Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0M1UA
|
||||
| Former ID |
DIB020295
|
||||
| Drug Name |
lysophosphatidylinositol
|
||||
| Synonyms |
LPI; L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Discovery agent | Investigative | [1] | ||
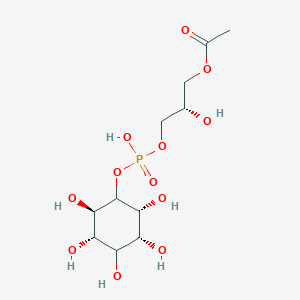
| Structure |
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C11H21O12P
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H21O12P/c1-4(12)21-2-5(13)3-22-24(19,20)23-11-9(17)7(15)6(14)8(16)10(11)18/h5-11,13-18H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/t5-,6-,7-,8+,9+,10+,11-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FBDBXJJQMHPGMP-IFUOQLDVSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor | Target Info | Agonist | [2] | |
| TRPV2 | Target Info | Activator | [3] | ||
| G-protein coupled receptor 55 | Target Info | Agonist | [4] | ||
| KEGG Pathway | cAMP signaling pathway | ||||
| Insulin secretion | |||||
| Reactome | Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | ||||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | Incretin Synthesis, Secretion, and InactivationWP1825:GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| GPCRs, Other | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | (http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/) Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4028). | ||||
| REF 2 | Lysophosphatidylcholine enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion via an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Jan 28;326(4):744-51. | ||||
| REF 3 | Lysophospholipids stimulate prostate cancer cell migration via TRPV2 channel activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Mar;1793(3):528-39. | ||||
| REF 4 | Screening beta-arrestin recruitment for the identification of natural ligands for orphan G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biomol Screen. 2013 Jun;18(5):599-609. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

