Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T78205
(Former ID: TTDR00987)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Long transient receptor potential channel 2 (TRPM2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
TrpC7; Transient receptor potential melastatin 2; Transient receptor potential channel 7; Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2; LTrpC2; LTrpC-2; Estrogen-responsive element-associated gene 1 protein; EREG1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TRPM2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Isoform 1: Nonselective, voltage-independent cation channel that mediates Na(+) and Ca(2+) influx, leading to increased cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels. Functions as ligand-gated ion channel. Binding of ADP-ribose to the cytoplasmic Nudix domain causes a conformation change; the channel is primed but still requires Ca(2+) binding to trigger channel opening. Extracellular calcium passes through the channel and increases channel activity. Contributes to Ca(2+) release from intracellular stores in response to ADP-ribose. Plays a role in numerous processes that involve signaling via intracellular Ca(2+) levels (Probable). Besides, mediates the release of lysosomal Zn(2+) stores in response to reactive oxygen species, leading to increased cytosolic Zn(2+) levels. Activated by moderate heat (35 to 40 degrees Celsius). Activated by intracellular ADP-ribose, beta-NAD (NAD(+)) and similar compounds, and by oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen or nitrogen species. The precise physiological activators are under debate; the true, physiological activators may be ADP-ribose and ADP-ribose-2'-phosphate. Activation by ADP-ribose and beta-NAD is strongly increased by moderate heat (35 to 40 degrees Celsius). Likewise, reactive oxygen species lower the threshold for activation by moderate heat (37 degrees Celsius). Plays a role in mediating behavorial and physiological responses to moderate heat and thereby contributes to body temperature homeostasis. Plays a role in insulin secretion, a process that requires increased cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels (By similarity). Required for normal IFNG and cytokine secretion and normal innate immune immunity in response to bacterial infection. Required for normal phagocytosis and cytokine release by macrophages exposed to zymosan (in vitro). Plays a role in dendritic cell differentiation and maturation, and in dendritic cell chemotaxis via its role in regulating cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and filopodia formation in response to reactive oxygen species via its role in increasing cytoplasmic Ca(2+) and Zn(2+) levels. Confers susceptibility to cell death following oxidative stress.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Transient receptor potential catioin channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MEPSALRKAGSEQEEGFEGLPRRVTDLGMVSNLRRSNSSLFKSWRLQCPFGNNDKQESLS
SWIPENIKKKECVYFVESSKLSDAGKVVCQCGYTHEQHLEEATKPHTFQGTQWDPKKHVQ EMPTDAFGDIVFTGLSQKVKKYVRVSQDTPSSVIYHLMTQHWGLDVPNLLISVTGGAKNF NMKPRLKSIFRRGLVKVAQTTGAWIITGGSHTGVMKQVGEAVRDFSLSSSYKEGELITIG VATWGTVHRREGLIHPTGSFPAEYILDEDGQGNLTCLDSNHSHFILVDDGTHGQYGVEIP LRTRLEKFISEQTKERGGVAIKIPIVCVVLEGGPGTLHTIDNATTNGTPCVVVEGSGRVA DVIAQVANLPVSDITISLIQQKLSVFFQEMFETFTESRIVEWTKKIQDIVRRRQLLTVFR EGKDGQQDVDVAILQALLKASRSQDHFGHENWDHQLKLAVAWNRVDIARSEIFMDEWQWK PSDLHPTMTAALISNKPEFVKLFLENGVQLKEFVTWDTLLYLYENLDPSCLFHSKLQKVL VEDPERPACAPAAPRLQMHHVAQVLRELLGDFTQPLYPRPRHNDRLRLLLPVPHVKLNVQ GVSLRSLYKRSSGHVTFTMDPIRDLLIWAIVQNRRELAGIIWAQSQDCIAAALACSKILK ELSKEEEDTDSSEEMLALAEEYEHRAIGVFTECYRKDEERAQKLLTRVSEAWGKTTCLQL ALEAKDMKFVSHGGIQAFLTKVWWGQLSVDNGLWRVTLCMLAFPLLLTGLISFREKRLQD VGTPAARARAFFTAPVVVFHLNILSYFAFLCLFAYVLMVDFQPVPSWCECAIYLWLFSLV CEEMRQLFYDPDECGLMKKAALYFSDFWNKLDVGAILLFVAGLTCRLIPATLYPGRVILS LDFILFCLRLMHIFTISKTLGPKIIIVKRMMKDVFFFLFLLAVWVVSFGVAKQAILIHNE RRVDWLFRGAVYHSYLTIFGQIPGYIDGVNFNPEHCSPNGTDPYKPKCPESDATQQRPAF PEWLTVLLLCLYLLFTNILLLNLLIAMFNYTFQQVQEHTDQIWKFQRHDLIEEYHGRPAA PPPFILLSHLQLFIKRVVLKTPAKRHKQLKNKLEKNEEAALLSWEIYLKENYLQNRQFQQ KQRPEQKIEDISNKVDAMVDLLDLDPLKRSGSMEQRLASLEEQVAQTAQALHWIVRTLRA SGFSSEADVPTLASQKAAEEPDAEPGGRKKTEEPGDSYHVNARHLLYPNCPVTRFPVPNE KVPWETEFLIYDPPFYTAERKDAAAMDPMGDTLEPLSTIQYNVVDGLRDRRSFHGPYTVQ AGLPLNPMGRTGLRGRGSLSCFGPNHTLYPMVTRWRRNEDGAICRKSIKKMLEVLVVKLP LSEHWALPGGSREPGEMLPRKLKRILRQEHWPSFENLLKCGMEVYKGYMDDPRNTDNAWI ETVAVSVHFQDQNDVELNRLNSNLHACDSGASIRWQVVDRRIPLYANHKTLLQKAAAEFG AHY Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine-5-diphosphoribose | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human TRPM2 bound to ADPR and calcium | PDB:6PUS | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.70 Å | Mutation | No | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
QESLSSWIPE
65 NIKKKECVYF75 VESSKLSDAG85 KVVCQCGYTH95 EQHLEEATKP105 HTFQGTQWDP 115 KKHVQEMPTD125 AFGDIVFTGL135 SQKVKKYVRV145 SQDTPSSVIY155 HLMTQHWGLD 165 VPNLLISVTG175 GAKNFNMKPR185 LKSIFRRGLV195 KVAQTTGAWI205 ITGGSHTGVM 215 KQVGEAVRDF225 SLSSSYKEGE235 LITIGVATWG245 TVHRREGLIH255 PTGSFPAEYI 265 LDEDGQGNLT275 CLDSNHSHFI285 LVDDGTHGQY295 GVEIPLRTRL305 EKFISEQTKE 315 RGGVAIKIPI325 VCVVLEGGPG335 TLHTIDNATT345 NGTPCVVVEG355 SGRVADVIAQ 365 VANLPVSDIT375 ISLIQQKLSV385 FFQEMFETFT395 ESRIVEWTKK405 IQDIVRRRQL 415 LTVFREGKDG425 QQDVDVAILQ435 ALLKASRSQD445 HFGHENWDHQ455 LKLAVAWNRV 465 DIARSEIFMD475 EWQWKPSDLH485 PTMTAALISN495 KPEFVKLFLE505 NGVQLKEFVT 515 WDTLLYLYEN525 LDPSCLFHSK535 LQKVLVEDPE545 RPACAPAAPR555 LQMHHVAQVL 565 RELLGDFTQP575 LYPRPRHGHV615 TFTMDPIRDL625 LIWAIVQNRR635 ELAGIIWAQS 645 QDCIAAALAC655 SKILKELSKE665 EEDTDSSEEM675 LALAEEYEHR685 AIGVFTECYR 695 KDEERAQKLL705 TRVSEAWGKT715 TCLQLALEAK725 DMKFVSHGGI735 QAFLTKVWWG 745 QLSVDNGLWR755 VTLCMLAFPL765 LLTGLISFRE775 KRLQDVGTPA785 ARARAFFTAP 795 VVVFHLNILS805 YFAFLCLFAY815 VLMVDFQPVP825 SWCECAIYLW835 LFSLVCEEMR 845 QLFYDPDECG855 LMKKAALYFS865 DFWNKLDVGA875 ILLFVAGLTC885 RLIPATLYPG 895 RVILSLDFIL905 FCLRLMHIFT915 ISKTLGPKII925 IVKRMMKDVF935 FFLFLLAVWV 945 VSFGVAKQAI955 LIHNERRVDW965 LFRGAVYHSY975 LTIFGFPEWL1024 TVLLLCLYLL 1034 FTNILLLNLL1044 IAMFNYTFQQ1054 VQEHTDQIWK1064 FQRHDLIEEY1074 HGRPAAPPPF 1084 ILLSHLQLFI1094 KRVVLKRHKQ1108 LKNKLEKNEE1118 AALLSWEIYL1128 KENYLQNRQF 1138 QQKQRPEQKI1148 EDISNKVDAM1158 VDLLDLDGDS1237 YHVNARHLLY1247 PNCPVTRFPV 1257 PNEKVPWETE1267 FLIYDPPFYT1277 AERKDAAAMD1287 PMGDTLEPLS1297 TIQYNVVDGL 1307 RDRRSFHGPY1317 TVQAGLPLNP1327 MGRTGLRGRG1337 SLSCFGPNHT1347 LYPMVTRWRR 1357 NEDGAICRKS1367 IKKMLEVLVV1377 KLPLSEHWAL1387 PGGSREPGEM1397 LPRKLKRILR 1407 QEHWPSFENL1417 LKCGMEVYKG1427 YMDDPRNTDN1437 AWIETVAVSV1447 HFQDQNDVEL 1457 NRLNSNLHAC1467 DSGASIRWQV1477 VDRRIPLYAN1487 HKTLLQKAAA1497 EFGAHY |
|||||
|
|
VAL173
4.894
THR174
3.036
GLY175
2.984
GLY176
3.262
ALA177
3.410
LYS178
3.445
ASN179
2.783
GLY208
4.822
SER210
3.959
THR212
4.067
MET215
4.604
THR275
4.023
TYR295
3.241
ILE299
4.823
ARG302
2.750
GLY332
3.955
GLY333
2.885
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: 1,5-[1-Deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose-1,5-O-diyl(oxylatophosphinylidene)oxy(oxylatophosphinylidene)(1-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose-5-O,1-diyl)]-2-bromo-4-amino-1,3,7-triaza-5-azonia-1H-indene | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human TRPM2 bound to 8-Br-cADPR and calcium | PDB:6PUU | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.70 Å | Mutation | No | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
QESLSSWIPE
65 NIKKKECVYF75 VESSKLSDAG85 KVVCQCGYTH95 EQHLEEATKP105 HTFQGTQWDP 115 KKHVQEMPTD125 AFGDIVFTGL135 SQKVKKYVRV145 SQDTPSSVIY155 HLMTQHWGLD 165 VPNLLISVTG175 GAKNFNMKPR185 LKSIFRRGLV195 KVAQTTGAWI205 ITGGSHTGVM 215 KQVGEAVRDF225 SLSSSYKEGE235 LITIGVATWG245 TVHRREGLIH255 PTGSFPAEYI 265 LDEDGQGNLT275 CLDSNHSHFI285 LVDDGTHGQY295 GVEIPLRTRL305 EKFISEQTKE 315 RGGVAIKIPI325 VCVVLEGGPG335 TLHTIDNATT345 NGTPCVVVEG355 SGRVADVIAQ 365 VANLPVSDIT375 ISLIQQKLSV385 FFQEMFETFT395 ESRIVEWTKK405 IQDIVRRRQL 415 LTVFREGKDG425 QQDVDVAILQ435 ALLKASRSQD445 HFGHENWDHQ455 LKLAVAWNRV 465 DIARSEIFMD475 EWQWKPSDLH485 PTMTAALISN495 KPEFVKLFLE505 NGVQLKEFVT 515 WDTLLYLYEN525 LDPSCLFHSK535 LQKVLVEDPE545 RPACAPAAPR555 LQMHHVAQVL 565 RELLGDFTQP575 LYPRPRHHVT616 FTMDPIRDLL626 IWAIVQNRRE636 LAGIIWAQSQ 646 DCIAAALACS656 KILKELSKEE666 EDTDSSEEML676 ALAEEYEHRA686 IGVFTECYRK 696 DEERAQKLLT706 RVSEAWGKTT716 CLQLALEAKD726 MKFVSHGGIQ736 AFLTKVWWGQ 746 LSVDNGLWRV756 TLCMLAFPLL766 LTGLISFREK776 RLQDVGTPAA786 RARAFFTAPV 796 VVFHLNILSY806 FAFLCLFAYV816 LMVDFQPVPS826 WCECAIYLWL836 FSLVCEEMRQ 846 LFYDPDECGL856 MKKAALYFSD866 FWNKLDVGAI876 LLFVAGLTCR886 LIPATLYPGR 896 VILSLDFILF906 CLRLMHIFTI916 SKTLGPKIII926 VKRMMKDVFF936 FLFLLAVWVV 946 SFGVAKQAIL956 IHNERRVDWL966 FRGAVYHSYL976 TIFGFPEWLT1025 VLLLCLYLLF 1035 TNILLLNLLI1045 AMFNYTFQQV1055 QEHTDQIWKF1065 QRHDLIEEYH1075 GRPAAPPPFI 1085 LLSHLQLFIK1095 RVVLKTPAKR1105 HKQLKNKLEK1115 NEEAALLSWE1125 IYLKENYLQN 1135 RQFQQKQRPE1145 QKIEDISNKV1155 DAMVDLLDLD1165 GDSYHVNARH1244 LLYPNCPVTR 1254 FPVPNEKVPW1264 ETEFLIYDPP1274 FYTAERKDAA1284 AMDPMGDTLE1294 PLSTIQYNVV 1304 DGLRDRRSFH1314 GPYTVQAGLP1324 LNPMGRTGLR1334 GRGSLSCFGP1344 NHTLYPMVTR 1354 WRRNEDGAIC1364 RKSIKKMLEV1374 LVVKLPLSEH1384 WALPGGSREP1394 GEMLPRKLKR 1404 ILRQEHWPSF1414 ENLLKCGMEV1424 YKGYMDDPRN1434 TDNAWIETVA1444 VSVHFQDQND 1454 VELNRLNSNL1464 HACDSGASIR1474 WQVVDRRIPL1484 YANHKTLLQK1494 AAAEFGAHY |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase, mitochondrial (NUDT9) | 35.862 (104/290) | 5.70E-45 |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
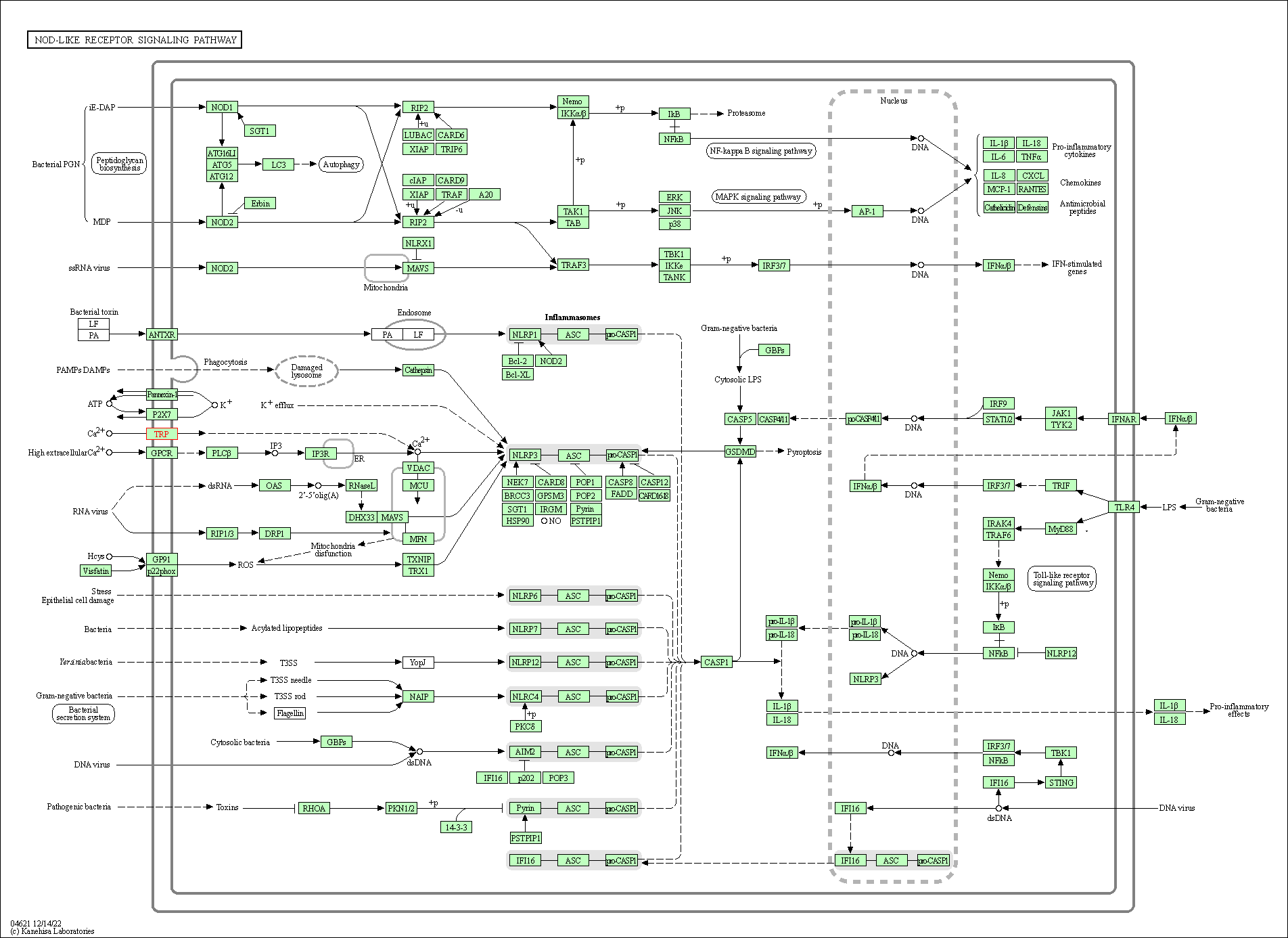
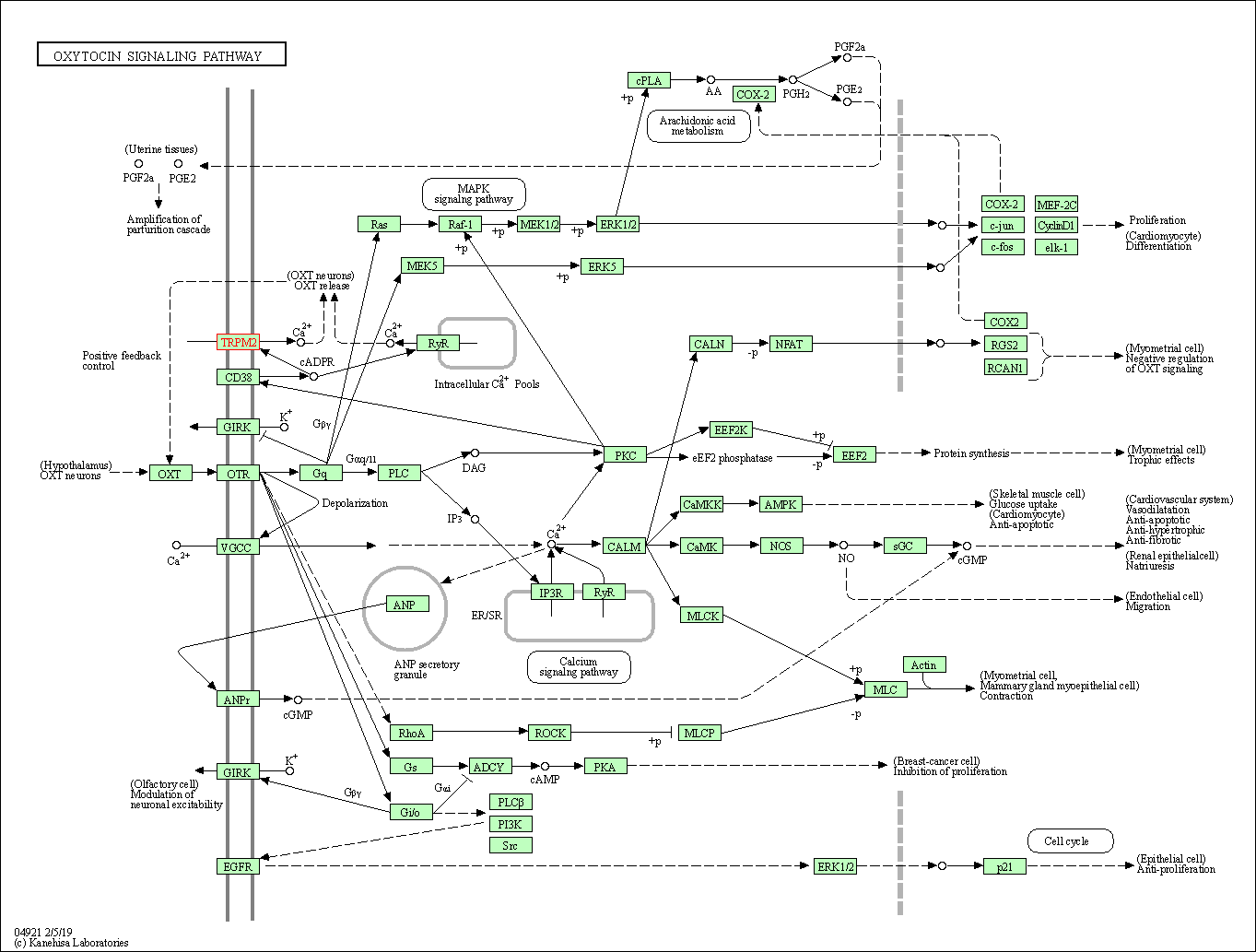
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TRP channels | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate and cyclic ADP-ribose regulate TRPM2 channels in T lymphocytes. FASEB J. 2006 May;20(7):962-4. | |||||
| REF 2 | Inhibition of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPM2 by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB). Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153(6):1324-30. | |||||
| REF 3 | Inhibition of TRPM2 cation channels by N-(p-amylcinnamoyl)anthranilic acid. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jun;148(3):264-73. | |||||
| REF 4 | ADP-ribose gating of the calcium-permeable LTRPC2 channel revealed by Nudix motif homology. Nature. 2001 May 31;411(6837):595-9. | |||||
| REF 5 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 494). | |||||
| REF 6 | Metabolite of SIR2 reaction modulates TRPM2 ion channel. J Biol Chem. 2006 May 19;281(20):14057-65. | |||||
| REF 7 | Ligand recognition and gating mechanism through three ligand-binding sites of human TRPM2 channel. Elife. 2019 Sep 12;8:e50175. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

