Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0P5SA
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000375
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Fluphenazine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
FLUPHENAZINE; Triflumethazine; Fluorophenazine; Fluorphenazine; Fluorfenazine; Siqualon; Elinol; 69-23-8; Phthorphenazine; Vespazine; Ftorphenazine; Siqualine; Sevinol; Pacinol; Fluphenazinum; Flufenazina; Prolixin; Flufenazin; Dapotum; Flufenazina [DCIT]; Yespazine; SQ 4918; Fluphenazine [INN:BAN]; Moditen (Tabl or elixir); Fluphenazinum [INN-Latin]; 2-(4-(3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)propyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethanol; 10-(3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazinopropyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine; UNII-S79426A41Z; HSDB 3334; Dapotum; Prolixine; Fluphenazine hydrochloride; Moditen Hcl; Permitil Concentrate; Prolixin Concentrate; S94; Anatensol (TN); Apo-Fluphenazine; Dapotum (TN); Dapotum D (TN); Dapotum Injektion (TN); Decanoate (TN); Deconoate (TN); Enanthate (TN); Fludecate (TN); Flunanthate (TN); Fluphenazine (INN); Hydrochloride, Fluphenazine; Lyogen (TN); Modecate (TN); Moditen (TN); Moditen Enanthate Injection (TN); Omca (TN); Permitil (TN); Prolixin (TN); Sediten (TN); Selecten (TN); Sevinol (TN); Sinqualone (TN); Trancin (TN)
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Psychotic disorder [ICD-11: 6A20-6A25] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antipsychotic Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Bristol-Myers Squibb
|
|||
| Structure |
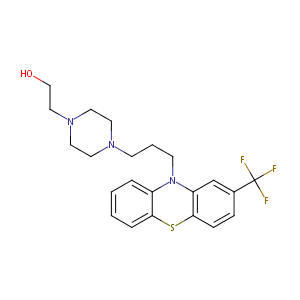 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C22H26F3N3OS
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1CN(CCN1CCCN2C3=CC=CC=C3SC4=C2C=C(C=C4)C(F)(F)F)CCO
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C22H26F3N3OS/c23-22(24,25)17-6-7-21-19(16-17)28(18-4-1-2-5-20(18)30-21)9-3-8-26-10-12-27(13-11-26)14-15-29/h1-2,4-7,16,29H,3,8-15H2
|
|||
| InChIKey |
PLDUPXSUYLZYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 69-23-8
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9223, 606306, 841998, 5329924, 7979286, 8152146, 10532904, 11111179, 11111180, 11212325, 11335686, 11360925, 11363183, 11364798, 11365745, 11367360, 11368307, 11369922, 11372419, 11372962, 11374514, 11375522, 11376469, 11378089, 11461897, 11466348, 11467468, 11485013, 11486275, 11489015, 11491235, 11492643, 11494103, 14832617, 24263032, 26751625, 29222507, 46506645, 47291093, 47291094, 47365145, 47588956, 47588957, 47662238, 47662239, 47736435, 47885368, 48110419, 48259193, 48259194
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:5123
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00935 ; BADD_D00937 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N05AB02
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000069238
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -1.188; p = 0.022). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.767; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 (log2FC = -0.906; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503 (log2FC = -1.37; p = 0.016). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Pretovella copri DSM 18205
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Pretovella copri DSM 18205 (log2FC = -0.809; p = 0.021). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli BW25113
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Escherichia coli BW25113 (log2FC = -1.081; p = 0.015). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Anaerostipes sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Anaerostipes sp. (log2FC = -1.751; p = 0.039). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.555; p = 0.015). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium ventriosum ATCC 27560
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Eubacterium ventriosum ATCC 27560 (log2FC = -3.029; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia intestinalis L1-82
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Fluphenazine can be metabolized by Roseburia intestinalis L1-82 (log2FC = -0.81; p = 0.042). | |||
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Parabacteroides distasonis was decreased by Fluphenazine dihydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 5.57E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Prevotella copri
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Prevotella copri was decreased by Fluphenazine dihydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 1.60E-03). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium rectale
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Eubacterium rectale was decreased by Fluphenazine dihydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 3.10E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia hominis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Roseburia hominis was decreased by Fluphenazine dihydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 2.51E-03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia intestinalis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Roseburia intestinalis was decreased by Fluphenazine dihydrochloride (adjusted p-values: 5.48E-03). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | 5-HT 1B receptor (HTR1B) | Target Info | Modulator | [5] |
| KEGG Pathway | cAMP signaling pathway | |||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||
| 5HT1 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Serotonin receptors | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | Serotonin HTR1 Group and FOS Pathway | |||
| Monoamine GPCRs | ||||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 204). | |||
| REF 2 | The antipsychotic drug, fluphenazine, effectively reverses mechanical allodynia in rat models of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Jan;195(4):559-68. | |||
| REF 3 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 4 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

