Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0AN7B
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000429
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Melatonin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
73-31-4; Melatonine; N-Acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine; Circadin; 5-Methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; N-[2-(5-Methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]acetamide; N-(2-(5-Methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)acetamide; Melatol; Melovine; Melatonex; N-[2-(5-methoxyindol-3-yl)ethyl]acetamide; Acetamide, N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-; UNII-JL5DK93RCL; N-(2-(5-Methoxyindol-3-yl)ethyl)acetamide; N-acetyl-5-methoxy-tryptamine; NSC 113928; CCRIS 3472; CHEMBL45; EINECS 200-797-7; JL5DK93RCL; Acetamide, N-(2-(5-methoxyindol-3-yl)ethyl)-; BRN 0205542; Circadin; Melapure; Melatonina; Posidorm; Vivitas; Night Rest; Pineal Hormone; Revital Melatonin; Rx Balance; Sleep Right; IN1244; M 5250; M1105; ML1; MT6; TNP00300; M-1200; M-1250; Mela-T; Melatonex, Melatonin; Melatonina (TN); NMR/14327425; Nature'S Harmony; PREVENTION 2 (MELATONIN); PREVENTION 3 (MELATONIN); PREVENTION 4 (MELATONIN); PREVENTION 5 (MELATONIN); PREVENTION 1 (MELATONIN) (PREVENTION 1); Acetamide, {N-[2-(5-methoxyindol-3-yl)ethyl]-}; Acetamide, N-[2-(5-methoxyindol-3-yl)ethyl]-(6CI,8CI); N-[2-(5-Methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)-ethyl]-acetamide; Acetamide, N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-(9CI); Acetamide, {N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-}; Acetamide, N-(2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-(9CI); 4-ACETAMIDO-4'-ISOTHIO-CYANATOSTILBENE-2,2'-DISULFONIC ACID; [3H]melatonin; N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]acetamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Insomnia [ICD-11: 7A00-7A0Z] | Approved | [1], [2], [3] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Central Nervous System Stimulants
|
|||
| Structure |
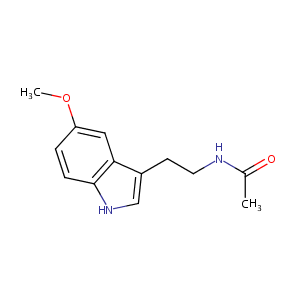 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C13H16N2O2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)NCCC1=CNC2=C1C=C(C=C2)OC
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C13H16N2O2/c1-9(16)14-6-5-10-8-15-13-4-3-11(17-2)7-12(10)13/h3-4,7-8,15H,5-6H2,1-2H3,(H,14,16)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
DRLFMBDRBRZALE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 73-31-4
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
2961, 4752, 105815, 410775, 798411, 841969, 893664, 3133753, 4906256, 7636333, 7961516, 7979886, 8144655, 8149639, 8150851, 10321385, 10534170, 10589869, 11111467, 11111468, 11111469, 11221066, 11335528, 11360767, 11363079, 11365641, 11368203, 11372325, 11373730, 11376365, 11408768, 11461739, 11466486, 11467606, 11485263, 11486211, 11489160, 11491208, 11491881, 11493999, 11536797, 11537588, 14773848, 17388930, 17389536, 17405348, 24278103, 24439254, 26612030, 26679682
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:16796
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01373 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N05CH01
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000073314
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Aeromonadales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Aeromonas
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Aeromonas was increased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Faecalibacterium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Faecalibacterium was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Lachnospiraceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Lachnospiraceae was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Lactobacillales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Streptococcaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Streptococcaceae was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Moraxellales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Moraxellaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Moraxellaceae was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Verrucomicrobiales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Akkermansia
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Akkermansia was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroidetes
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroidetes was increased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Firmicutes
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Firmicutes was increased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Gammaproteobacteria
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Sleep deprived mice | Experimental Sample | Frozen colon content | |
| Disease or Condition | Intestinal barrier dysfunction | |||
| Description | The abundance of Gammaproteobacteria was decreased by Melatonin (p < 0.05). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Melatonin receptor type 1A (MTNR1A) | Target Info | Binder | [5], [6], [7] |
| Quinone reductase 2 (NQO2) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [8] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| Circadian entrainment | ||||
| Reactome | Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||
| Small Ligand GPCRs | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 224). | |||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 3 | Melatonin and melatonergic drugs on sleep: possible mechanisms of action. Int J Neurosci. 2009;119(6):821-46. | |||
| REF 4 | Role of melatonin in sleep deprivation-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in mice. J Pineal Res. 2019 Aug;67(1):e12574. | |||
| REF 5 | The human MT1 melatonin receptor stimulates cAMP production in the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y cells via a calcium-calmodulin signal transduction pathway. J Neuroendocrinol. 2005 Mar;17(3):170-8. | |||
| REF 6 | Coexpression of MT1 and RORalpha1 melatonin receptors in the Syrian hamster Harderian gland. J Pineal Res. 2005 Aug;39(1):21-6. | |||
| REF 7 | Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin mt(1) and MT(2) receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(5):877-86. | |||
| REF 8 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

