Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0E0ZS
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC011105
|
|||
| Drug Name |
N-(4'-Isonicotinoylbiphenyl-3-yl)acetamide
|
|||
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL1215730; BDBM50324614
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Discovery agent [ICD-11: N.A.] | Investigative | [1] | |
| Structure |
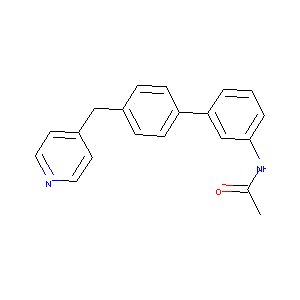 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C20H18N2O
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)NC1=CC=CC(=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CC3=CC=NC=C3
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C20H18N2O/c1-15(23)22-20-4-2-3-19(14-20)18-7-5-16(6-8-18)13-17-9-11-21-12-10-17/h2-12,14H,13H2,1H3,(H,22,23)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
HURKLDLRCGKBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Steroid 11-beta-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] |
| Steroid 17-alpha-monooxygenase (S17AH) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | |
| BioCyc | Superpathway of steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||
| Glucocorticoid biosynthesis | ||||
| Androgen biosynthesis | ||||
| Mineralocorticoid biosynthesis | ||||
| KEGG Pathway | Steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | ||||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | ||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Androgen and Estrogen Metabolism | |||
| Steroidogenesis | ||||
| Reactome | Androgen biosynthesis | |||
| Glucocorticoid biosynthesis | ||||
| Endogenous sterols | ||||
| WikiPathways | Metapathway biotransformation | |||
| Steroid Biosynthesis | ||||
| Oxidation by Cytochrome P450 | ||||
| Metabolism of steroid hormones and vitamin D | ||||
| Glucocorticoid & Mineralcorticoid Metabolism | ||||
| Prostate Cancer | ||||
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | ||||
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Replacement of imidazolyl by pyridyl in biphenylmethylenes results in selective CYP17 and dual CYP17/CYP11B1 inhibitors for the treatment of prosta... J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 12;53(15):5749-58. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

