Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T95438
(Former ID: TTDNR00670)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (SLC1A2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Solute carrier family 1 member 2; Sodium-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter 2; Glutamate/aspartatetransporter II; Glutamate/aspartate transporter II; GLT1; EAAT2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
SLC1A2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Functions as a symporter that transports one amino acid molecule together with two or three Na(+) ions and one proton, in parallel with the counter-transport of one K(+) ion. Mediates Cl(-) flux that is not coupled to amino acid transport; this avoids the accumulation of negative charges due to aspartate and Na(+) symport. Essential for the rapid removal of released glutamate from the synaptic cleft, and for terminating the postsynaptic action of glutamate. Sodium-dependent, high-affinity amino acid transporter that mediates the uptake of L-glutamate and also L-aspartate and D-aspartate.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MASTEGANNMPKQVEVRMHDSHLGSEEPKHRHLGLRLCDKLGKNLLLTLTVFGVILGAVC
GGLLRLASPIHPDVVMLIAFPGDILMRMLKMLILPLIISSLITGLSGLDAKASGRLGTRA MVYYMSTTIIAAVLGVILVLAIHPGNPKLKKQLGPGKKNDEVSSLDAFLDLIRNLFPENL VQACFQQIQTVTKKVLVAPPPDEEANATSAVVSLLNETVTEVPEETKMVIKKGLEFKDGM NVLGLIGFFIAFGIAMGKMGDQAKLMVDFFNILNEIVMKLVIMIMWYSPLGIACLICGKI IAIKDLEVVARQLGMYMVTVIIGLIIHGGIFLPLIYFVVTRKNPFSFFAGIFQAWITALG TASSAGTLPVTFRCLEENLGIDKRVTRFVLPVGATINMDGTALYEAVAAIFIAQMNGVVL DGGQIVTVSLTATLASVGAASIPSAGLVTMLLILTAVGLPTEDISLLVAVDWLLDRMRTS VNVVGDSFGAGIVYHLSKSELDTIDSQHRVHEDIEMTKTQSIYDDMKNHRESNSNQCVYA AHNSVIVDECKVTLAANGKSADCSVEEEPWKREK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T71PEL | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: WAY-213613 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of human excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2) in complex with WAY-213613 | PDB:7XR6 | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.40 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
RLCDKLGKNL
45 LLTLTVFGVI55 LGAVCGGLLR65 LASPIHPDVV75 MLIAFPGDIL85 MRMLKMLILP 95 LIISSLITGL105 SGLDAKASGR115 LGTRAMVYYM125 STTIIAAVLG135 VILVLAIHPG 145 NPKVSSLDAF168 LDLIRNLFPE178 NLVQACFQQI188 QTVTKVIKKG233 LEFKDGMNVL 243 GLIGFFIAFG253 IAMGKMGDQA263 KLMVDFFNIL273 NEIVMKLVIM283 IMWYSPLGIA 293 CLICGKIIAI303 KDLEVVARQL313 GMYMVTVIIG323 LIIHGGIFLP333 LIYFVVTRKN 343 PFSFFAGIFQ353 AWITALGTAS363 SAGTLPVTFR373 CLEENLGIDK383 RVTRFVLPVG 393 ATINMDGTAL403 YEAVAAIFIA413 QMNGVVLDGG423 QIVTVSLTAT433 LASVGAASIP 443 SAGLVTMLLI453 LTAVGLPTED463 ISLLVAVDWL473 LDRMRTSVNV483 VGDSFGAGIV 493 YHLSKSELDT503 IDSQ
|
|||||
|
|
ALA362
3.815
SER363
3.629
SER364
2.797
ALA365
4.810
MET398
3.929
THR401
3.230
TYR404
3.581
GLU405
4.677
ALA439
3.663
ALA440
3.750
GLY446
3.122
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Cholesterol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Inward-facing structure of human EAAT2 in the WAY213613-bound state | PDB:7VR7 | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.49 Å | Mutation | No | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
NLLLTLTVFG
53 VILGAVCGGL63 LRLASPIHPD73 VVMLIAFPGD83 ILMRMLKMLI93 LPLIISSLIT 103 GLSGLDGRLG117 TRAMVYYMST127 TIIAAVLGVI137 LVLAIHPGNP147 SSLDAFLDLI 172 RNLFPENLVQ182 ACFQQIQTVT192 KIKKGLEFKD238 GMNVLGLIGF248 FIAFGIAMGK 258 MGDQAKLMVD268 FFNILNEIVM278 KLVIMIMWYS288 PLGIACLICG298 KIIAIKDLEV 308 VARQLGMYMV318 TVIIGLIIHG328 GIFLPLIYFV338 VTRKNPFSFF348 AGIFQAWITA 358 LGTASSAGTL368 PVTFRCLEEN378 LGIDKRVTRF388 VLPVGATINM398 DGTALYEAVA 408 AIFIAQMNGV418 VLDGGQIVTV428 SLTATLASVG438 AASIPSAGLV448 TMLLILTAVG 458 LPTEDISLLV468 AVDWLLDRMR478 TSVNVVGDSF488 GAGIVYHLSK498 SE |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
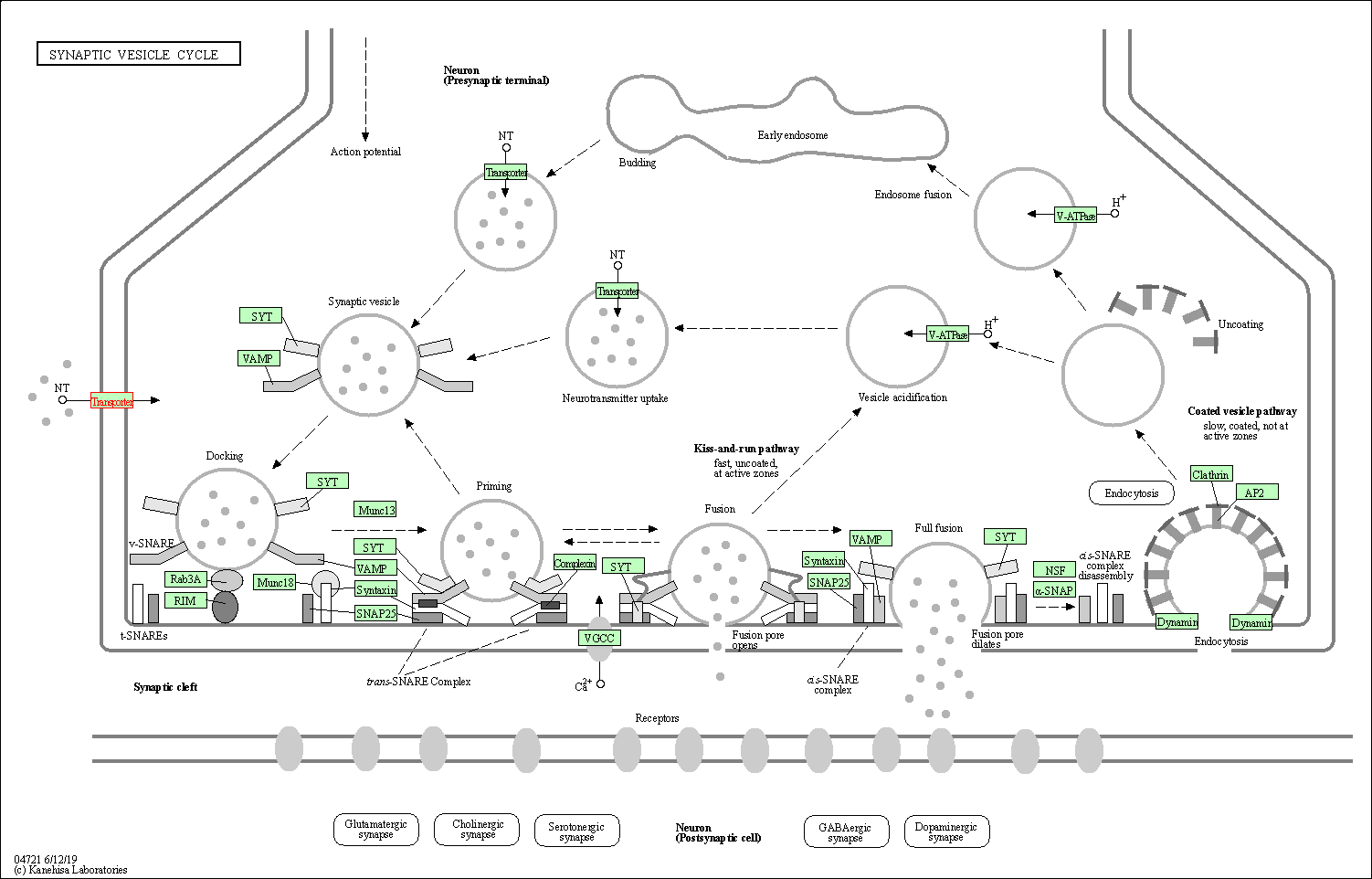
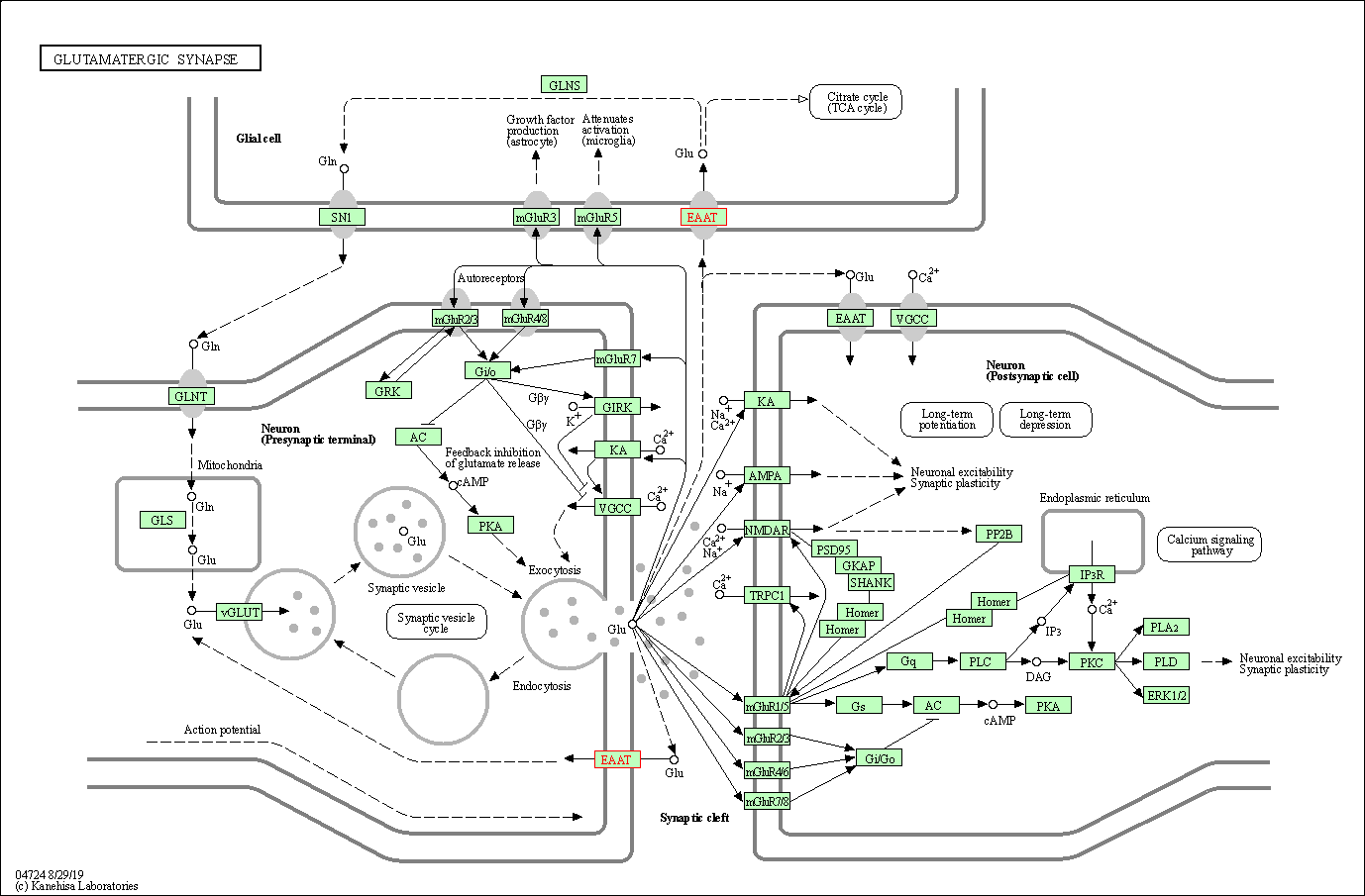
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synaptic vesicle cycle | hsa04721 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glutamatergic synapse | hsa04724 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 1 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 0.00E+00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.56E-01 | Radiality | 1.22E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.00E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.00E+00 | Eccentricity | 14 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panther Pathway | [+] 2 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Ionotropic glutamate receptor pathway | |||||
| 2 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor group III pathway | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Contrasting modes of action of methylglutamate derivatives on the excitatory amino acid transporters, EAAT1 and EAAT2. Mol Pharmacol. 1997 May;51(5):809-15. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 869). | |||||
| REF 3 | DL-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate, a potent blocker of excitatory amino acid transporters. Mol Pharmacol. 1998 Feb;53(2):195-201. | |||||
| REF 4 | Characterization of novel aryl-ether, biaryl, and fluorene aspartic acid and diaminopropionic acid analogs as potent inhibitors of the high-affinit... Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Oct;68(4):974-82. | |||||
| REF 5 | Characterization of the tritium-labeled analog of L-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate binding to glutamate transporters. Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Jan;71(1):294-302. | |||||
| REF 6 | Structural basis of ligand binding modes of human EAAT2. Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 9;13(1):3329. | |||||
| REF 7 | Structural insights into inhibitory mechanism of human excitatory amino acid transporter EAAT2. Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 11;13(1):4714. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

