Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T38338
(Former ID: TTDS00529)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Voltage-gated calcium channel alpha Cav2.2 (CACNA1B)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Voltage-gated calcium channel alpha subunit Cav2.2; Voltage-dependent N-type calcium channel alpha-1B subunit; N-type Ca2+ channel; Calcium channel, L type, alpha-1 polypeptide isoform 5; CACNA1B; Brain calcium channel III; BIII
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CACNA1B
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Migraine [ICD-11: 8A80] | |||||
| 2 | Non-thrombocytopenic purpura [ICD-11: 3B60] | |||||
| 3 | Pain [ICD-11: MG30-MG3Z] | |||||
| Function |
Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1B gives rise to N-type calcium currents. N-type calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group and are blocked by omega-conotoxin-GVIA (omega-CTx-GVIA) and by omega-agatoxin- IIIA (omega-Aga-IIIA). They are however insensitive to dihydropyridines (DHP), and omega-agatoxin-IVA (omega-Aga-IVA). Calcium channels containing alpha-1B subunit may play a role in directed migration of immature neurons.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Voltage-gated ion channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MVRFGDELGGRYGGPGGGERARGGGAGGAGGPGPGGLQPGQRVLYKQSIAQRARTMALYN
PIPVKQNCFTVNRSLFVFSEDNVVRKYAKRITEWPPFEYMILATIIANCIVLALEQHLPD GDKTPMSERLDDTEPYFIGIFCFEAGIKIIALGFVFHKGSYLRNGWNVMDFVVVLTGILA TAGTDFDLRTLRAVRVLRPLKLVSGIPSLQVVLKSIMKAMVPLLQIGLLLFFAILMFAII GLEFYMGKFHKACFPNSTDAEPVGDFPCGKEAPARLCEGDTECREYWPGPNFGITNFDNI LFAILTVFQCITMEGWTDILYNTNDAAGNTWNWLYFIPLIIIGSFFMLNLVLGVLSGEFA KERERVENRRAFLKLRRQQQIERELNGYLEWIFKAEEVMLAEEDRNAEEKSPLDVLKRAA TKKSRNDLIHAEEGEDRFADLCAVGSPFARASLKSGKTESSSYFRRKEKMFRFFIRRMVK AQSFYWVVLCVVALNTLCVAMVHYNQPRRLTTTLYFAEFVFLGLFLTEMSLKMYGLGPRS YFRSSFNCFDFGVIVGSVFEVVWAAIKPGSSFGISVLRALRLLRIFKVTKYWSSLRNLVV SLLNSMKSIISLLFLLFLFIVVFALLGMQLFGGQFNFQDETPTTNFDTFPAAILTVFQIL TGEDWNAVMYHGIESQGGVSKGMFSSFYFIVLTLFGNYTLLNVFLAIAVDNLANAQELTK DEEEMEEAANQKLALQKAKEVAEVSPMSAANISIAARQQNSAKARSVWEQRASQLRLQNL RASCEALYSEMDPEERLRFATTRHLRPDMKTHLDRPLVVELGRDGARGPVGGKARPEAAE APEGVDPPRRHHRHRDKDKTPAAGDQDRAEAPKAESGEPGAREERPRPHRSHSKEAAGPP EARSERGRGPGPEGGRRHHRRGSPEEAAEREPRRHRAHRHQDPSKECAGAKGERRARHRG GPRAGPREAESGEEPARRHRARHKAQPAHEAVEKETTEKEATEKEAEIVEADKEKELRNH QPREPHCDLETSGTVTVGPMHTLPSTCLQKVEEQPEDADNQRNVTRMGSQPPDPNTIVHI PVMLTGPLGEATVVPSGNVDLESQAEGKKEVEADDVMRSGPRPIVPYSSMFCLSPTNLLR RFCHYIVTMRYFEVVILVVIALSSIALAAEDPVRTDSPRNNALKYLDYIFTGVFTFEMVI KMIDLGLLLHPGAYFRDLWNILDFIVVSGALVAFAFSGSKGKDINTIKSLRVLRVLRPLK TIKRLPKLKAVFDCVVNSLKNVLNILIVYMLFMFIFAVIAVQLFKGKFFYCTDESKELER DCRGQYLDYEKEEVEAQPRQWKKYDFHYDNVLWALLTLFTVSTGEGWPMVLKHSVDATYE EQGPSPGYRMELSIFYVVYFVVFPFFFVNIFVALIIITFQEQGDKVMSECSLEKNERACI DFAISAKPLTRYMPQNRQSFQYKTWTFVVSPPFEYFIMAMIALNTVVLMMKFYDAPYEYE LMLKCLNIVFTSMFSMECVLKIIAFGVLNYFRDAWNVFDFVTVLGSITDILVTEIAETNN FINLSFLRLFRAARLIKLLRQGYTIRILLWTFVQSFKALPYVCLLIAMLFFIYAIIGMQV FGNIALDDDTSINRHNNFRTFLQALMLLFRSATGEAWHEIMLSCLSNQACDEQANATECG SDFAYFYFVSFIFLCSFLMLNLFVAVIMDNFEYLTRDSSILGPHHLDEFIRVWAEYDPAA CGRISYNDMFEMLKHMSPPLGLGKKCPARVAYKRLVRMNMPISNEDMTVHFTSTLMALIR TALEIKLAPAGTKQHQCDAELRKEISVVWANLPQKTLDLLVPPHKPDEMTVGKVYAALMI FDFYKQNKTTRDQMQQAPGGLSQMGPVSLFHPLKATLEQTQPAVLRGARVFLRQKSSTSL SNGGAIQNQESGIKESVSWGTQRTQDAPHEARPPLERGHSTEIPVGRSGALAVDVQMQSI TRRGPDGEPQPGLESQGRAASMPRLAAETQPVTDASPMKRSISTLAQRPRGTHLCSTTPD RPPPSQASSHHHHHRCHRRRDRKQRSLEKGPSLSADMDGAPSSAVGPGLPPGEGPTGCRR ERERRQERGRSQERRQPSSSSSEKQRFYSCDRFGGREPPKPKPSLSSHPTSPTAGQEPGP HPQGSGSVNGSPLLSTSGASTPGRGGRRQLPQTPLTPRPSITYKTANSSPIHFAGAQTSL PAFSPGRLSRGLSEHNALLQRDPLSQPLAPGSRIGSDPYLGQRLDSEASVHALPEDTLTF EEAVATNSGRSSRTSYVSSLTSQSHPLRRVPNGYHCTLGLSSGGRARHSYHHPDQDHWC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 3 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Hesperidin | Drug Info | Approved | Vascular purpura | [2] | |
| 2 | LOMERIZINE | Drug Info | Approved | Migraine | [2], [3] | |
| 3 | Ziconotide | Drug Info | Approved | Pain | [4], [5] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Cilnidipine | Drug Info | Phase 3 | High blood pressure | [6], [7] | |
| 2 | Ralfinamide | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Neuropathic pain | [8] | |
| 3 | CNV-2197944 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Pain | [9] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 3 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ritanserin | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 3 | Anxiety disorder | [10], [11] | |
| 2 | PD-0204318 | Drug Info | Terminated | Pain | [13] | |
| 3 | TH-9229 | Drug Info | Terminated | Reperfusion injury | [14] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CNSB-004 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Pain | [12] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 6 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 11 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Hesperidin | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 2 | LOMERIZINE | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | PD-157667 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 4 | PD-29361 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 5 | GNF-PF-3464 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 6 | KYS-05090 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 7 | NSC-180246 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 8 | NSC-87509 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 9 | PD-151307 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 10 | PD-167341 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 11 | PD-32577 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| Blocker | [+] 6 Blocker drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ziconotide | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Cilnidipine | Drug Info | [17], [18] | |||
| 3 | Ralfinamide | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | CNV-2197944 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 5 | Ritanserin | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 6 | Conotoxin | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CNSB-004 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 2 | TH-9229 | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 3 | CPU-228 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 1 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PD-0204318 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| Blocker (channel blocker) | [+] 1 Blocker (channel blocker) drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | omega-conotoxin GVIA | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| Inhibitor (gating inhibitor) | [+] 1 Inhibitor (gating inhibitor) drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TROX-1 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Cholesterol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human N-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.2 in the presence of ziconotide at 3.0 Angstrom resolution | PDB:7MIX | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | No | [32] |
| PDB Sequence |
KYAKRITEWP
95 PFEYMILATI105 IANCIVLALE115 QHLPDGDKTP125 MSERLDDTEP135 YFIGIFCFEA 145 GIKIIALGFV155 SYLRNGWNVM169 DFVVVLTGIL179 ATAGTDFDLR189 TLRAVRVLRP 199 LKLVSGIPSL209 QVVLKSIMKA219 MVPLLQIGLL229 LFFAILMFAI239 IGLEFYMGKF 249 HKACFPNSTD259 AEPVGDFPCG269 KEAPARLCEG279 DTECREYWPG289 PNFGITNFDN 299 ILFAILTVFQ309 CITMEGWTDI319 LYNTNDAAGN329 TWNWLYFIPL339 IIIGSFFMLN 349 LVLGVLSGEF359 AKERERVENR369 RAFLKLRRQQ379 QIERELNGYL389 EWIFKAEEVM 399 LAEEDRNFRR466 KEKMFRFFIR476 RMVKAQSFYW486 VVLCVVALNT496 LCVAMVHYNQ 506 PRRLTTTLYF516 AEFVFLGLFL526 TEMSLKMYGL536 GPRSYFRSSF546 NCFDFGVIVG 556 SVFEVVWAAI566 KPGSSFGISV576 LRALRLLRIF586 KVTKYWSSLR596 NLVVSLLNSM 606 KSIISLLFLL616 FLFIVVFALL626 GMQLFGGQFN636 FQDETPTTNF646 DTFPAAILTV 656 FQILTGEDWN666 AVMYHGIESQ676 GGVSKGMFSS686 FYFIVLTLFG696 NYTLLNVFLA 706 IAVDNLANAQ716 ELTKDEEEME726 EAANQKLALQ736 KAKEVAEVSP746 MSAANISIAA 756 RQQNSAKARS766 VWEQRASQLR776 LQNLRASCEA786 LRRFCHYIVT1148 MRYFEVVILV 1158 VIALSSIALA1168 AEDPVRTDSP1178 RNNALKYLDY1188 IFTGVFTFEM1198 VIKMIDLWNI 1221 LDFIVVSGAL1231 VAFAFSGSKG1241 KDINTIKSLR1251 VLRVLRPLKT1261 IKRLPKLKAV 1271 FDCVVNSLKN1281 VLNILIVYML1291 FMFIFAVIAV1301 QLFKGKFFYC1311 TDESKELERD 1321 CRGQYLDYEK1331 EEVEAQPRQW1341 KKYDFHYDNV1351 LWALLTLFTV1361 STGEGWPMVL 1371 KHSVDATYEE1381 QGPSPGYRME1391 LSIFYVVYFV1401 VFPFFFVNIF1411 VALIIITFQE 1421 QGDKVMSECS1431 LEKNERACID1441 FAISAKPLTR1451 YMPQNRQSFQ1461 YKTWTFVVSP 1471 PFEYFIMAMI1481 ALNTVVLMMK1491 FYDAPYEYEL1501 MLKCLNIVFT1511 SMFSMECVLK 1521 IIAFGVLNYF1531 RDAWNVFDFV1541 TVLGSITDIL1551 VTEIAETNNF1561 INLSFLRLFR 1571 AARLIKLLRQ1581 GYTIRILLWT1591 FVQSFKALPY1601 VCLLIAMLFF1611 IYAIIGMQVF 1621 GNIALDDDTS1631 INRHNNFRTF1641 LQALMLLFRS1651 ATGEAWHEIM1661 LSCLSNQACD 1671 EQANATECGS1681 DFAYFYFVSF1691 IFLCSFLMLN1701 LFVAVIMDNF1711 EYLTRDSSIL 1721 GPHHLDEFIR1731 VWAEYDPAAC1741 GRISYNDMFE1751 MLKHMSPPLG1761 LGKKCPARVA 1771 YKRLVRMNMP1781 ISNEDMTVHF1791 TSTLMALIRT1801 ALEIKLAPAG1811 TKQHQCDAEL 1821 RKEISVVWAN1831 LPQKTL
|
|||||
|
|
ASN299
3.605
ILE300
4.080
LEU301
4.257
PHE572
3.544
GLY573
4.289
LEU577
3.829
LEU1162
3.601
ILE1165
3.608
ALA1166
4.502
ALA1168
4.044
ALA1169
3.771
PRO1178
3.669
ARG1179
3.270
ALA1182
4.044
LEU1186
3.599
PHE1190
4.262
ASN1245
4.940
LYS1248
4.706
PHE1292
3.588
PHE1296
3.541
ILE1299
3.603
LEU1303
3.733
GLU1391
3.333
LEU1392
3.646
ILE1394
3.453
PHE1395
3.514
VAL1398
3.774
VAL1402
4.989
VAL1486
3.927
MET1489
3.594
MET1490
3.619
PHE1492
3.474
PHE1611
4.724
PHE1641
4.032
LEU1642
3.988
SER1666
3.276
GLY1680
4.642
SER1681
3.549
ASP1682
3.314
PHE1683
4.118
PHE1686
3.973
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: PD173212 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human N-type voltage gated calcium channel CaV2.2-alpha2/delta1-beta1 complex, bound to PD173212 | PDB:7VFV | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | No | [33] |
| PDB Sequence |
NVVRKYAKRI
91 TEWPPFEYMI101 LATIIANCIV111 LALEQHLPDG121 DKTPMSERLD131 DTEPYFIGIF 141 CFEAGIKIIA151 LGFVFHKGSY161 LRNGWNVMDF171 VVVLTGILAT181 AGTDFDLRTL 191 RAVRVLRPLK201 LVSGIPSLQV211 VLKSIMKAMV221 PLLQIGLLLF231 FAILMFAIIG 241 LEFYMGKFHK251 ACFPNSTDAE261 PVGDFPCGKE271 APARLCEGDT281 ECREYWPGPN 291 FGITNFDNIL301 FAILTVFQCI311 TMEGWTDILY321 NTNDAAGNTW331 NWLYFIPLII 341 IGSFFMLNLV351 LGVLSGEFAK361 ERERVENRRA371 FLKLRRQQQI381 ERELNGYLEW 391 IFKAEEVMLA401 EEDRNSYFRR466 KEKMFRFFIR476 RMVKAQSFYW486 VVLCVVALNT 496 LCVAMVHYNQ506 PRRLTTTLYF516 AEFVFLGLFL526 TEMSLKMYGL536 GPRSYFRSSF 546 NCFDFGVIVG556 SVFEVVWAAI566 KPGSSFGISV576 LRALRLLRIF586 KVTKYWSSLR 596 NLVVSLLNSM606 KSIISLLFLL616 FLFIVVFALL626 GMQLFGGQFN636 FQDETPTTNF 646 DTFPAAILTV656 FQILTGEDWN666 AVMYHGIESQ676 GGVSKGMFSS686 FYFIVLTLFG 696 NYTLLNVFLA706 IAVDNLANAQ716 ELTKDEEEME726 EAANQKLALQ736 KAKEVAARSV 767 WEQRASQLRL777 QNLRASRRFC1143 HYIVTMRYFE1153 VVILVVIALS1163 SIALAAEDPV 1173 RTDSPRNNAL1183 KYLDYIFTGV1193 FTFEMVIKMI1203 DLGLLLHPGA1213 YFRDLWNILD 1223 FIVVSGALVA1233 FAFSGSKGKD1243 INTIKSLRVL1253 RVLRPLKTIK1263 RLPKLKAVFD 1273 CVVNSLKNVL1283 NILIVYMLFM1293 FIFAVIAVQL1303 FKGKFFYCTD1313 ESKELERDCR 1323 GQYLDYEKEE1333 VEAQPRQWKK1343 YDFHYDNVLW1353 ALLTLFTVST1363 GEGWPMVLKH 1373 SVDATYEEQG1383 PSPGYRMELS1393 IFYVVYFVVF1403 PFFFVNIFVA1413 LIIITFQEQK 1434 NERACIDFAI1444 SAPQNRQSFQ1461 YKTWTFVVSP1471 PFEYFIMAMI1481 ALNTVVLMMK 1491 FYDAPYEYEL1501 MLKCLNIVFT1511 SMFSMECVLK1521 IIAFGVLNYF1531 RDAWNVFDFV 1541 TVLGSITDIL1551 VTEIAETNNF1561 INLSFLRLFR1571 AARLIKLLRQ1581 GYTIRILLWT 1591 FVQSFKALPY1601 VCLLIAMLFF1611 IYAIIGMQVF1621 GNIALDDDTS1631 INRHNNFRTF 1641 LQALMLLFRS1651 ATGEAWHEIM1661 LSCLSNQACD1671 EQANATECGS1681 DFAYFYFVSF 1691 IFLCSFLMLN1701 LFVAVIMDNF1711 EYLTRDSSIL1721 GPHHLDEFIR1731 VWANDMFEML 1753 KHMSVHFTST1794 LMALIRTALE1804 ITKQHQCDAE1820 LRKEISVVWA1830 NLPQKTLDLL 1840 VPPHKP
|
|||||
|
|
MET313
3.825
PHE345
3.610
LEU348
3.666
LEU352
3.902
VAL1282
4.055
LEU1286
3.750
TYR1289
1.377
MET1293
4.728
PHE1359
3.185
SER1362
3.967
THR1363
3.670
PHE1403
3.873
PHE1407
4.291
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Synaptic vesicle cycle | hsa04721 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
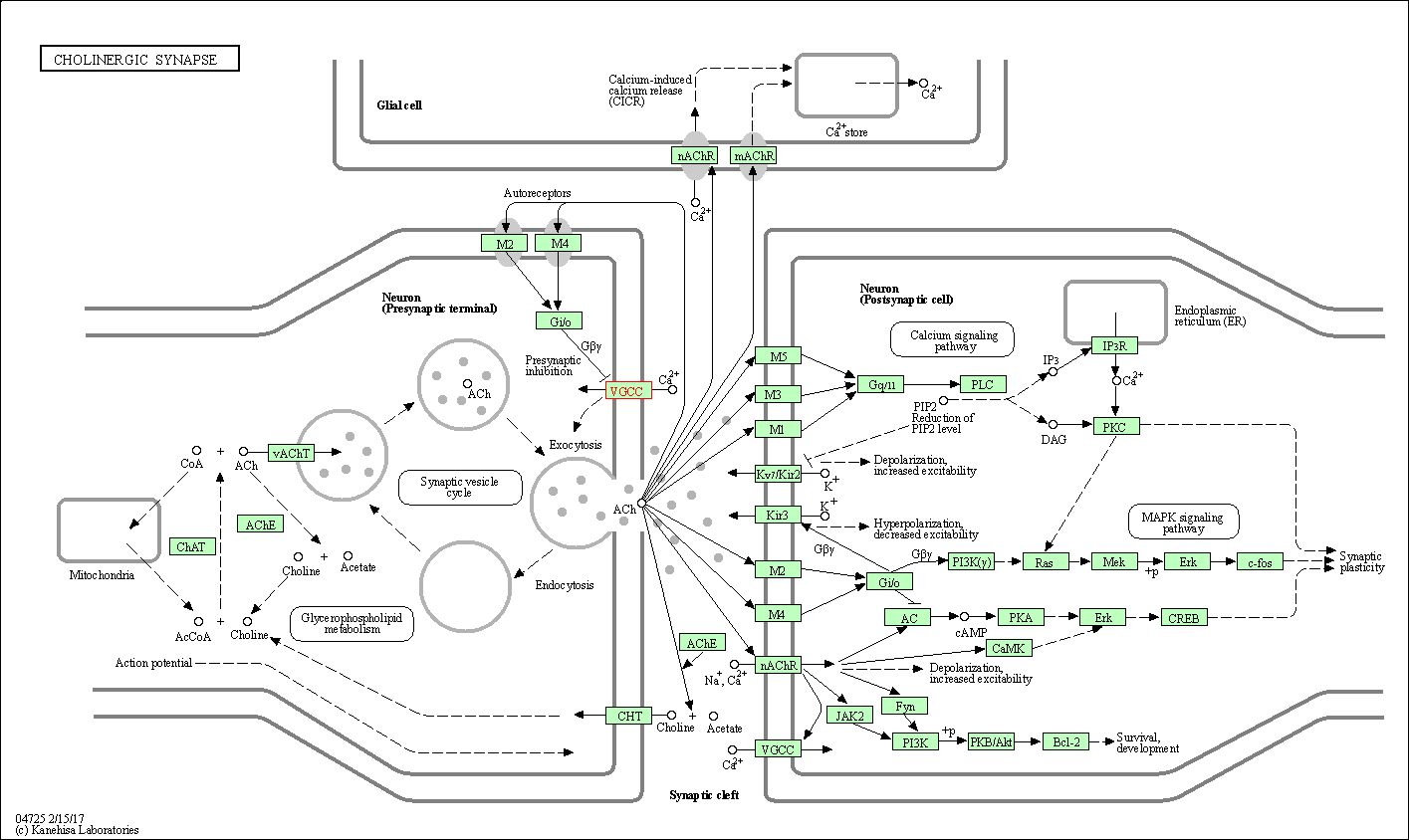
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
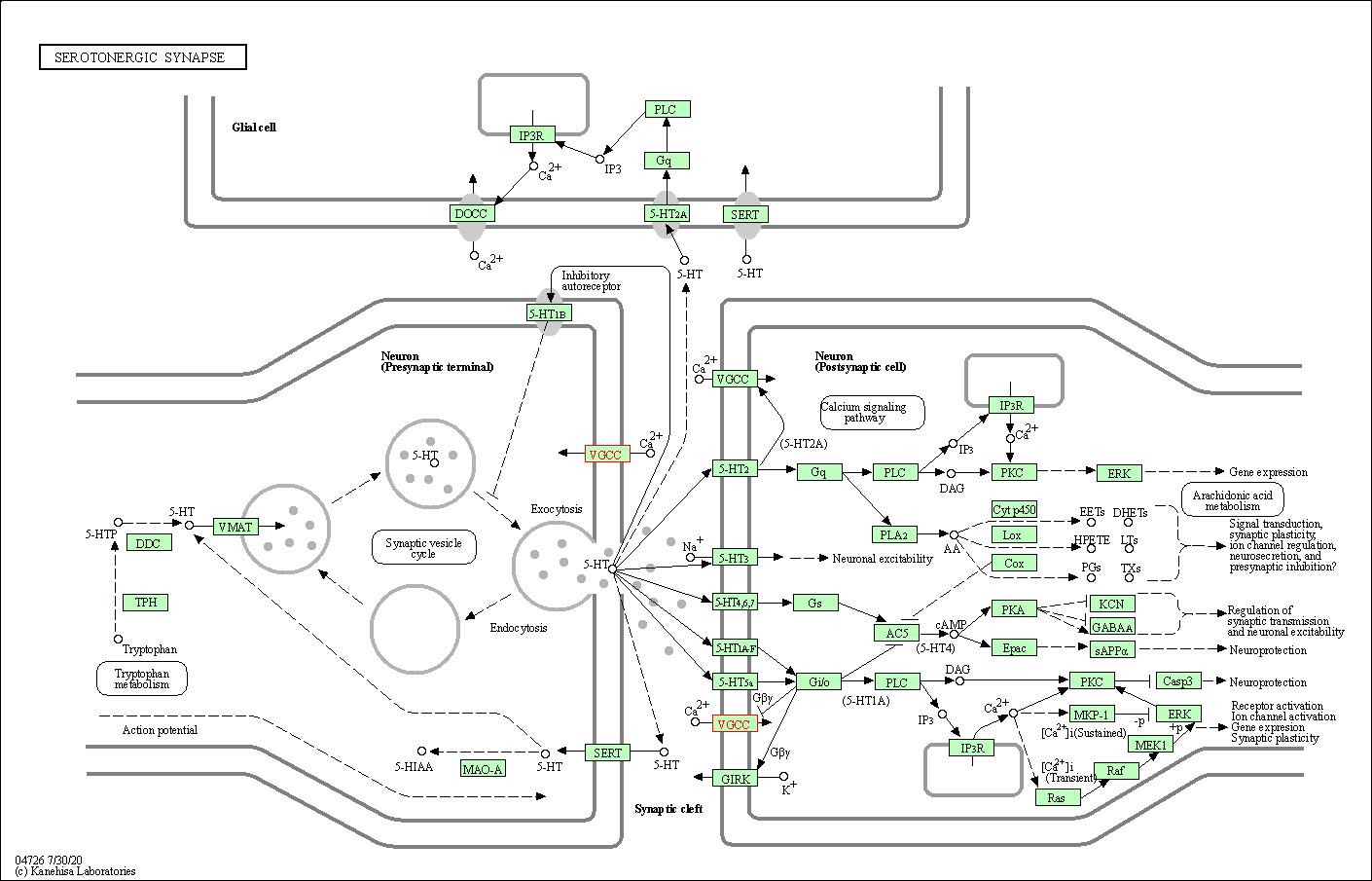
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
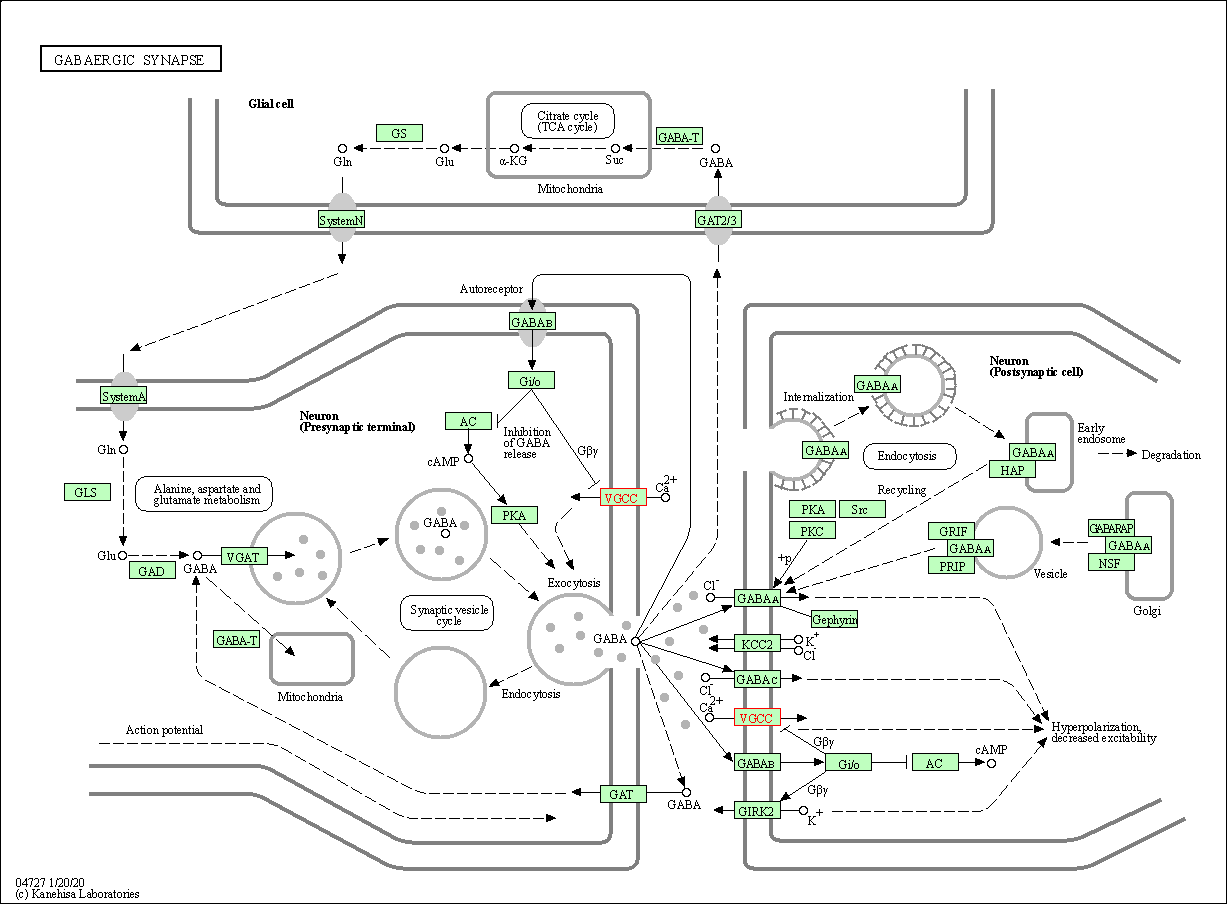
| GABAergic synapse | hsa04727 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
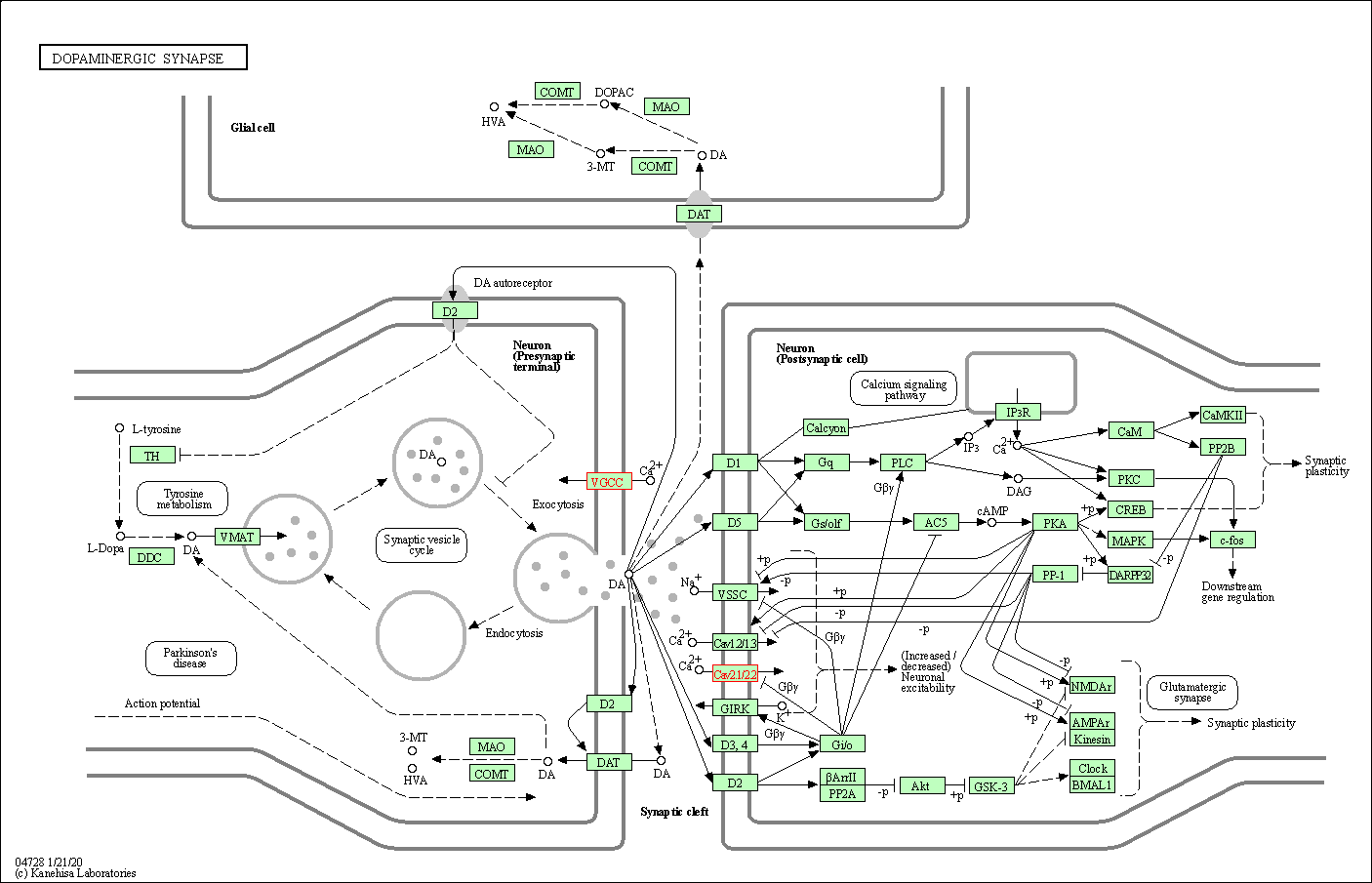
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 4.71E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.84E-01 | Radiality | 1.31E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.63E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.41E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 12 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | MAPK signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Synaptic vesicle cycle | |||||
| 4 | Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | |||||
| 5 | Cholinergic synapse | |||||
| 6 | Serotonergic synapse | |||||
| 7 | GABAergic synapse | |||||
| 8 | Dopaminergic synapse | |||||
| 9 | Taste transduction | |||||
| 10 | Type II diabetes mellitus | |||||
| 11 | Morphine addiction | |||||
| 12 | Nicotine addiction | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 7 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gq alpha and Go alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| 2 | Ionotropic glutamate receptor pathway | |||||
| 3 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor group III pathway | |||||
| 4 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor group II pathway | |||||
| 5 | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 6 | Endogenous cannabinoid signaling | |||||
| 7 | GABA-B receptor II signaling | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Depolarization of the Presynaptic Terminal Triggers the Opening of Calcium Channels | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell | |||||
| 2 | Synaptic Vesicle Pathway | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging treatments for traumatic brain injury. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):67-84. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002033) | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2536). | |||||
| REF 5 | 2004 approvals: the demise of the blockbuster. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005 Feb;4(2):93-4. | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7767). | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02145104) Efficacy/Safety of Cilnidipine Plus Valsartan Versus Valsartan in Patients With Hypertension. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Emerging drugs in neuropathic pain. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 Mar;12(1):113-26. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01848730) Efficacy and Safety of CNV2197944 Versus Placebo in Patients With Post-herpetic Neuralgia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 97). | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800000237) | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800029021) | |||||
| REF 13 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800014952) | |||||
| REF 14 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800008159) | |||||
| REF 15 | In silico identification and biochemical evaluation of novel inhibitors of NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 (NQO2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Dec 15;20(24):7331-6. | |||||
| REF 16 | Synthesis and SAR of novel 2-arylthiazolidinones as selective analgesic N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Feb 1;17(3):662-7. | |||||
| REF 17 | N- and L-type calcium channel antagonist improves glomerular dynamics, reverses severe nephrosclerosis, and inhibits apoptosis and proliferation in an l-NAME/SHR model. J Hypertens. 2002 May;20(5):993-1000. | |||||
| REF 18 | Pharmacology of N-type Ca2+ channels distributed in cardiovascular system (Review). Int J Mol Med. 1999 May;3(5):455-66. | |||||
| REF 19 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Convergence Pharmaceuticals Ltd. | |||||
| REF 20 | N,N-dialkyl-dipeptidylamines as novel N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Mar 22;9(6):907-12. | |||||
| REF 21 | CNSB004 (Leconotide) causes antihyperalgesia without side effects when given intravenously: a comparison with ziconotide in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2010 Feb;11(2):262-73. | |||||
| REF 22 | US patent application no. 2012,0172,429, Permanently charged sodium and calcium channel blockers as anti- inflammatory agents. | |||||
| REF 23 | Synthesis and biological activity of substituted bis-(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanes as N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Aug 16;9(16):2447-52. | |||||
| REF 24 | Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines as N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998 Sep 22;8(18):2415-8. | |||||
| REF 25 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800008159) | |||||
| REF 26 | Treatment with conotoxin, an 'N-type' calcium channel blocker, in neuronal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 24;537(1-2):256-62. | |||||
| REF 27 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 533). | |||||
| REF 28 | Discovery of potent T-type calcium channel blocker. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Nov 1;17(21):5740-3. | |||||
| REF 29 | Novel omega-conotoxins from Conus catus discriminate among neuronal calcium channel subtypes. J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 10;275(45):35335-44. | |||||
| REF 30 | Synthesis of a series of 4-benzyloxyaniline analogues as neuronal N-type calcium channel blockers with improved anticonvulsant and analgesic proper... J Med Chem. 1999 Oct 7;42(20):4239-49. | |||||
| REF 31 | Analgesic effects of a substituted N-triazole oxindole (TROX-1), a state-dependent, voltage-gated calcium channel 2 blocker. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Aug;334(2):545-55. | |||||
| REF 32 | Structure of human Ca(v)2.2 channel blocked by the painkiller ziconotide. Nature. 2021 Aug;596(7870):143-147. | |||||
| REF 33 | Closed-state inactivation and pore-blocker modulation mechanisms of human Ca(V)2.2. Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 2;37(5):109931. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

