Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0CS2F
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000425
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Loperamide
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Ioperamide; Loperacap; Loperamida; Loperamidum; Kaopectate II; Loperamide Monohydrochloride; Pepto Diarrhea Control; Apo-Loperamide; Diamide (TN); Diarr-Eze; Dimor (TN); Imodium (TN); Imodium A-D Caplets; Loperamida [INN-Spanish]; Loperamide (INN); Loperamide [INN:BAN]; Loperamidum [INN-Latin]; Lopex (TN); Maalox Anti-Diarrheal; Nu-Loperamide; PMS-Loperamide; Pepto (TN); R-18553; Rho-Loperamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Diarrhea [ICD-11: ME05.1] | Approved | [1] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antidiarrheals
|
|||
| Company |
Janssen Pharmaceutica
|
|||
| Structure |
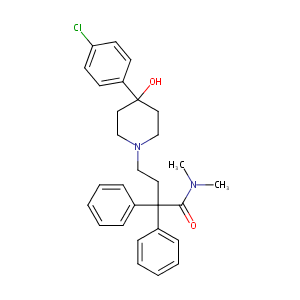 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C29H33ClN2O2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)C(=O)C(CCN1CCC(CC1)(C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)O)(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C29H33ClN2O2/c1-31(2)27(33)29(24-9-5-3-6-10-24,25-11-7-4-8-12-25)19-22-32-20-17-28(34,18-21-32)23-13-15-26(30)16-14-23/h3-16,34H,17-22H2,1-2H3
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RDOIQAHITMMDAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 53179-11-6
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9291, 5686070, 7979790, 8152483, 10590039, 11111380, 11112740, 11113732, 11119963, 11120451, 11120939, 11121446, 11121926, 11147046, 11335390, 11360629, 11362515, 11363268, 11365077, 11365830, 11367639, 11368392, 11370301, 11370302, 11372088, 11373240, 11374823, 11375801, 11376554, 11461601, 11466172, 11467292, 11485552, 11485923, 11489554, 11490830, 11492957, 11494188, 14809921, 26751916, 26751917, 29223069, 46504591, 47216522, 47364910, 47515062, 47515063, 47588737, 47662002, 47662003
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:6532
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01314 ; BADD_D01315 ; BADD_D02428 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
A07DA03
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=053179116
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Alistipes indistinctus DSM22520
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Alistipes indistinctus DSM22520 (log2FC = -0.373; p = 0.022). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides coprophilus DSM 18228
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides coprophilus DSM 18228 (log2FC = -0.467; p = 0.025). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -0.761; p = 0.014). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides eggerthii DSM20697 (log2FC = -0.584; p = 0.009). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.559; p = 0.024). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 (log2FC = -0.551; p = 0.034). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10 (log2FC = -0.436; p = 0.041). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.536; p = 0.02). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183 (log2FC = -0.439; p = 0.024). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.777; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 (log2FC = -0.76; p = 0.024). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.442; p = 0.009). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.651; p = 0.007). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503 (log2FC = -0.613; p = 0.004). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli BW25113
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Escherichia coli BW25113 (log2FC = -0.594; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Providencia rettgeri DSM 1131
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Providencia rettgeri DSM 1131 (log2FC = -0.399; p = 0.007). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Erysipelotrichales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989 (log2FC = -0.478; p = 0.016). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.761; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.731; p = 0.007). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sporogenes ATCC 15579
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Clostridium sporogenes ATCC 15579 (log2FC = -0.447; p = 0.047). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia intestinalis L1-82
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Loperamide can be metabolized by Roseburia intestinalis L1-82 (log2FC = -0.492; p = 0.001). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [3] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | N-oxide reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Loperamide | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity | |||
| Description | Loperamide oxide can be metabolized to Loperamide by gut microbiota through N-oxide reduction, which results in the increase of the drug's activity. | |||
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bacteroides uniformis was decreased by Loperamide hydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 7.38E-03). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium rectale
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Eubacterium rectale was decreased by Loperamide hydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 2.89E-03). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Opioid receptor delta (OPRD1) | Target Info | Binder | [5] |
| KEGG Pathway | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | ||||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||
| Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gq alpha and Go alpha mediated pathway | ||||
| Enkephalin release | ||||
| Opioid proenkephalin pathway | ||||
| Opioid proopiomelanocortin pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Peptide ligand-binding receptors | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||
| Peptide GPCRs | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 2 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 3 | The metabolic effect of gut microbiota on drugs. Drug Metab Rev. 2020 Feb;52(1):139-156. | |||
| REF 4 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 5 | Loperamide: evidence of interaction with mu and delta opioid receptors. Life Sci. 1983;33 Suppl 1:315-8. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

