Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T89041
(Former ID: TTDS00241)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Steroid 17-alpha-monooxygenase (S17AH)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Steroid 17-alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase; P450c17; P450-C17; P450 17; CYPXVII; CYP17A1; CYP 17; 17 alpha-Hydroxylase/C17-20-lyase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CYP17A1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||||
| Function |
Conversion of pregnenolone and progesterone to their 17- alpha-hydroxylated products and subsequently to dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione. Catalyzes both the 17-alpha-hydroxylation and the 17,20-lyase reaction. Involved in sexual development during fetal life and at puberty.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.14.14.19
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MWELVALLLLTLAYLFWPKRRCPGAKYPKSLLSLPLVGSLPFLPRHGHMHNNFFKLQKKY
GPIYSVRMGTKTTVIVGHHQLAKEVLIKKGKDFSGRPQMATLDIASNNRKGIAFADSGAH WQLHRRLAMATFALFKDGDQKLEKIICQEISTLCDMLATHNGQSIDISFPVFVAVTNVIS LICFNTSYKNGDPELNVIQNYNEGIIDNLSKDSLVDLVPWLKIFPNKTLEKLKSHVKIRN DLLNKILENYKEKFRSDSITNMLDTLMQAKMNSDNGNAGPDQDSELLSDNHILTTIGDIF GAGVETTTSVVKWTLAFLLHNPQVKKKLYEEIDQNVGFSRTPTISDRNRLLLLEATIREV LRLRPVAPMLIPHKANVDSSIGEFAVDKGTEVIINLWALHHNEKEWHQPDQFMPERFLNP AGTQLISPSVSYLPFGAGPRSCIGEILARQELFLIMAWLLQRFDLEVPDDGQLPSLEGIP KVVFLIDSFKVKIKVRQAWREAQAEGST Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T05PKX | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ABIRATERONE | Drug Info | Approved | Prostate cancer | [1], [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Abiraterone acetate | Drug Info | Approved | Prostate cancer | [4] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 5 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TAK-700 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Prostate cancer | [5] | |
| 2 | TAVT-45 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Prostate cancer | [6] | |
| 3 | Seviteronel | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Breast cancer | [7] | |
| 4 | CFG920 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Prostate cancer | [8] | |
| 5 | DST-2970 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Prostate cancer | [9] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ABIRATERONE | Drug Info | [1], [3] | |||
| 2 | Abiraterone acetate | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 3 | TAK-700 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 93 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TAVT-45 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 2 | Seviteronel | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 3 | CFG920 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | DST-2970 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 5 | 1-((9H-Fluoren-2-yl)ethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 6 | 1-((9H-Fluoren-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 7 | 1-(1-(4'-Ethylbiphenyl-4-yl)propyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 8 | 1-(1-(4-thiophen-3-yl-phenyl)propyl)-1Himidazole | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 9 | 1-(1-(4-thiophen-3-ylphenyl)ethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 10 | 1-(1-(Biphenyl-4-yl)allyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 11 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-2-methyl-propyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 12 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-2-phenyl-ethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 13 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-3-methyl-butyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 14 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-butyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 15 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-ethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 16 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-pentyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 17 | 1-(1-Biphenyl-4-yl-propyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 18 | 1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 19 | 1-(3,4-difluorobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 20 | 1-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 21 | 1-(3,5-dibromobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 22 | 1-(3,5-dichlorobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 23 | 1-(3,5-difluorobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 24 | 1-(3-(4-chlorophenyl)propyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 25 | 1-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)propyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 26 | 1-(3-phenylpropyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 27 | 1-(4-Bromobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 28 | 1-(4-bromophenethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 29 | 1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 30 | 1-(4-chlorophenethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 31 | 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 32 | 1-(4-iodobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 33 | 1-(4-methyl-benzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 34 | 1-(4-nitrobenzyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 35 | 1-(Bis-biphenyl-4-yl-methyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 36 | 1-Ethyl-5-(imidazol-1-yl-phenyl-methyl)-1H-indole | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 37 | 1-Imidazol-1-ylmethyl-4-nitro-xanthen-9-one | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 38 | 1-Imidazol-1-ylmethylxanthen-9-one | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 39 | 2,3,4,5-Tetrafluoro-6-pentafluorophenylazo-phenol | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 40 | 2,3,5,6-Tetrafluoro-4-pentafluorophenylazo-phenol | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 41 | 2-(1-Imidazol-1-yl-ethyl)-9H-carbazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 42 | 3-(1-Chloro-7-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)-pyridine | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 43 | 3-(1-ethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)-pyridine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 44 | 3-(1-methyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)-pyridine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 45 | 3-(6-Ethoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)-pyridine | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 46 | 3-(6-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)pyridine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 47 | 3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)pyridine | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 48 | 3-fluoro-4'-(1-(pyridin-4-yl)propyl)biphenyl-4-ol | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 49 | 3-Fluoro-4'-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)biphenyl-4-ol | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 50 | 3-[(4'-Hydroxybiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 51 | 3-[4-Fluoro-indan-(1Z)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 52 | 4'-(1-(pyridin-4-yl)propyl)biphenyl-3-ol | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 53 | 4'-(2-methyl-1-(pyridin-4-yl)propyl)biphenyl-3-ol | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 54 | 4'-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)biphenyl-3,4-diamine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 55 | 4'-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)biphenyl-3,4-diol | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 56 | 4'-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)biphenyl-3-amine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 57 | 4'-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)biphenyl-4-amine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 58 | 4'-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)biphenyl-4-carboxamide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 59 | 4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 60 | 4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)phenol | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 61 | 4-((3',4'-Difluorobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl)pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 62 | 4-(4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 63 | 4-(4-(thiophen-2-yl)benzyl)pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 64 | 4-(4-(thiophen-3-yl)benzyl)pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 65 | 4-Bromo-1-imidazol-1-ylmethyl-xanthen-9-one | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 66 | 4-Indan-(1Z)-ylidenemethyl-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 67 | 4-[(3'-Hydroxybiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 68 | 4-[(4'-Hydroxybiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 69 | 4-[1-(4'-Methoxybiphenyl-4-yl)propyl]pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 70 | 4-[4-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)benzyl]pyridine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 71 | 4-[5-Bromo-indan-(1E)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 72 | 4-[5-Bromo-indan-(1Z)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 73 | 4-[5-Chloro-indan-(1E)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 74 | 4-[5-Chloro-indan-(1Z)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 75 | 4-[5-Fluoro-indan-(1E)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 76 | 4-[5-Fluoro-indan-(1Z)-ylidenemethyl]-pyridine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 77 | 5-[4-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)phenyl]-1H-indole | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 78 | 5-[5-Fluoro-indan-(1E)-ylidenemethyl]-pyrimidine | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 79 | 6-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)naphthalen-2-ol | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 80 | 6-(pyridin-3-yl)-2-naphthonitrile | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 81 | 6-Pyridin-3-yl-3,4-dihydroquinoline-2(1H)-thione | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 82 | 6-Pyridin-3-yl-naphthalen-2-ol | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 83 | 6-[4-(Pyridin-4-ylmethyl)phenyl]naphthalen-2-ol | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 84 | 7-(1-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethyl)-9H-fluoren-2-ol | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 85 | ANG-3407 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 86 | ISOCONAZOLE | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 87 | N-(4'-Isonicotinoylbiphenyl-3-yl)acetamide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 88 | N-3-(4-bromophenyl)propyl imidazole | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 89 | Rac-4'-(1-Imidazol-1-yl-propyl)-biphenyl-3,4-diol | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 90 | Rac-4'-(1-Imidazol-1-yl-propyl)-biphenyl-3,5-diol | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 91 | Rac-4'-(1-Imidazol-1-yl-propyl)-biphenyl-3-ol | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 92 | Rac-4'-(1-Imidazol-1-yl-propyl)-biphenyl-4-ol | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 93 | VN/107-1 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Abiraterone | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1 mutant N52Y with inhibitor abiraterone | PDB:6WR1 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.85 Å | Mutation | Yes | [32] |
| PDB Sequence |
KSLLSLPLVG
38 SLPFLPRHGH48 MHNYFFKLQK58 KYGPIYSVRM68 GTKTTVIVGH78 HQLAKEVLIK 88 KGKDFSGRPQ98 MATLDIASNN108 RKGIAFADSG118 AHWQLHRRLA128 MATFALFKKL 142 EKIICQEIST152 LCDMLATHNG162 QSIDISFPVF172 VAVTNVISLI182 CFNTSYKNGD 192 PELNVIQNYN202 EGIIDNLSKD212 SLVDLVPWLK222 IFPNKTLEKL232 KSHVKIRNDL 242 LNKILENYKE252 KFRSDSITNM262 LDTLMQAKMN272 SDSELLSDNH291 ILTTIGDIFG 301 AGVETTTSVV311 KWTLAFLLHN321 PQVKKKLYEE331 IDQNVGFSRT341 PTISDRNRLL 351 LLEATIREVL361 RLRPVAPMLI371 PHKANVDSSI381 GEFAVDKGTE391 VIINLWALHH 401 NEKEWHQPDQ411 FMPERFLNPA421 GTQLISPSVS431 YLPFGAGPRS441 CIGEILARQE 451 LFLIMAWLLQ461 RFDLEVPDDG471 QLPSLEGIPK481 VVFLIDSFKV491 KIKVRQAWRE 501
|
|||||
|
|
ALA105
4.531
ALA113
2.600
PHE114
2.778
ILE198
4.614
TYR201
2.365
ASN202
1.978
GLU203
4.941
ILE205
2.475
ILE206
2.458
LEU209
3.262
ARG239
2.570
GLY297
3.134
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Pregnenolone | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1 mutant A105L with substrate pregnenolone | PDB:4NKW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.50 Å | Mutation | Yes | [33] |
| PDB Sequence |
LLSLPLVGSL
40 PFLPRHGHMH50 NNFFKLQKKY60 GPIYSVRMGT70 KTTVIVGHHQ80 LAKEVLIKKG 90 KDFSGRPQMA100 TLDILSNNRK110 GIAFADSGAH120 WQLHRRLAMA130 TFALFKDGDQ 140 KLEKIICQEI150 STLCDMLATH160 NGQSIDISFP170 VFVAVTNVIS180 LICFNTSYKN 190 GDPELNVIQN200 YNEGIIDNLS210 KDSLVDLVPW220 LKIFPNKTLE230 KLKSHVKIRN 240 DLLNKILENY250 KEKFRSDSIT260 NMLDTLMQAK270 MNSDSELLSD289 NHILTTIGDI 299 FGAGVETTTS309 VVKWTLAFLL319 HNPQVKKKLY329 EEIDQNVGFS339 RTPTISDRNR 349 LLLLEATIRE359 VLRLRPVAPM369 LIPHKANVDS379 SIGEFAVDKG389 TEVIINLWAL 399 HHNEKEWHQP409 DQFMPERFLN419 PAGTQLISPS429 VSYLPFGAGP439 RSCIGEILAR 449 QELFLIMAWL459 LQRFDLEVPD469 DGQLPSLEGI479 PKVVFLIDSF489 KVKIKVRQAW 499 REAQ
|
|||||
|
|
LEU105
2.231
ALA113
2.748
PHE114
2.500
TYR201
3.582
ASN202
1.820
ILE205
2.097
ILE206
2.652
LEU209
2.808
LEU214
4.835
ARG239
2.863
GLY297
3.655
ASP298
2.675
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis | hsa00140 | Affiliated Target |
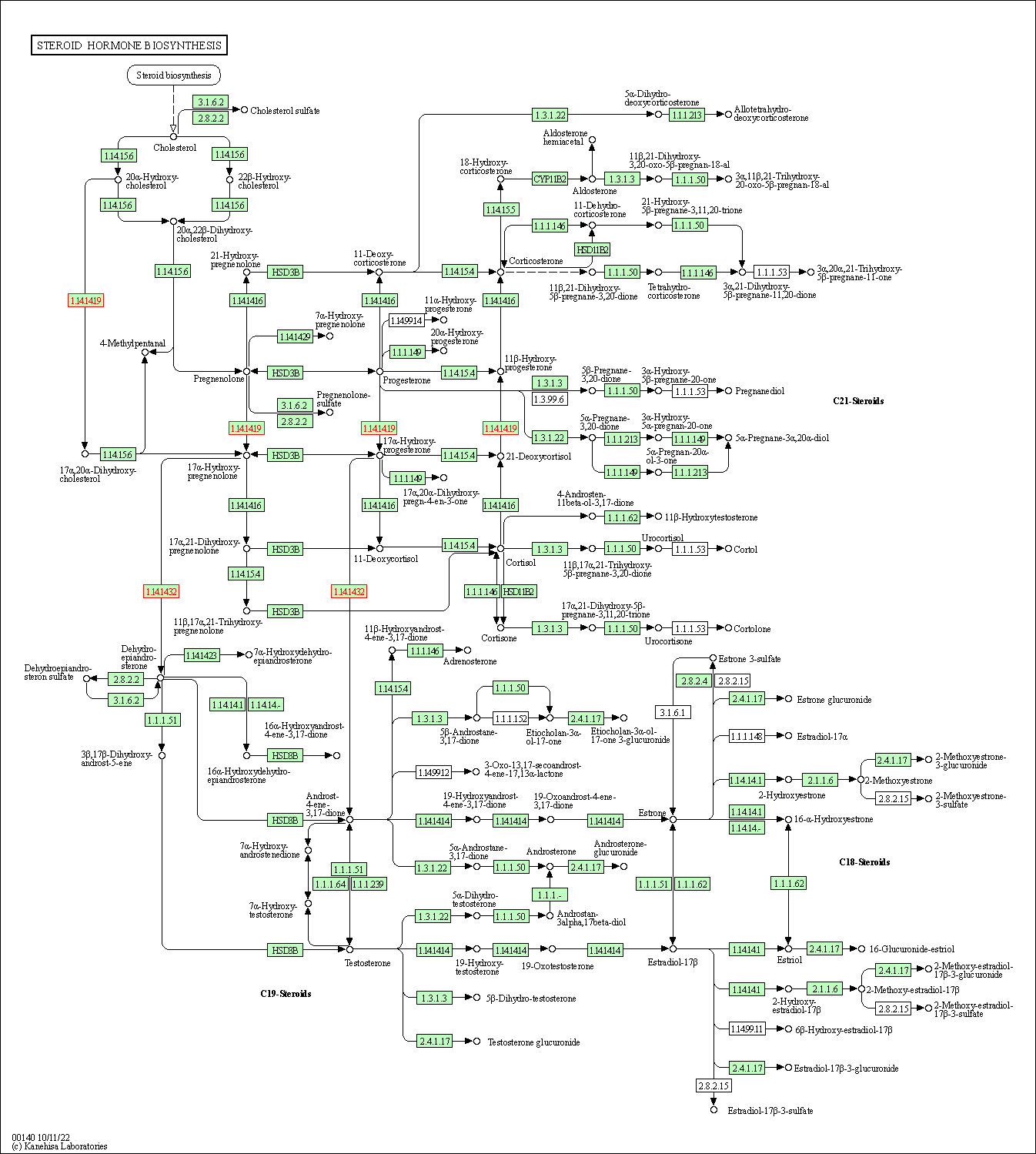
|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | hsa04913 | Affiliated Target |
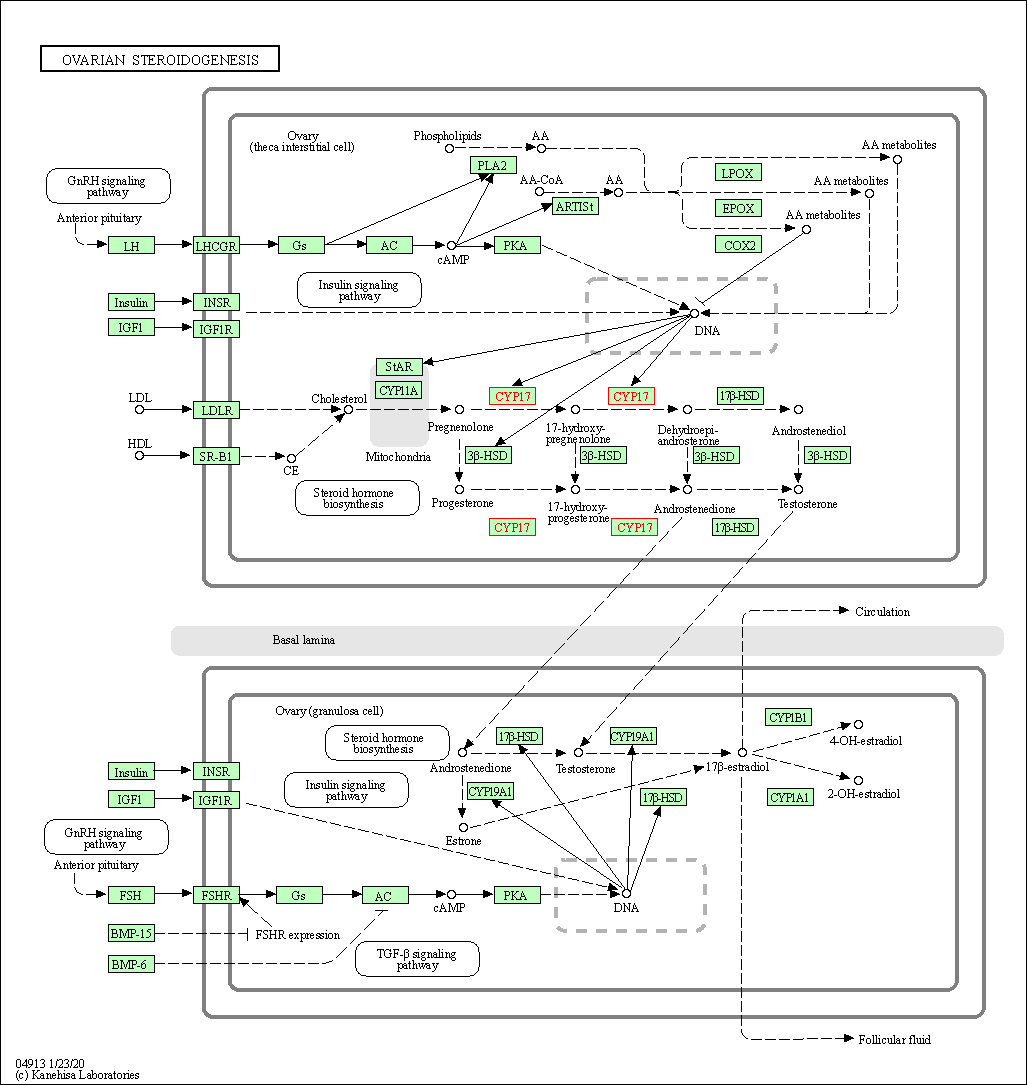
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |
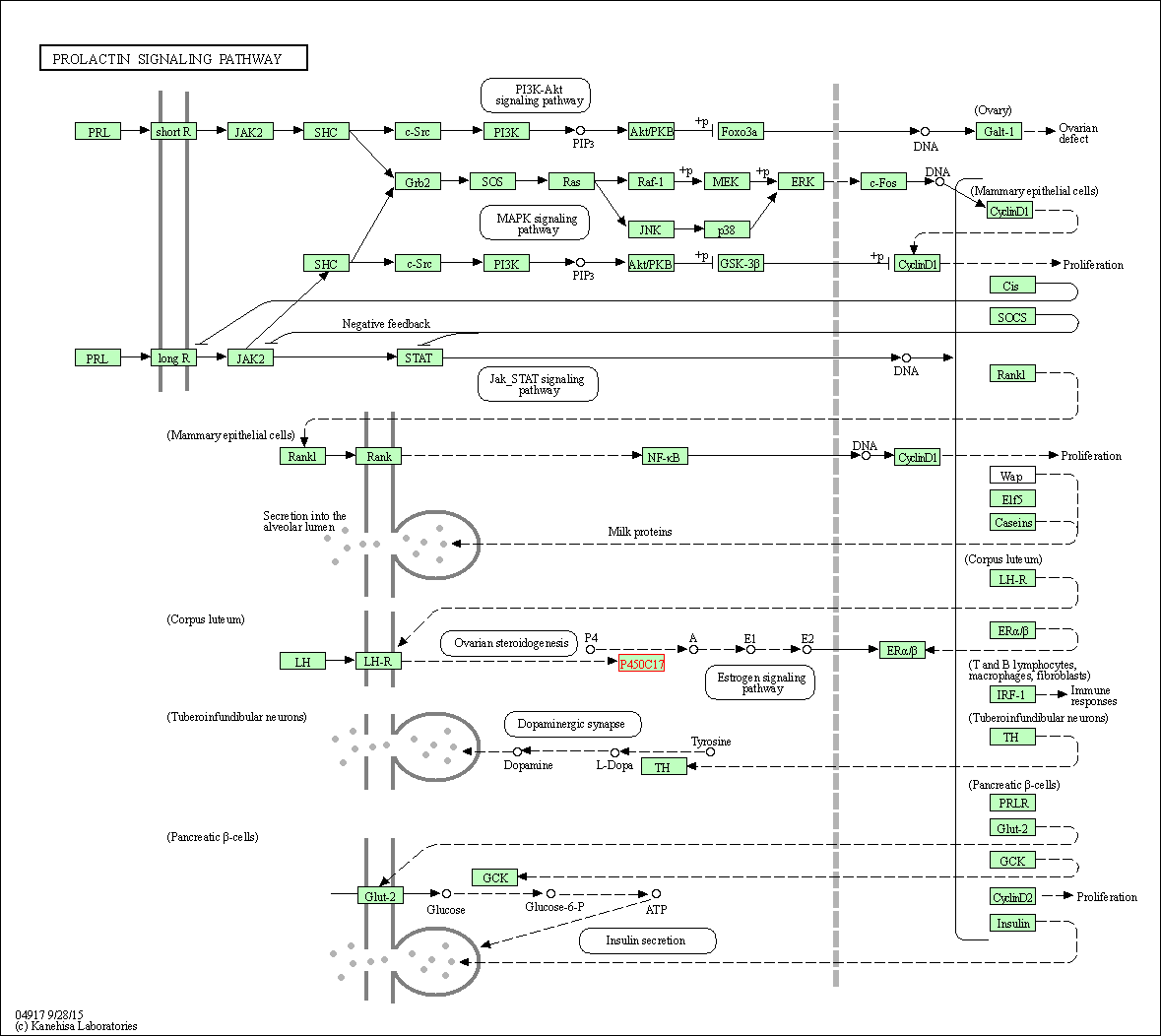
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cortisol synthesis and secretion | hsa04927 | Affiliated Target |
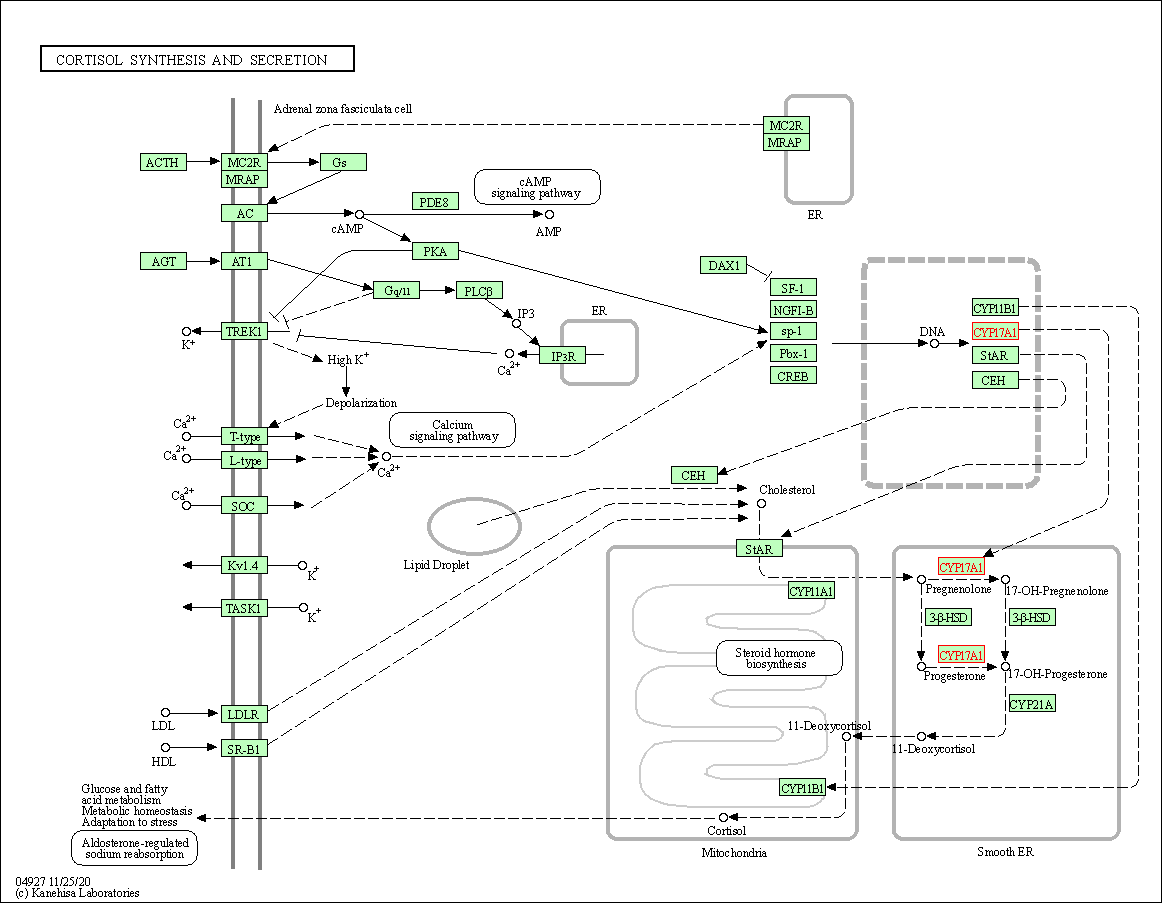
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 15 | Degree centrality | 1.61E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 6.51E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.63E-01 | Radiality | 1.24E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 4.10E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 9.80E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.39E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 3 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Superpathway of steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Glucocorticoid biosynthesis | |||||
| 3 | Androgen biosynthesis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | |||||
| 4 | Prolactin signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 2 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Androgen and Estrogen Metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Steroidogenesis | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Androgen biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Glucocorticoid biosynthesis | |||||
| 3 | Endogenous sterols | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 7 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Metapathway biotransformation | |||||
| 2 | Steroid Biosynthesis | |||||
| 3 | Oxidation by Cytochrome P450 | |||||
| 4 | Metabolism of steroid hormones and vitamin D | |||||
| 5 | Glucocorticoid & Mineralcorticoid Metabolism | |||||
| 6 | Prostate Cancer | |||||
| 7 | Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | 2011 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Feb 1;11(2):91-4. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6745). | |||||
| REF 3 | Selective blockade of androgenic steroid synthesis by novel lyase inhibitors as a therapeutic strategy for treating metastatic prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2005 Dec;96(9):1241-6. | |||||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 5 | Orteronel (TAK-700), a novel non-steroidal 17,20-lyase inhibitor: effects on steroid synthesis in human and monkey adrenal cells and serum steroid levels in cynomolgus monkeys. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Apr;129(3-5):115-28. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04887506) Phase 3 Study Investigating the Efficacy and Safety of TAVT-45 (Abiraterone Acetate) Granules for Oral Suspension (Novel Abiraterone Acetate Formulation) Relative to a Reference Abiraterone Acetate Formulation in Patients With mCSPC & mCRPC. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 8 | Recent progress in pharmaceutical therapies for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 4;14(7):13958-78. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04291664) PK and Dose Escalation and Expansion Study of DST-2970. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | CYP17A1 inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Steroids.2015 Mar;95:80-7. | |||||
| REF 11 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Tavanta Therapeutics | |||||
| REF 12 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of DisperSol Technologies. | |||||
| REF 13 | Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling studies of methylene imidazole substituted biaryls as inhibitors of human 17alpha-hydroxyl... Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Aug 15;16(16):7715-27. | |||||
| REF 14 | Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling studies of methyleneimidazole substituted biaryls as inhibitors of human 17alpha-hydroxyla... Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Feb 15;16(4):1992-2010. | |||||
| REF 15 | Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of a range of potent benzyl imidazole-based compounds as potential inhibitors of the enzyme complex 17alpha-hy... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Aug 1;16(15):4011-5. | |||||
| REF 16 | Synthesis, biochemical evaluation and rationalisation of the inhibitory activity of a range of 4-substituted phenyl alkyl imidazole-based inhibitor... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Sep 15;16(18):4752-6. | |||||
| REF 17 | Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of a range of (4-substituted phenyl)sulfonate derivatives of 4-hydroxybenzyl imidazole-based compounds as pote... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Sep 1;20(17):5345-8. | |||||
| REF 18 | New selective nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors: synthesis and inhibitory activity of 2,3 or 5-(alpha-azolylbenzyl)-1H-indoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Feb 8;9(3):333-6. | |||||
| REF 19 | A new class of nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors: design and synthesis of chromone and xanthone derivatives and inhibition of the P450 enzymes aromatase and 17 alpha-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase. J Med Chem. 2001 Mar 1;44(5):672-80. | |||||
| REF 20 | Novel highly potent and selective nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors: synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationships investigation. J Med Chem. 2010 Jul 22;53(14):5347-51. | |||||
| REF 21 | Hydroxyperfluoroazobenzenes: novel inhibitors of enzymes of androgen biosynthesis. J Med Chem. 1990 Sep;33(9):2452-5. | |||||
| REF 22 | Heteroaryl-substituted naphthalenes and structurally modified derivatives: selective inhibitors of CYP11B2 for the treatment of congestive heart fa... J Med Chem. 2005 Oct 20;48(21):6632-42. | |||||
| REF 23 | Synthesis and evaluation of heteroaryl-substituted dihydronaphthalenes and indenes: potent and selective inhibitors of aldosterone synthase (CYP11B... J Med Chem. 2006 Apr 6;49(7):2222-31. | |||||
| REF 24 | In vivo active aldosterone synthase inhibitors with improved selectivity: lead optimization providing a series of pyridine substituted 3,4-dihydro-... J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 25;51(24):8077-87. | |||||
| REF 25 | Isopropylidene substitution increases activity and selectivity of biphenylmethylene 4-pyridine type CYP17 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2010 Jul 8;53(13):5049-53. | |||||
| REF 26 | Replacement of imidazolyl by pyridyl in biphenylmethylenes results in selective CYP17 and dual CYP17/CYP11B1 inhibitors for the treatment of prosta... J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 12;53(15):5749-58. | |||||
| REF 27 | Synthesis and evaluation of (pyridylmethylene)tetrahydronaphthalenes/-indanes and structurally modified derivatives: potent and selective inhibitor... J Med Chem. 2005 Mar 10;48(5):1563-75. | |||||
| REF 28 | Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling studies of novel ACD- and ABD-ring steroidomimetics as inhibitors of CYP17. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Jan 1;18(1):267-73. | |||||
| REF 29 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1361). | |||||
| REF 30 | Three dimensional pharmacophore modeling of human CYP17 inhibitors. Potential agents for prostate cancer therapy. J Med Chem. 2003 Jun 5;46(12):2345-51. | |||||
| REF 31 | Novel CYP17 inhibitors: synthesis, biological evaluation, structure-activity relationships and modelling of methoxy- and hydroxy-substituted methyl... Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jul;44(7):2765-75. | |||||
| REF 32 | Human Cytochrome P450 17A1 Structures with Metabolites of Prostate Cancer Drug Abiraterone Reveal Substrate-Binding Plasticity and a Second Steroid Binding Site | |||||
| REF 33 | Structures of human steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1 with substrates. J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 21;289(47):32952-64. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

