Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0Q1CD
|
||||
| Former ID |
DCL000243
|
||||
| Drug Name |
Tanomastat
|
||||
| Synonyms |
Tanomastat (USAN/INN); (2S)-4-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)phenyl]-4-oxo-2-(phenylsulfanylmethyl)butanoic acid
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Pancreatic cancer; Lung cancer; Ovarian cancer; Osteoarthritis [ICD9: 140-229, 157, 162, 183, 715; ICD10:C25, C33-C34, C56, M15-M19, M47] | Discontinued in Phase 3 | [1], [2] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
||||
| Company |
Bayer
|
||||
| Structure |
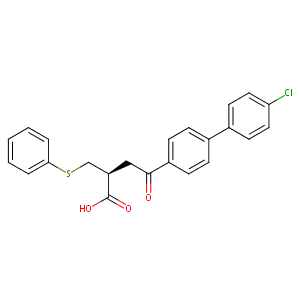
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C23H19ClO3S
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H19ClO3S/c24-20-12-10-17(11-13-20)16-6-8-18(9-7-16)22(25)14-19(23(26)27)15-28-21-4-2-1-3-5-21/h1-13,19H,14-15H2,(H,26,27)/t19-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
JXAGDPXECXQWBC-LJQANCHMSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 179545-77-8
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | 72 kDa type IV collagenase | Target Info | Inhibitor | [3], [4], [5], [6] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Leukocyte transendothelial migration | ||||
| GnRH signaling pathway | |||||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathways in cancer | |||||
| Proteoglycans in cancer | |||||
| Bladder cancer | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | Leptin Signaling Pathway | ||||
| TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| ID Signaling Pathway | |||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Alzheimer disease-presenilin pathway | ||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | LPA receptor mediated events | ||||
| Plasma membrane estrogen receptor signaling | |||||
| Osteopontin-mediated events | |||||
| Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2 | |||||
| Angiopoietin receptor Tie2-mediated signaling | |||||
| Direct p53 effectors | |||||
| amb2 Integrin signaling | |||||
| ATF-2 transcription factor network | |||||
| FOXM1 transcription factor network | |||||
| Regulation of nuclear beta catenin signaling and target gene transcription | |||||
| Syndecan-2-mediated signaling events | |||||
| Reactome | Collagen degradation | ||||
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | |||||
| Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | |||||
| Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) | |||||
| EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells | |||||
| WikiPathways | Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | ||||
| AGE/RAGE pathway | |||||
| Matrix Metalloproteinases | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | (http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/) Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6468). | ||||
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800010243) | ||||
| REF 3 | Tumour microenvironment - opinion: validating matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets and anti-targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006 Mar;6(3):227-39. | ||||
| REF 4 | A phase III randomized trial of BAY 12-9566 (tanomastat) as maintenance therapy in patients with advanced ovarian cancer responsive to primary surgery and paclitaxel/platinum containing chemotherapy:a National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study. Gynecol Oncol. 2006 Aug;102(2):300-8. Epub 2006 Jan 25. | ||||
| REF 5 | Conflicting results from clinical observations and murine models: what is the role of plasminogen activators in tumor growth? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Jun 7;98(11):726-7. | ||||
| REF 6 | Radiation therapy and biological compounds for consolidation therapy in advanced ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2008 Mar-Apr;18 Suppl 1:44-6. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

