Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T03279
(Former ID: TTDI03520)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-3 (RSK3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
pp90RSK2; p90RSK3; p90-RSK 3; S6K-alpha-3; Ribosomal S6 kinase 2; RSK2; RSK-2; MAPKAPK1B; MAPKAPK-1b; MAPKAP kinase 1b; MAPK-activated protein kinase 1b; MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 1b; Insulin-stimulated protein kinase 1; ISPK1; ISPK-1; 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
RPS6KA3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Mature B-cell leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||||
| Function |
In fibroblast, is required for EGF-stimulated phosphorylation of CREB1 and histone H3 at 'Ser-10', which results in the subsequent transcriptional activation of several immediate-early genes. In response to mitogenic stimulation (EGF and PMA), phosphorylates and activates NR4A1/NUR77 and ETV1/ER81 transcription factors and the cofactor CREBBP. Upon insulin-derived signal, acts indirectly on the transcription regulation of several genes by phosphorylating GSK3B at 'Ser-9' and inhibiting its activity. Phosphorylates RPS6 in response to serum or EGF via an mTOR-independent mechanism and promotes translation initiation by facilitating assembly of the preinitiation complex. In response to insulin, phosphorylates EIF4B, enhancing EIF4B affinity for the EIF3 complex and stimulating cap-dependent translation. Is involved in the mTOR nutrient-sensing pathway by directly phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-1798', which potently inhibits TSC2 ability to suppress mTOR signaling, and mediates phosphorylation of RPTOR, which regulates mTORC1 activity and may promote rapamycin-sensitive signaling independently of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mediates cell survival by phosphorylating the pro-apoptotic proteins BAD and DAPK1 and suppressing their pro-apoptotic function. Promotes the survival of hepatic stellate cells by phosphorylating CEBPB in response to the hepatotoxin carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Is involved in cell cycle regulation by phosphorylating the CDK inhibitor CDKN1B, which promotes CDKN1B association with 14-3-3 proteins and prevents its translocation to the nucleus and inhibition of G1 progression. In LPS-stimulated dendritic cells, is involved in TLR4-induced macropinocytosis, and in myeloma cells, acts as effector of FGFR3-mediated transformation signaling, after direct phosphorylation at Tyr-529 by FGFR3. Negatively regulates EGF-induced MAPK1/3 phosphorylation via phosphorylation of SOS1. Phosphorylates SOS1 at 'Ser-1134' and 'Ser-1161' that create YWHAB and YWHAE binding sites and which contribute to the negative regulation of MAPK1/3 phosphorylation. Phosphorylates EPHA2 at 'Ser-897', the RPS6KA-EPHA2 signaling pathway controls cell migration. Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of ERK (MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1) signaling and mediates mitogenic and stress-induced activation of the transcription factors CREB1, ETV1/ER81 and NR4A1/NUR77, regulates translation through RPS6 and EIF4B phosphorylation, and mediates cellular proliferation, survival, and differentiation by modulating mTOR signaling and repressing pro-apoptotic function of BAD and DAPK1.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MPLAQLADPWQKMAVESPSDSAENGQQIMDEPMGEEEINPQTEEVSIKEIAITHHVKEGH
EKADPSQFELLKVLGQGSFGKVFLVKKISGSDARQLYAMKVLKKATLKVRDRVRTKMERD ILVEVNHPFIVKLHYAFQTEGKLYLILDFLRGGDLFTRLSKEVMFTEEDVKFYLAELALA LDHLHSLGIIYRDLKPENILLDEEGHIKLTDFGLSKESIDHEKKAYSFCGTVEYMAPEVV NRRGHTQSADWWSFGVLMFEMLTGTLPFQGKDRKETMTMILKAKLGMPQFLSPEAQSLLR MLFKRNPANRLGAGPDGVEEIKRHSFFSTIDWNKLYRREIHPPFKPATGRPEDTFYFDPE FTAKTPKDSPGIPPSANAHQLFRGFSFVAITSDDESQAMQTVGVHSIVQQLHRNSIQFTD GYEVKEDIGVGSYSVCKRCIHKATNMEFAVKIIDKSKRDPTEEIEILLRYGQHPNIITLK DVYDDGKYVYVVTELMKGGELLDKILRQKFFSEREASAVLFTITKTVEYLHAQGVVHRDL KPSNILYVDESGNPESIRICDFGFAKQLRAENGLLMTPCYTANFVAPEVLKRQGYDAACD IWSLGVLLYTMLTGYTPFANGPDDTPEEILARIGSGKFSLSGGYWNSVSDTAKDLVSKML HVDPHQRLTAALVLRHPWIVHWDQLPQYQLNRQDAPHLVKGAMAATYSALNRNQSPVLEP VGRSTLAQRRGIKKITSTAL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T14DX3 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BI-D1870 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 7 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Indole-based analog 14 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | PMID27410995-Compound-Figure3j | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivative 35 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 4 | BI-D1870 | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 5 | BIX 02565 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 6 | PMID22564207C25b | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 7 | PMID22765894C8h | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | RSK2 N-terminal kinase domain in complex with ORF45 | PDB:7OPO | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.75 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
VSIKEIAITH
54 HVKEGHEKAD64 PSQFELLKVL74 GQGSFGKVFL84 VKKISGSDAR94 QLYAMKVLKK 104 ATLKVRDRDI121 LVEVNHPFIV131 KLHYAFQTEG141 KLYLILDFLR151 GGDLFTRLSK 161 EVMFTEEDVK171 FYLAELALAL181 DHLHSLGIIY191 RDLKPENILL201 DEEGHIKLTD 211 FGLSKESIDH221 EKKAYSFTVE233 YMAPEVVNRR243 GHTQSADWWS253 FGVLMFEMLT 263 GTLPFQGKDR273 KETMTMILKA283 KLGMPQFLSP293 EAQSLLRMLF303 KRNPANRLGA 313 GPDGVEEIKR323 HSFFSTIDWN333 KLYRREIHPP343 FKPAT
|
|||||
|
|
LEU74
3.633
GLY75
3.700
GLN76
3.868
GLY77
3.560
SER78
2.870
PHE79
3.303
GLY80
4.377
VAL82
3.477
ALA98
3.279
LYS100
2.932
VAL131
4.123
LEU147
4.312
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: (2s)-2-Cyano-3-(1h-Indazol-5-Yl)propanamide | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | RSK2 CTD bound to 2-cyano-3-(1H-indazol-5-yl)acrylamide | PDB:4JG6 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
SIVQQLHRNS
415 IQFTDGYEVK425 EDISVCKRCI440 HKATNMEFAV450 KIIDKSKRDP460 TEEIEILLRY 470 GQHPNIITLK480 DVYDDGKYVY490 VVTELMKGGE500 LLDKILRQKF510 FSEREASAVL 520 FTITKTVEYL530 HAQGVVHRDL540 KPSNILYVDE550 SGNPESIRIC560 DFGFAKQLRA 570 ENGLLMTPCY580 TANFVAPEVL590 ERQGYDAACD600 IWSLGVLLYT610 MLTGYTPFAN 620 GPDDTPEEIL630 ARIGSGKFSL640 SGGYWNSVSD650 TAKDLVSKML660 HVDPHQRLTA 670 ALVLRHPWIV680 HWDQLPQYQL690 NRQDAPHLVK700 GAMAATYSAL710 NR |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
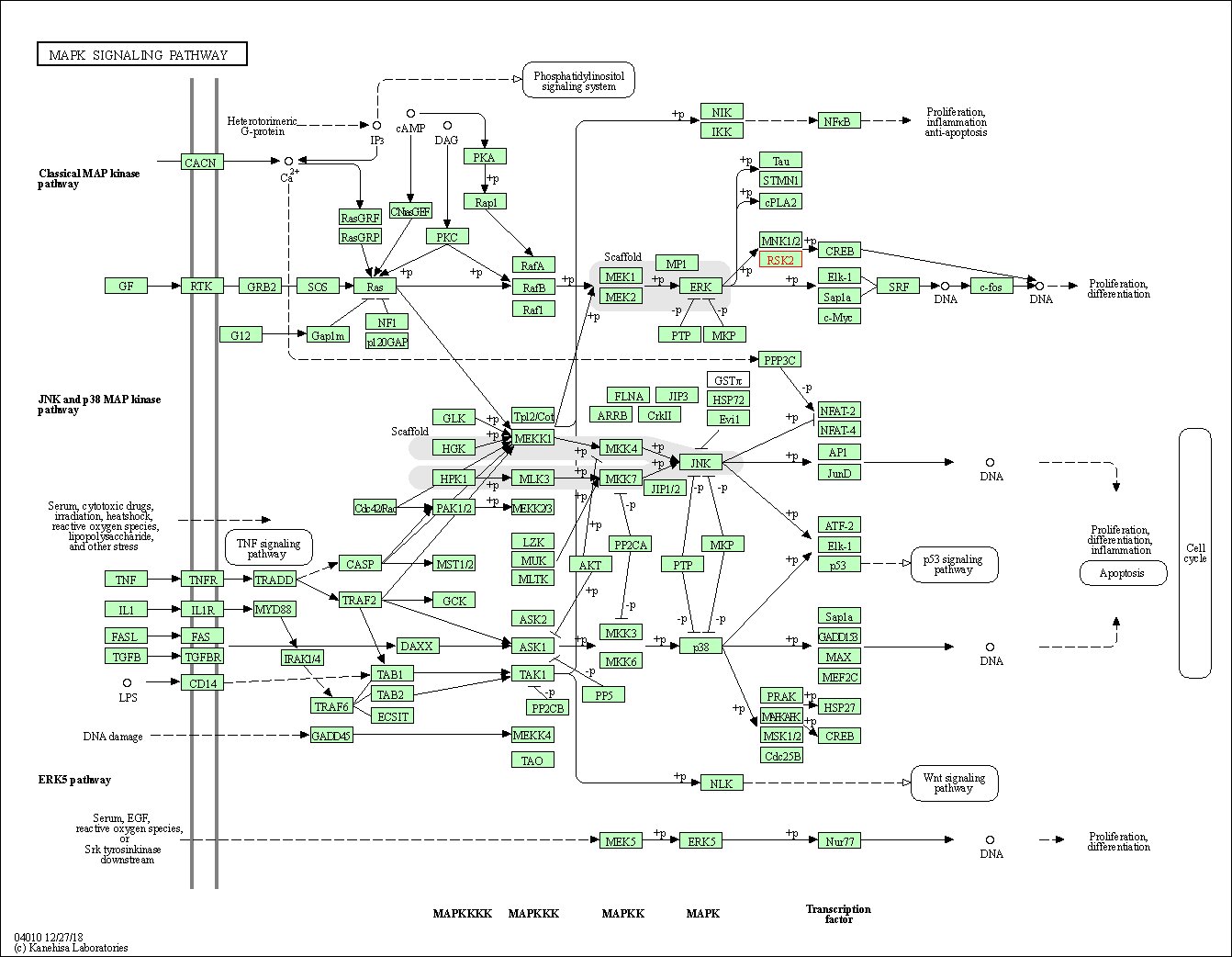
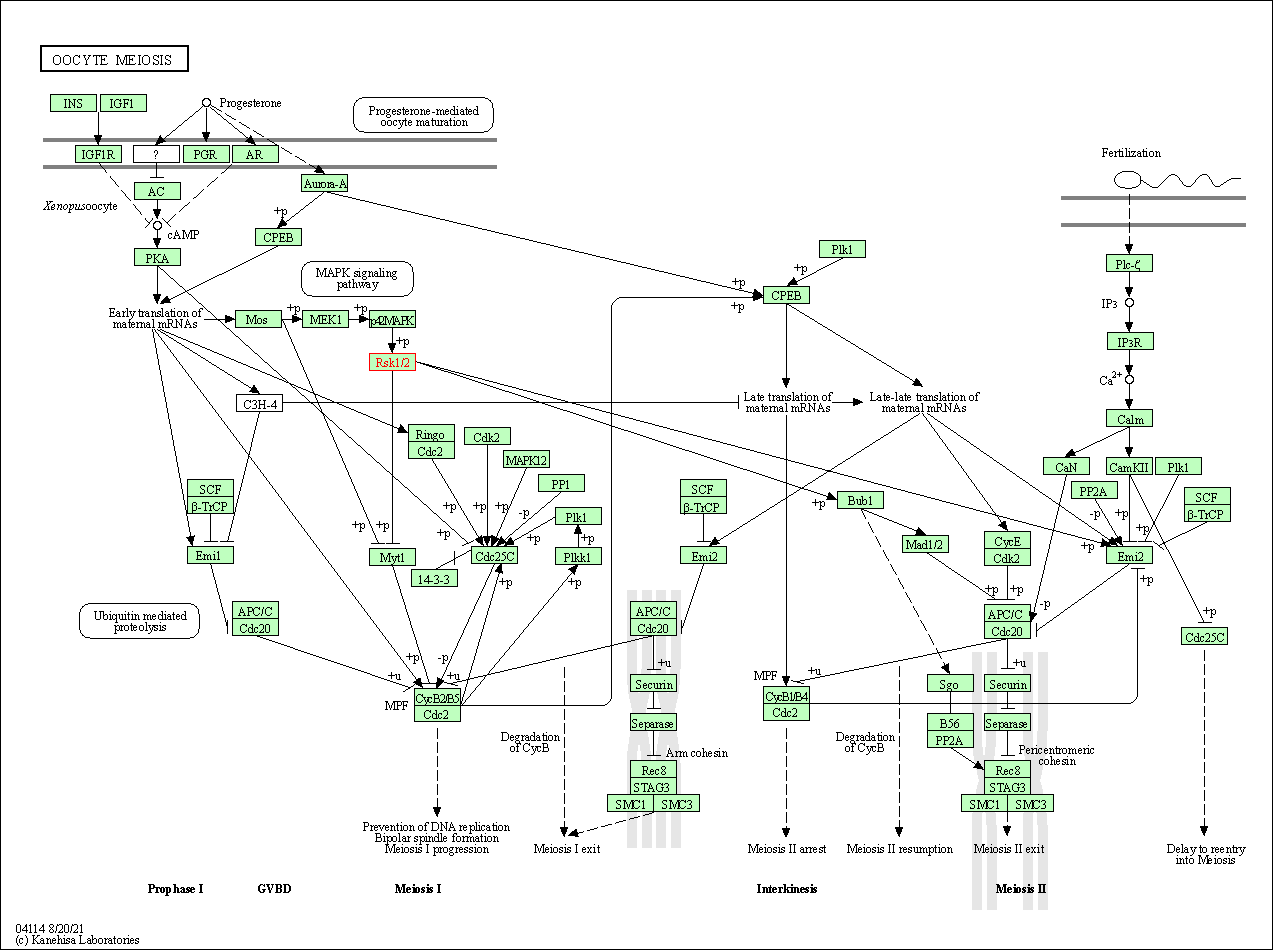
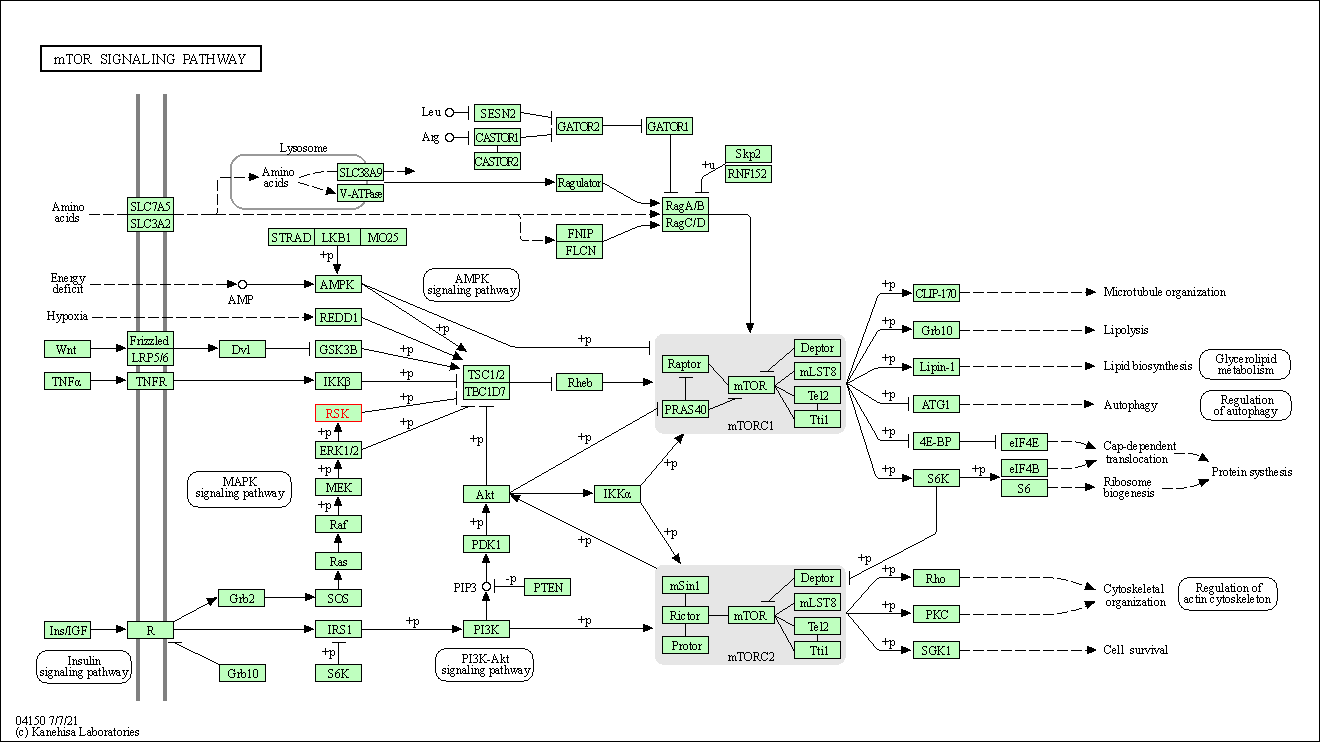
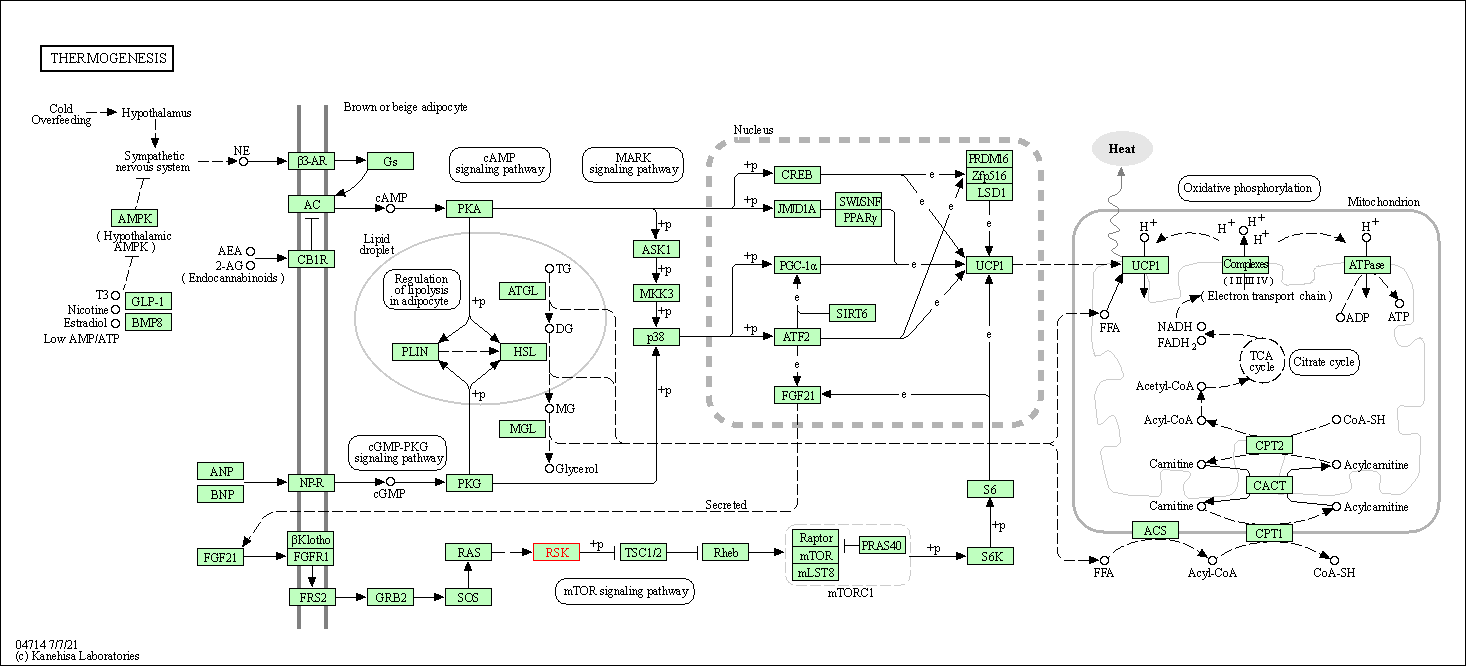
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oocyte meiosis | hsa04114 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 8.22E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.31E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 4.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.60E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.16E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) modulators: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Sep;26(9):1061-78. | |||||
| REF 2 | BI-D1870 is a specific inhibitor of the p90 RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) isoforms in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J. 2007 Jan 1;401(1):29-38. | |||||
| REF 3 | Indole RSK inhibitors. Part 2: optimization of cell potency and kinase selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jan 1;22(1):738-42. | |||||
| REF 4 | Discovery of an orally efficacious inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase. J Med Chem. 2012 May 24;55(10):4580-93. | |||||
| REF 5 | The design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Aug 1;22(15):4979-85. | |||||
| REF 6 | A non-catalytic herpesviral protein reconfigures ERK-RSK signaling by targeting kinase docking systems in the host. Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 25;13(1):472. | |||||
| REF 7 | Electrophilic fragment-based design of reversible covalent kinase inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Apr 10;135(14):5298-301. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

