Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T35940
(Former ID: TTDR00148)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
ERK activator kinase 1 (MEK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PRKMK1; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; MKK1; MEK 1; MAPKK 1; MAPK/ERKkinase 1; MAPK/ERK kinase 1; MAP kinase kinase 1; Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAP2K1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||||
| 2 | Thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | |||||
| Function |
Binding of extracellular ligands such as growth factors, cytokines and hormones to their cell-surface receptors activates RAS and this initiates RAF1 activation. RAF1 then further activates the dual-specificity protein kinases MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Both MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2 function specifically in the MAPK/ERK cascade, and catalyze the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in a Thr-Glu-Tyr sequence located in the extracellular signal-regulated kinases MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2, leading to their activation and further transduction of the signal within the MAPK/ERK cascade. Depending on the cellular context, this pathway mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation, predominantly through the regulation of transcription, metabolism and cytoskeletal rearrangements. One target of the MAPK/ERK cascade is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG), a nuclear receptor that promotes differentiation and apoptosis. MAP2K1/MEK1 has been shown to export PPARG from the nucleus. The MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC), as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.12.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MPKKKPTPIQLNPAPDGSAVNGTSSAETNLEALQKKLEELELDEQQRKRLEAFLTQKQKV
GELKDDDFEKISELGAGNGGVVFKVSHKPSGLVMARKLIHLEIKPAIRNQIIRELQVLHE CNSPYIVGFYGAFYSDGEISICMEHMDGGSLDQVLKKAGRIPEQILGKVSIAVIKGLTYL REKHKIMHRDVKPSNILVNSRGEIKLCDFGVSGQLIDSMANSFVGTRSYMSPERLQGTHY SVQSDIWSMGLSLVEMAVGRYPIPPPDAKELELMFGCQVEGDAAETPPRPRTPGRPLSSY GMDSRPPMAIFELLDYIVNEPPPKLPSGVFSLEFQDFVNKCLIKNPAERADLKQLMVHAF IKRSDAEEVDFAGWLCSTIGLNQPSTPTHAAGV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T39RV3 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Selumetinib | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Melanoma | [2] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | RDEA-436 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 12 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Selumetinib | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Diamidothiazole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | Pyridic ketone derivative 1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 4 | RDEA-436 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 5 | 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 6 | 4,5-Dibromo-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid amide | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 7 | 5-phenylamino-4-cyano-3-hydroxy-isothiazole | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 8 | ALDISIN | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 9 | DEBROMOHYMENIALDISINE | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 10 | OROIDIN | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 11 | PD98059 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 12 | REVERSINE | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Binimetinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the BRAF:MEK1 kinases in complex with AMPPNP and Binimetinib | PDB:7M0U | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.09 Å | Mutation | Yes | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
DEQQRKRLEA
52 FLTQKQKVGE62 LKDDDFEKIS72 ELGAGNGGVV82 FKVSHKPSGL92 VMARKLIHLE 102 IKPAIRNQII112 RELQVLHECN122 SPYIVGFYGA132 FYSDGEISIC142 MEHMDGGSLD 152 QVLKKAGRIP162 EQILGKVSIA172 VIKGLTYLRE182 KHKIMHRDVK192 PSNILVNSRG 202 EIKLCDFGVS212 GQLIDAMANA222 FVGTRSYMSP232 ERLQGTHYSV242 QSDIWSMGLS 252 LVEMAVGRYP262 IPPPDAKELE272 LMPMAIFELL314 DYIVNEPPPK324 LPSGVFSLEF 334 QDFVNKCLIK344 NPAERADLKQ354 LMVHAFIKRS364 DAEEVDFAGW374 LCSTIGLNQP 384 S
|
|||||
|
|
GLY79
3.461
GLY80
3.268
LYS97
3.449
ILE99
4.249
LEU115
3.460
LEU118
3.873
ILE126
4.572
VAL127
3.608
GLY128
4.774
PHE129
4.819
ILE141
3.199
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Trametinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the BRAF:MEK1 kinases in complex with AMPPNP and Trametinib | PDB:7M0Y | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.45 Å | Mutation | Yes | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
DEQQRKRLEA
52 FLTQKQKVGE62 LKDDDFEKIS72 ELGAGNGGVV82 FKVSHKPSGL92 VMARKLIHLE 102 IKPAIRNQII112 RELQVLHECN122 SPYIVGFYGA132 FYSDGEISIC142 MEHMDGGSLD 152 QVLKKAGRIP162 EQILGKVSIA172 VIKGLTYLRE182 KHKIMHRDVK192 PSNILVNSRG 202 EIKLCDFGVS212 GQLIDAMANA222 FVGTRSYMSP232 ERLQGTHYSV242 QSDIWSMGLS 252 LVEMAVGRYP262 IPPPDAKELE272 LMPMAIFELL314 DYIVNEPPPK324 LPSGVFSLEF 334 QDFVNKCLIK344 NPAERADLKQ354 LMVHAFIKRS364 DAEEVDFAGW374 LCSTIGLN |
|||||
|
|
ASN78
4.514
GLY79
4.095
GLY80
4.840
LYS97
3.211
ILE99
4.634
LEU115
3.317
LEU118
3.970
ILE126
4.561
VAL127
3.325
GLY128
4.712
PHE129
4.606
ILE141
3.221
MET143
3.665
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|


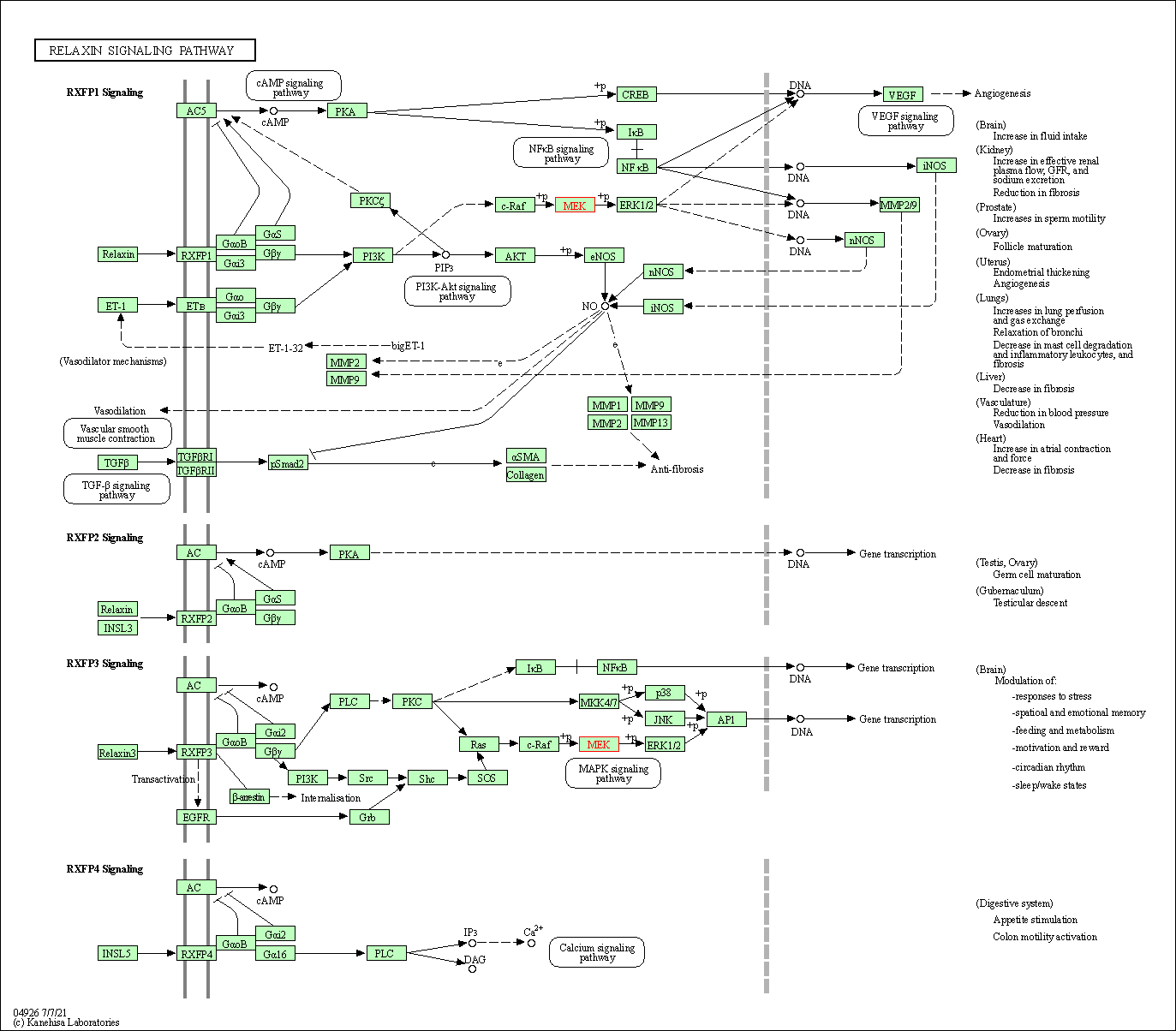
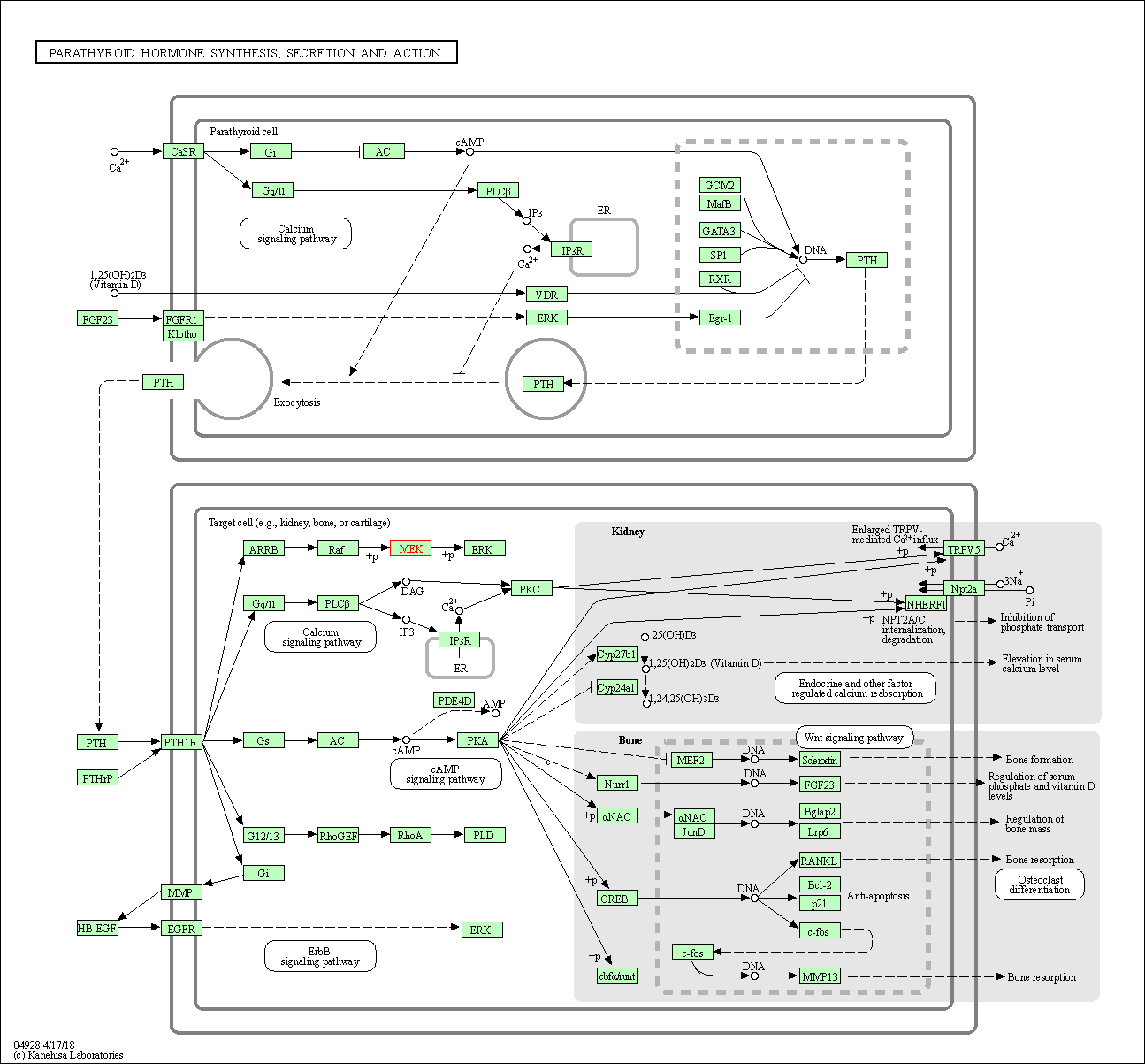

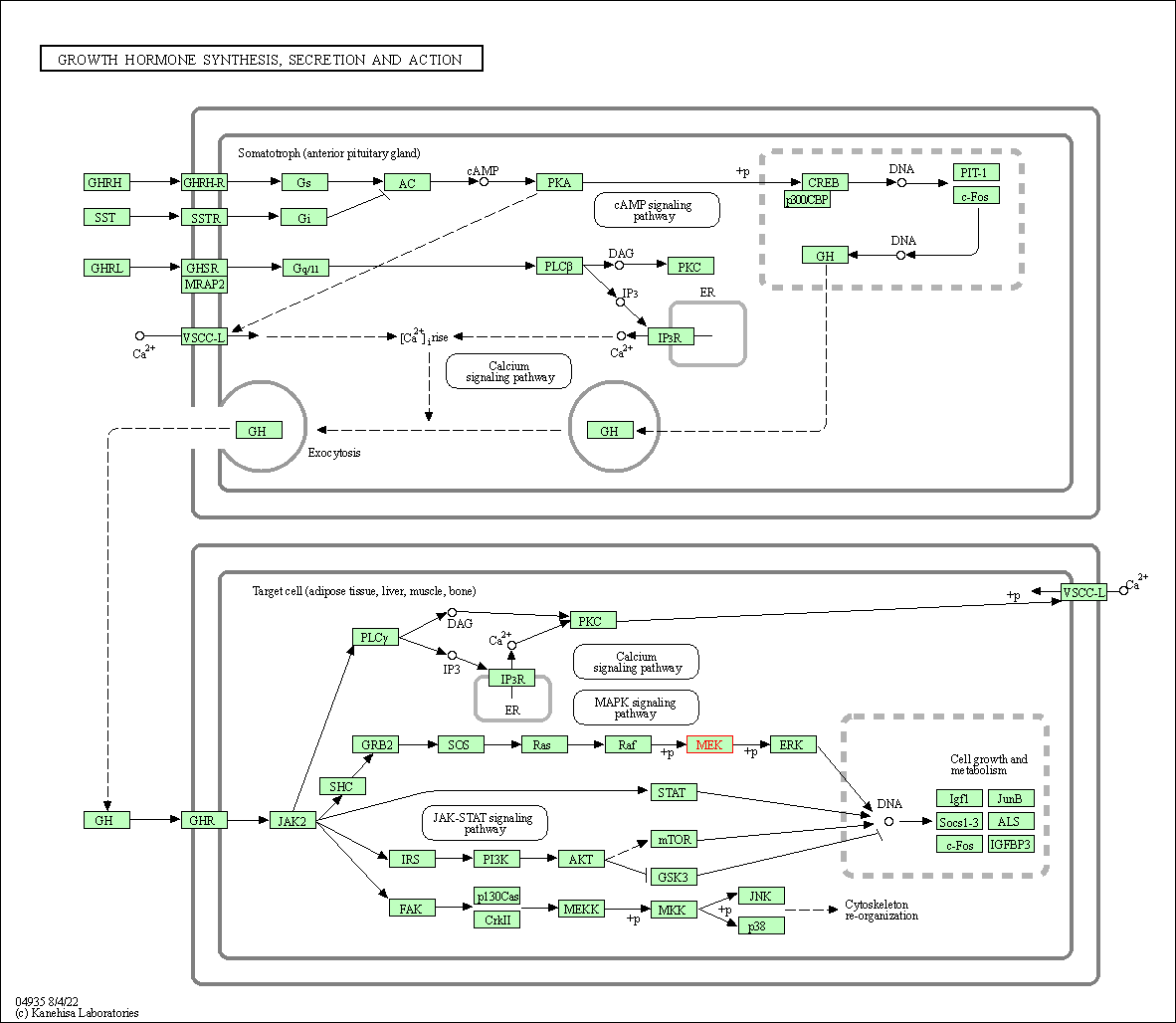
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oocyte meiosis | hsa04114 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
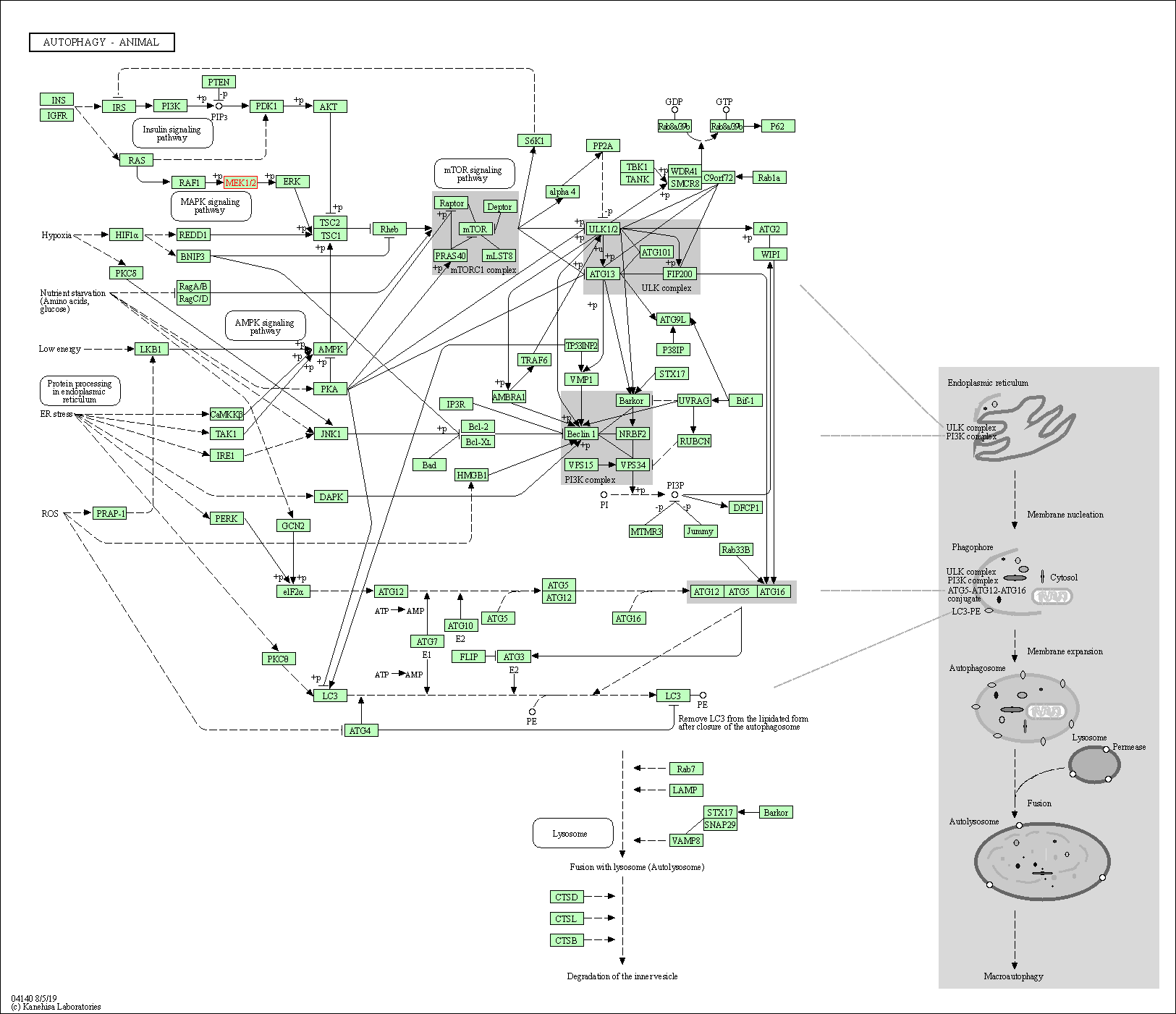
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
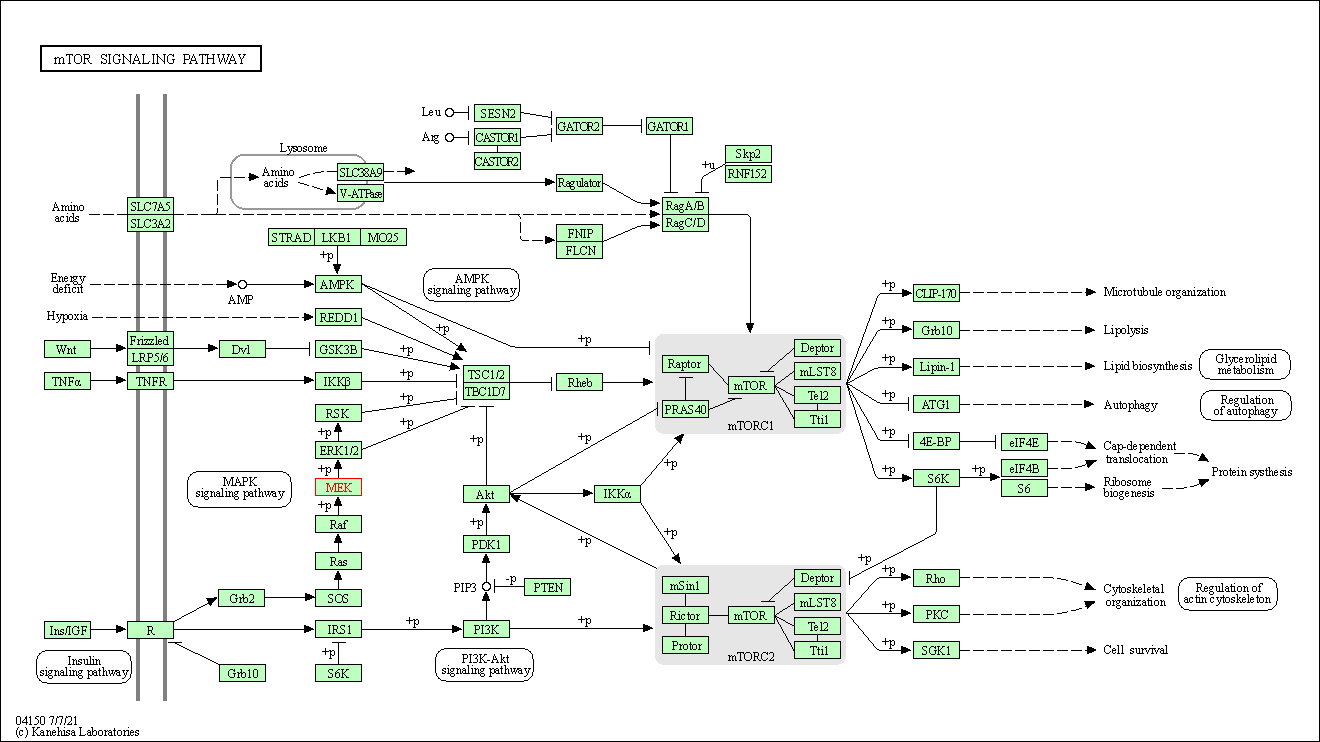
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
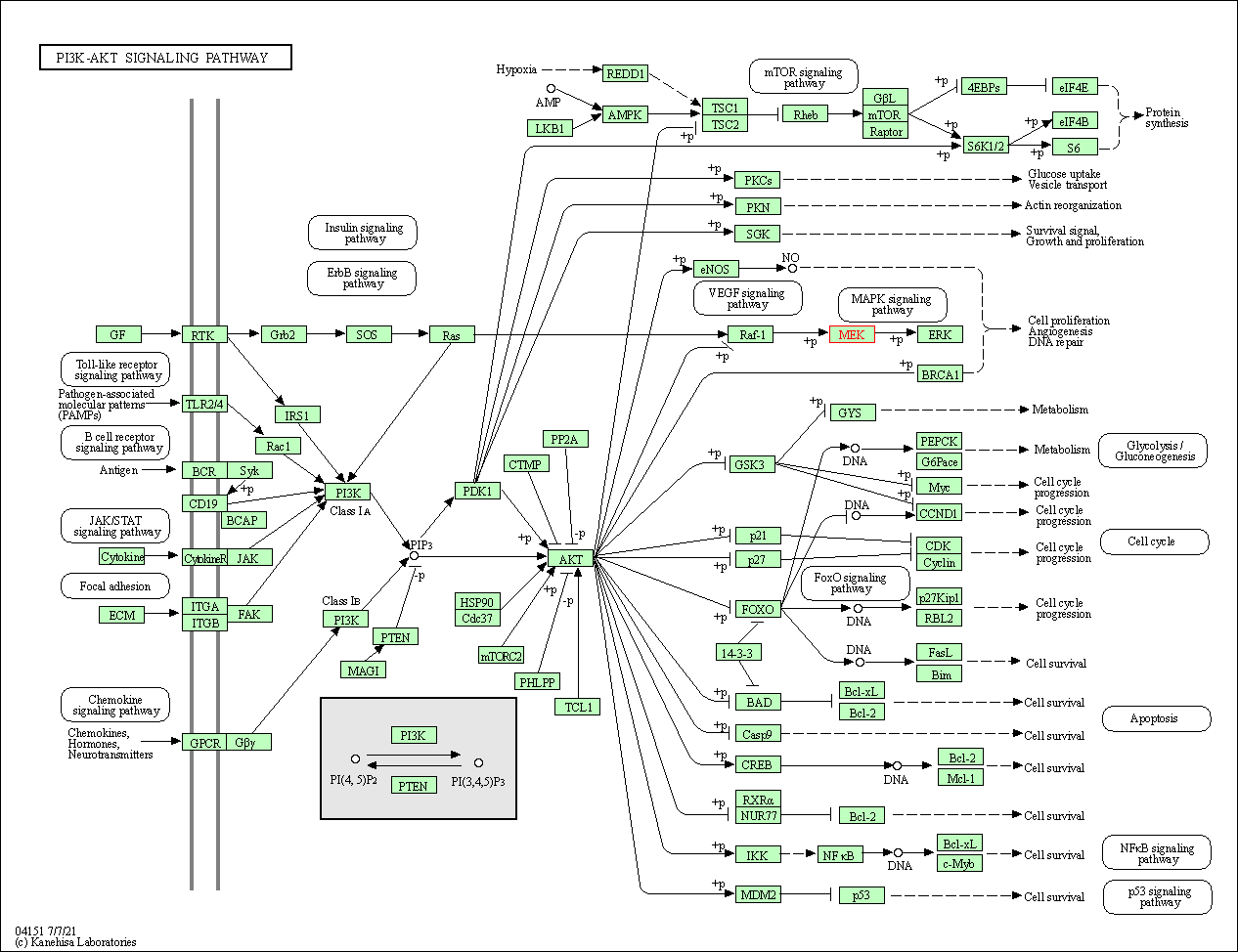
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
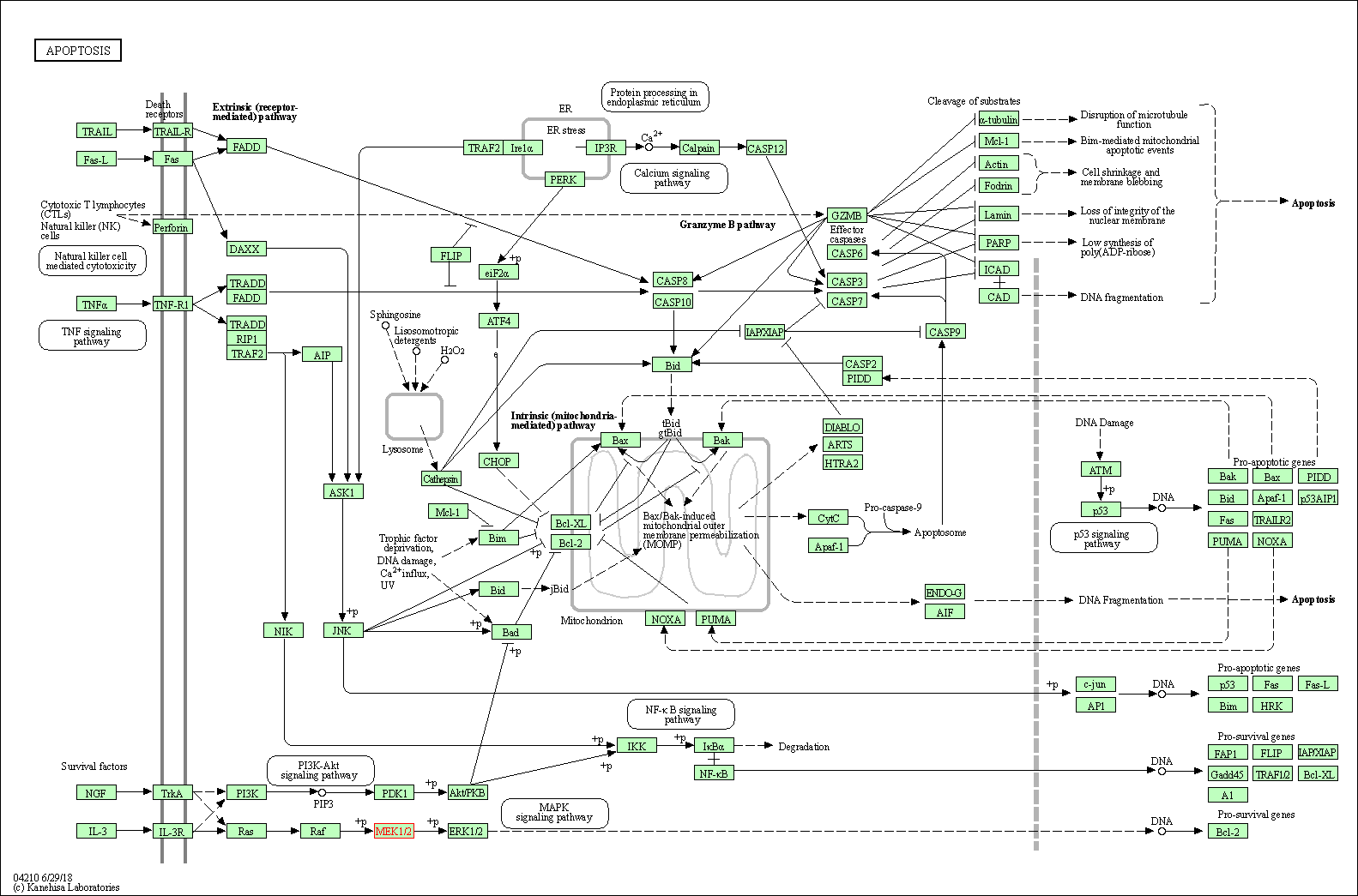
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gap junction | hsa04540 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Melanogenesis | hsa04916 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 31 | Degree centrality | 3.33E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 7.75E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.48E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.25E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.37E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01933932) Assess Efficacy & Safety of Selumetinib in Combination With Docetaxel in Patients Receiving 2nd Line Treatment for v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog (KRAS) Positive NSCLC (SELECT-1) | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800028258) | |||||
| REF 4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy: a patent review (2009 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(9):953-70. | |||||
| REF 5 | MEK inhibitors in oncology: a patent review (2015-Present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Aug;27(8):887-906. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of MedKoo Biosciences. | |||||
| REF 7 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 8 | Aldisine alkaloids from the Philippine sponge Stylissa massa are potent inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1 (MEK-1). J Med Chem. 2002 Jan 17;45(2):529-32. | |||||
| REF 9 | Discovery of 3-hydroxy-4-carboxyalkylamidino-5-arylamino-isothiazoles as potent MEK1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Aug 1;16(15):3975-80. | |||||
| REF 10 | The MEK1 inhibitor PD98059 sensitizes C8161 melanoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Melanoma Res. 2001 Feb;11(1):11-9. | |||||
| REF 11 | Reversine increases the plasticity of lineage-committed mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 19;104(25):10482-7. | |||||
| REF 12 | Allosteric MEK inhibitors act on BRAF/MEK complexes to block MEK activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 7;118(36):e2107207118. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

