Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D05WZF
|
||||
| Former ID |
DNC005106
|
||||
| Drug Name |
P2,P3 Ketoamide derivative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Discovery agent | Investigative | [1] | ||
| Structure |
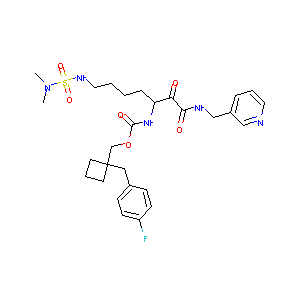
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C28H38FN5O6S
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)S(=O)(=O)NCCCCC(C(=O)C(=O)NCC1=CN=CC=C1)NC(=O)OCC2<br />(CCC2)CC3=CC=C(C=C3)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C28H38FN5O6S/c1-34(2)41(38,39)32-16-4-3-8-24(25(35)26(36)31-19-22-7-5-15-30-18-22)33-27(37)40-20-28(13-6-14-28)17-21-9-11-23(29)12-10-21/h5,7,9-12,15,18,24,32H,3-4,6,8,13-14,16-17,19-20H2,1-2H3,(H,31,36)(H,33,37)/t24-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
AAYZJXOZLLKNGZ-DEOSSOPVSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Cathepsin K | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | |
| Cathepsin S | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | ||
| KEGG Pathway | Lysosome | ||||
| Osteoclast differentiation | |||||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| Rheumatoid arthritishsa04142:Lysosome | |||||
| Phagosome | |||||
| Antigen processing and presentation | |||||
| Tuberculosis | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | ||||
| RANKL Signaling Pathway | |||||
| IL2 Signaling PathwayNetPath_22:Leptin Signaling Pathway | |||||
| IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Reactome | Collagen degradation | ||||
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | |||||
| Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | |||||
| Trafficking and processing of endosomal TLR | |||||
| MHC class II antigen presentationR-HSA-1236977:Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway | |||||
| Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures | |||||
| MHC class II antigen presentation | |||||
| WikiPathways | RANKL/RANK Signaling Pathway | ||||
| Osteoclast SignalingWP2796:Class I MHC mediated antigen processing & presentation | |||||
| Trafficking and processing of endosomal TLR | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Oct 4;14(19):4897-902.Potent and selective P2-P3 ketoamide inhibitors of cathepsin K with good pharmacokinetic properties via favorable P1', P1, and/or P3 substitutions. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

