Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0Q4XQ
|
||||
| Former ID |
DAP000526
|
||||
| Drug Name |
Ethosuximide
|
||||
| Synonyms |
Aethosuccimidum; Aethosuximide; Asamid; Atysmal; Capitus; Emeside; Ethosuccimid; Ethosuccimide; Ethosuccinimide; Ethosuxide; Ethosuximidum; Ethylmethylsuccimide; Ethymal; Etomal; Etosuccimide; Etosuximid; Etosuximida; Etosuximide; Mesentol; Pemal; Pemalin; Pentinimid; Peptinimid; Petinimid; Petnidan; Piknolepsin; Pyknolepsinum; Ronton; Simatin; Succimal; Succimitin; Suksilep; Suxilep; Suximal; Suxin; Suxinutin; Thetamid; Thilopemal; Zaraondan; Zarodan; Zarondan; Zarontin; Zartalin; Aethosuximide [German]; Desitin Brand of Ethosuximide; Epileo Petit MAL; Etosuccimide [DCIT]; Etosuximida Faes; Faes Brand of Ethosuximide; Fortbenton Brand of Ethosuximide; Jenapharm Brand of Ethosuximide; Katwijk Brand of Ethosuximide; LAB Brand of Ethosuximide; Parke Davis Brand of Ethosuximide; Pfizer Brand of Ethosuximide; United Drug Brand of Ethosuximide; Warner Lambert Brand of Ethosuximide; Wernigerode Brand of Ethosuximide; Cl 366; E 7138; E0746; H 940; PM 671; CN-10395; Ethosuximidum [INN-Latin]; Etosuximida [INN-Spanish]; Faes, Etosuximida; H-490; N-Ethyl methylsuccinimide; PM-671; Simatin(E); Warner-Lambert Brand of Ethosuximide; Zarondan-Saft; Zarontin (TN); C.I. 366; CN-10,395; Piknole.psi.n; Pyknole.psi.num; Alpha-Ethyl-alpha-methylsuccinimide; Alpha-Methyl-alpha-ethylsuccinimide; Ethosuximide (JP15/USP/INN); Ethosuximide [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; Gamma-Methyl-gamma-ethylsuccinimide; Gamma-Methyl-gamma-ethyl-succinimide; Gamma-ethyl-gamma-methyl-succinimide; (+-)-2-Ethyl-2-methylsuccinimide; 2-Ethyl-2-methylsuccinimide; 2-Methyl-2-ethylsuccinimide; 3-Ethyl-3-methyl-2, 5-pyrrolidinedion; 3-Ethyl-3-methyl-2,5-pyrrolidinedione; 3-Ethyl-3-methylpyrrolidine-2,5-dione; 3-Ethyl-3-methylpyrroline-2,5-dione; 3-Ethyl-3-methylsuccinimide; 3-Methyl-3-ethylpyrrolidine-2,5-dione; 3-Methyl-3-ethylsuccinimide
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Epilepsy [ICD10:G40] | Approved | [1], [2] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Analgesics
|
||||
| Company |
Pfizer
|
||||
| Structure |
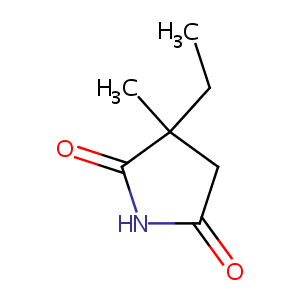
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C7H11NO2
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C7H11NO2/c1-3-7(2)4-5(9)8-6(7)10/h3-4H2,1-2H3,(H,8,9,10)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
HAPOVYFOVVWLRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 77-67-8
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9708, 110249, 221102, 5235097, 7847605, 7979200, 8149853, 8152091, 10321579, 10535639, 11109647, 11335393, 11360632, 11364279, 11366841, 11369403, 11372107, 11374481, 11377565, 11447536, 11461604, 11466193, 11467313, 11485201, 11485686, 11489299, 11490759, 11492865, 11495199, 15219092, 17405095, 24278423, 26612325, 26679258, 26747515, 26747516, 29222429, 46507617, 47365063, 47365064, 47440135, 47885289, 48034988, 48110335, 48334365, 48415978, 49698794, 50048516, 50106318, 50106319
|
||||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N03AD01
|
||||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000077678
|
||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel alpha-1G subunit | Target Info | Blocker | [3], [4], [5] | |
| KEGG Pathway | MAPK signaling pathway | ||||
| Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| Circadian entrainment | |||||
| Type II diabetes mellitus | |||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Endogenous cannabinoid signaling | ||||
| GABA-B receptor II signaling | |||||
| Nicotine pharmacodynamics pathway | |||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Regulation of nuclear beta catenin signaling and target gene transcription | ||||
| PathWhiz Pathway | Muscle/Heart Contraction | ||||
| Reactome | NCAM1 interactions | ||||
| WikiPathways | NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth | ||||
| Nicotine Activity on Chromaffin Cells | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 040253. | ||||
| REF 2 | (http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/) Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7182). | ||||
| REF 3 | Effects of ethosuximide, a T-type Ca(2+) channel blocker, on dorsal horn neuronal responses in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;415(2-3):141-9. | ||||
| REF 4 | Block of cloned human T-type calcium channels by succinimide antiepileptic drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Nov;60(5):1121-32. | ||||
| REF 5 | Maladaptive homeostatic plasticity in a rodent model of central pain syndrome: thalamic hyperexcitability after spinothalamic tract lesions. J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):11959-69. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

