Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D03QAQ
|
||||
| Former ID |
DNC001346
|
||||
| Drug Name |
SN429
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Thrombosis [ICD9: 437.6, 453, 671.5, 671.9; ICD10:I80-I82] | Investigative | [535728] | ||
| Structure |
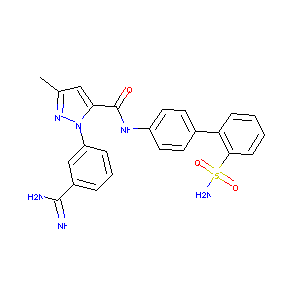
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C24H22N6O3S
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=NN(C(=C1)C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3S(=O)(=O)N)C<br />4=CC=CC(=C4)C(=N)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C24H22N6O3S/c1-15-13-21(30(29-15)19-6-4-5-17(14-19)23(25)26)24(31)28-18-11-9-16(10-12-18)20-7-2-3-8-22(20)34(27,32)33/h2-14H,1H3,(H3,25,26)(H,28,31)(H2,27,32,33)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
APFKCRTWNKCURW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 106243-16-7
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Coagulation factor Xa | Target Info | Inhibitor | [535728] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Complement and coagulation cascades | ||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Blood coagulation | ||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Beta2 integrin cell surface interactions | ||||
| PathWhiz Pathway | Coagulation | ||||
| Reactome | Extrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation | ||||
| Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation | |||||
| Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation | |||||
| Gamma-carboxylation of protein precursors | |||||
| Transport of gamma-carboxylated protein precursors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus | |||||
| Removal of aminoterminal propeptides from gamma-carboxylated proteins | |||||
| References | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

