Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T13726
(Former ID: TTDR01073)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha (RXRA)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Retinoid X receptor alpha; RXRalpha; Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group B member 1; NR2B1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
RXRA
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Kaposi sarcoma [ICD-11: 2B57] | |||||
| 2 | Mycosis fungoides [ICD-11: 2B01] | |||||
| Function |
Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. The high affinity ligand for RXRs is 9-cis retinoic acid. RXRA serves as a common heterodimeric partner for a number of nuclear receptors. In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone acetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression. On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and associate with the coactivators leading to transcriptional activation. The RXRA/PPARA heterodimer is required for PPARA transcriptional activity on fatty acid oxidation genes such as ACOX1 and the P450 system genes. Receptor for retinoic acid.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Nuclear hormone receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MDTKHFLPLDFSTQVNSSLTSPTGRGSMAAPSLHPSLGPGIGSPGQLHSPISTLSSPING
MGPPFSVISSPMGPHSMSVPTTPTLGFSTGSPQLSSPMNPVSSSEDIKPPLGLNGVLKVP AHPSGNMASFTKHICAICGDRSSGKHYGVYSCEGCKGFFKRTVRKDLTYTCRDNKDCLID KRQRNRCQYCRYQKCLAMGMKREAVQEERQRGKDRNENEVESTSSANEDMPVERILEAEL AVEPKTETYVEANMGLNPSSPNDPVTNICQAADKQLFTLVEWAKRIPHFSELPLDDQVIL LRAGWNELLIASFSHRSIAVKDGILLATGLHVHRNSAHSAGVGAIFDRVLTELVSKMRDM QMDKTELGCLRAIVLFNPDSKGLSNPAEVEALREKVYASLEAYCKHKYPEQPGRFAKLLL RLPALRSIGLKCLEHLFFFKLIGDTPIDTFLMEMLEAPHQMT Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A02162 ; BADD_A02367 ; BADD_A02556 ; BADD_A04820 ; BADD_A06050 ; BADD_A06355 ; BADD_A06560 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T45XTW | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Alitretinoin | Drug Info | Approved | Kaposi sarcoma | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Bexarotene | Drug Info | Approved | Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | [4], [5] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 4 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Agonist | [+] 4 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Alitretinoin | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | CD3254 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 3 | methoprene acid | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 4 | phytanic acid | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Bexarotene | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 4 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | (5BETA)-PREGNANE-3,20-DIONE | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 2 | 2-chloro-5-nitro-N-phenylbenzamide | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 3 | AGN-34 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | Tributylstannanyl | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 3 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LG100754 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 2 | PA451 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 3 | UVI3003 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Alitretinoin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | PPARgamma-RXRalpha(S427F) heterodimer in complex with SRC-1, rosiglitazone, and 9-cis-retanoic acid | PDB:5JI0 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.98 Å | Mutation | Yes | [15] |
| PDB Sequence |
NEDMPVERIL
236 EAELAVEPKT246 ETYVENDPVT266 NICQAADKQL276 FTLVEWAKRI286 PHFSELPLDD 296 QVILLRAGWN306 ELLIASFSHR316 SIAVKDGILL326 ATGLHVHRNS336 AHSAGVGAIF 346 DRVLTELVSK356 MRDMQMDKTE366 LGCLRAIVLF376 NPDSKGLSNP386 AEVEALREKV 396 YASLEAYCKH406 KYPEQPGRFA416 KLLLRLPALR426 FIGLKCLEHL436 FFFKLIGDTT 449 FLMEML
|
|||||
|
|
ILE268
3.287
ALA271
4.114
ALA272
4.003
GLN275
2.989
TRP305
3.534
ASN306
4.054
LEU309
3.942
ILE310
4.553
PHE313
3.082
ARG316
2.712
ILE324
4.149
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Tretinoin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | hRXRalpha & mLXRalpha with an indole Pharmacophore, SB786875 | PDB:3FC6 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.06 Å | Mutation | No | [16] |
| PDB Sequence |
SANEDMPVER
234 ILEAELAVDP264 VTNICQAADK274 QLFTLVEWAK284 RIPHFSELPL294 DDQVILLRAG 304 WNELLIASFS314 HRSIAVKDGI324 LLATGLHVHR334 NSAHSAGVGA344 IFDRVLTELV 354 SKMRDMQMDK364 TELGCLRAIV374 LFNPDSKGLS384 NPAEVEALRE394 KVYASLEAYC 404 KHKYPEQPGR414 FAKLLLRLPA424 LRSIGLKCLE434 HLFFFKLDTF450 LMEMLEA |
|||||
|
|
VAL265
4.398
ILE268
3.809
CYS269
4.244
ALA271
3.388
ALA272
3.270
GLN275
3.608
TRP305
3.746
ASN306
4.622
LEU309
4.030
ILE310
4.172
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |
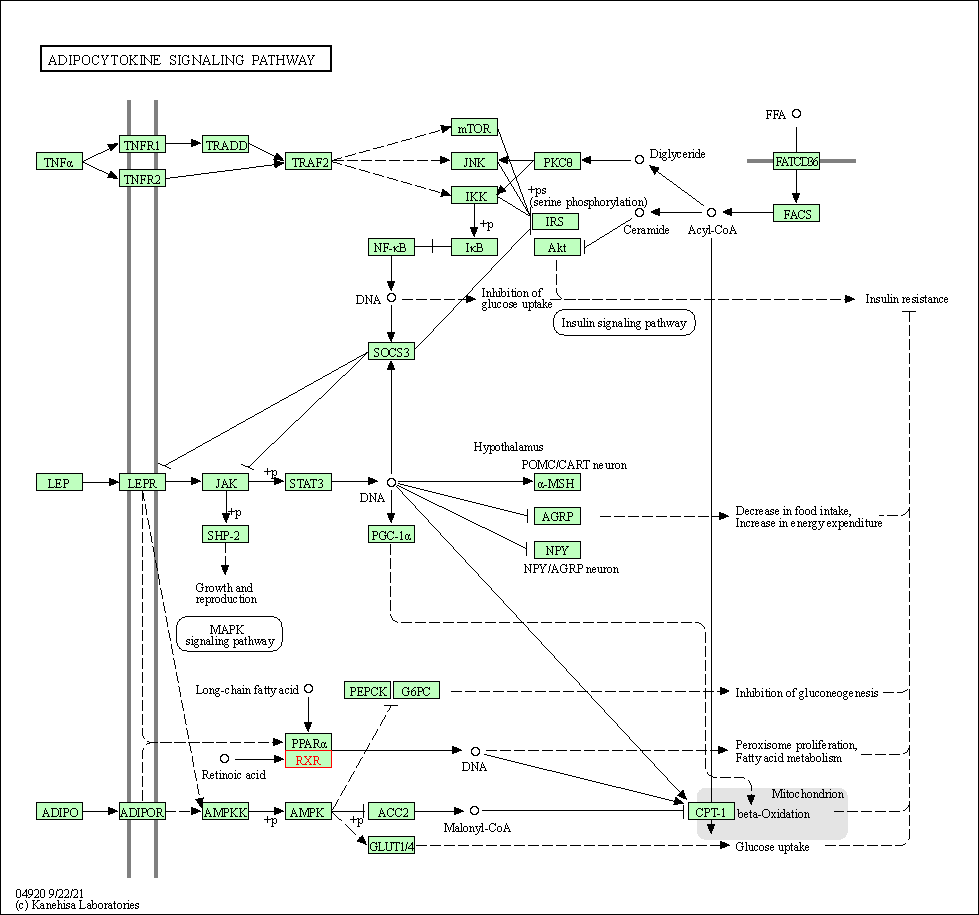
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |
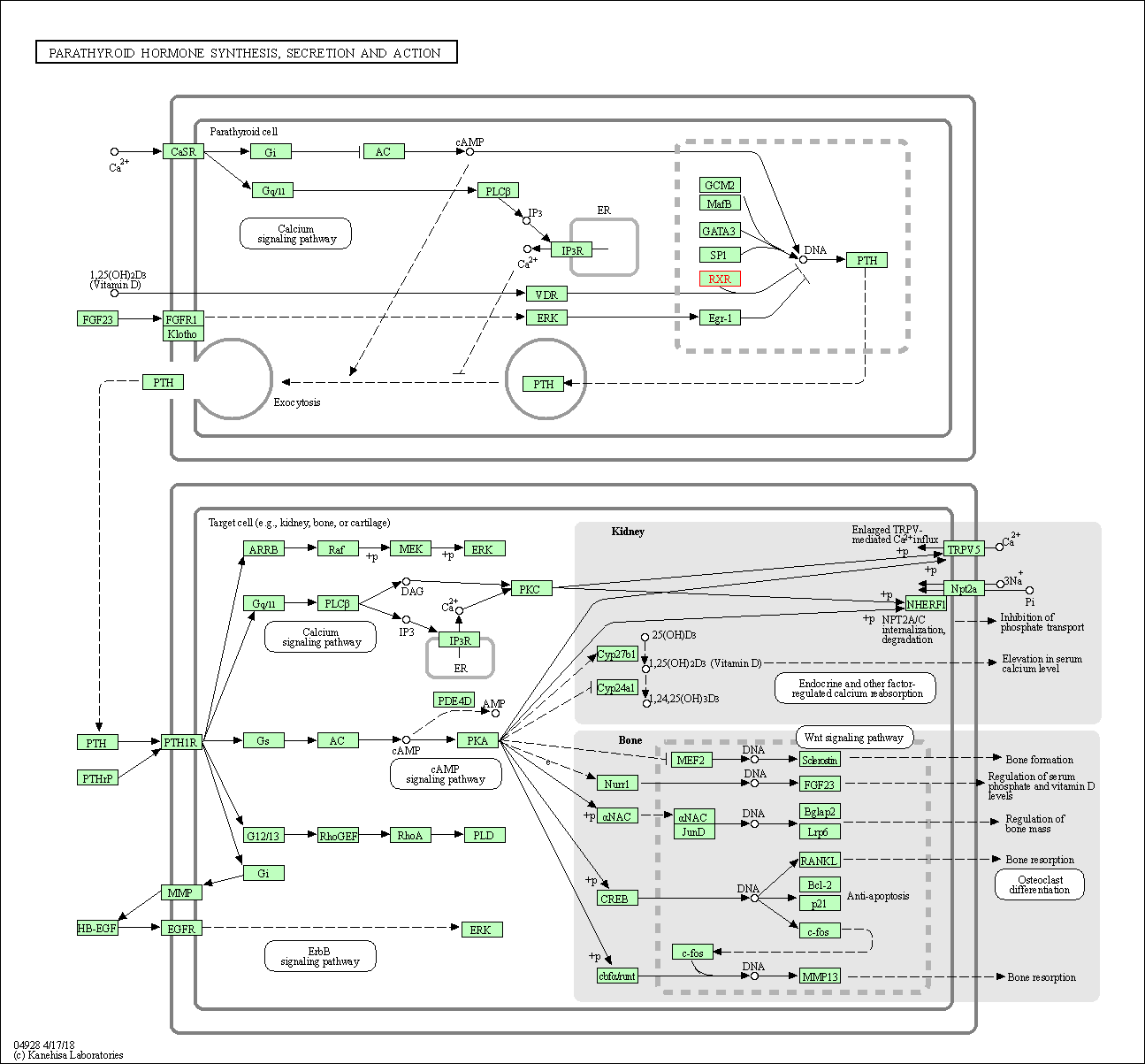
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Bile secretion | hsa04976 | Affiliated Target |
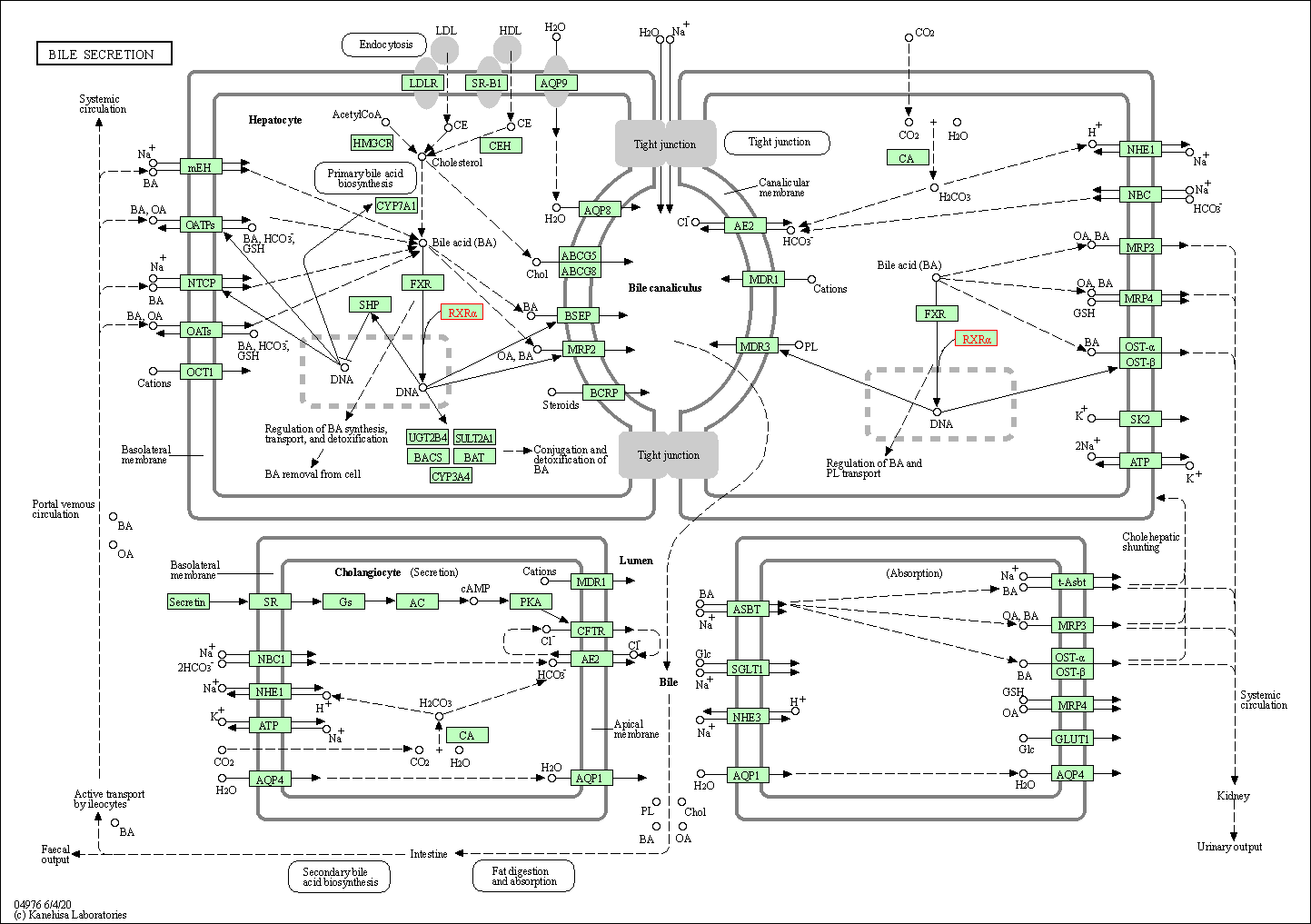
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 31 | Degree centrality | 3.33E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 6.25E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.38E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.22E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.95E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.82E-02 | Eccentricity | 10 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):30-4. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2645). | |||||
| REF 3 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2807). | |||||
| REF 5 | Emerging drugs in cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Jun;13(2):345-61. | |||||
| REF 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 7 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 8 | Farnesoid X receptor: from structure to potential clinical applications. J Med Chem. 2005 Aug 25;48(17):5383-403. | |||||
| REF 9 | Co-regulator recruitment and the mechanism of retinoic acid receptor synergy. Nature. 2002 Jan 10;415(6868):187-92. | |||||
| REF 10 | The rexinoid LG100754 is a novel RXR:PPARgamma agonist and decreases glucose levels in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 2001 Aug;15(8):1360-9. | |||||
| REF 11 | Activation of mammalian retinoid X receptors by the insect growth regulator methoprene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 20;92(13):6157-60. | |||||
| REF 12 | Novel retinoid X receptor antagonists: specific inhibition of retinoid synergism in RXR-RAR heterodimer actions. J Med Chem. 2002 Aug 1;45(16):3327-30. | |||||
| REF 13 | Phytanic acid is a retinoid X receptor ligand. Eur J Biochem. 1996 Feb 15;236(1):328-33. | |||||
| REF 14 | Characterization of the interaction between retinoic acid receptor/retinoid X receptor (RAR/RXR) heterodimers and transcriptional coactivators thro... J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 14;280(2):1625-33. | |||||
| REF 15 | PPARgamma-RXRalpha(S427F) heterodimer in complex with SRC-1, rosiglitazone, and 9-cis-retanoic acid | |||||
| REF 16 | Synthesis and SAR of potent LXR agonists containing an indole pharmacophore. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Feb 15;19(4):1097-100. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

