Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T99333
(Former ID: TTDI03098)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Voltage-gated calcium channel alpha Cav1.4 (CACNA1F)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav1.4; Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1F; CACNAF1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CACNA1F
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Isoform 1: Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1F gives rise to L-type calcium currents. Long-lasting (L-type) calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group. They are blocked by dihydropyridines (DHP), phenylalkylamines, and by benzothiazepines. Activates at more negative voltages and does not undergo calcium-dependent inactivation (CDI), due to incoming calcium ions, during depolarization.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Voltage-gated ion channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MSESEGGKDTTPEPSPANGAGPGPEWGLCPGPPAVEGESSGASGLGTPKRRNQHSKHKTV
AVASAQRSPRALFCLTLANPLRRSCISIVEWKPFDILILLTIFANCVALGVYIPFPEDDS NTANHNLEQVEYVFLVIFTVETVLKIVAYGLVLHPSAYIRNGWNLLDFIIVVVGLFSVLL EQGPGRPGDAPHTGGKPGGFDVKALRAFRVLRPLRLVSGVPSLHIVLNSIMKALVPLLHI ALLVLFVIIIYAIIGLELFLGRMHKTCYFLGSDMEAEEDPSPCASSGSGRACTLNQTECR GRWPGPNGGITNFDNFFFAMLTVFQCVTMEGWTDVLYWMQDAMGYELPWVYFVSLVIFGS FFVLNLVLGVLSGEFSKEREKAKARGDFQKQREKQQMEEDLRGYLDWITQAEELDMEDPS ADDNLGSMAEEGRAGHRPQLAELTNRRRGRLRWFSHSTRSTHSTSSHASLPASDTGSMTE TQGDEDEEEGALASCTRCLNKIMKTRVCRRLRRANRVLRARCRRAVKSNACYWAVLLLVF LNTLTIASEHHGQPVWLTQIQEYANKVLLCLFTVEMLLKLYGLGPSAYVSSFFNRFDCFV VCGGILETTLVEVGAMQPLGISVLRCVRLLRIFKVTRHWASLSNLVASLLNSMKSIASLL LLLFLFIIIFSLLGMQLFGGKFNFDQTHTKRSTFDTFPQALLTVFQILTGEDWNVVMYDG IMAYGGPFFPGMLVCIYFIILFICGNYILLNVFLAIAVDNLASGDAGTAKDKGGEKSNEK DLPQENEGLVPGVEKEEEEGARREGADMEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEGAGGVELLQEVVPKE KVVPIPEGSAFFCLSQTNPLRKGCHTLIHHHVFTNLILVFIILSSVSLAAEDPIRAHSFR NHILGYFDYAFTSIFTVEILLKMTVFGAFLHRGSFCRSWFNMLDLLVVSVSLISFGIHSS AISVVKILRVLRVLRPLRAINRAKGLKHVVQCVFVAIRTIGNIMIVTTLLQFMFACIGVQ LFKGKFYTCTDEAKHTPQECKGSFLVYPDGDVSRPLVRERLWVNSDFNFDNVLSAMMALF TVSTFEGWPALLYKAIDAYAEDHGPIYNYRVEISVFFIVYIIIIAFFMMNIFVGFVIITF RAQGEQEYQNCELDKNQRQCVEYALKAQPLRRYIPKNPHQYRVWATVNSAAFEYLMFLLI LLNTVALAMQHYEQTAPFNYAMDILNMVFTGLFTIEMVLKIIAFKPKHYFTDAWNTFDAL IVVGSIVDIAVTEVNNGGHLGESSEDSSRISITFFRLFRVMRLVKLLSKGEGIRTLLWTF IKSFQALPYVALLIAMIFFIYAVIGMQMFGKVALQDGTQINRNNNFQTFPQAVLLLFRCA TGEAWQEIMLASLPGNRCDPESDFGPGEEFTCGSNFAIAYFISFFMLCAFLIINLFVAVI MDNFDYLTRDWSILGPHHLDEFKRIWSEYDPGAKGRIKHLDVVALLRRIQPPLGFGKLCP HRVACKRLVAMNMPLNSDGTVTFNATLFALVRTSLKIKTEGNLEQANQELRIVIKKIWKR MKQKLLDEVIPPPDEEEVTVGKFYATFLIQDYFRKFRRRKEKGLLGNDAAPSTSSALQAG LRSLQDLGPEMRQALTCDTEEEEEEGQEGVEEEDEKDLETNKATMVSQPSARRGSGISVS LPVGDRLPDSLSFGPSDDDRGTPTSSQPSVPQAGSNTHRRGSGALIFTIPEEGNSQPKGT KGQNKQDEDEEVPDRLSYLDEQAGTPPCSVLLPPHRAQRYMDGHLVPRRRLLPPTPAGRK PSFTIQCLQRQGSCEDLPIPGTYHRGRNSGPNRAQGSWATPPQRGRLLYAPLLLVEEGAA GEGYLGRSSGPLRTFTCLHVPGTHSDPSHGKRGSADSLVEAVLISEGLGLFARDPRFVAL AKQEIADACRLTLDEMDNAASDLLAQGTSSLYSDEESILSRFDEEDLGDEMACVHAL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cardiac muscle contraction | hsa04260 | Affiliated Target |
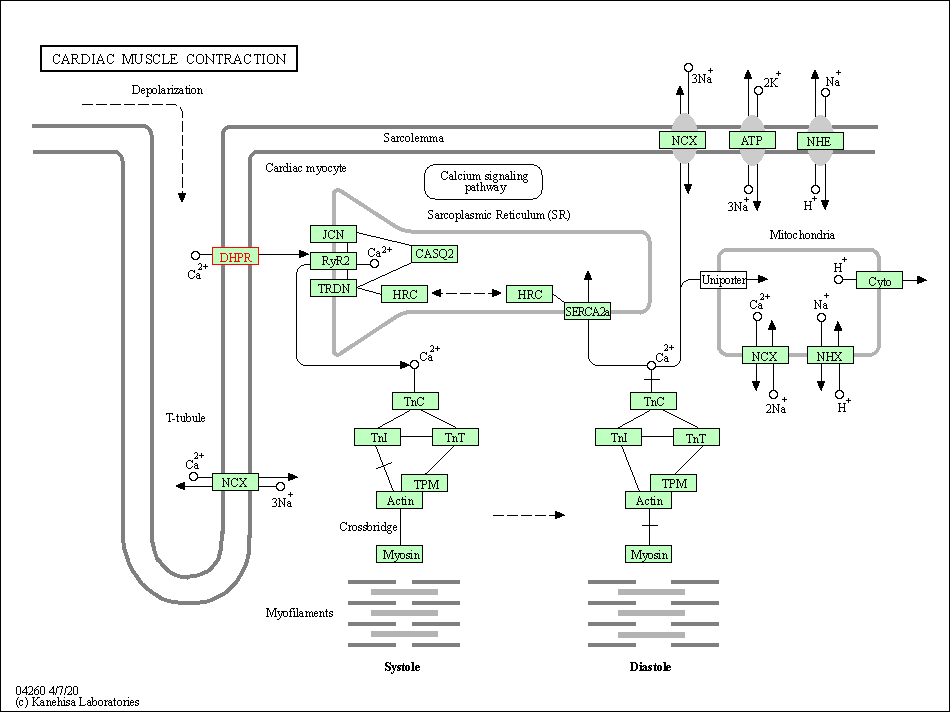
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
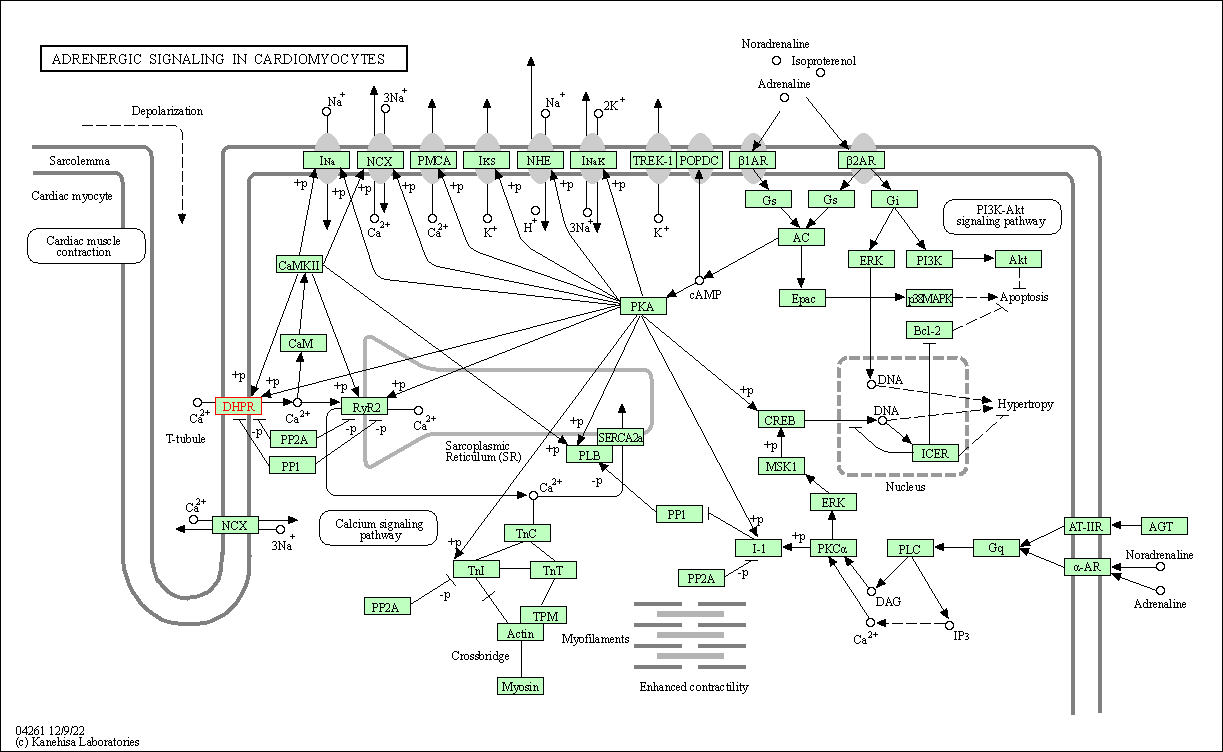
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |
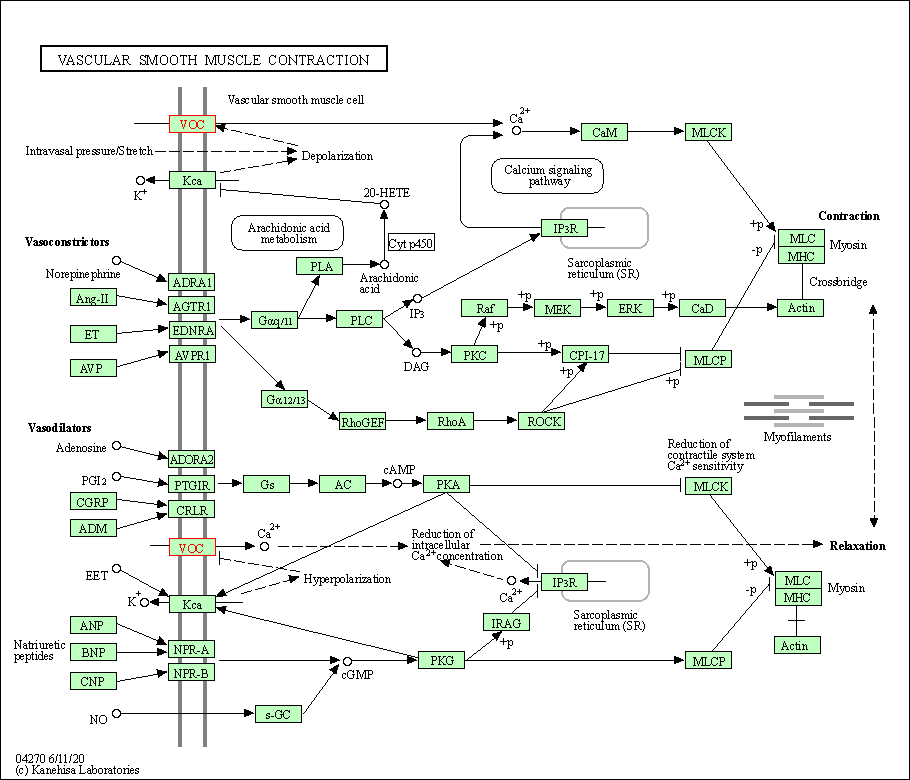
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |
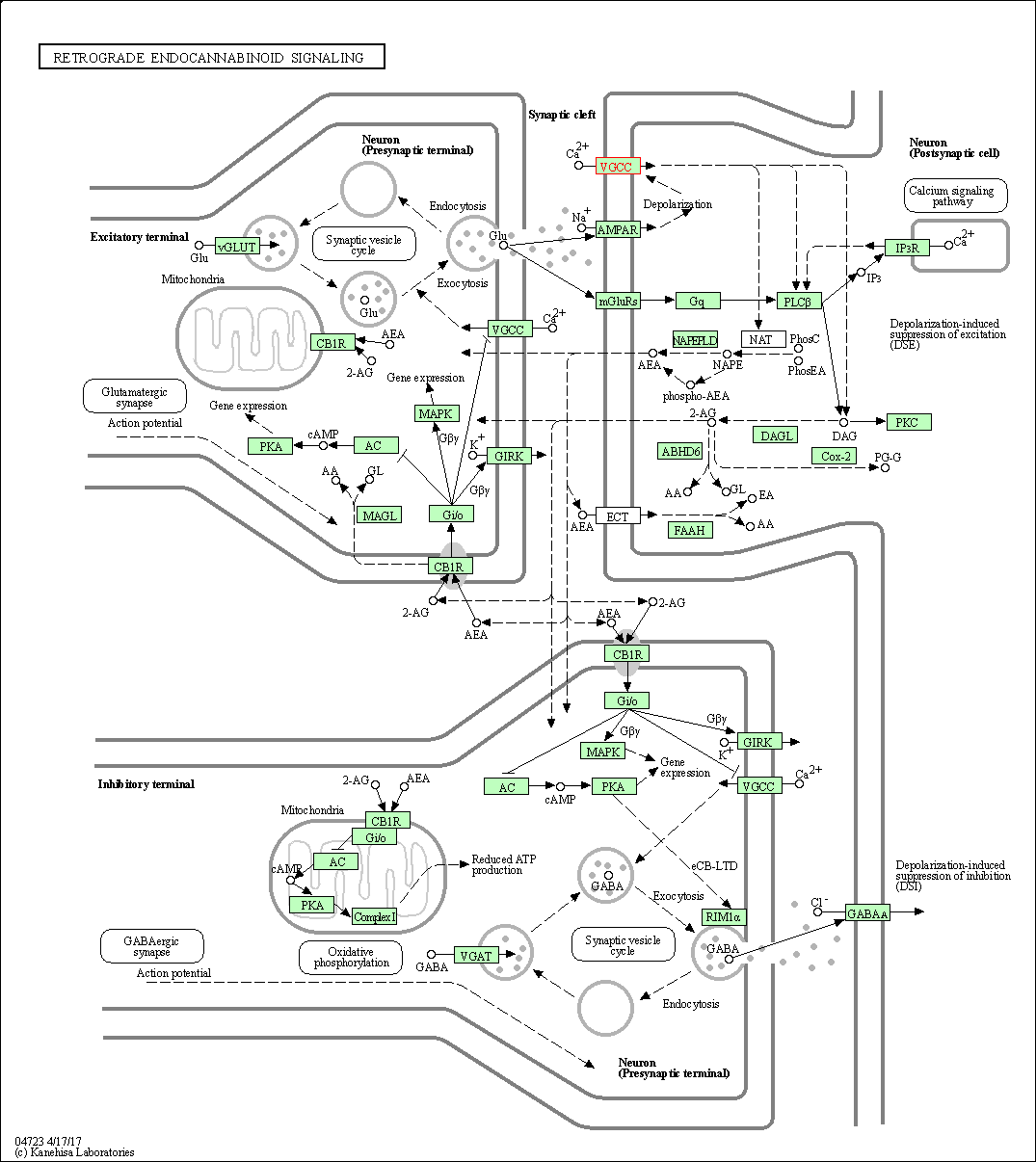
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GABAergic synapse | hsa04727 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Renin secretion | hsa04924 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cortisol synthesis and secretion | hsa04927 | Affiliated Target |
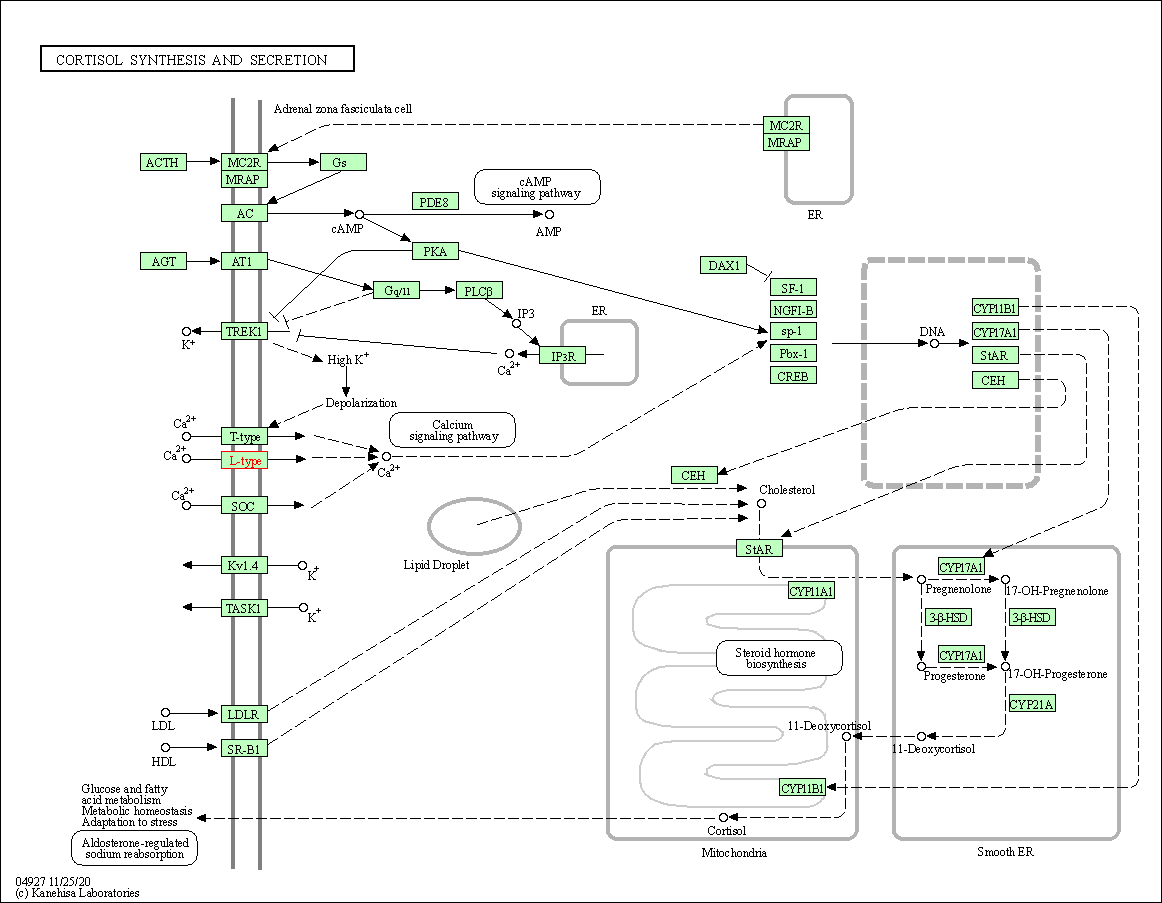
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |
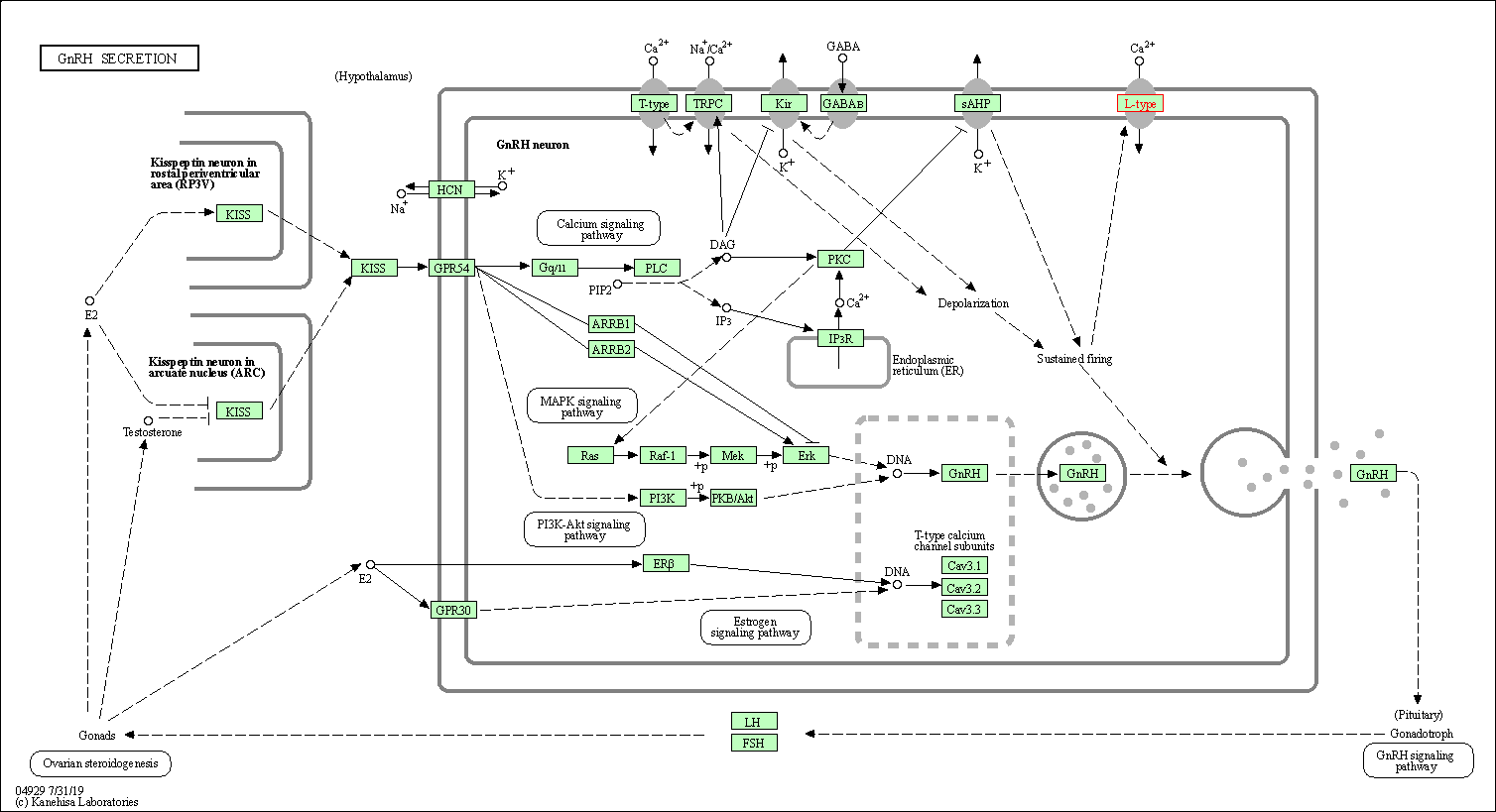
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
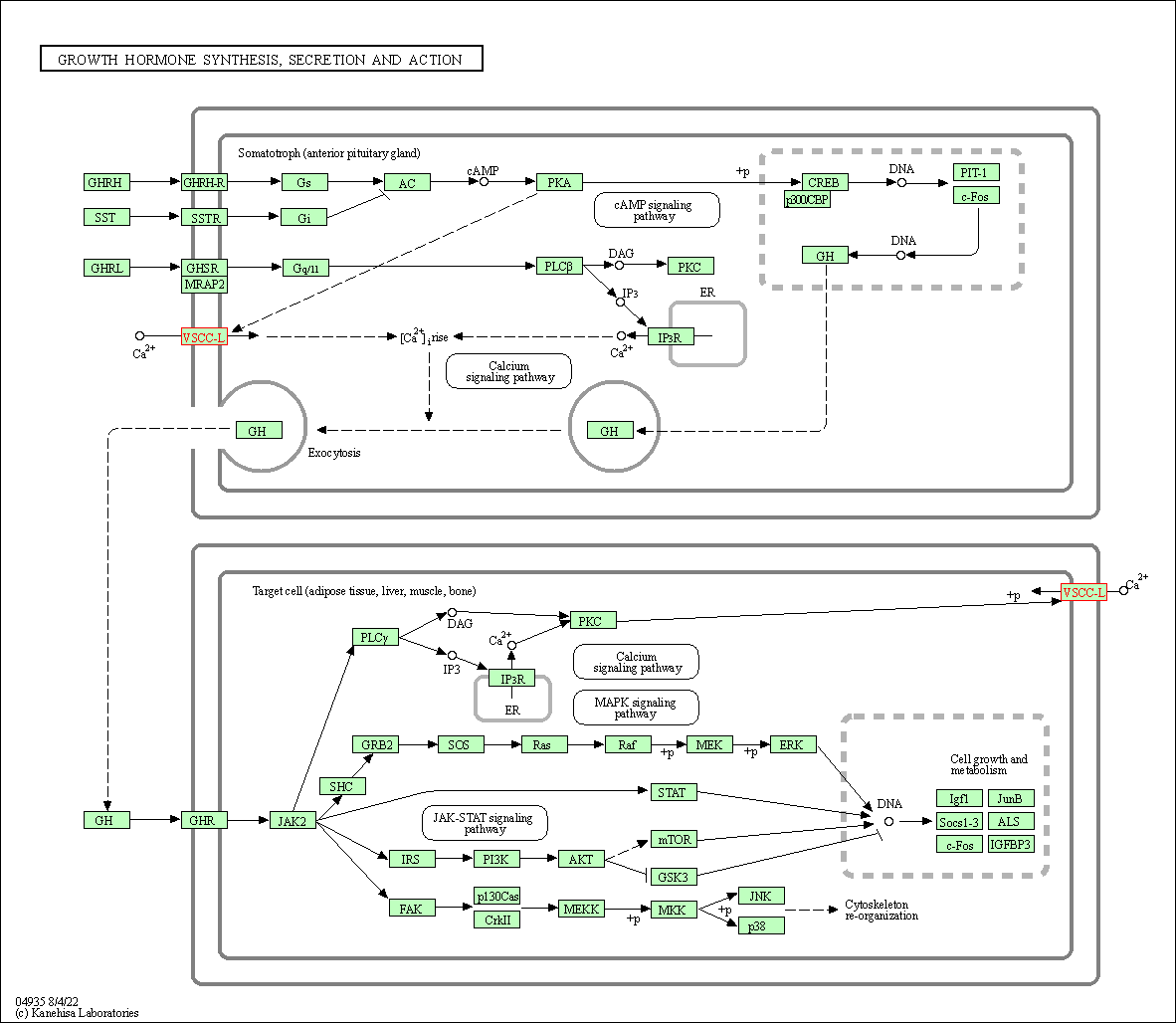
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 8 | Degree centrality | 8.59E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.07E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.67E-01 | Radiality | 1.26E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 5.36E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 8.50E+00 | Topological coefficient | 3.35E-01 | Eccentricity | 14 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Functional characterization of the L-type Ca2+ channel Cav1.4alpha1 from mouse retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Feb;45(2):708-13. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 531). | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

