Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T93325
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Spliceosome-associated protein 155 (SF3B1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Splicing factor 3B subunit 1; SF3b155; SAP155; SAP 155; Pre-mRNA-splicing factor SF3b 155 kDa subunit
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
SF3B1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Involved in pre-mRNA splicing as a component of the splicing factor SF3B complex. SF3B complex is required for 'A' complex assembly formed by the stable binding of U2 snRNP to the branchpoint sequence (BPS) in pre-mRNA. Sequence independent binding of SF3A/SF3B complex upstream of the branch site is essential, it may anchor U2 snRNP to the pre-mRNA. May also be involved in the assembly of the 'E' complex. Belongs also to the minor U12-dependent spliceosome, which is involved in the splicing of rare class of nuclear pre-mRNA intron.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
SF3B1 family
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAKIAKTHEDIEAQIREIQGKKAALDEAQGVGLDSTGYYDQEIYGGSDSRFAGYVTSIAA
TELEDDDDDYSSSTSLLGQKKPGYHAPVALLNDIPQSTEQYDPFAEHRPPKIADREDEYK KHRRTMIISPERLDPFADGGKTPDPKMNARTYMDVMREQHLTKEEREIRQQLAEKAKAGE LKVVNGAAASQPPSKRKRRWDQTADQTPGATPKKLSSWDQAETPGHTPSLRWDETPGRAK GSETPGATPGSKIWDPTPSHTPAGAATPGRGDTPGHATPGHGGATSSARKNRWDETPKTE RDTPGHGSGWAETPRTDRGGDSIGETPTPGASKRKSRWDETPASQMGGSTPVLTPGKTPI GTPAMNMATPTPGHIMSMTPEQLQAWRWEREIDERNRPLSDEELDAMFPEGYKVLPPPAG YVPIRTPARKLTATPTPLGGMTGFHMQTEDRTMKSVNDQPSGNLPFLKPDDIQYFDKLLV DVDESTLSPEEQKERKIMKLLLKIKNGTPPMRKAALRQITDKAREFGAGPLFNQILPLLM SPTLEDQERHLLVKVIDRILYKLDDLVRPYVHKILVVIEPLLIDEDYYARVEGREIISNL AKAAGLATMISTMRPDIDNMDEYVRNTTARAFAVVASALGIPSLLPFLKAVCKSKKSWQA RHTGIKIVQQIAILMGCAILPHLRSLVEIIEHGLVDEQQKVRTISALAIAALAEAATPYG IESFDSVLKPLWKGIRQHRGKGLAAFLKAIGYLIPLMDAEYANYYTREVMLILIREFQSP DEEMKKIVLKVVKQCCGTDGVEANYIKTEILPPFFKHFWQHRMALDRRNYRQLVDTTVEL ANKVGAAEIISRIVDDLKDEAEQYRKMVMETIEKIMGNLGAADIDHKLEEQLIDGILYAF QEQTTEDSVMLNGFGTVVNALGKRVKPYLPQICGTVLWRLNNKSAKVRQQAADLISRTAV VMKTCQEEKLMGHLGVVLYEYLGEEYPEVLGSILGALKAIVNVIGMHKMTPPIKDLLPRL TPILKNRHEKVQENCIDLVGRIADRGAEYVSAREWMRICFELLELLKAHKKAIRRATVNT FGYIAKAIGPHDVLATLLNNLKVQERQNRVCTTVAIAIVAETCSPFTVLPALMNEYRVPE LNVQNGVLKSLSFLFEYIGEMGKDYIYAVTPLLEDALMDRDLVHRQTASAVVQHMSLGVY GFGCEDSLNHLLNYVWPNVFETSPHVIQAVMGALEGLRVAIGPCRMLQYCLQGLFHPARK VRDVYWKIYNSIYIGSQDALIAHYPRIYNDDKNTYIRYELDYIL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: 1-Piperazinecarboxylic acid, 4-cycloheptyl-, (2S,3S,4E,6S,7R,10R)-7,10-dihydroxy-2-((1E,3E,5R)-5-hydroxy-6-((2R,3R)-3-((1R,2S)-2-hydroxy-1-methylbutyl)oxiranyl)-1,5-dimethyl-1,3-hexadienyl)-3,7-dimethyl-12-oxooxacyclododec-4-en-6-yl ester | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | SF3b spliceosomal complex bound to E7107 | PDB:5ZYA | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.95 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
EEQKERKIMK
499 LLLKIKNGTP509 PMRKAALRQI519 TDKAREFGAG529 PLFNQILPLL539 MSPTLEDQER 549 HLLVKVIDRI559 LYKLDDLVRP569 YVHKILVVIE579 PLLIDEDYYA589 RVEGREIISN 599 LAKAAGLATM609 ISTMRPDIDN619 MDEYVRNTTA629 RAFAVVASAL639 GIPSLLPFLK 649 AVCKSKKSWQ659 ARHTGIKIVQ669 QIAILMGCAI679 LPHLRSLVEI689 IEHGLVDEQQ 699 KVRTISALAI709 AALAEAATPY719 GIESFDSVLK729 PLWKGIRQHR739 GKGLAAFLKA 749 IGYLIPLMDA759 EYANYYTREV769 MLILIREFQS779 PDEEMKKIVL789 KVVKQCCGTD 799 GVEANYIKTE809 ILPPFFKHFW819 QHRMALDRRN829 YRQLVDTTVE839 LANKVGAAEI 849 ISRIVDDLKD859 EAEQYRKMVM869 ETIEKIMGNL879 GAADIDHKLE889 EQLIDGILYA 899 FQEQTTEDSV909 MLNGFGTVVN919 ALGKRVKPYL929 PQICGTVLWR939 LNNKSAKVRQ 949 QAADLISRTA959 VVMKTCQEEK969 LMGHLGVVLY979 EYLGEEYPEV989 LGSILGALKA 999 IVNVIGMHKM1009 TPPIKDLLPR1019 LTPILKNRHE1029 KVQENCIDLV1039 GRIADRGAEY 1049 VSAREWMRIC1059 FELLELLKAH1069 KKAIRRATVN1079 TFGYIAKAIG1089 PHDVLATLLE 1105 RQNRVCTTVA1115 IAIVAETCSP1125 FTVLPALMNE1135 YRVPELNVQN1145 GVLKSLSFLF 1155 EYIGEMGKDY1165 IYAVTPLLED1175 ALMDRDLVHR1185 QTASAVVQHM1195 SLGVYGFGCE 1205 DSLNHLLNYV1215 WPNVFETSPH1225 VIQAVMGALE1235 GLRVAIGPCR1245 MLQYCLQGLF 1255 HPARKVRDVY1265 WKIYNSIYIG1275 SQDALIAHYP1285 RIYNDDKNTY1295 IRYELDYIL |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: [(Z,2S)-5-[[(2R,3R,5S,6S)-6-[(2E,4E)-5-[(2R,3R,4S,6S)-3,4-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]-3-methylpenta-2,4-dienyl]-2,5-dimethyloxan-3-yl]amino]-5-oxopent-3-en-2-yl] acetate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of a minimal SF3B core in complex with spliceostatin A (form I) | PDB:7B9C | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
NLPFLKPDDI
472 QYFDKLLVDV482 DESTLSPEEQ492 KERKIMKLLL502 KIKNGTPPMR512 KAALRQITDK 522 AREFGAGPLF532 NQILPLLMSP542 TLEDQERHLL552 VKVIDRILYK562 LDDLVRPYVH 572 KILVVIEPLL582 IDEDYYARVE592 GREIISNLAK602 AAGLATMIST612 MRPDIDNMDE 622 YVRNTTARAF632 AVVASALGIP642 SLLPFLKAVC652 KSKKSWQARH662 TGIKIVQQIA 672 ILMGCAILPH682 LRSLVEIIEH692 GLVDEQQKVR702 TISALAIAAL712 AEAATPYGIE 722 SFDSVLKPLW732 KGIRQHRGKG742 LAAFLKAIGY752 LIPLMDAEYA762 NYYTREVMLI 772 LIREFQSPDE782 EMKKIVLKVV792 KQCCGTDGVE802 ANYIKTEILP812 PFFKHFWQHR 822 MALDRRNYRQ832 LVDTTVELAN842 KVGAAEIISR852 IVDDLKDEAE862 QYRKMVMETI 872 EKIMGNLGAA882 DIDHKLEEQL892 IDGILYAFQE902 QTTEDSVMLN912 GFGTVVNALG 922 KRVKPYLPQI932 CGTVLWRLNN942 KSAKVRQQAA952 DLISRTAVVM962 KTCQEEKLMG 972 HLGVVLYEYL982 GEEYPEVLGS992 ILGALKAIVN1002 VIGMHKMTPP1012 IKDLLPRLTP 1022 ILKNRHEKVQ1032 ENCIDLVGRI1042 ADRGAEYVSA1052 REWMRICFEL1062 LELLKAHKKA 1072 IRRATVNTFG1082 YIAKAIGPHD1092 VLATLLNNLK1102 VQERQNRVCT1112 TVAIAIVAET 1122 CSPFTVLPAL1132 MNEYRVPELN1142 VQNGVLKSLS1152 FLFEYIGEMG1162 KDYIYAVTPL 1172 LEDALMDRDL1182 VHRQTASAVV1192 QHMSLGVYGF1202 GCEDSLNHLL1212 NYVWPNVFET 1222 SPHVIQAVMG1232 ALEGLRVAIG1242 PCRMLQYCLQ1252 GLFHPARKVR1262 DVYWKIYNSI 1272 YIGSQDALIA1282 HYPRIYNDDK1292 NTYIRYELDY1302 IL
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 65 kDa regulatory subunit A alpha isoform (PPP2R1A) | 21.069 (134/636) | 5.14E-04 |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spliceosome | hsa03040 | Affiliated Target |
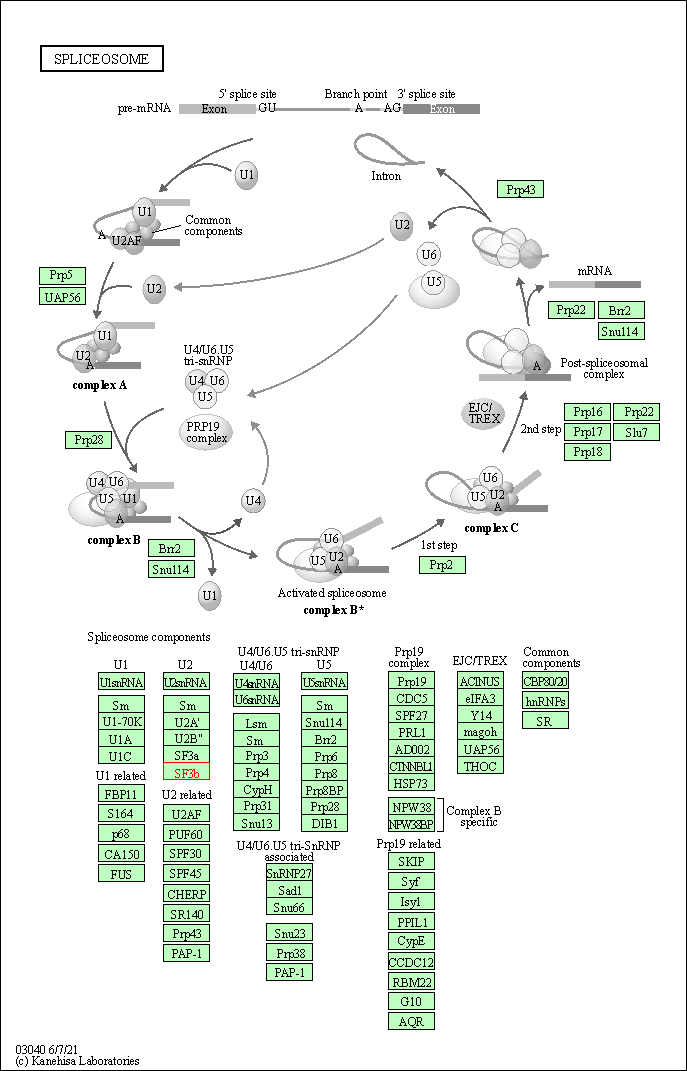
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Transcription | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 82 | Degree centrality | 8.81E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 7.04E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.07E-01 | Radiality | 1.36E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 4.74E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.02E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.61E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 1 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Spliceosome | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Discoveries, target identifications, and biological applications of natural products that inhibit splicing factor 3B subunit 1. Nat Prod Rep. 2016 May 4;33(5):637-47. | |||||
| REF 2 | The cryo-EM structure of the SF3b spliceosome complex bound to a splicing modulator reveals a pre-mRNA substrate competitive mechanism of action. Genes Dev. 2018 Feb 1;32(3-4):309-320. | |||||
| REF 3 | Structural basis of intron selection by U2 snRNP in the presence of covalent inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 23;12(1):4491. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

