Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T77350
(Former ID: TTDI03483)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Proteasome beta-8 (PS beta-8)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Y2; Really interesting new gene 10 protein; RING10; Proteasome subunit beta-5i; Proteasome subunit beta type-8; Proteasome component C13; PSMB5i; Multicatalytic endopeptidase complex subunit C13; Macropain subunit C13; Low molecular mass protein 7; LMP7
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PSMB8
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83] | |||||
| Function |
The proteasome has an ATP-dependent proteolytic activity. This subunit is involved in antigen processing to generate class I binding peptides. Replacement of PSMB5 by PSMB8 increases the capacity of the immunoproteasome to cleave model peptides after hydrophobic and basic residues. Acts as a major component of interferon gamma-induced sensitivity. Plays a key role in apoptosis via the degradation of the apoptotic inhibitor MCL1. May be involved in the inflammatory response pathway. In cancer cells, substitution of isoform 1 (E2) by isoform 2 (E1) results in immunoproteasome deficiency. Required for the differentiation of preadipocytes into adipocytes. The proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex which is characterized by its ability to cleave peptides with Arg, Phe, Tyr, Leu, and Glu adjacent to the leaving group at neutral or slightly basic pH.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Peptidase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.4.25.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MALLDVCGAPRGQRPESALPVAGSGRRSDPGHYSFSMRSPELALPRGMQPTEFFQSLGGD
GERNVQIEMAHGTTTLAFKFQHGVIAAVDSRASAGSYISALRVNKVIEINPYLLGTMSGC AADCQYWERLLAKECRLYYLRNGERISVSAASKLLSNMMCQYRGMGLSMGSMICGWDKKG PGLYYVDEHGTRLSGNMFSTGSGNTYAYGVMDSGYRPNLSPEEAYDLGRRAIAYATHRDS YSGGVVNMYHMKEDGWVKVESTDVSDLLHQYREANQ Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | M3258 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Multiple myeloma | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 32 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | M3258 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 2 | Dipeptide analog 1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | Peptide analog 11 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 4 | Peptide analog 13 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | Peptide analog 17 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 6 | Peptide analog 19 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 7 | Peptide analog 21 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 8 | Peptide analog 23 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 9 | Peptide analog 25 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 10 | Peptide analog 27 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 11 | Peptide analog 28 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 12 | Peptide analog 31 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 13 | Peptide analog 33 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 14 | Peptide analog 34 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 15 | Peptide analog 41 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 16 | PMID29865878-Compound-43 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 17 | PMID29865878-Compound-44 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 18 | PMID29865878-Compound-46 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 19 | PMID29865878-Compound-48 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 20 | PMID29865878-Compound-49 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 21 | PMID29865878-Compound-51 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 22 | PMID29865878-Compound-53 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 23 | PMID29865878-Compound-55 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 24 | PMID29865878-Compound-57 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 25 | PMID29865878-Compound-58 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 26 | PMID29865878-Compound-59 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 27 | PMID29865878-Compound-61 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 28 | PMID29865878-Compound-62 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 29 | PMID29865878-Compound-63 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 30 | PMID29865878-Compound-64 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 31 | PMID29865878-Compound-8 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 32 | HT1042 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
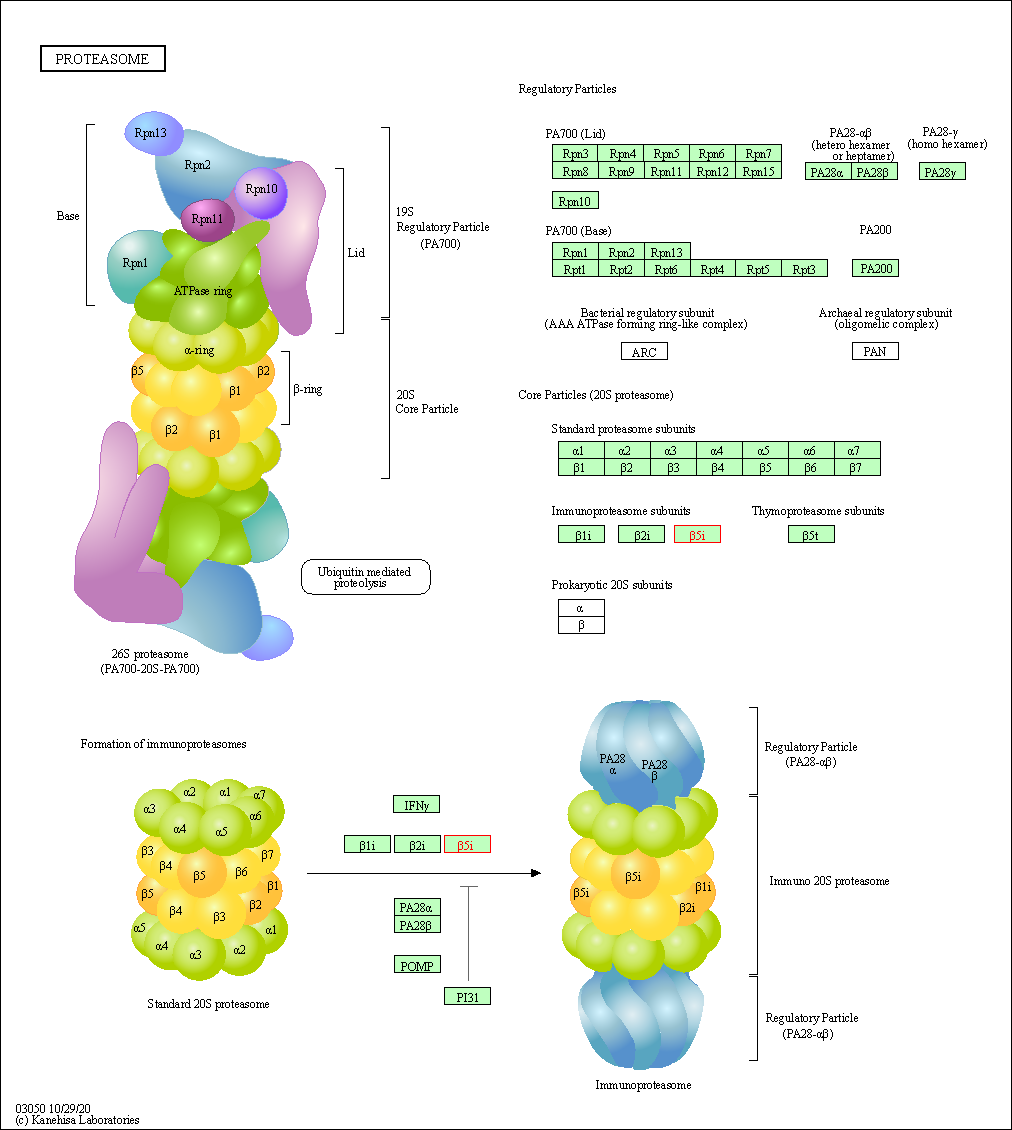
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteasome | hsa03050 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 48 | Degree centrality | 5.16E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.26E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.23E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.48E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.32E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | A patent review of immunoproteasome inhibitors.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Jul;28(7):517-540. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04075721) First in Human Dose Escalation of M3258 as a Single Agent and Expansion Study of M3258 in Combination With Dexamethasone. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of EMD Serono. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2408). | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

