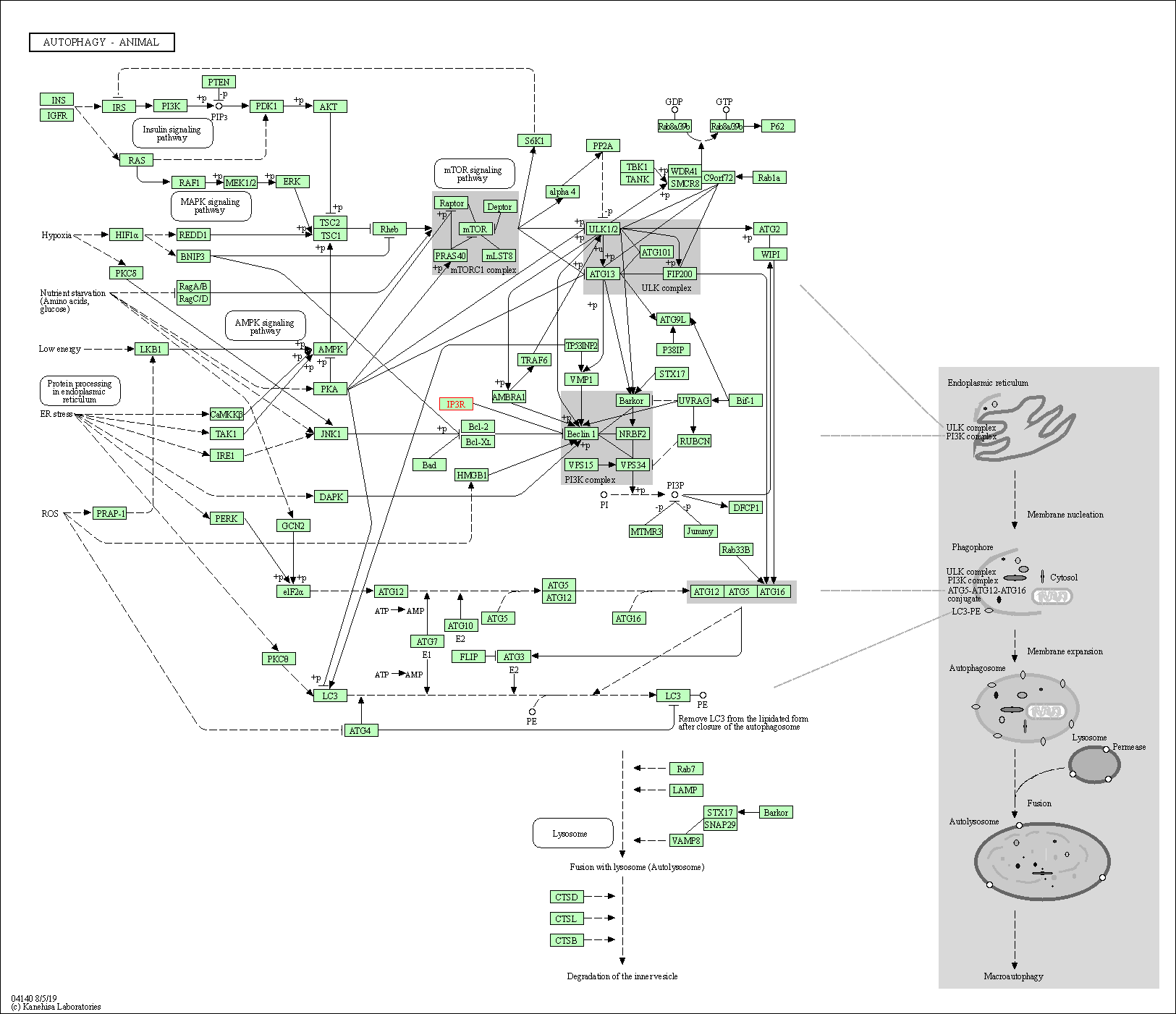
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
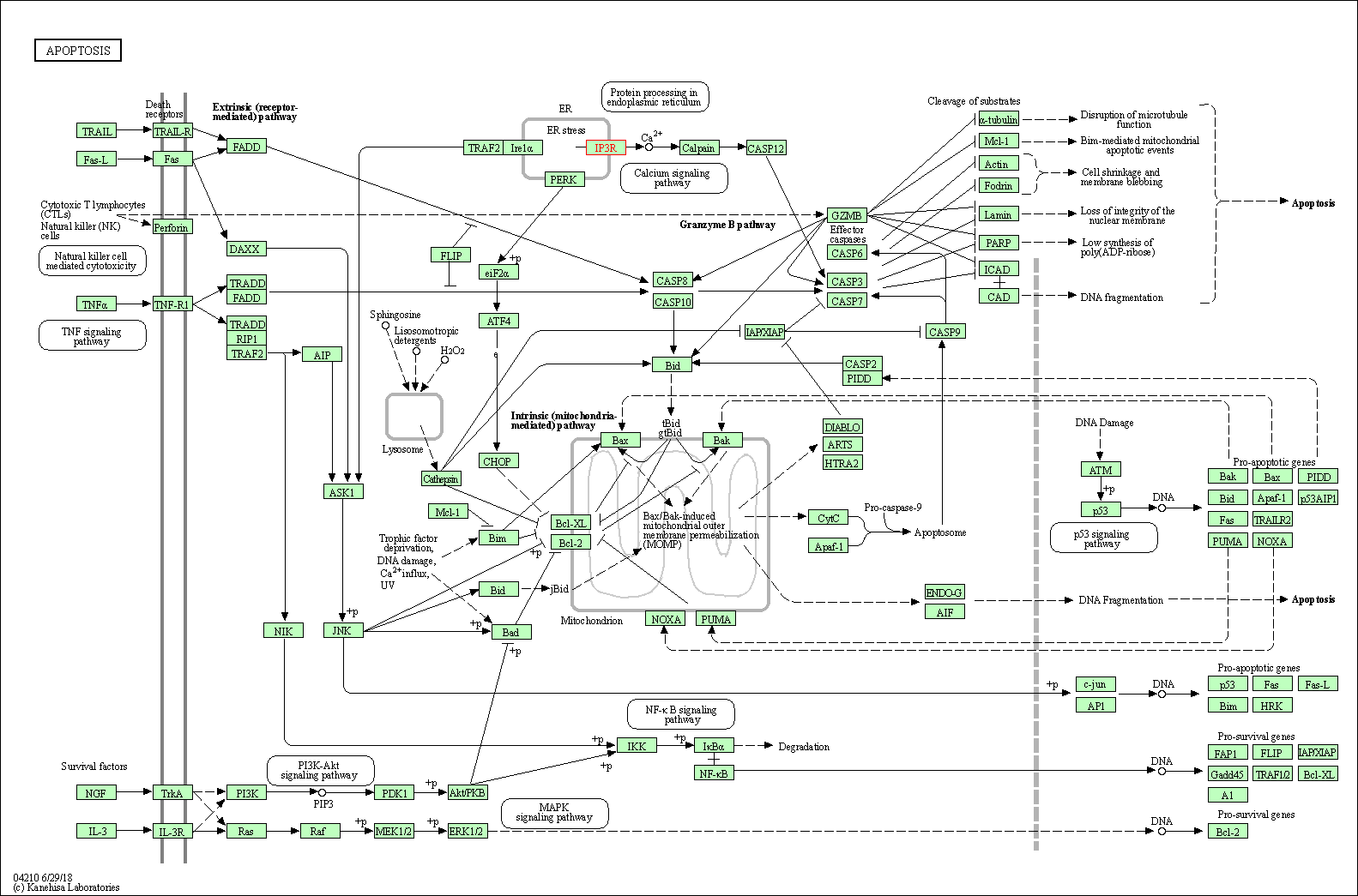
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
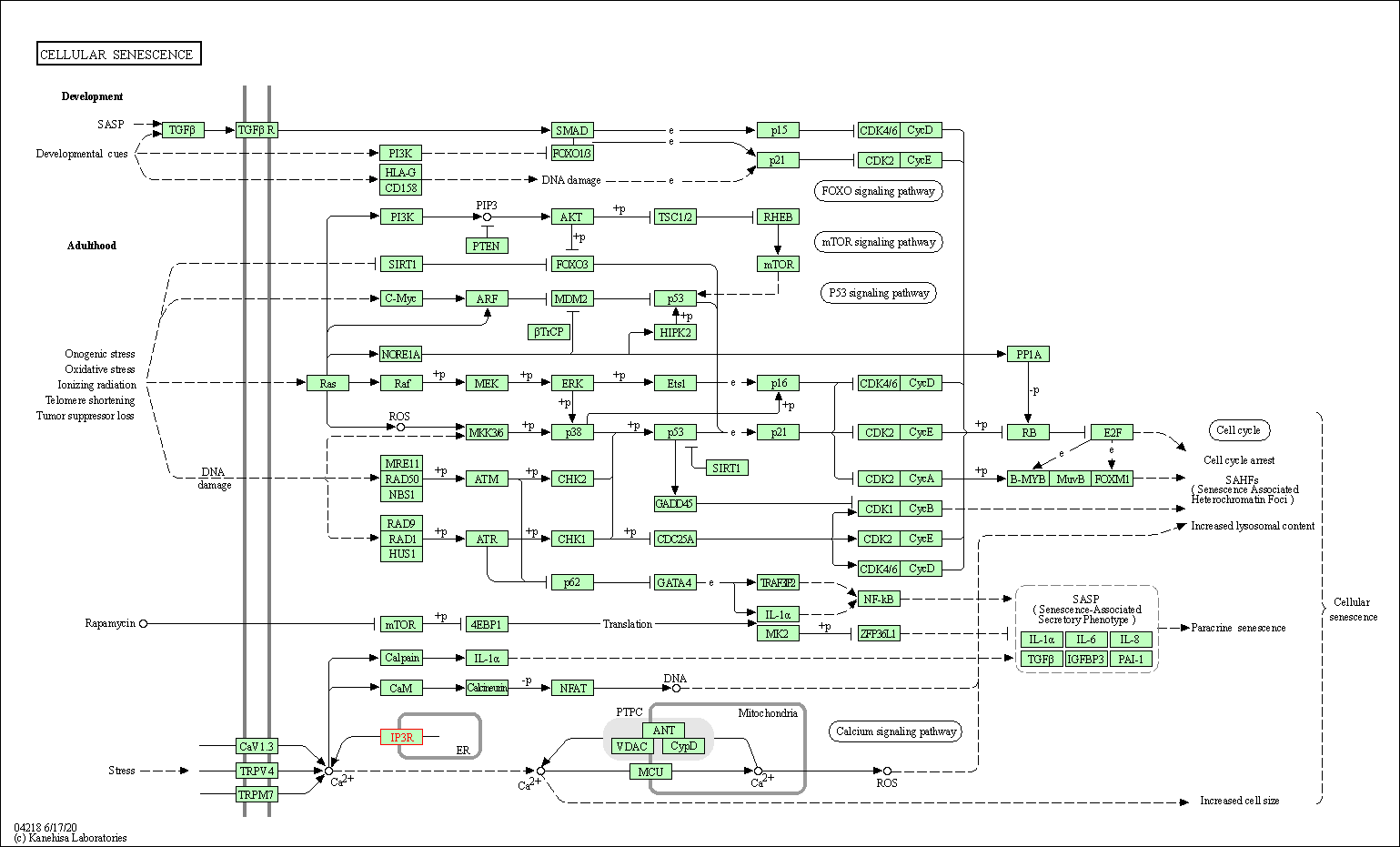
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
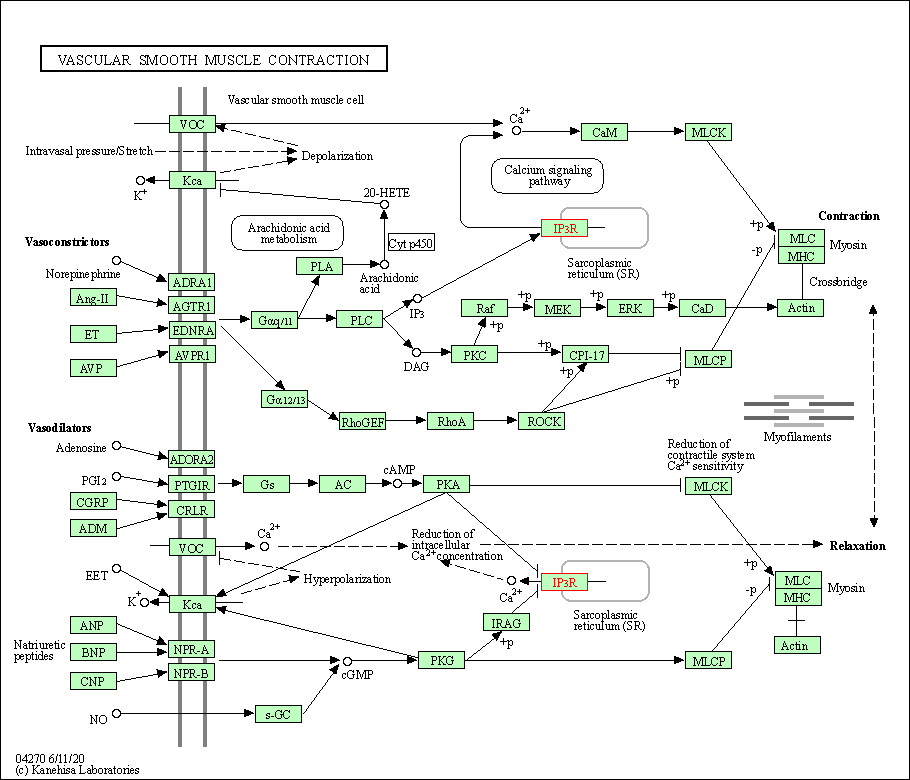
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gap junction | hsa04540 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
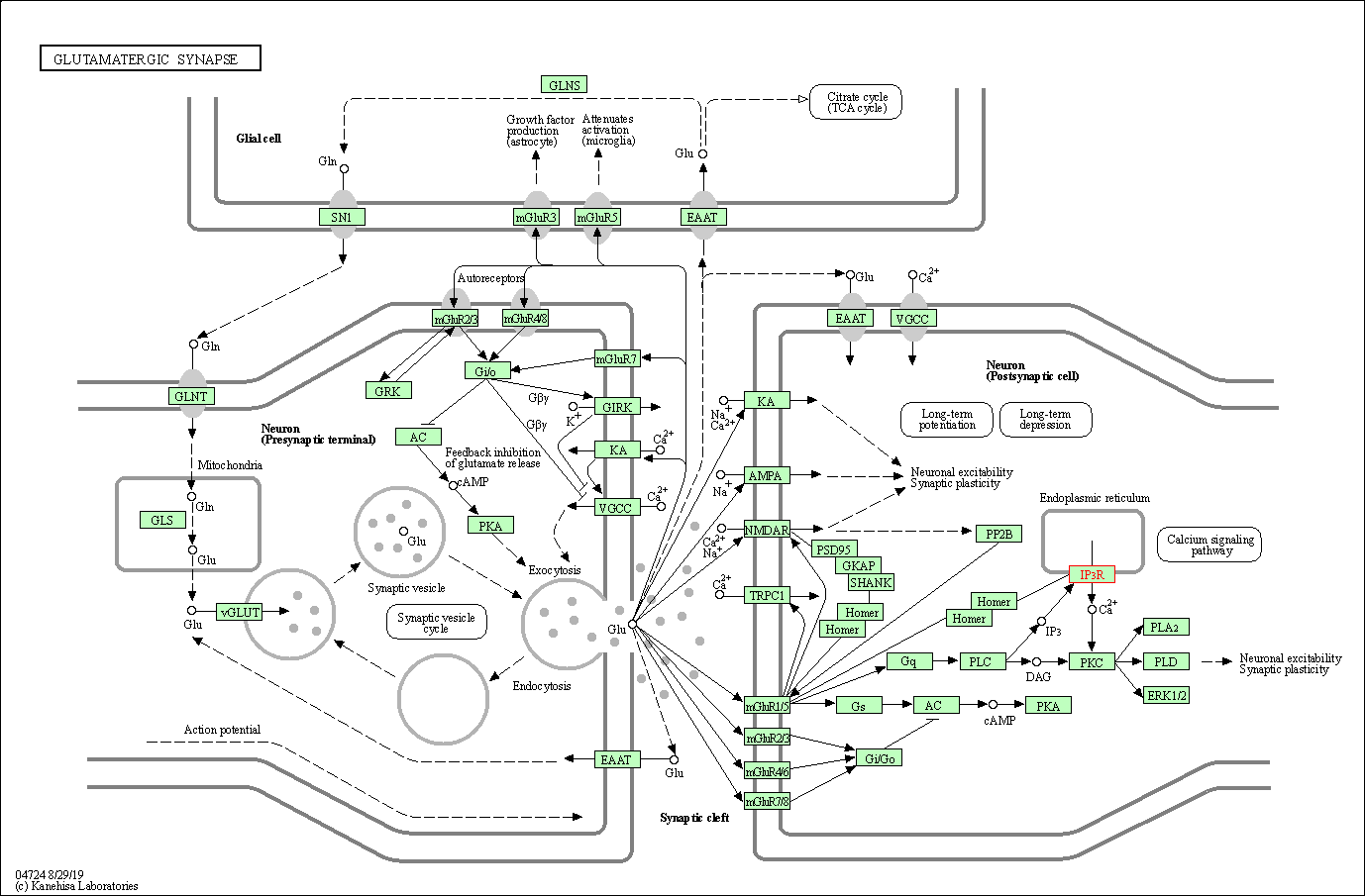
| Glutamatergic synapse | hsa04724 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
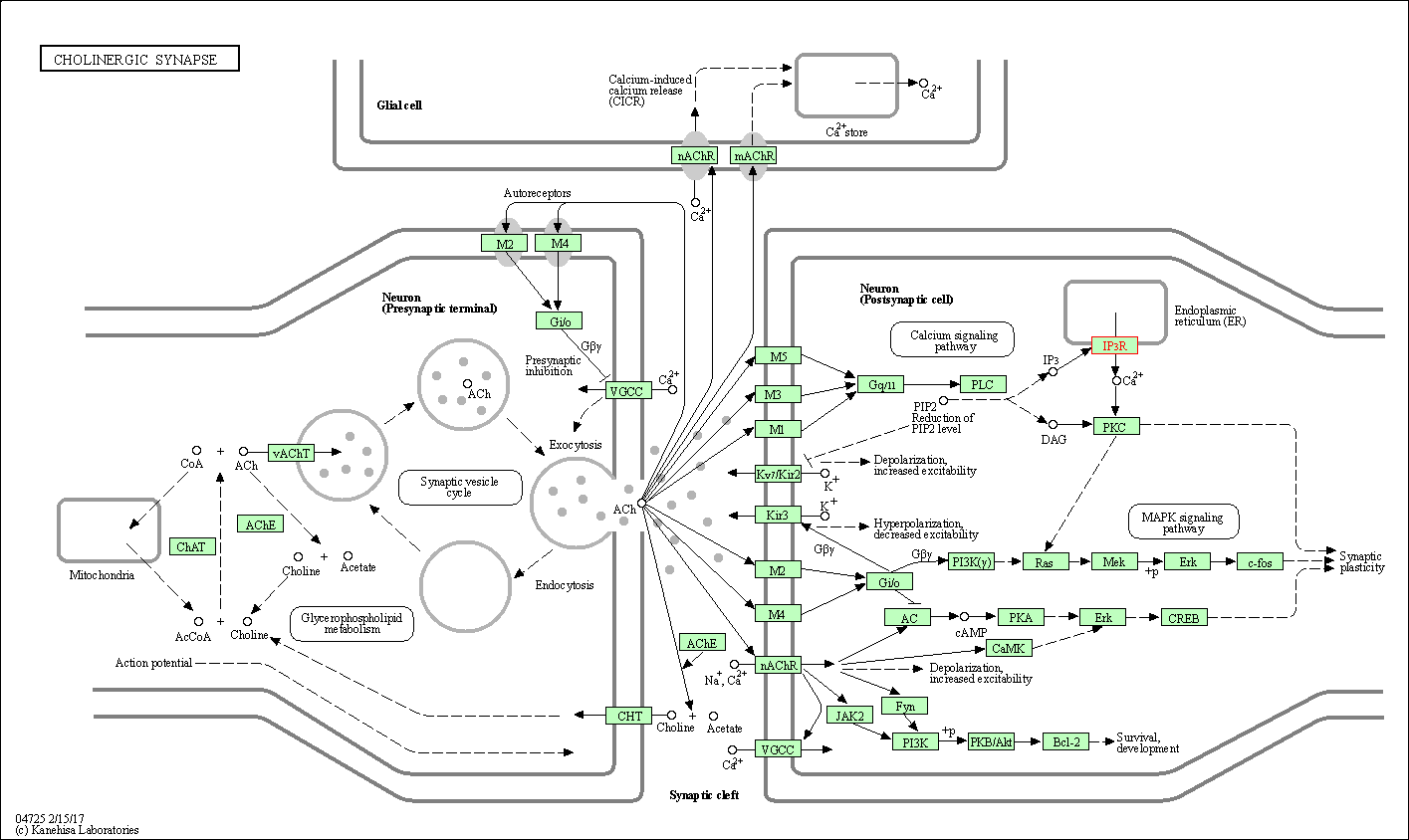
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
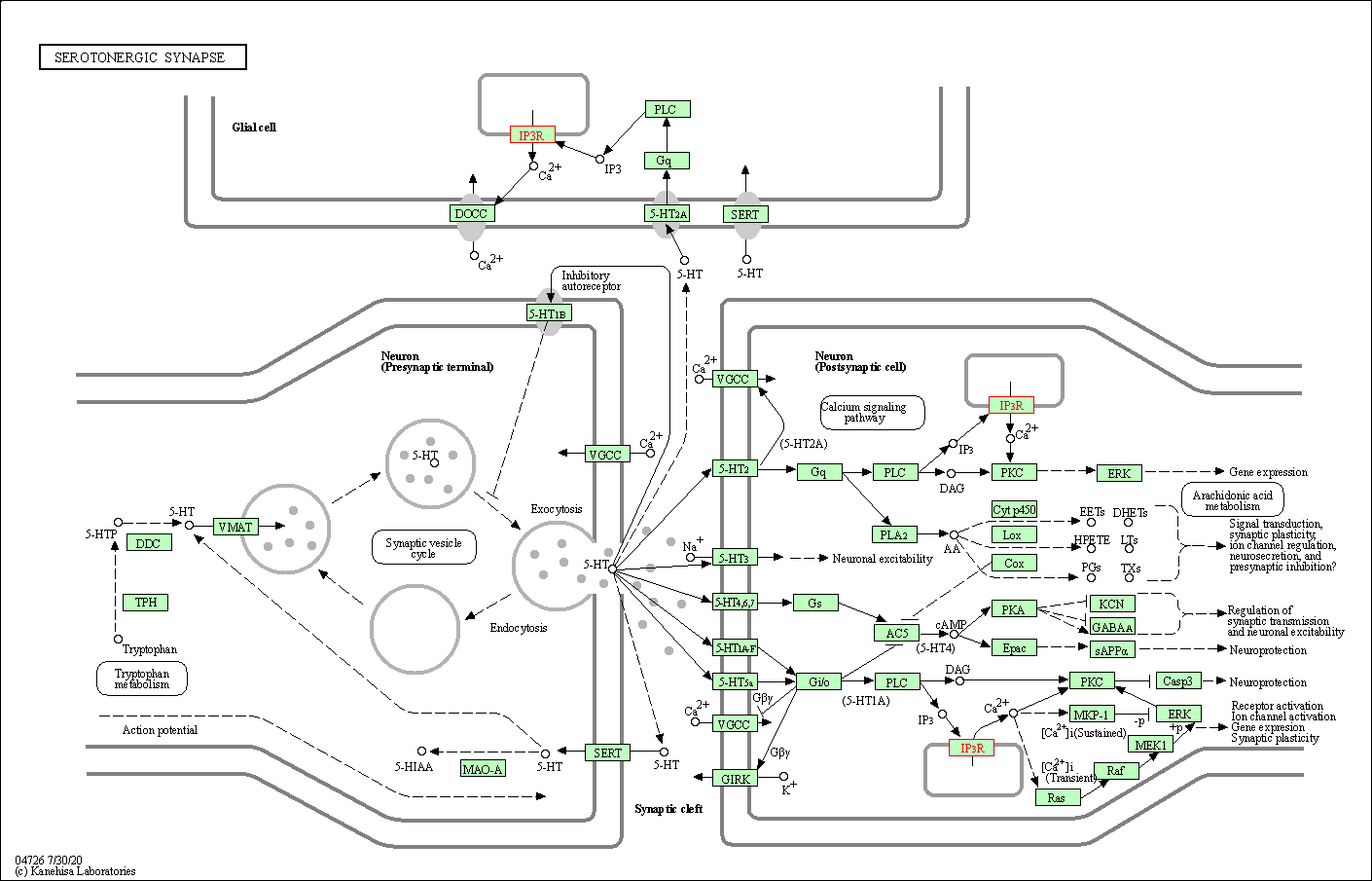
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
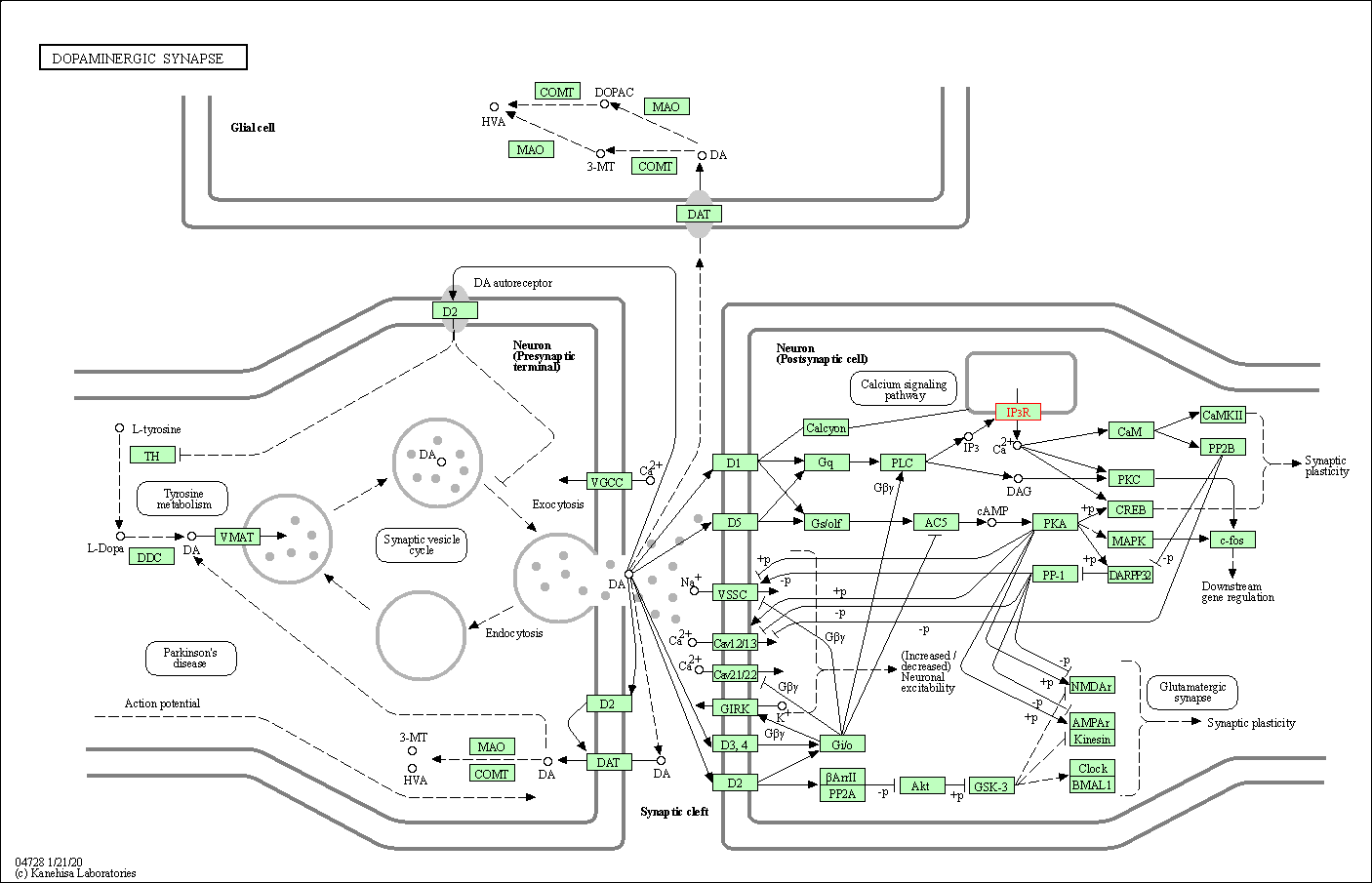
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
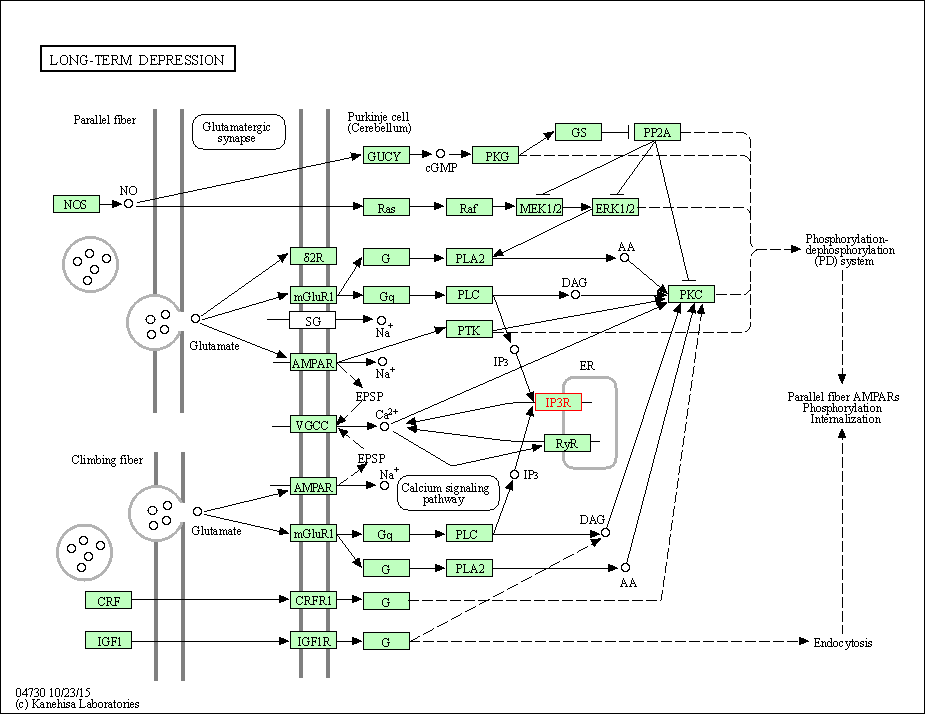
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
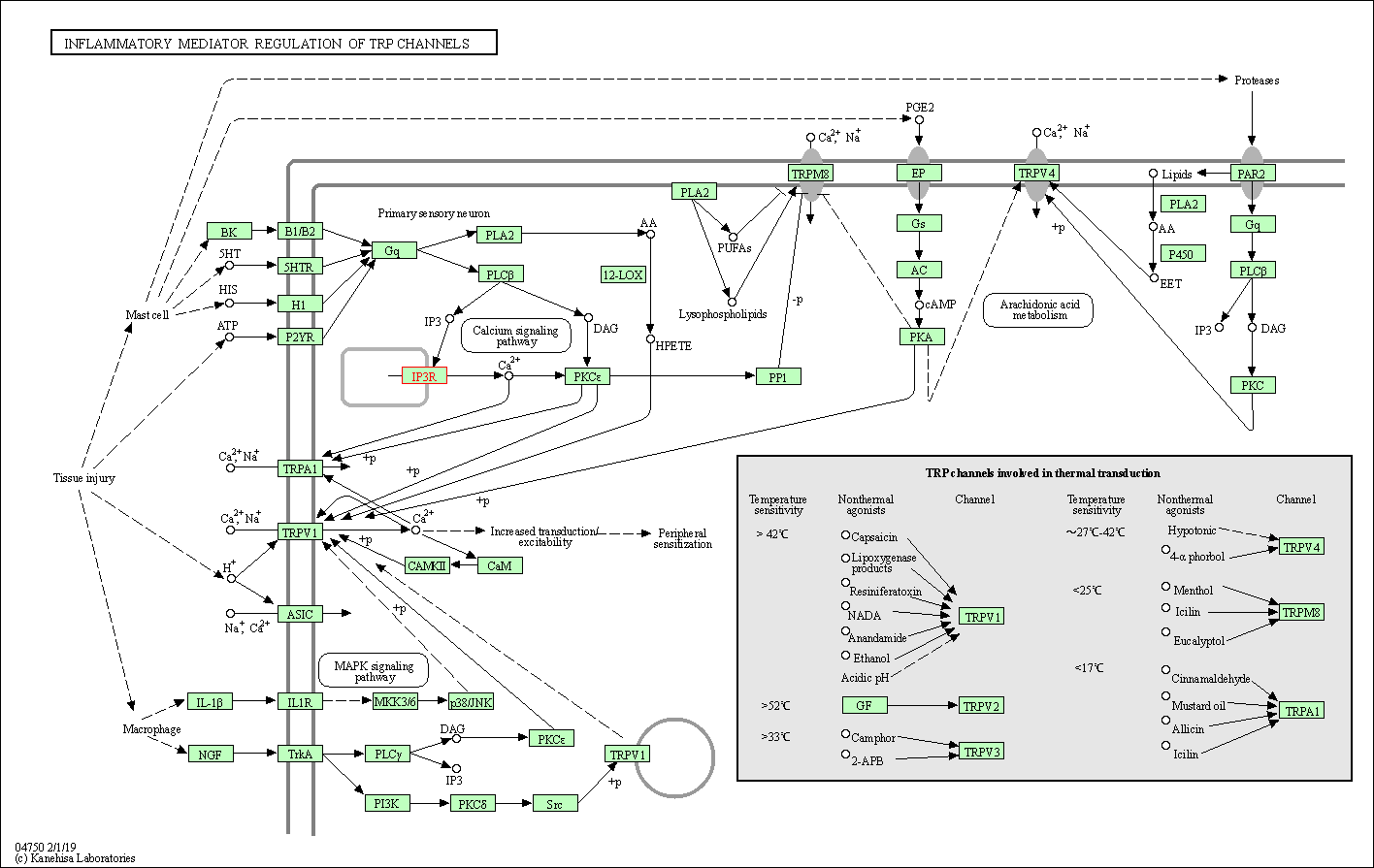
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
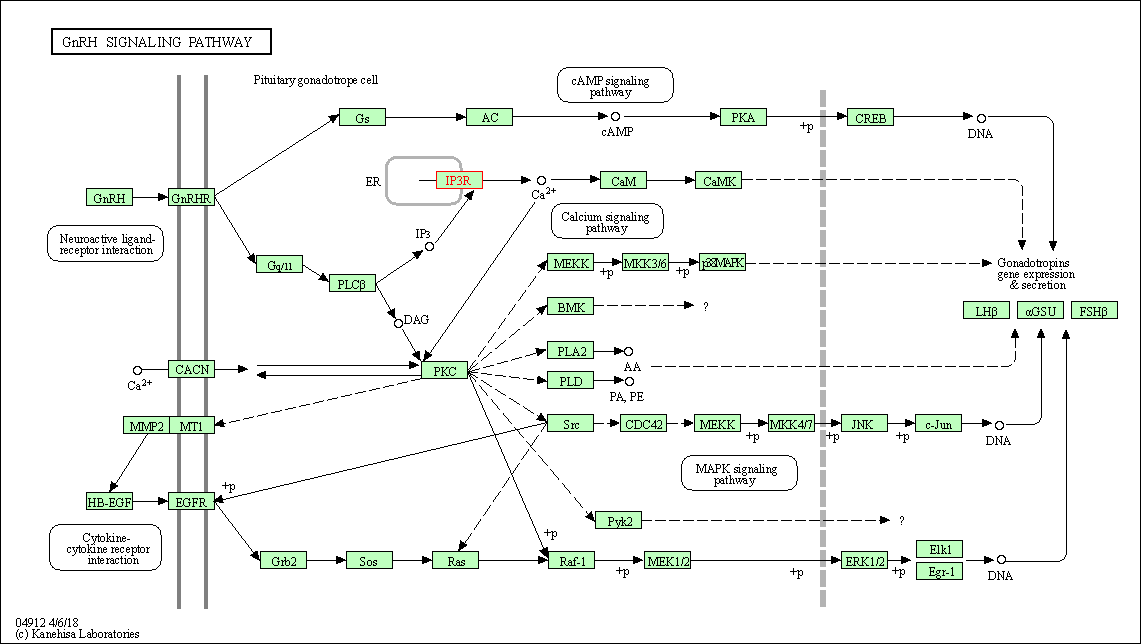
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
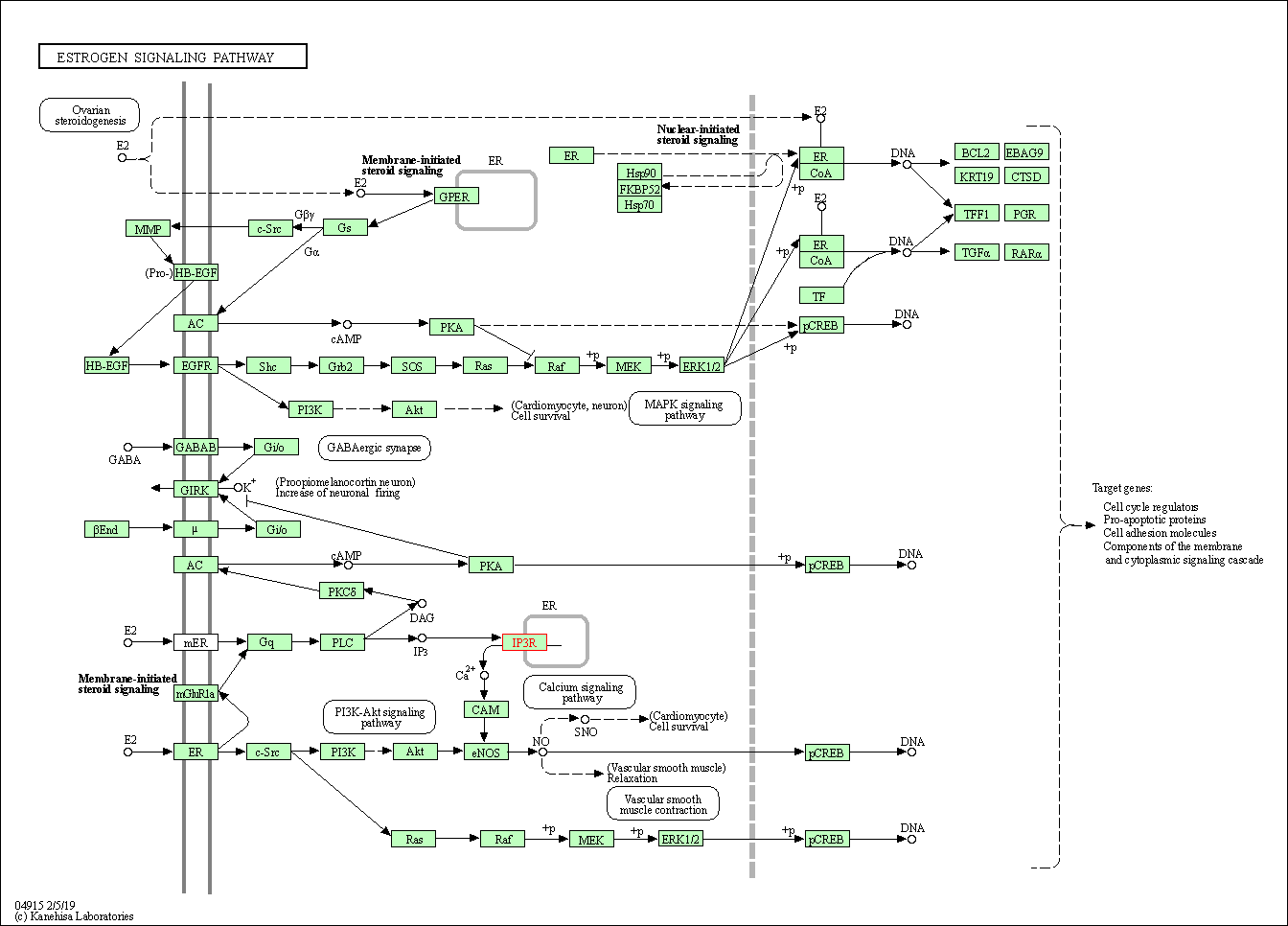
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone synthesis | hsa04918 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Renin secretion | hsa04924 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
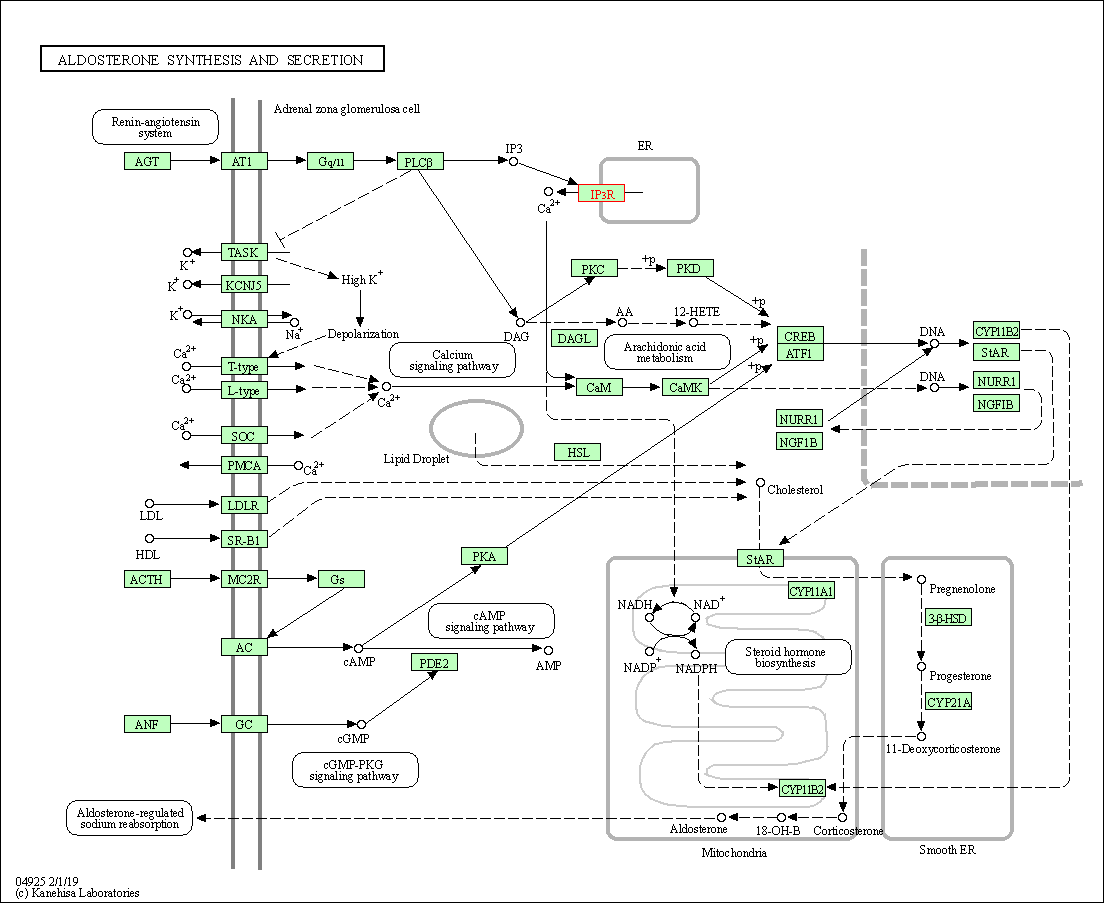
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
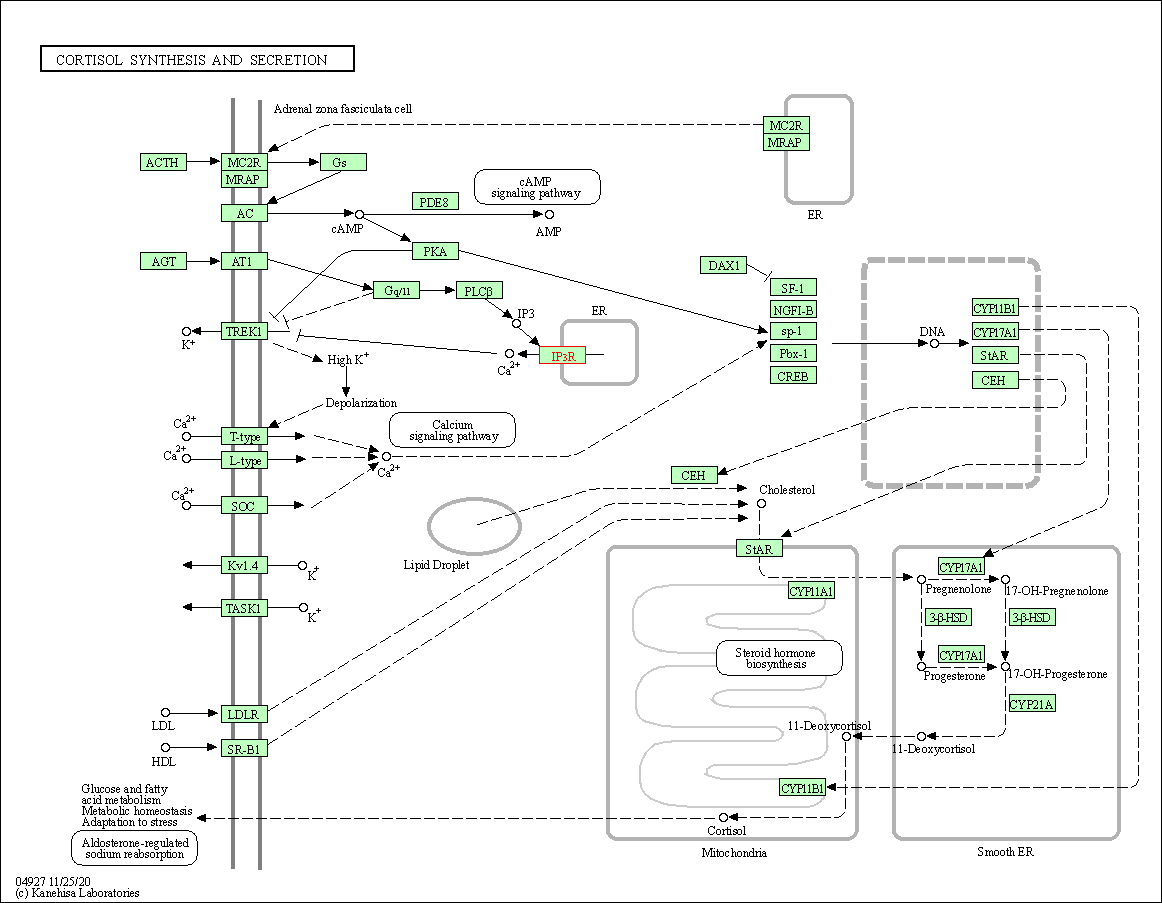
| Cortisol synthesis and secretion | hsa04927 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
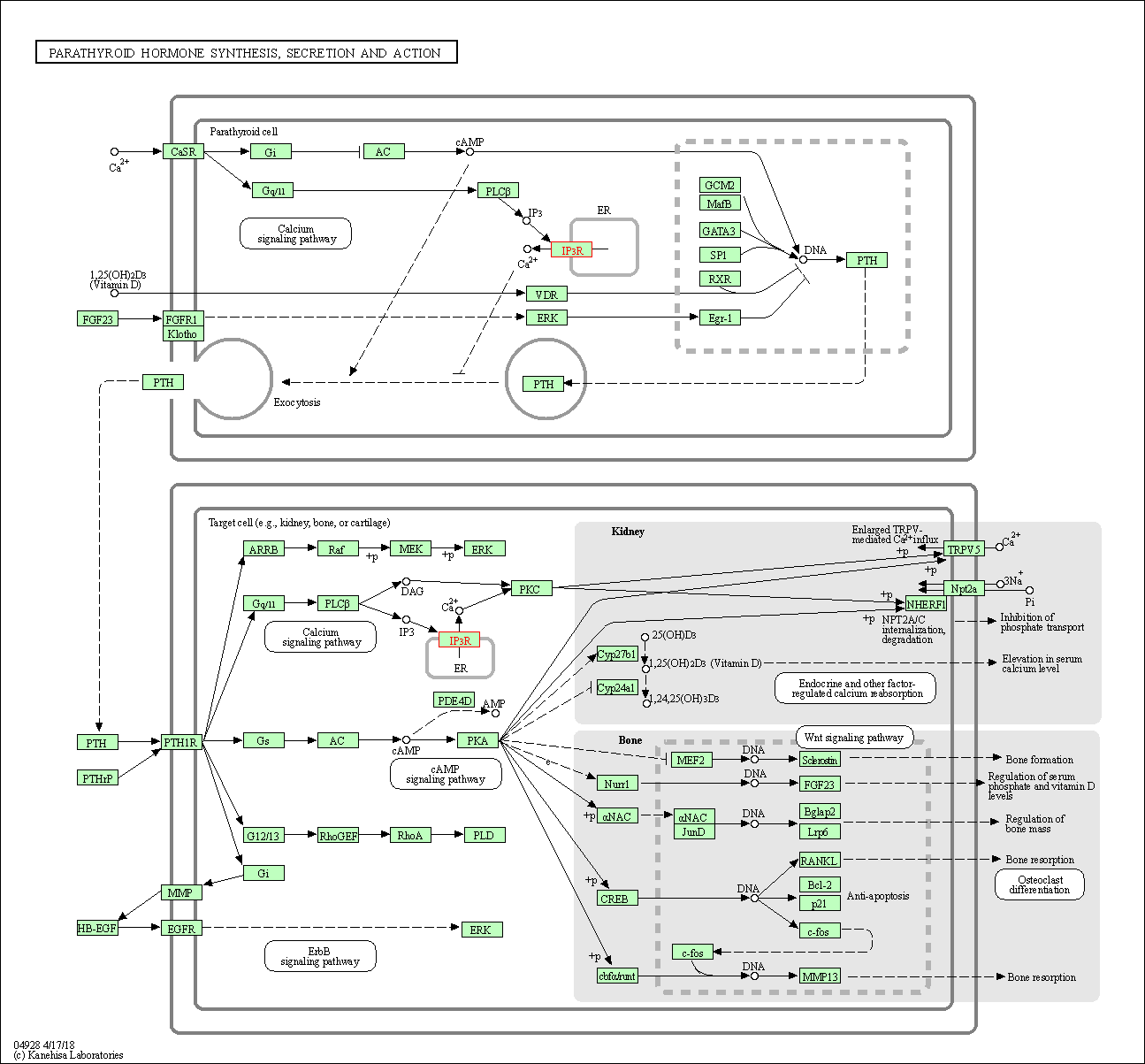
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
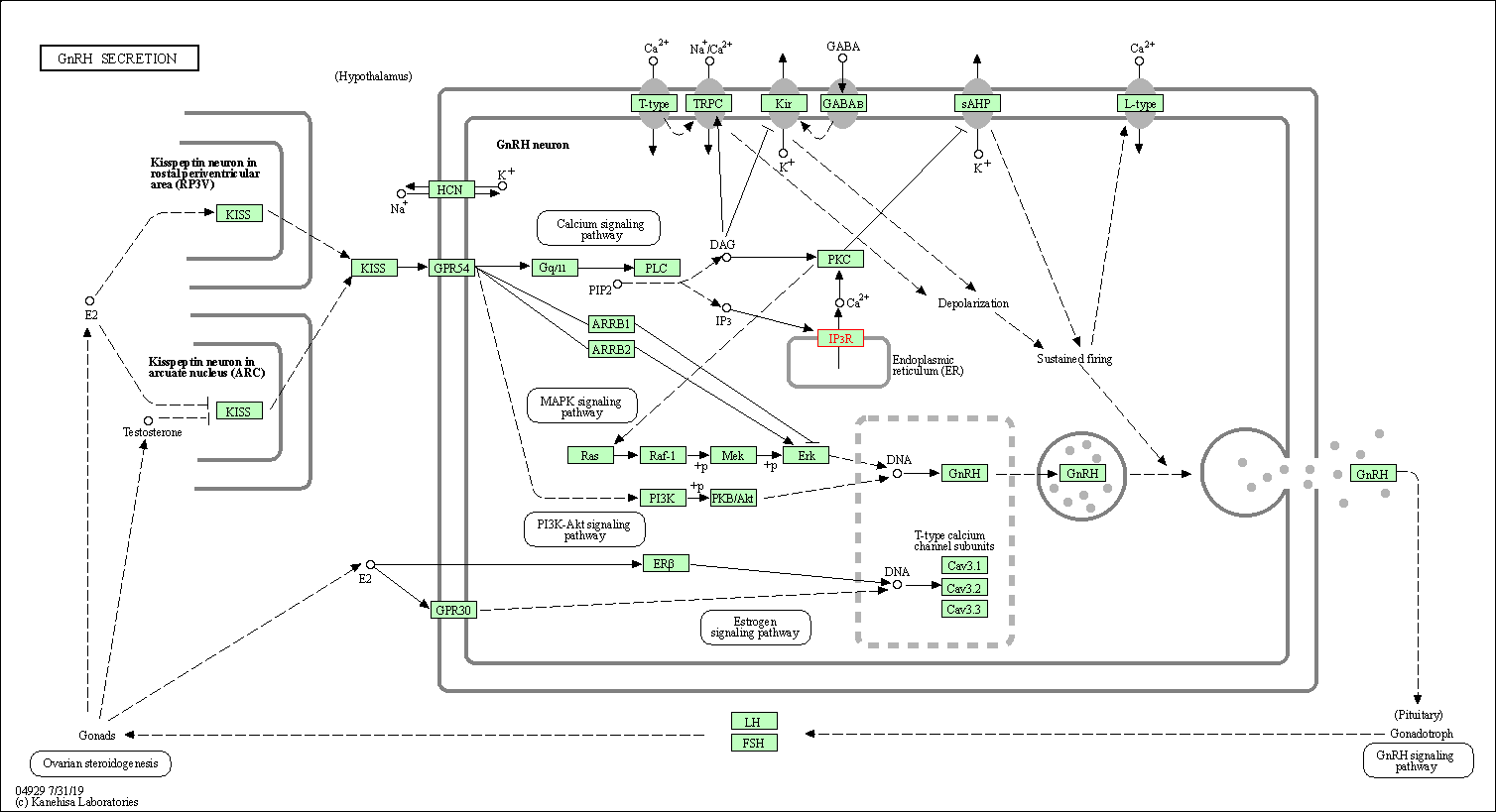
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
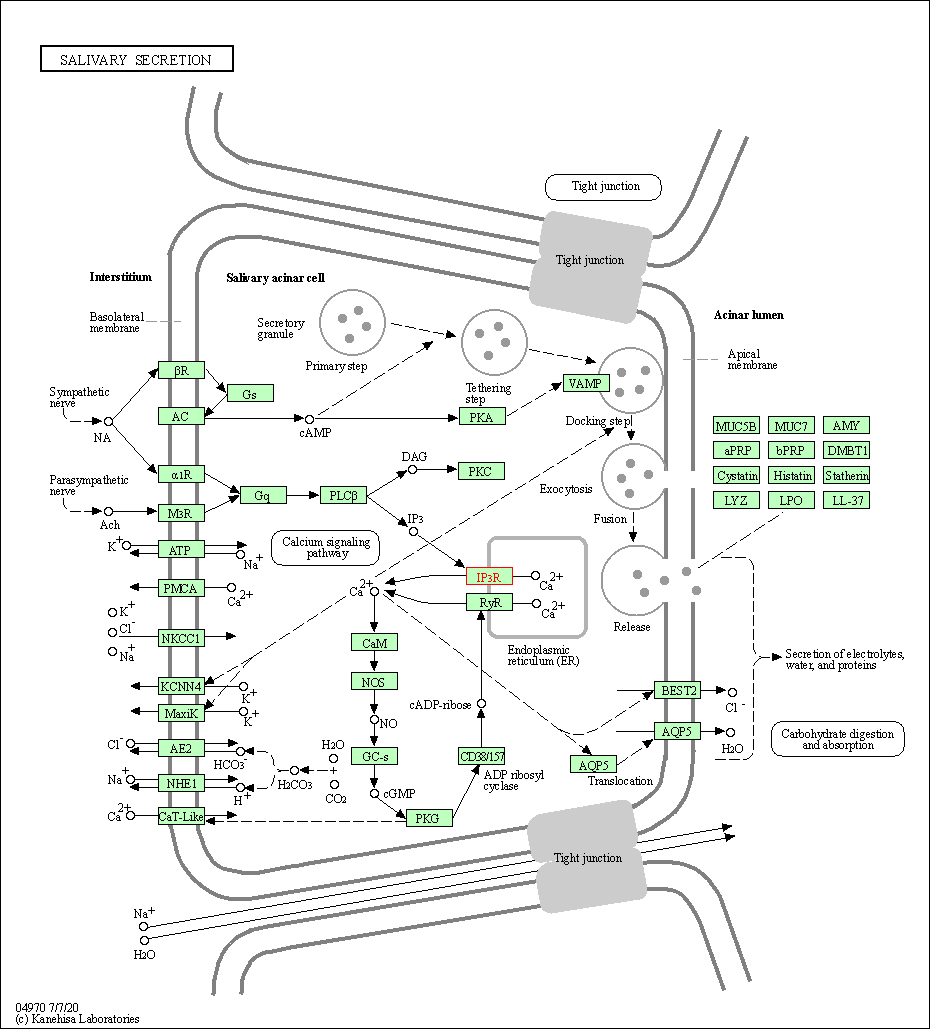
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
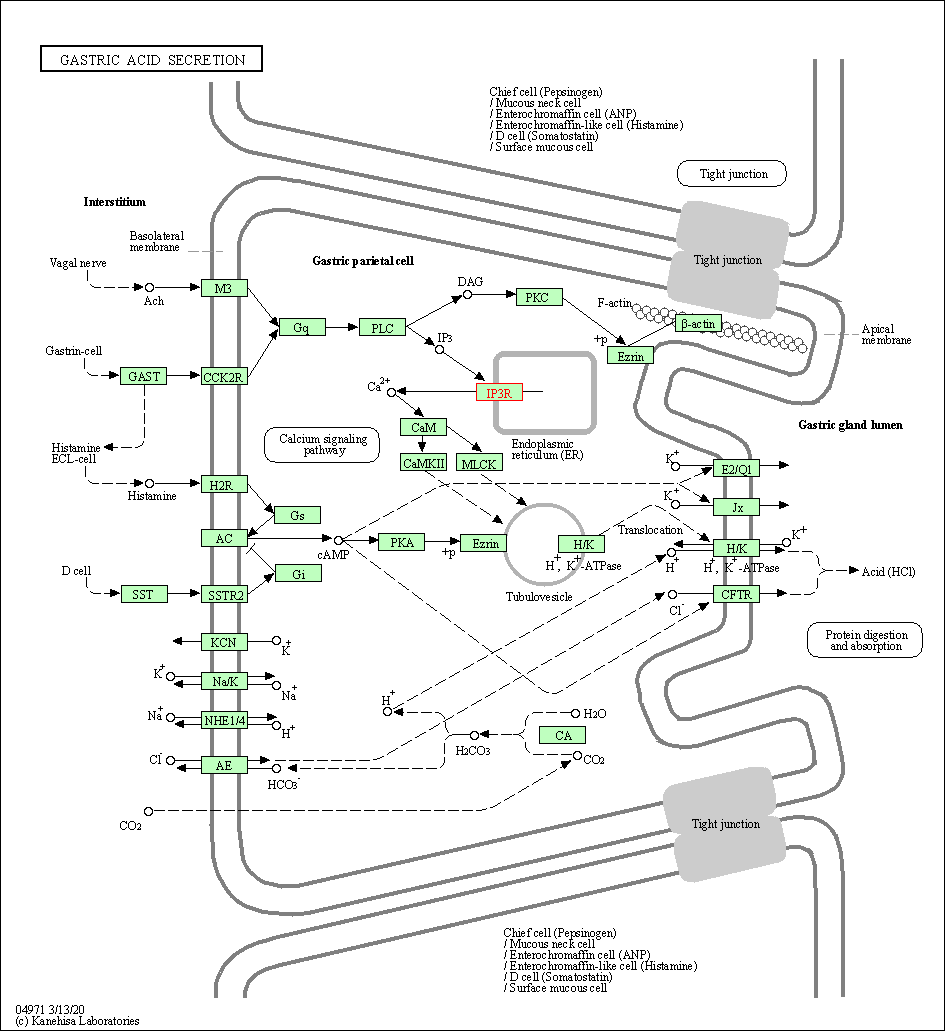
| Gastric acid secretion | hsa04971 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
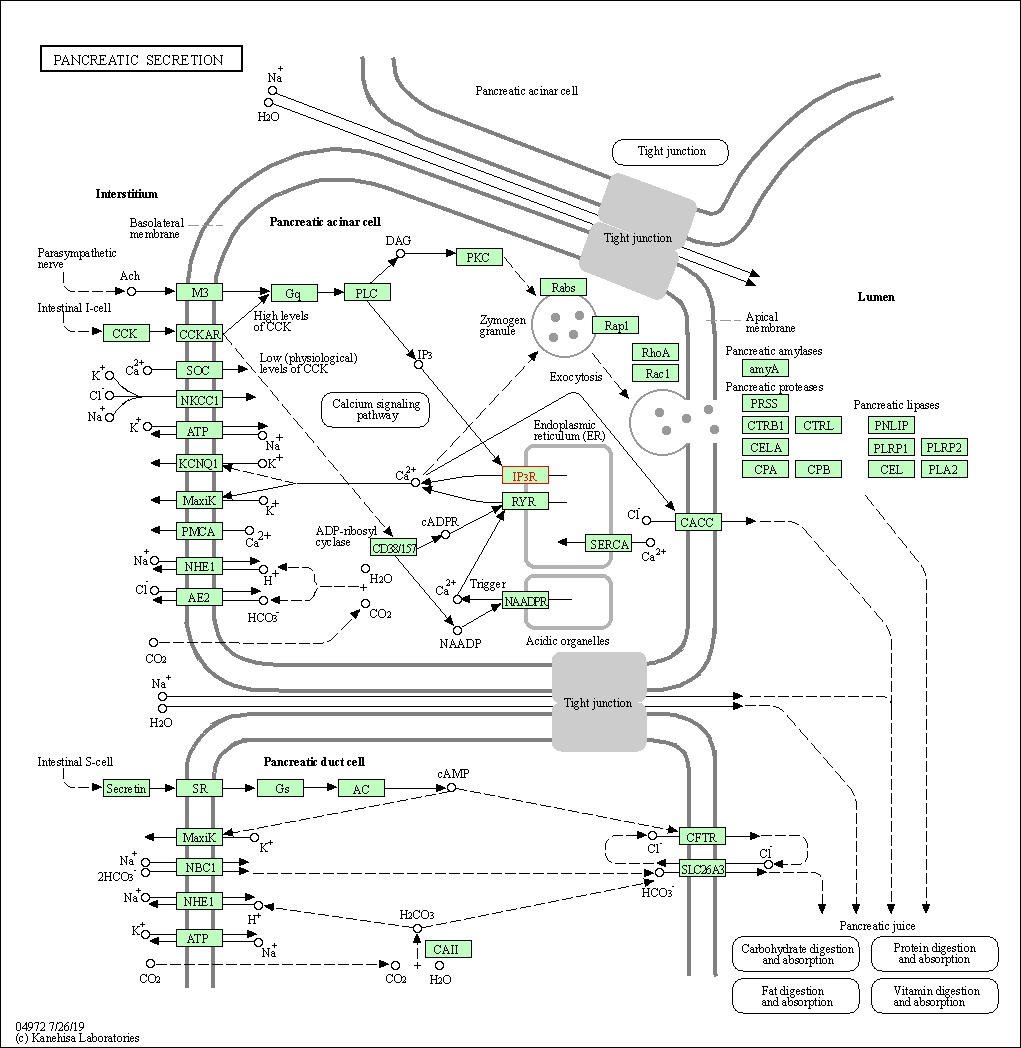
| Pancreatic secretion | hsa04972 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 22 | Degree centrality | 2.36E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.37E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.36E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.06E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.99E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.73E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 743). | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

