Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T28025
(Former ID: TTDR00099)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Proto-oncogene c-Fos (c-Fos)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
G0S7; G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7; Cellular oncogene fos; C-fos
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
FOS
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
In the heterodimer, FOS and JUN/AP-1 basic regions each seems to interact with symmetrical DNA half sites. On TGF-beta activation, forms a multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP1/SMAD-binding site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated signaling. Has a critical function in regulating the development of cells destined to form and maintain the skeleton. It is thought to have an important role in signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. In growing cells, activates phospholipid synthesis, possibly by activating CDS1 and PI4K2A. This activity requires Tyr-dephosphorylation and association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Nuclear phosphoprotein which forms a tight but non-covalently linked complex with the JUN/AP-1 transcription factor.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Basic leucine zipper bZIP
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MMFSGFNADYEASSSRCSSASPAGDSLSYYHSPADSFSSMGSPVNAQDFCTDLAVSSANF
IPTVTAISTSPDLQWLVQPALVSSVAPSQTRAPHPFGVPAPSAGAYSRAGVVKTMTGGRA QSIGRRGKVEQLSPEEEEKRRIRRERNKMAAAKCRNRRRELTDTLQAETDQLEDEKSALQ TEIANLLKEKEKLEFILAAHRPACKIPDDLGFPEEMSVASLDLTGGLPEVATPESEEAFT LPLLNDPEPKPSVEPVKSISSMELKTEPFDDFLFPASSRPSGSETARSVPDMDLSGSFYA ADWEPLHSGSLGMGPMATELEPLCTPVVTCTPSCTAYTSSFVFTYPEADSFPSCAAAHRK GSSSNEPSSDSLSSPTLLAL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A00142 ; BADD_A01208 ; BADD_A02521 ; BADD_A03956 ; BADD_A05675 ; BADD_A05962 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T63GUB | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
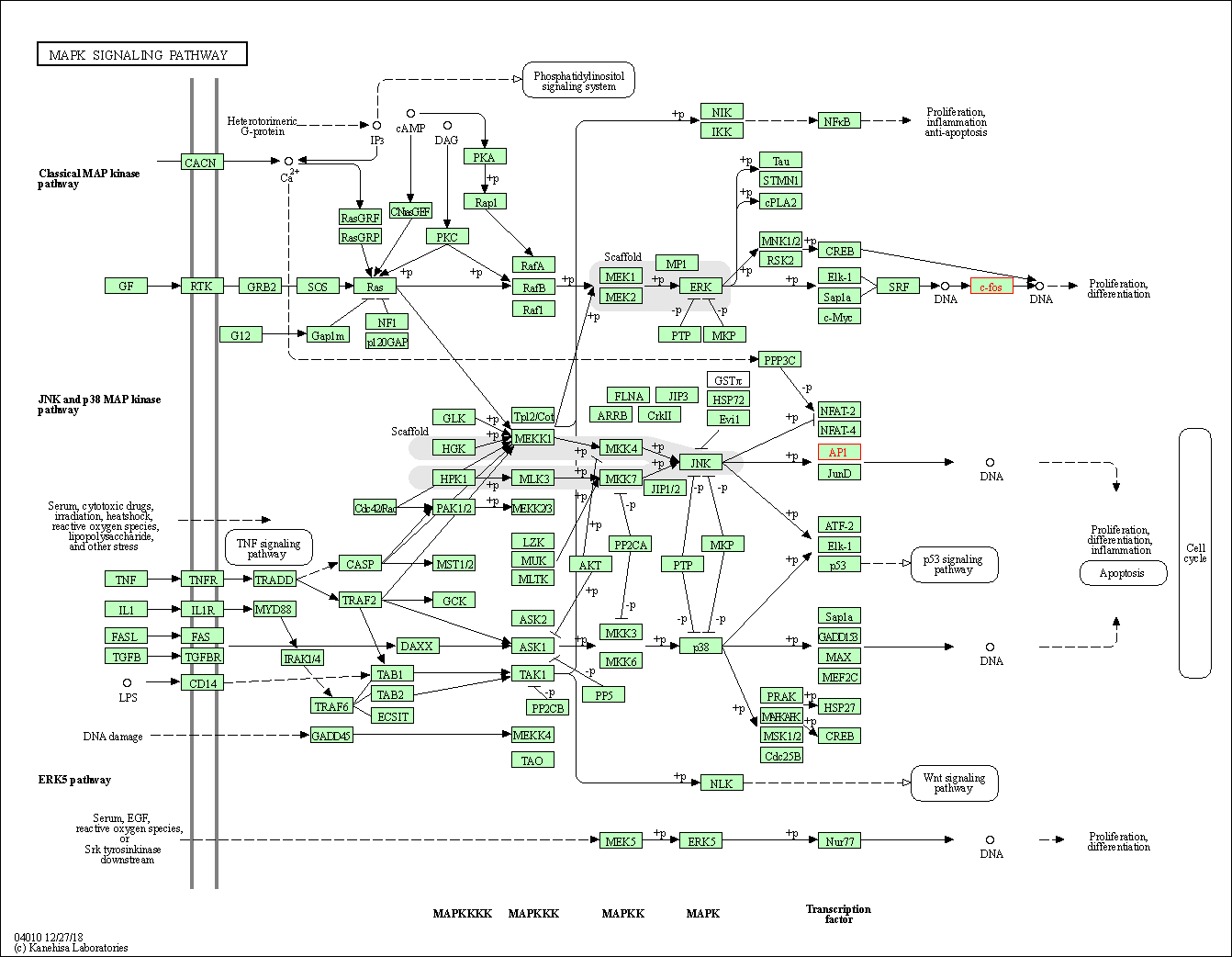
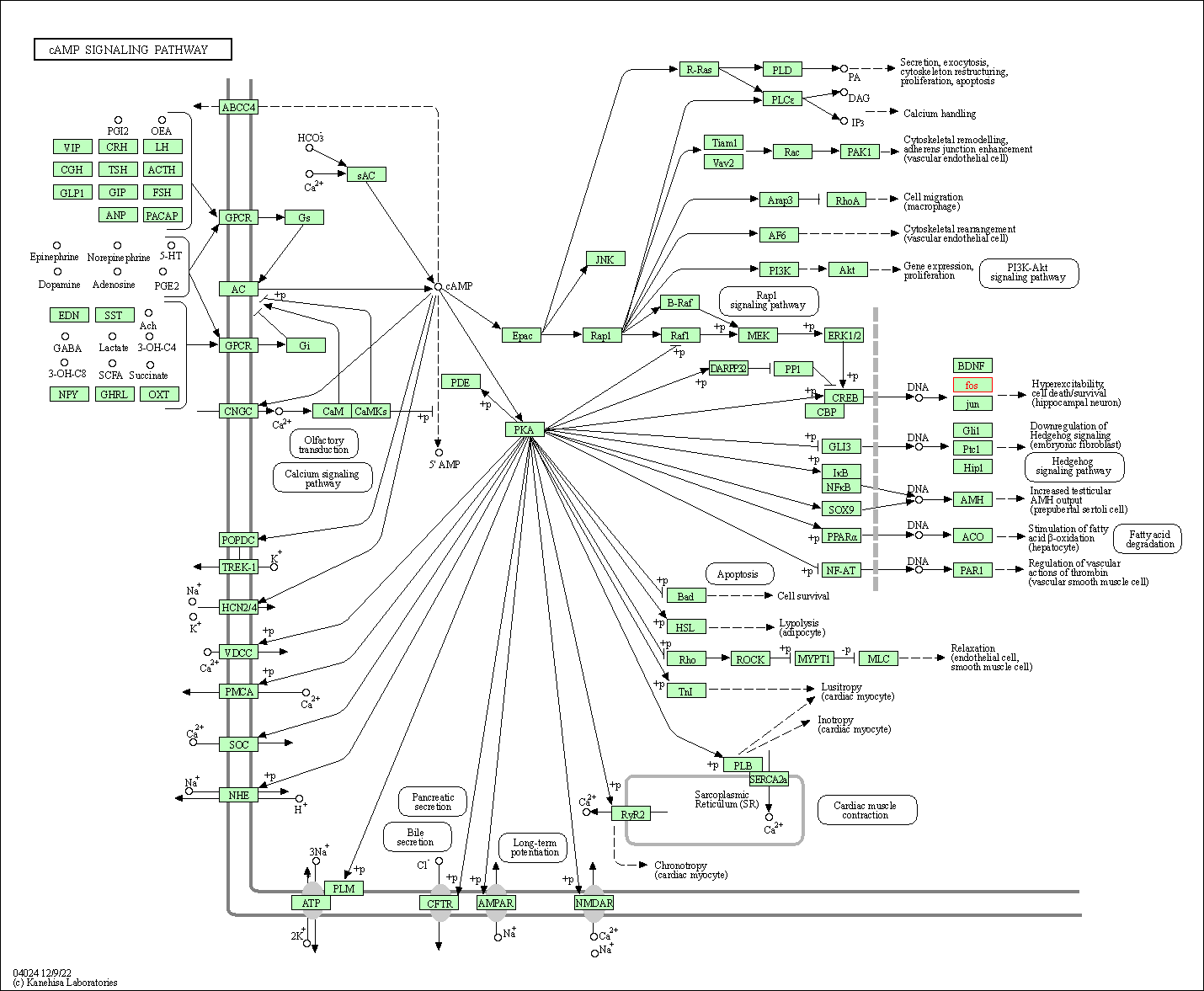
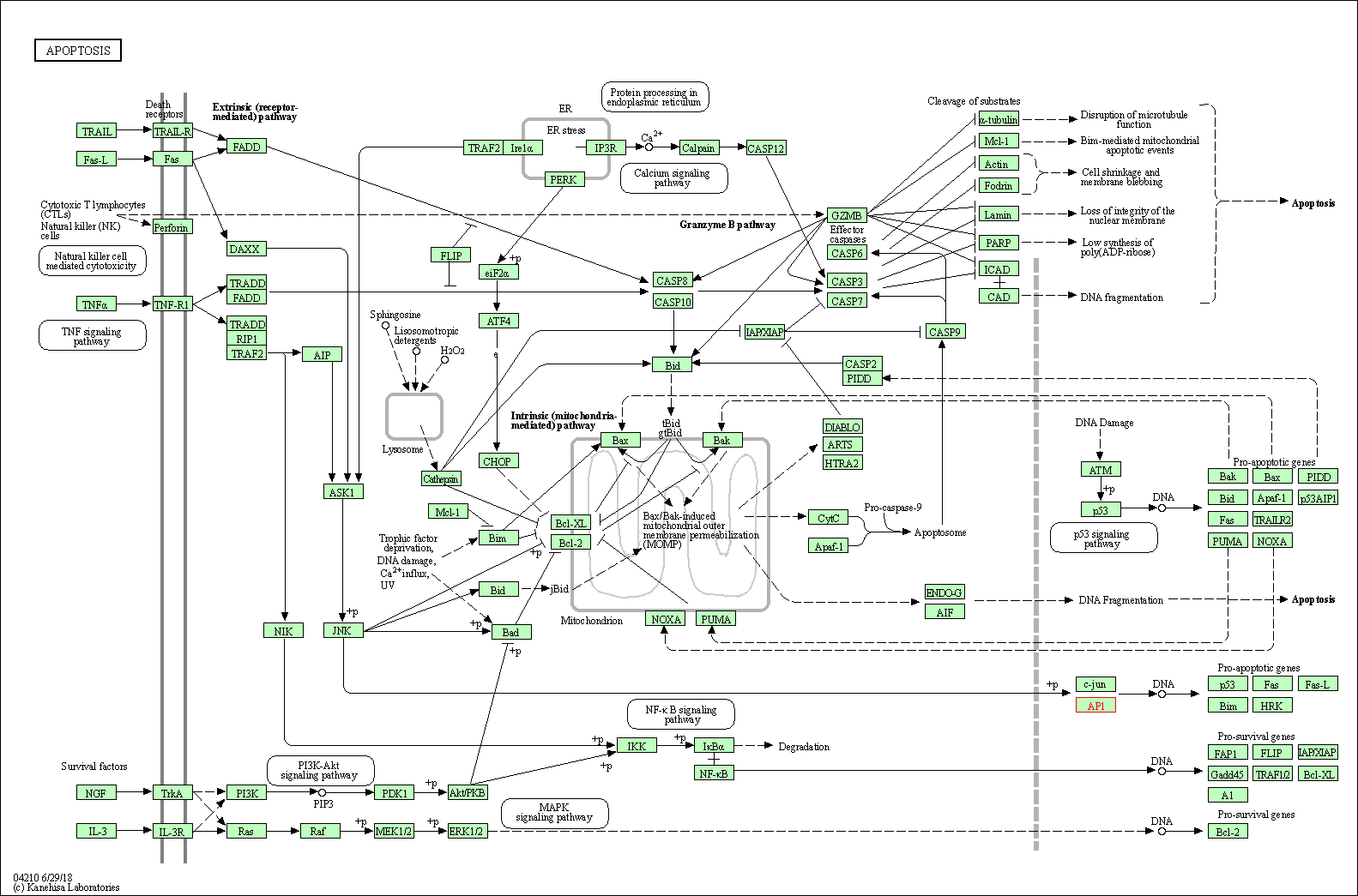
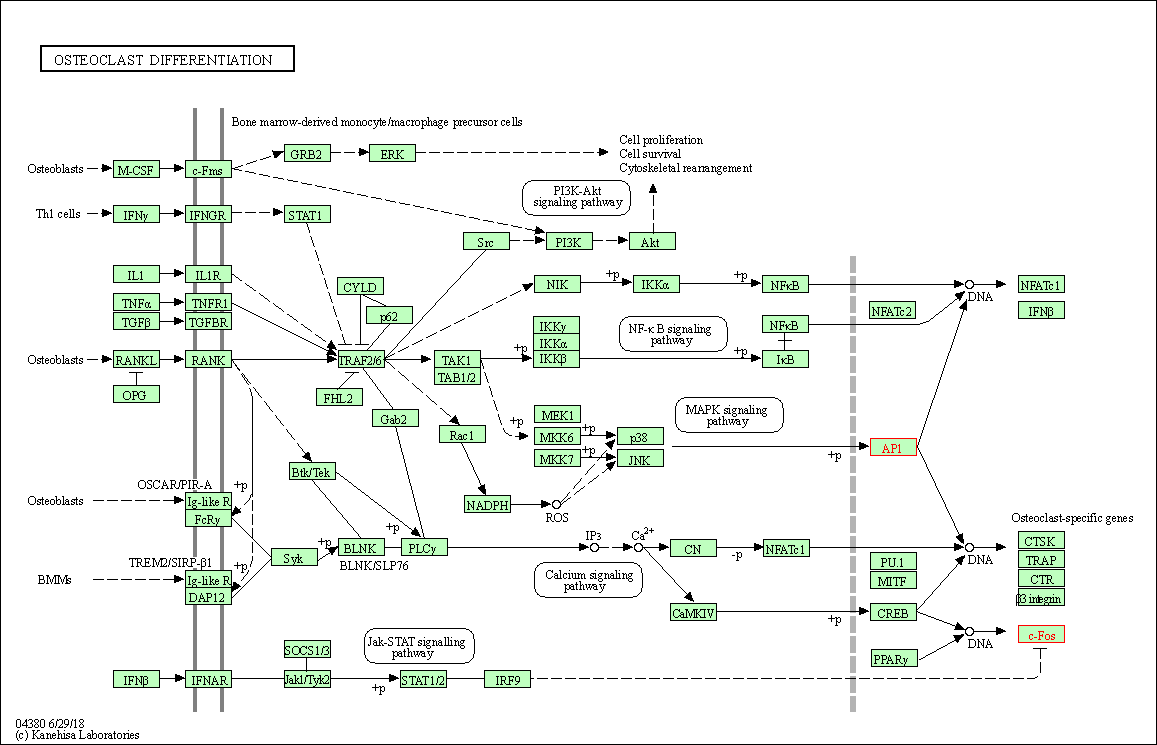

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
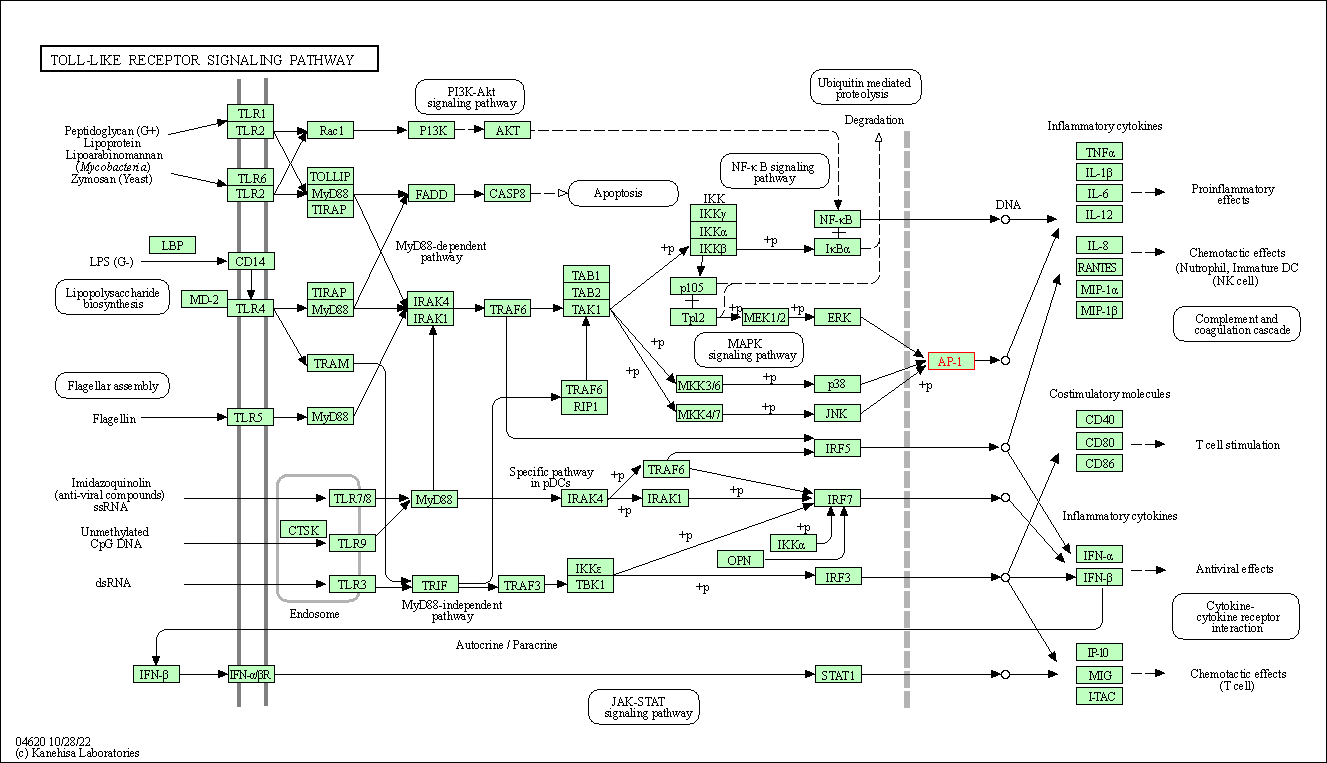
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
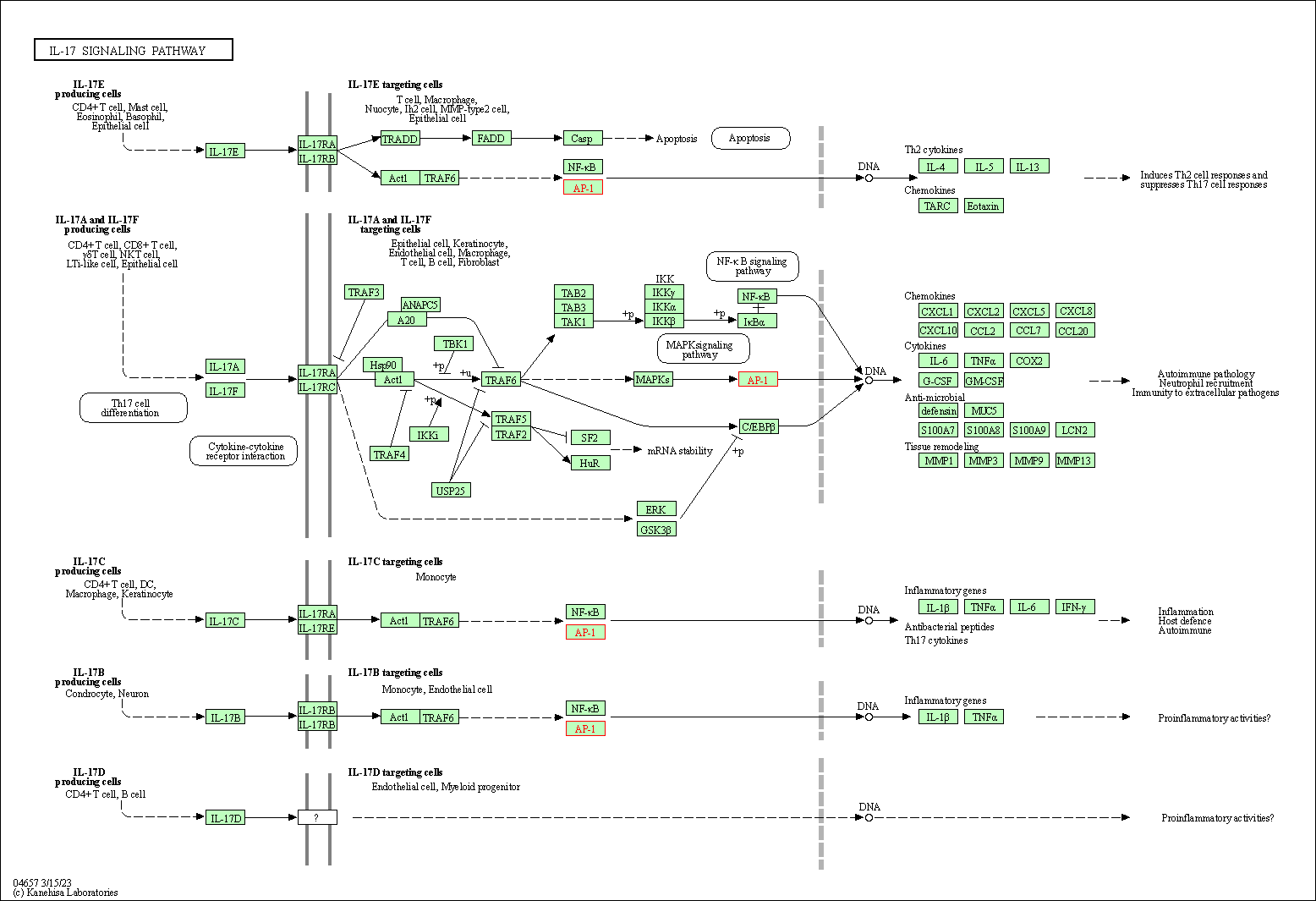
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
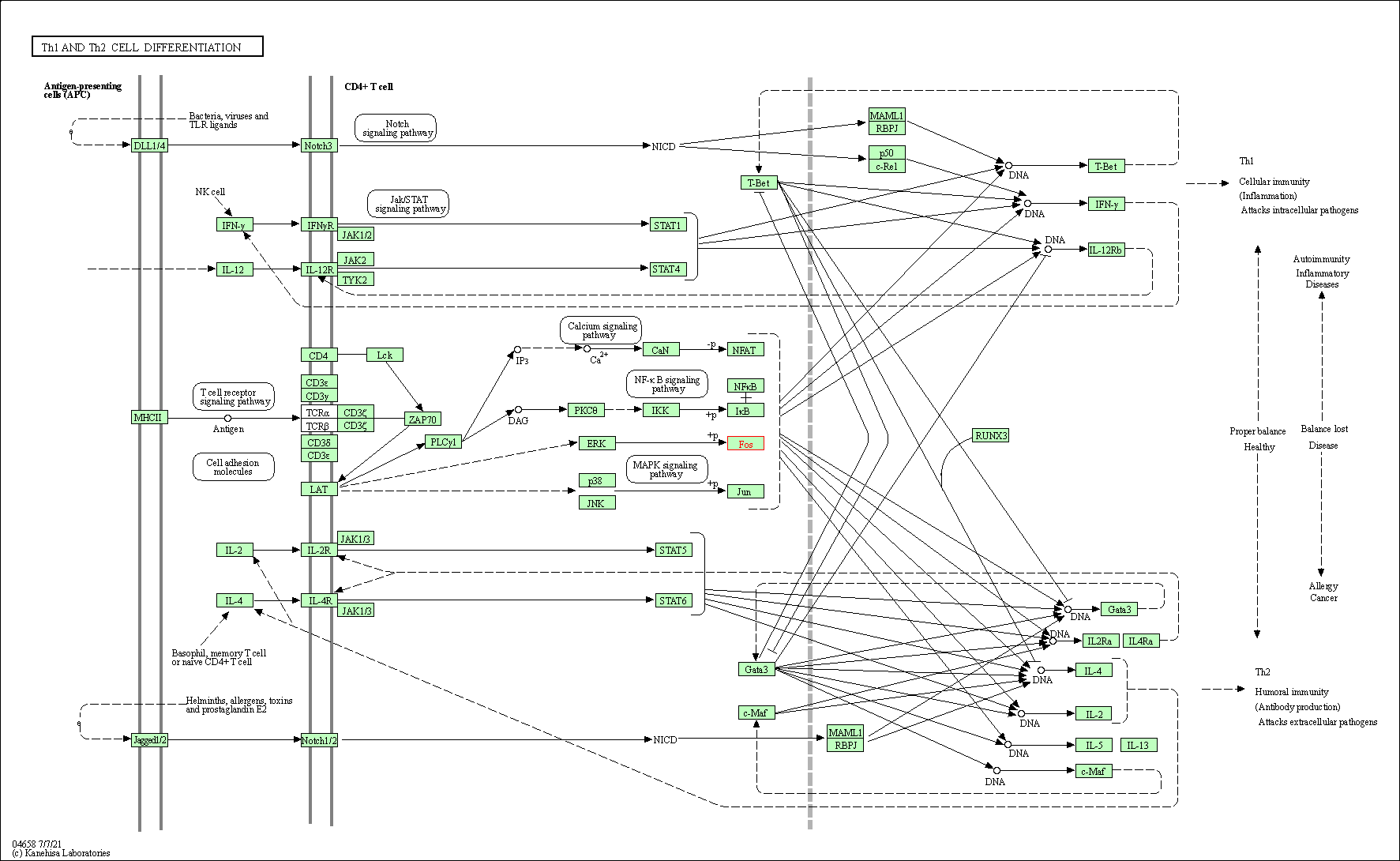
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
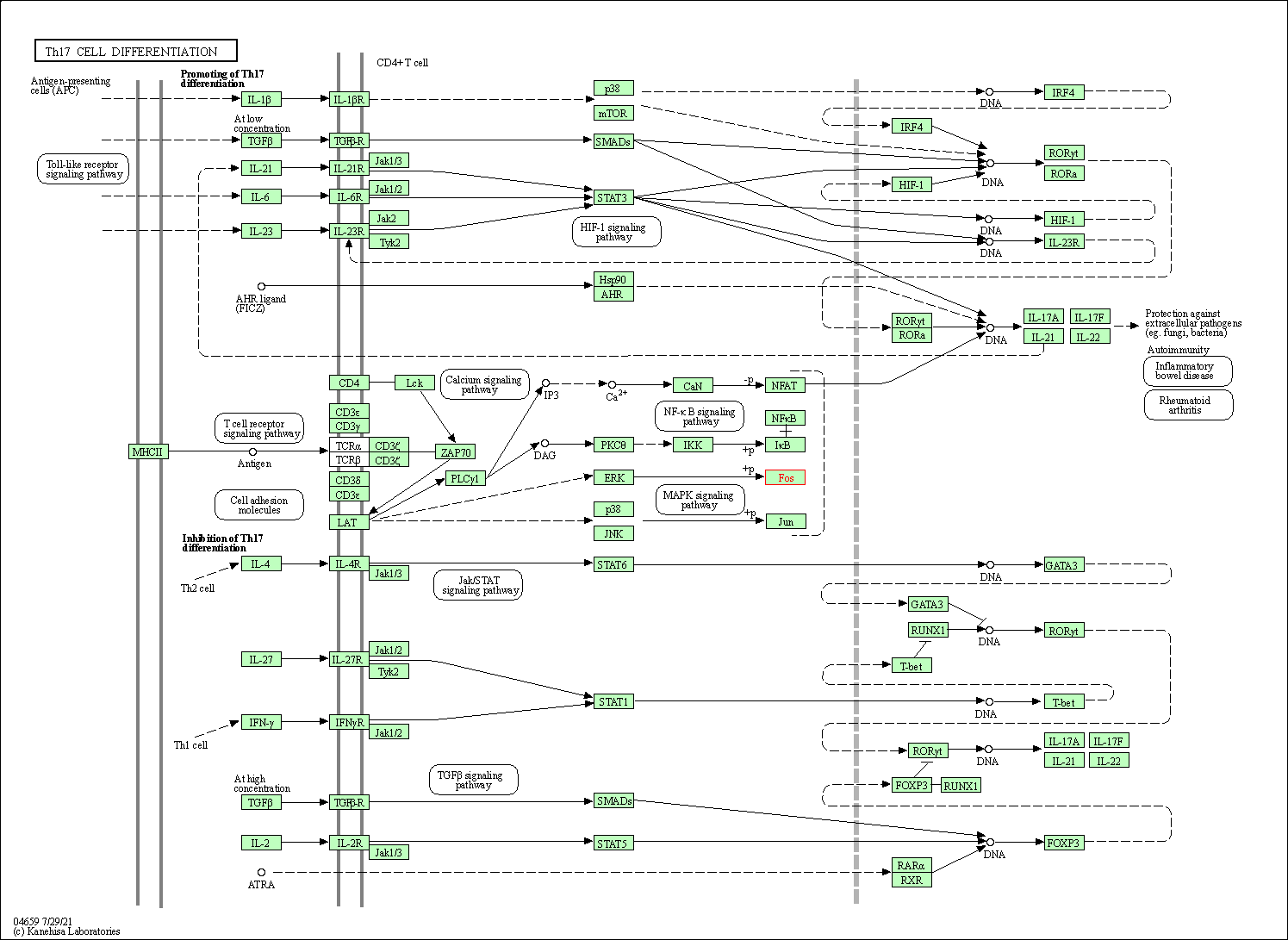
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
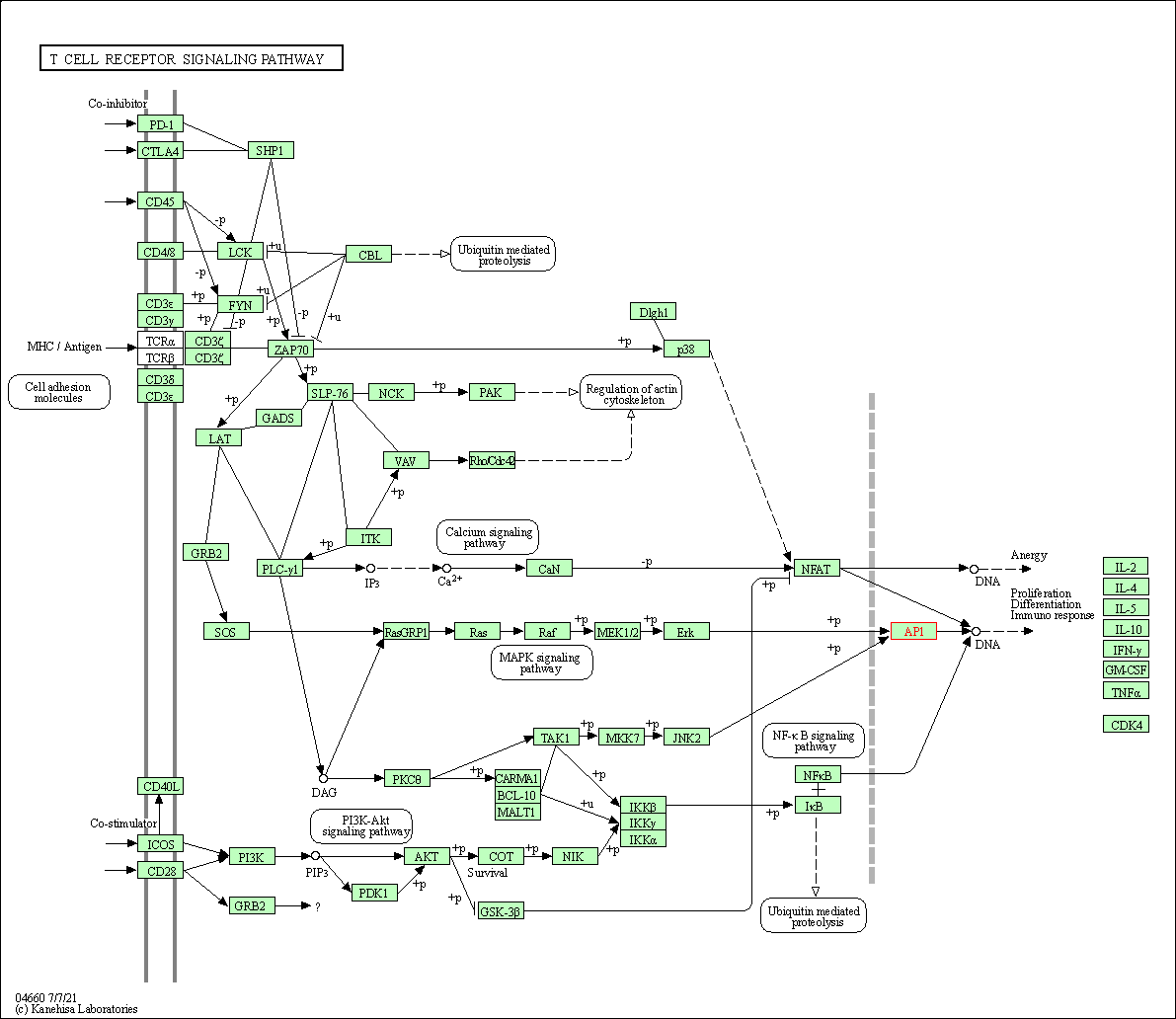
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
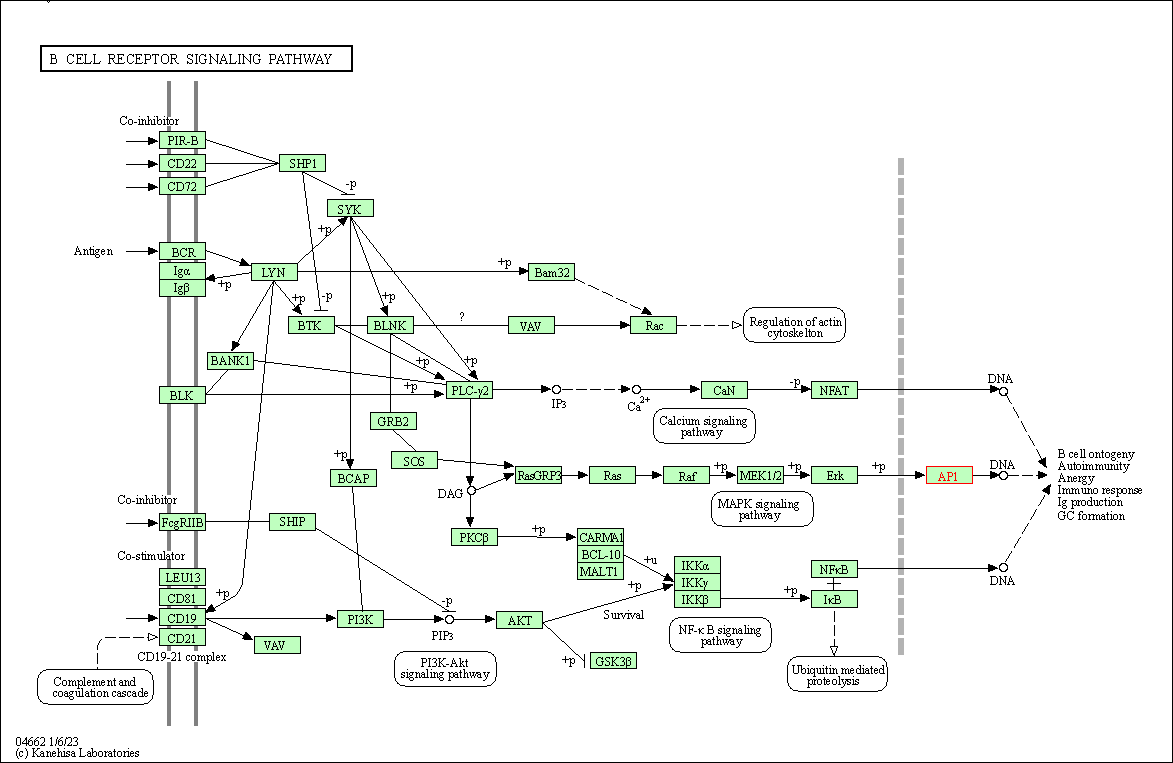
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
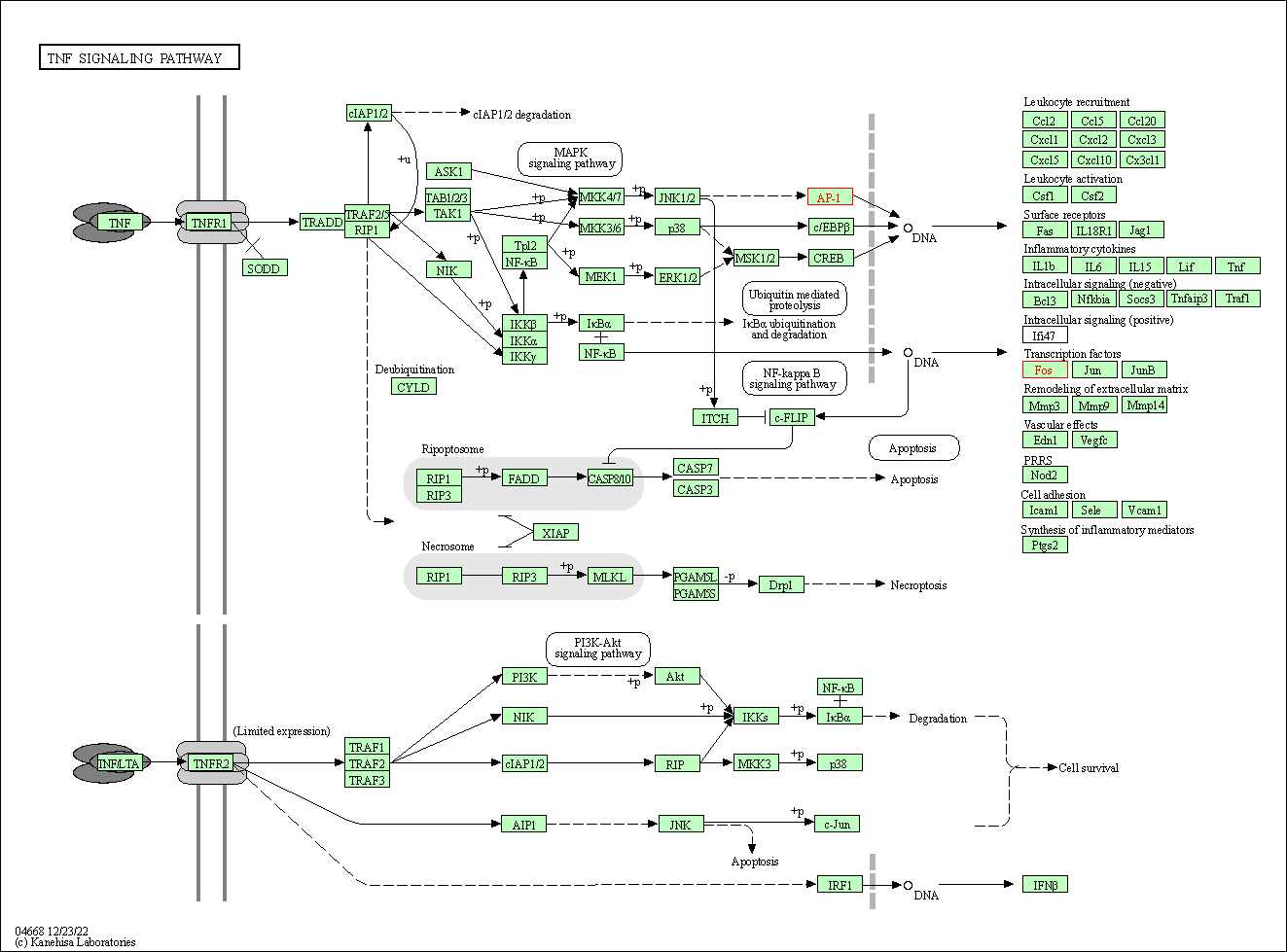
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
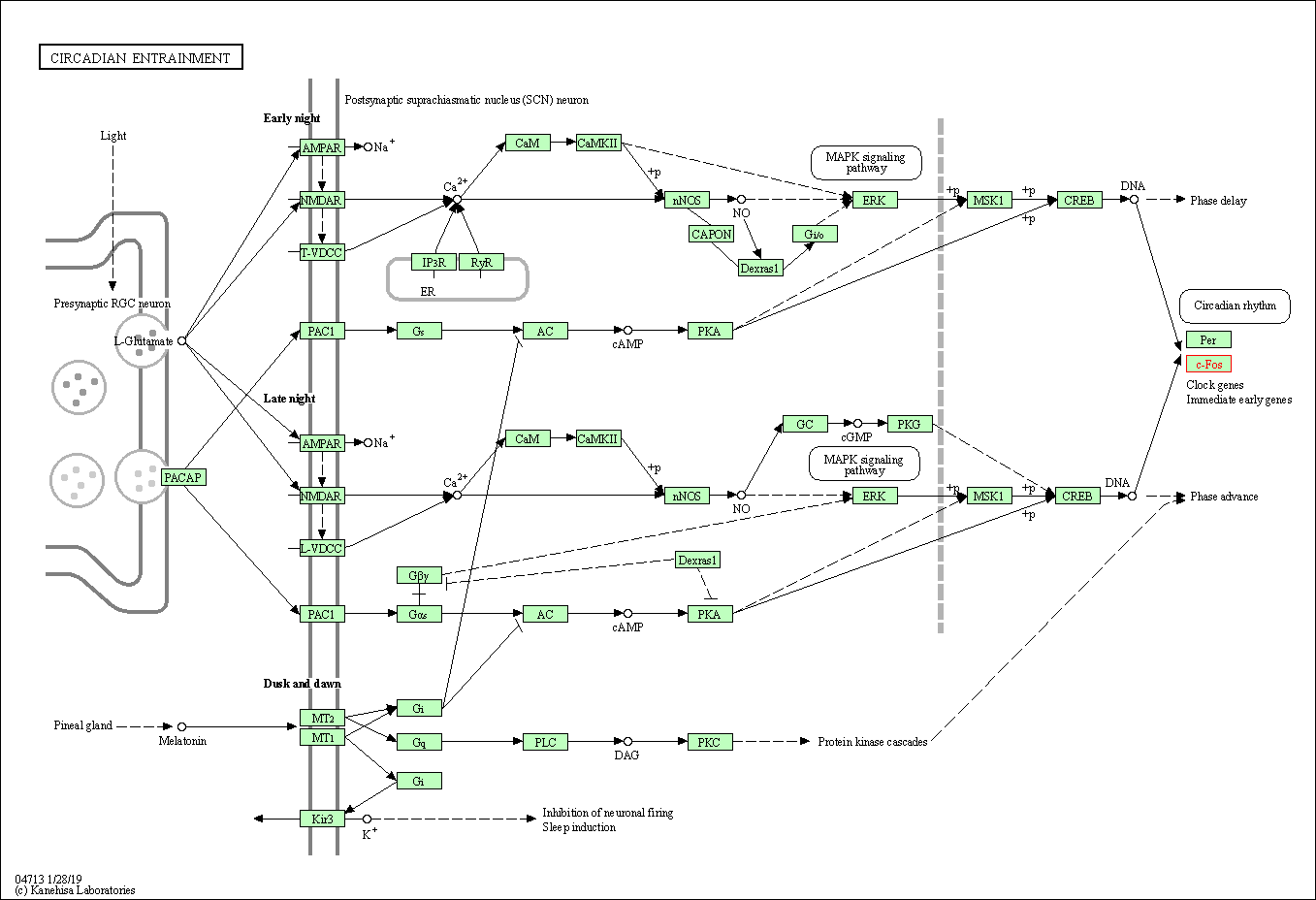
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
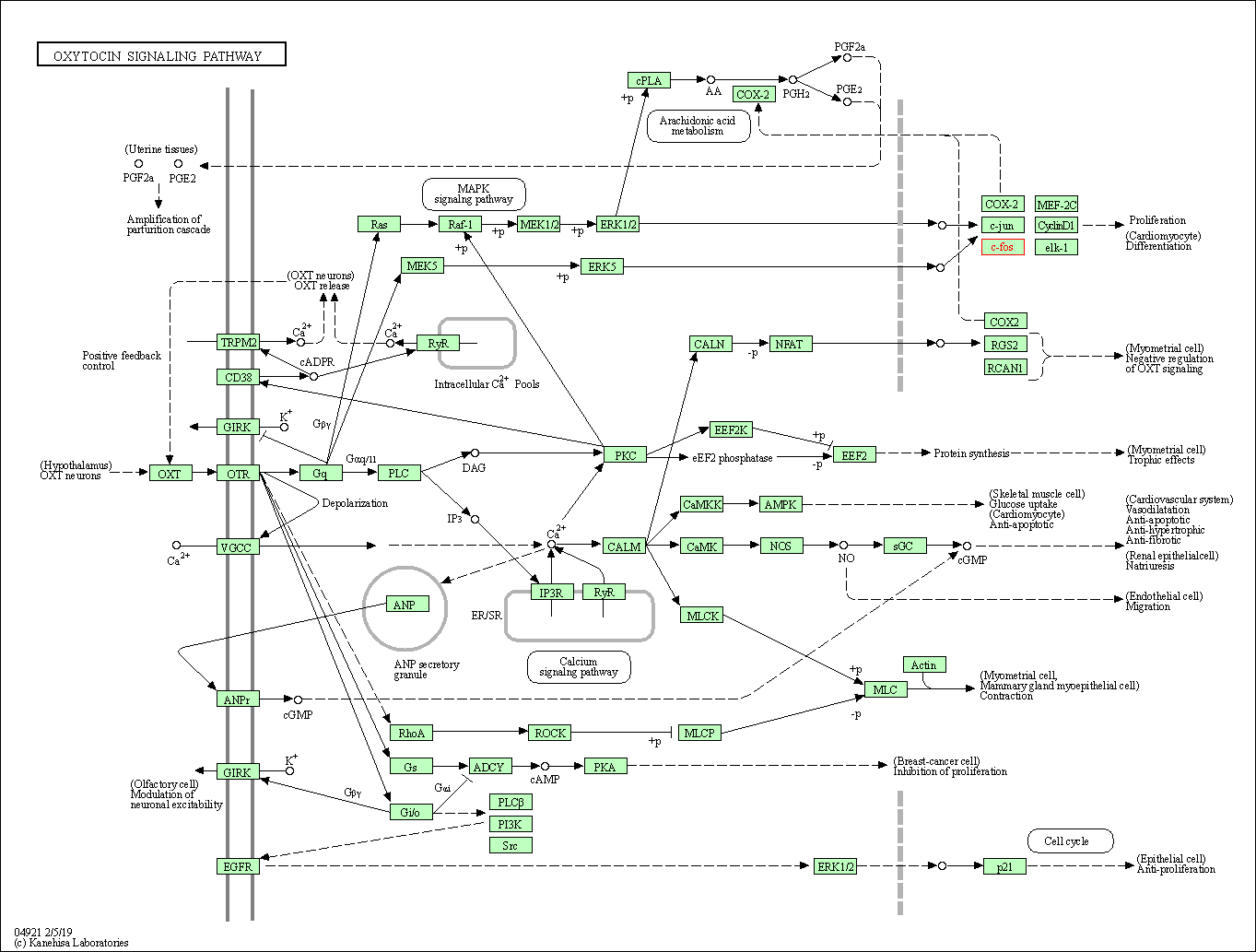
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
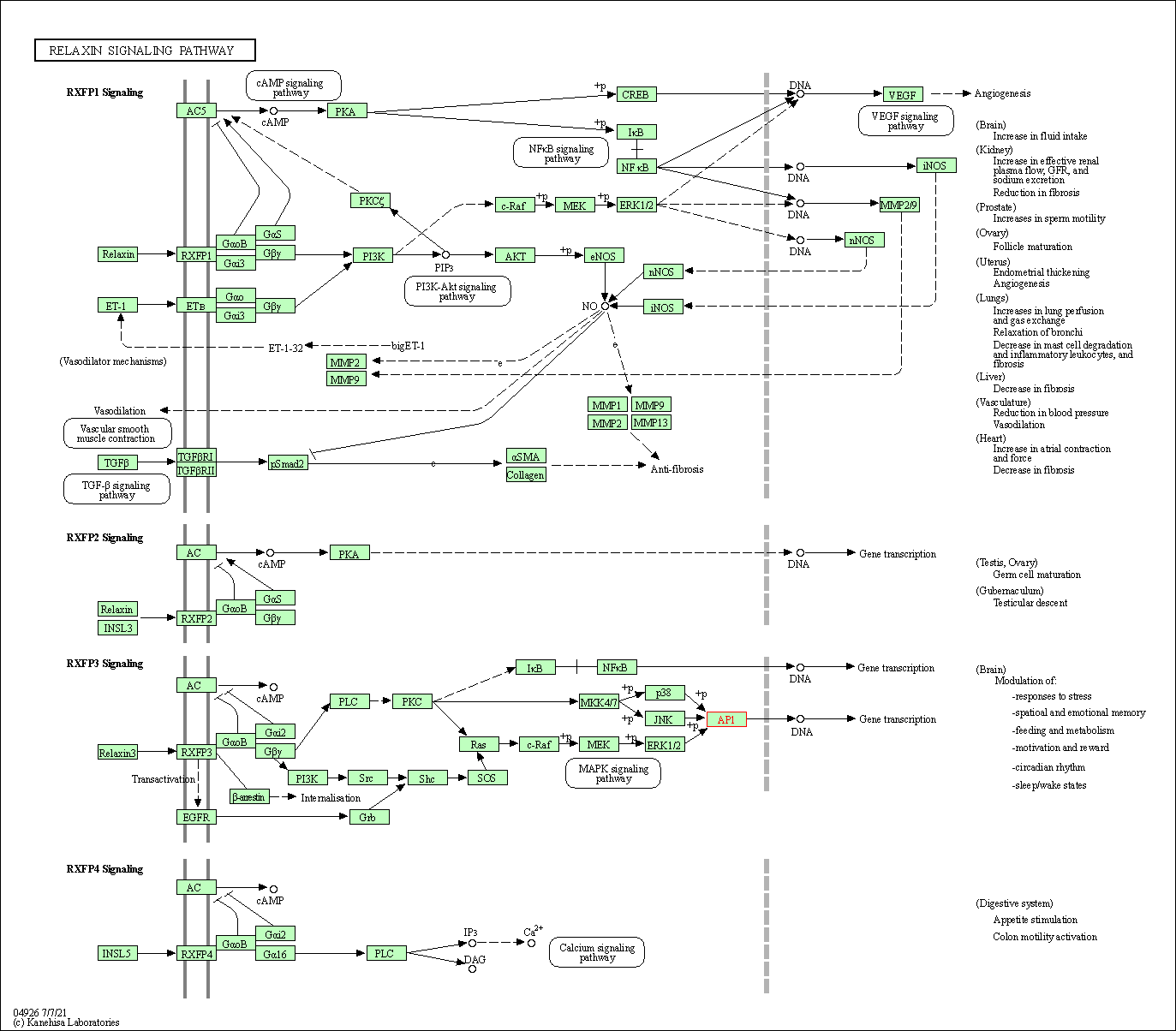
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
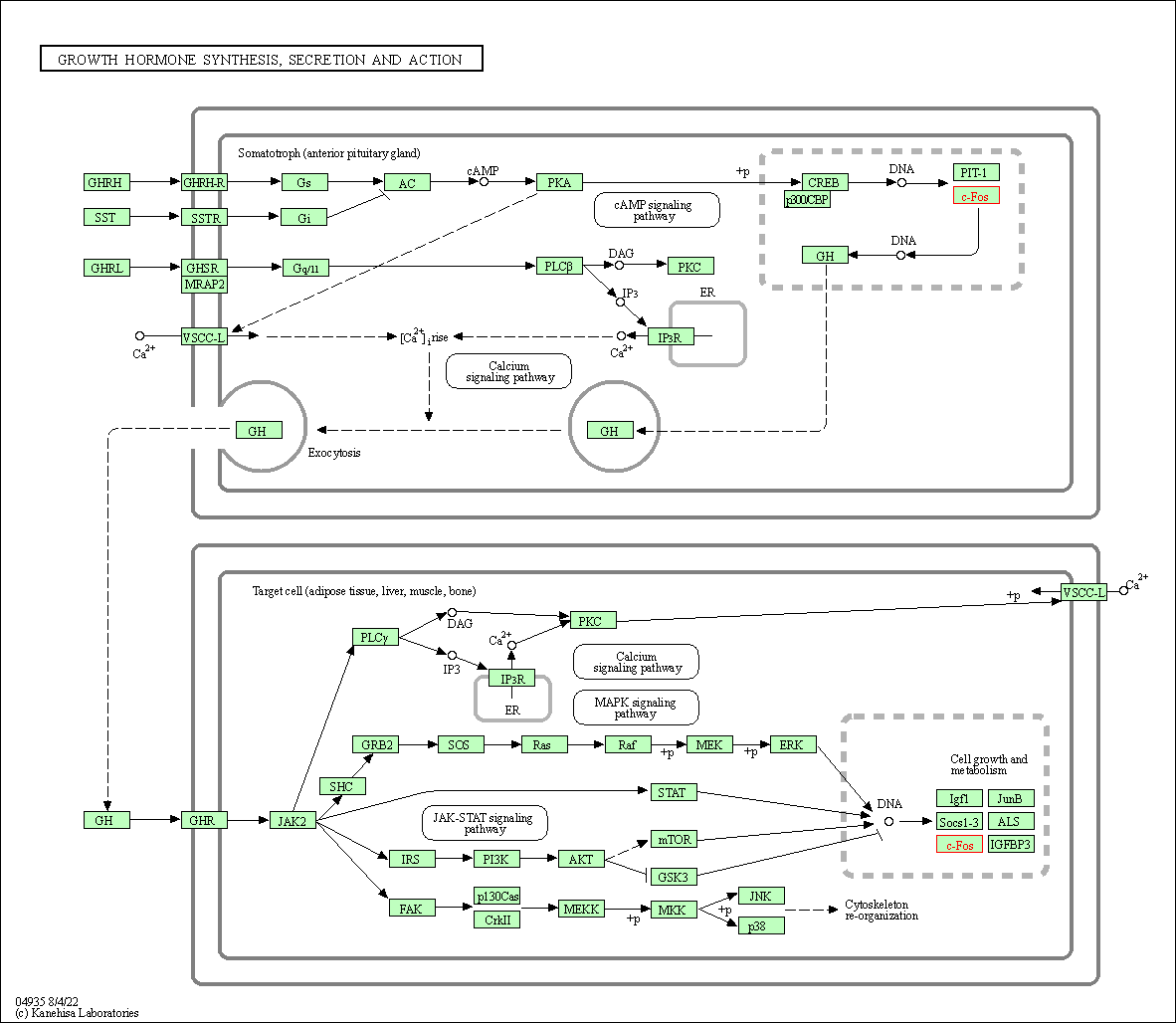
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 47 | Degree centrality | 5.05E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.03E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.61E-01 | Radiality | 1.45E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.91E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.04E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.94E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Proto-oncogene c-fos induction in thiamine-deficient encephalopathy. Protective effects of nicardipine on pyrithiamine-induced lesions. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Sep;118(2):175-80. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

