Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D08XWZ
|
|||
| Former ID |
DIB015418
|
|||
| Drug Name |
ALX-0646
|
|||
| Synonyms |
ALC-2527XX; ALC-900XX; ALC-901XX; ALC-902XX; ALC-905XX; ALC-907XX; ALC-913; ALC-918; ALC-918XX; ALC-947XX; ALC-948XX; ALC-962XX; ALC-963XX; ALC-973XX; ALC-974XX; ALX-2324; ALX-2325; ALX-2326; ALX-2354XX; ALX-2355XX; ALX-2356XX; ALX-2357XX; ALX-2436XX; ALX-2437XX; ALX-2458XX; ALX-2459XX; ALX-2476XX; ALX-2477XX; ALX-2503XX; ALX-2504XX; ALX-2581; ALX-2582; ALX-2592; ALX-646CL; ALX-912
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Migraine [ICD-11: 8A80; ICD-10: G43, G43.9; ICD-9: 346] | Discontinued in Phase 1 | [1] | |
| Company |
NPS Allelix Corp
|
|||
| Structure |
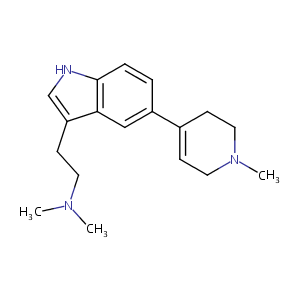 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C18H25N3
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN1CCC(=CC1)C2=CC3=C(C=C2)NC=C3CCN(C)C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C18H25N3/c1-20(2)9-6-16-13-19-18-5-4-15(12-17(16)18)14-7-10-21(3)11-8-14/h4-5,7,12-13,19H,6,8-11H2,1-3H3
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RQTZMTMTBWAQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 208464-67-9
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | 5-HT 1D receptor (HTR1D) | Target Info | Agonist | [2] |
| KEGG Pathway | cAMP signaling pathway | |||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||
| 5HT1 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Serotonin receptors | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | Serotonin HTR1 Group and FOS Pathway | |||
| Monoamine GPCRs | ||||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800008400) | |||
| REF 2 | Sustained pain relief with dihydroergotamine in migraine is potentially due to persistent binding to 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors. . The Journal of Headache and Pain 201314(Suppl 1):P75. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

