Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0A5SE
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP001444
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Febuxostat
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Adenuric; TEI; Uloric; Febuxostat [USAN]; S1547; TMX 67; Tei 6720; TMX-67; Tei-6720; Uloric (TN); Febuxostat (JAN/USAN/INN); TMX-67, Adenuric, Uloric, Febuxostat; 111GE013; 2-(3-CYANO-4-ISOBUTOXY-PHENYL)-4-METHYL-5-THIAZOLE-CARBOXYLIC ACID; 2-(3-Cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl)-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylic acid;2-(3-Cyano-4-isobutoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-5-thiazolecarboxylic acid; 2-[3-cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Hyperuricaemia [ICD-11: 5C55.Y] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Company |
Takeda
|
|||
| Structure |
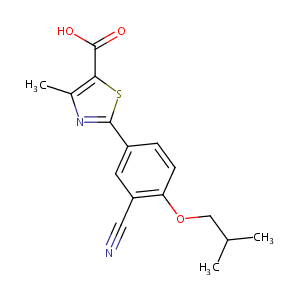 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C16H16N2O3S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(SC(=N1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)OCC(C)C)C#N)C(=O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C16H16N2O3S/c1-9(2)8-21-13-5-4-11(6-12(13)7-17)15-18-10(3)14(22-15)16(19)20/h4-6,9H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,19,20)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
BQSJTQLCZDPROO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 144060-53-7
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
827254, 4484625, 7848269, 7890737, 10243499, 12014717, 14899120, 29311812, 46506708, 50064429, 53197612, 57344764, 92719385, 93307960, 99431926, 103765728, 104142020, 104253203, 104381153, 118047349, 119526879, 121362144, 124757329, 124893781, 125001903, 125164133, 125645402, 126620851, 126652673, 126667078, 127554532, 134338644, 135089359, 135565727, 135692175, 135697551, 135723459, 136367945, 136920430, 137171680, 141631602, 144075735, 144115972, 144206555, 151981114, 152227348, 152258563, 152344198, 160647398, 160813538
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:31596
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00870 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
M04AA03
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -0.642; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697 (log2FC = -0.371; p = 0.023). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859 (log2FC = -0.856; p = 0.011). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.61; p = 0.031). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 (log2FC = -0.412; p = 0.021). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10 (log2FC = -0.678; p = 0.024). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.75; p = 0.015). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731 (log2FC = -0.429; p = 0.035). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.513; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.703; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 (log2FC = -1.128; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.488; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.723; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503 (log2FC = -0.417; p = 0.025). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184 (log2FC = -0.39; p = 0.022). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium ruminantium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Bifidobacterium ruminantium (log2FC = -0.35; p = 0.009). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.611; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Febuxostat can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.618; p = 0.005). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase (XDH) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [2], [4] |
| BioCyc | Purine nucleotides degradation | |||
| Urate biosynthesis/inosine 5'-phosphate degradation | ||||
| Guanosine nucleotides degradation | ||||
| Adenosine nucleotides degradation | ||||
| Retinoate biosynthesis II | ||||
| KEGG Pathway | Purine metabolism | |||
| Caffeine metabolism | ||||
| Drug metabolism - other enzymes | ||||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Peroxisome | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Adenine and hypoxanthine salvage pathway | |||
| Purine metabolism | ||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Caffeine Metabolism | |||
| Purine Metabolism | ||||
| Reactome | Purine catabolism | |||
| WikiPathways | Oxidative Stress | |||
| Effects of Nitric Oxide | ||||
| Metabolism of nucleotides | ||||
| Selenium Micronutrient Network | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6817). | |||
| REF 2 | Hughes B: 2009 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Feb;9(2):89-92. | |||
| REF 3 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 4 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Takeda (2009). | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

