Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T48069
(Former ID: TTDS00269)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF1R)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor; Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IGF-IR; IGF-I receptor; IGF-1R; IGF-1 receptor; CD221 antigen; CD221
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IGF1R
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Multiple structural anomalies syndrome [ICD-11: LD2F] | |||||
| 2 | Pituitary gland disorder [ICD-11: 5A60-5A61] | |||||
| 3 | Thyrotoxicosis [ICD-11: 5A02] | |||||
| Function |
Binds IGF1 with high affinity and IGF2 and insulin (INS) with a lower affinity. The activated IGF1R is involved in cell growth and survival control. IGF1R is crucial for tumor transformation and survival of malignant cell. Ligand binding activates the receptor kinase, leading to receptor autophosphorylation, and tyrosines phosphorylation of multiple substrates, that function as signaling adapter proteins including, the insulin-receptor substrates (IRS1/2), Shc and 14-3-3 proteins. Phosphorylation of IRSs proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway and the Ras-MAPK pathway. The result of activating the MAPK pathway is increased cellular proliferation, whereas activating the PI3K pathway inhibits apoptosis and stimulates protein synthesis. Phosphorylated IRS1 can activate the 85 kDa regulatory subunit of PI3K (PIK3R1), leading to activation of several downstream substrates, including protein AKT/PKB. AKT phosphorylation, in turn, enhances protein synthesis through mTOR activation and triggers the antiapoptotic effects of IGFIR through phosphorylation and inactivation of BAD. In parallel to PI3K-driven signaling, recruitment of Grb2/SOS by phosphorylated IRS1 or Shc leads to recruitment of Ras and activation of the ras-MAPK pathway. In addition to these two main signaling pathways IGF1R signals also through the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway (JAK/STAT). Phosphorylation of JAK proteins can lead to phosphorylation/activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins. In particular activation of STAT3, may be essential for the transforming activity of IGF1R. The JAK/STAT pathway activates gene transcription and may be responsible for the transforming activity. JNK kinases can also be activated by the IGF1R. IGF1 exerts inhibiting activities on JNK activation via phosphorylation and inhibition of MAP3K5/ASK1, which is able to directly associate with the IGF1R. Receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates actions of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MKSGSGGGSPTSLWGLLFLSAALSLWPTSGEICGPGIDIRNDYQQLKRLENCTVIEGYLH
ILLISKAEDYRSYRFPKLTVITEYLLLFRVAGLESLGDLFPNLTVIRGWKLFYNYALVIF EMTNLKDIGLYNLRNITRGAIRIEKNADLCYLSTVDWSLILDAVSNNYIVGNKPPKECGD LCPGTMEEKPMCEKTTINNEYNYRCWTTNRCQKMCPSTCGKRACTENNECCHPECLGSCS APDNDTACVACRHYYYAGVCVPACPPNTYRFEGWRCVDRDFCANILSAESSDSEGFVIHD GECMQECPSGFIRNGSQSMYCIPCEGPCPKVCEEEKKTKTIDSVTSAQMLQGCTIFKGNL LINIRRGNNIASELENFMGLIEVVTGYVKIRHSHALVSLSFLKNLRLILGEEQLEGNYSF YVLDNQNLQQLWDWDHRNLTIKAGKMYFAFNPKLCVSEIYRMEEVTGTKGRQSKGDINTR NNGERASCESDVLHFTSTTTSKNRIIITWHRYRPPDYRDLISFTVYYKEAPFKNVTEYDG QDACGSNSWNMVDVDLPPNKDVEPGILLHGLKPWTQYAVYVKAVTLTMVENDHIRGAKSE ILYIRTNASVPSIPLDVLSASNSSSQLIVKWNPPSLPNGNLSYYIVRWQRQPQDGYLYRH NYCSKDKIPIRKYADGTIDIEEVTENPKTEVCGGEKGPCCACPKTEAEKQAEKEEAEYRK VFENFLHNSIFVPRPERKRRDVMQVANTTMSSRSRNTTAADTYNITDPEELETEYPFFES RVDNKERTVISNLRPFTLYRIDIHSCNHEAEKLGCSASNFVFARTMPAEGADDIPGPVTW EPRPENSIFLKWPEPENPNGLILMYEIKYGSQVEDQRECVSRQEYRKYGGAKLNRLNPGN YTARIQATSLSGNGSWTDPVFFYVQAKTGYENFIHLIIALPVAVLLIVGGLVIMLYVFHR KRNNSRLGNGVLYASVNPEYFSAADVYVPDEWEVAREKITMSRELGQGSFGMVYEGVAKG VVKDEPETRVAIKTVNEAASMRERIEFLNEASVMKEFNCHHVVRLLGVVSQGQPTLVIME LMTRGDLKSYLRSLRPEMENNPVLAPPSLSKMIQMAGEIADGMAYLNANKFVHRDLAARN CMVAEDFTVKIGDFGMTRDIYETDYYRKGGKGLLPVRWMSPESLKDGVFTTYSDVWSFGV VLWEIATLAEQPYQGLSNEQVLRFVMEGGLLDKPDNCPDMLFELMRMCWQYNPKMRPSFL EIISSIKEEMEPGFREVSFYYSEENKLPEPEELDLEPENMESVPLDPSASSSSLPLPDRH SGHKAENGPGPGVLVLRASFDERQPYAHMNGGRKNERALPLPQSSTC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T42XY2 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 3 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Mecasermin | Drug Info | Approved | Growth failure | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Somatomedin-1 | Drug Info | Approved | Hormone deficiency | [4] | |
| 3 | Teprotumumab | Drug Info | Approved | Graves disease | [5] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 16 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | OSI-906 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Solid tumour/cancer | [6], [7] | |
| 2 | Rinfabate | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Solid tumour/cancer | [8] | |
| 3 | AMG 479 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Breast cancer | [9] | |
| 4 | AXL-1717 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [10], [11] | |
| 5 | Cixutumumab | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Non-small-cell lung cancer | [12] | |
| 6 | MM-141 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [13] | |
| 7 | R1507 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Graves ophthalmopathy | [14] | |
| 8 | TT-100 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Non-small-cell lung cancer | [15] | |
| 9 | VPI-2690B | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic nephropathy | [16] | |
| 10 | AEW-541 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Multiple myeloma | [17] | |
| 11 | BIIB 022 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Non-small-cell lung cancer | [18] | |
| 12 | Cyclolignan picropodophyllin | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Colorectal cancer | [19] | |
| 13 | FPI-1434 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [20] | |
| 14 | HF-0299 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Pain | [21] | |
| 15 | RG-7010 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Motor neurone disease | [22] | |
| 16 | SAR446159 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Parkinson disease | [23] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 3 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AVE-1642 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Breast cancer | [24] | |
| 2 | KW-2450 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1/2 | Breast cancer | [25] | |
| 3 | Figitumumab | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Malignant adrenal gland cancer | [26] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 2 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BMS-695735 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Solid tumour/cancer | [27] | |
| 2 | EGFR/IGFR tandem adnectin | Drug Info | Preclinical | Solid tumour/cancer | [28] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 19 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Mecasermin | Drug Info | [1], [29], [30], [31] | |||
| 2 | OSI-906 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 3 | AMG 479 | Drug Info | [34], [35] | |||
| 4 | AXL-1717 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 5 | R1507 | Drug Info | [39], [40] | |||
| 6 | TT-100 | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 7 | AEW-541 | Drug Info | [42], [43], [44] | |||
| 8 | Cyclolignan picropodophyllin | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 9 | Figitumumab | Drug Info | [51], [52] | |||
| 10 | BMS-695735 | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 11 | EGFR/IGFR tandem adnectin | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 12 | 4-((1H-indazol-6-ylamino)methyl)benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 13 | 4-((naphthalen-2-ylamino)methyl)benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 14 | Alpha-D-Mannose | Drug Info | [56] | |||
| 15 | AMP-PNP | Drug Info | [57] | |||
| 16 | BMS-536924 | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| 17 | Fucose | Drug Info | [56] | |||
| 18 | JB-1 | Drug Info | [59] | |||
| 19 | NVP-ADW742 | Drug Info | [59] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 7 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Somatomedin-1 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 2 | Rinfabate | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 3 | Cixutumumab | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 4 | MM-141 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 5 | HF-0299 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 6 | RG-7010 | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 7 | KW-2450 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 3 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Teprotumumab | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 2 | VPI-2690B | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | BIIB 022 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: BMS-754807 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R-WT) complex with BMS-754807 [1-(4-((5-cyclopropyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino)pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl)-N-(6-fluoro-3-pyridinyl)-2-methyl-L-prolinamide] | PDB:3I81 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.08 Å | Mutation | No | [60] |
| PDB Sequence |
DVYVPDEWEV
964 AREKITMSRE974 LGQGSFGMVY984 EGVAKGVVKD994 EPETRVAIKT1004 VNEAASMRER 1014 IEFLNEASVM1024 KEFNCHHVVR1034 LLGVVSQGQP1044 TLVIMELMTR1054 GDLKSYLRSL 1064 RPEENNPVLA1075 PPSLSKMIQM1085 AGEIADGMAY1095 LNANKFVHRD1105 LAARNCMVAE 1115 DFTVKIGDFG1125 MTRDIYETDY1135 YRLLPVRWMS1150 PESLKDGVFT1160 TYSDVWSFGV 1170 VLWEIATLAE1180 QPYQGLSNEQ1190 VLRFVMEGGL1200 LDKPDNCPDM1210 LFELMRMCWQ 1220 YNPKMRPSFL1230 EIISSIKEEM1240 EPGFREVSFY1250 YSEENK
|
|||||
|
|
LEU975
3.488
GLY976
3.813
GLN977
3.471
GLY978
4.828
VAL983
3.531
ALA1001
3.444
LYS1003
4.050
VAL1033
4.472
MET1049
3.552
GLU1050
2.880
LEU1051
3.929
MET1052
2.995
THR1053
3.305
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: AEW-541 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of NVP-AEW541 in complex with IGF-1R kinase | PDB:5HZN | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.20 Å | Mutation | Yes | [61] |
| PDB Sequence |
AADVYVPDEW
989 EVAREKITMS999 RELGQGSFGM1009 VYEGVAKGVV1019 KDEPETRVAI1029 KTVNEAASMR 1039 ERIEFLNEAS1049 VMKEFNCHHV1059 VRLLGVVSQG1069 QPTLVIMELM1079 TRGDLKSYLR 1089 SLRPAPPSLS1107 KMIQMAGEIA1117 DGMAYLNANK1127 FVHRDLAARN1137 CMVAEDFTVK 1147 IGDFGMTRDI1157 YETDYYRKGG1167 KGLLPVRWMS1177 PESLKDGVFT1187 TYSDVWSFGV 1197 VLWEIATLAE1207 QPYQGLSNEQ1217 VLRFVMEGGL1227 LDKPDNCPDM1237 LFELMRMCWQ 1247 YNPKMRPSFL1257 EIISSIKEEM1267 EPGFREVSFY1277 YSEENK
|
|||||
|
|
LEU1002
3.785
GLY1003
3.123
GLN1004
3.449
GLY1005
3.529
SER1006
4.196
PHE1007
3.667
VAL1010
3.868
ALA1028
3.484
LYS1030
2.596
PHE1044
3.829
GLU1047
3.511
ALA1048
4.207
MET1051
3.979
VAL1060
3.590
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
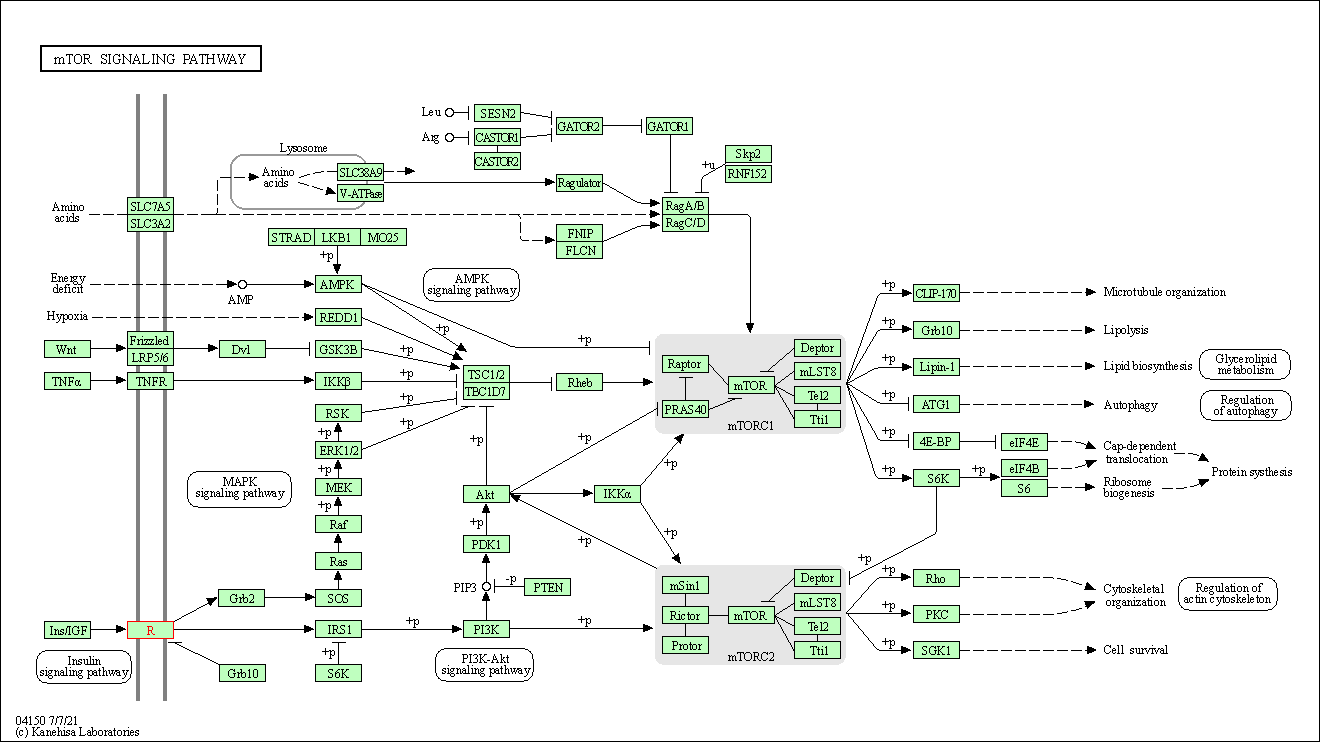
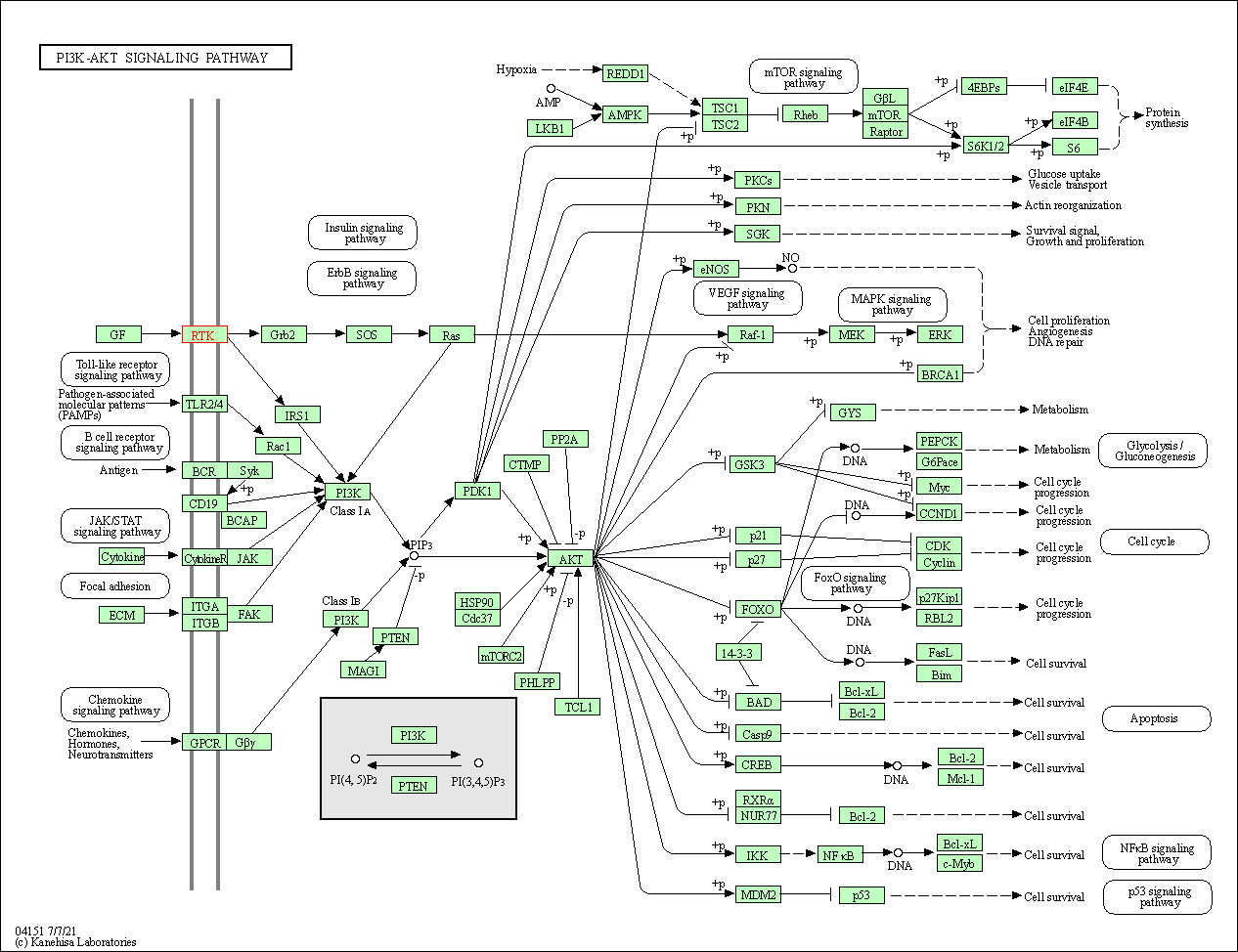
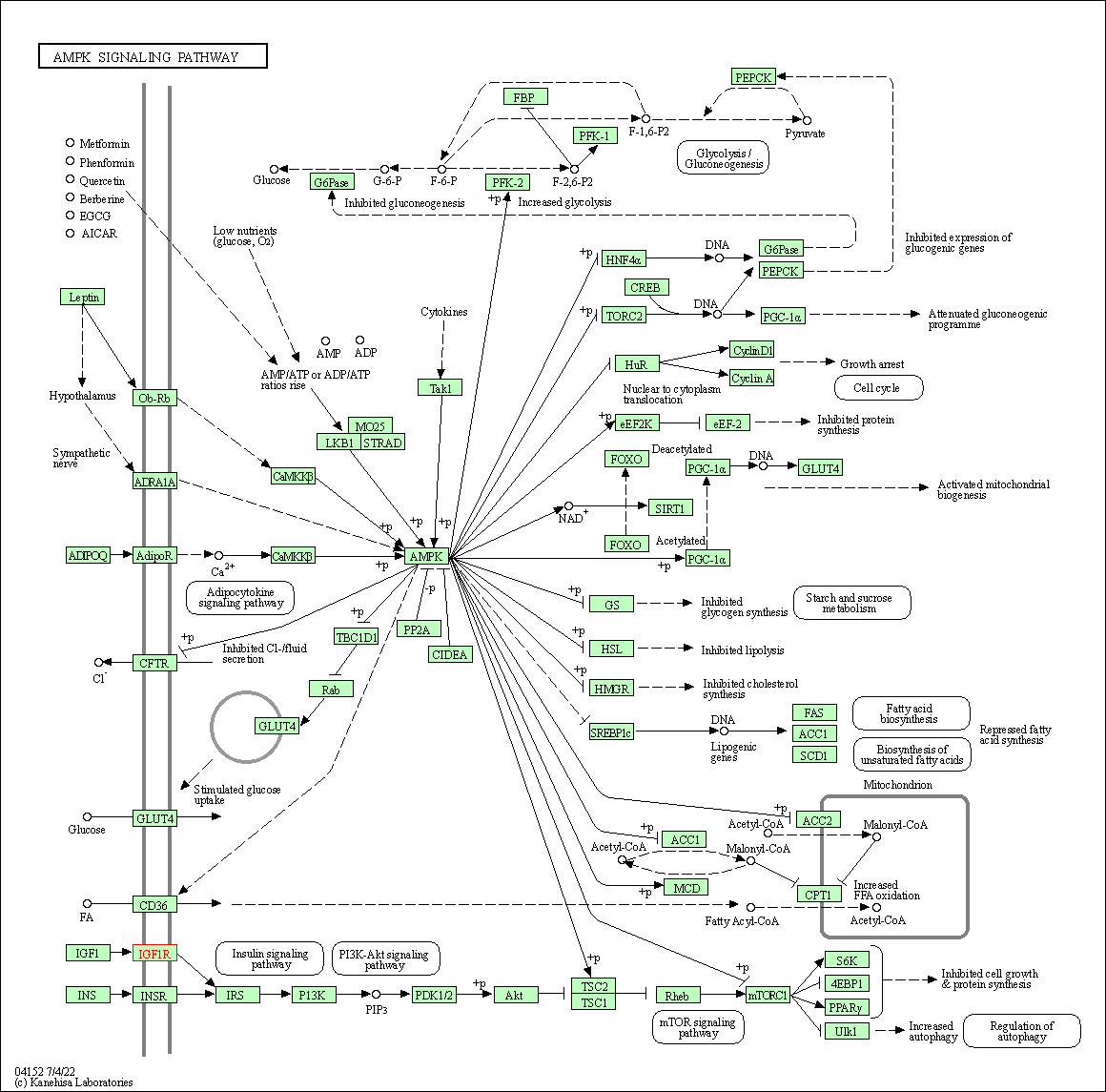
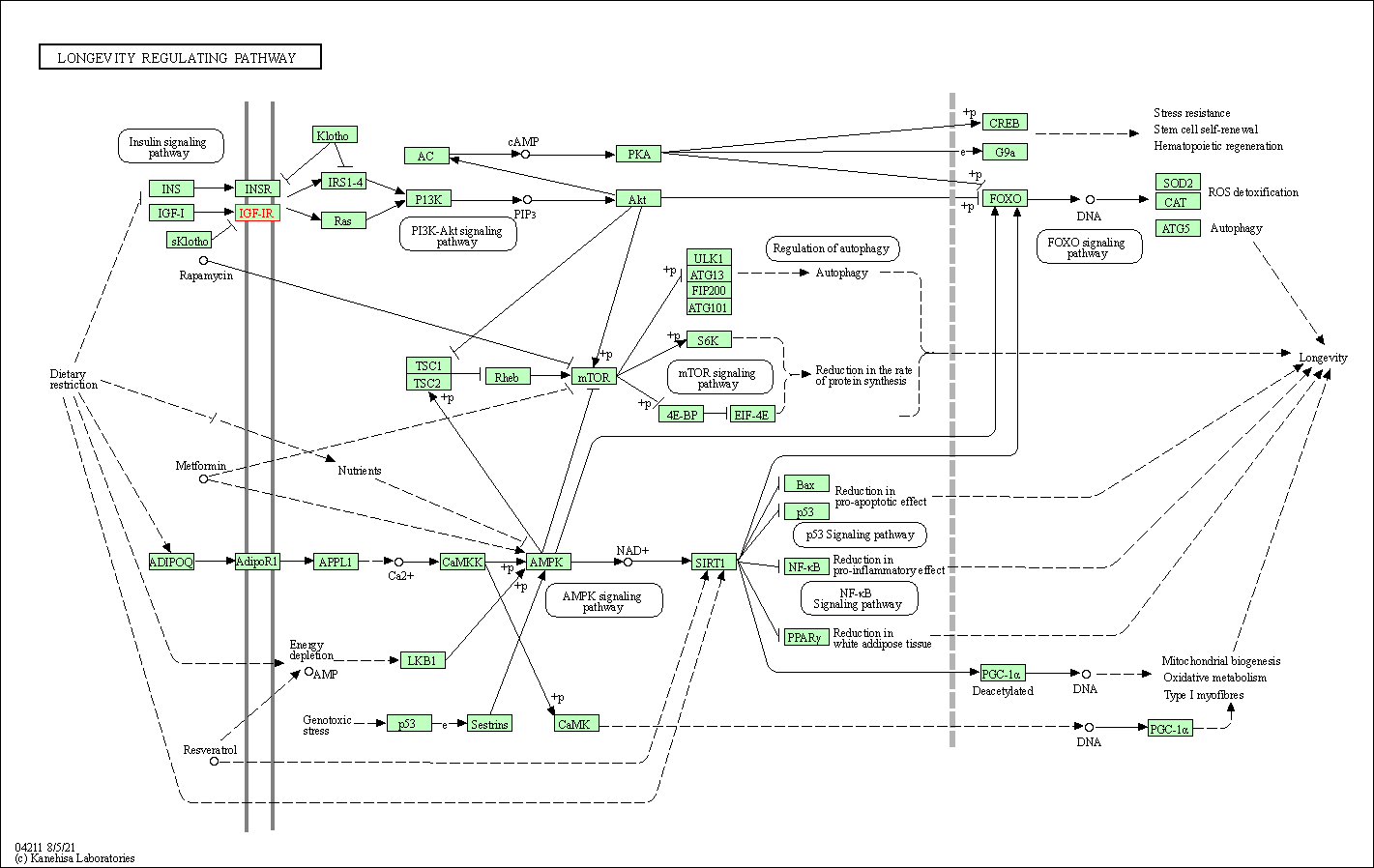
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
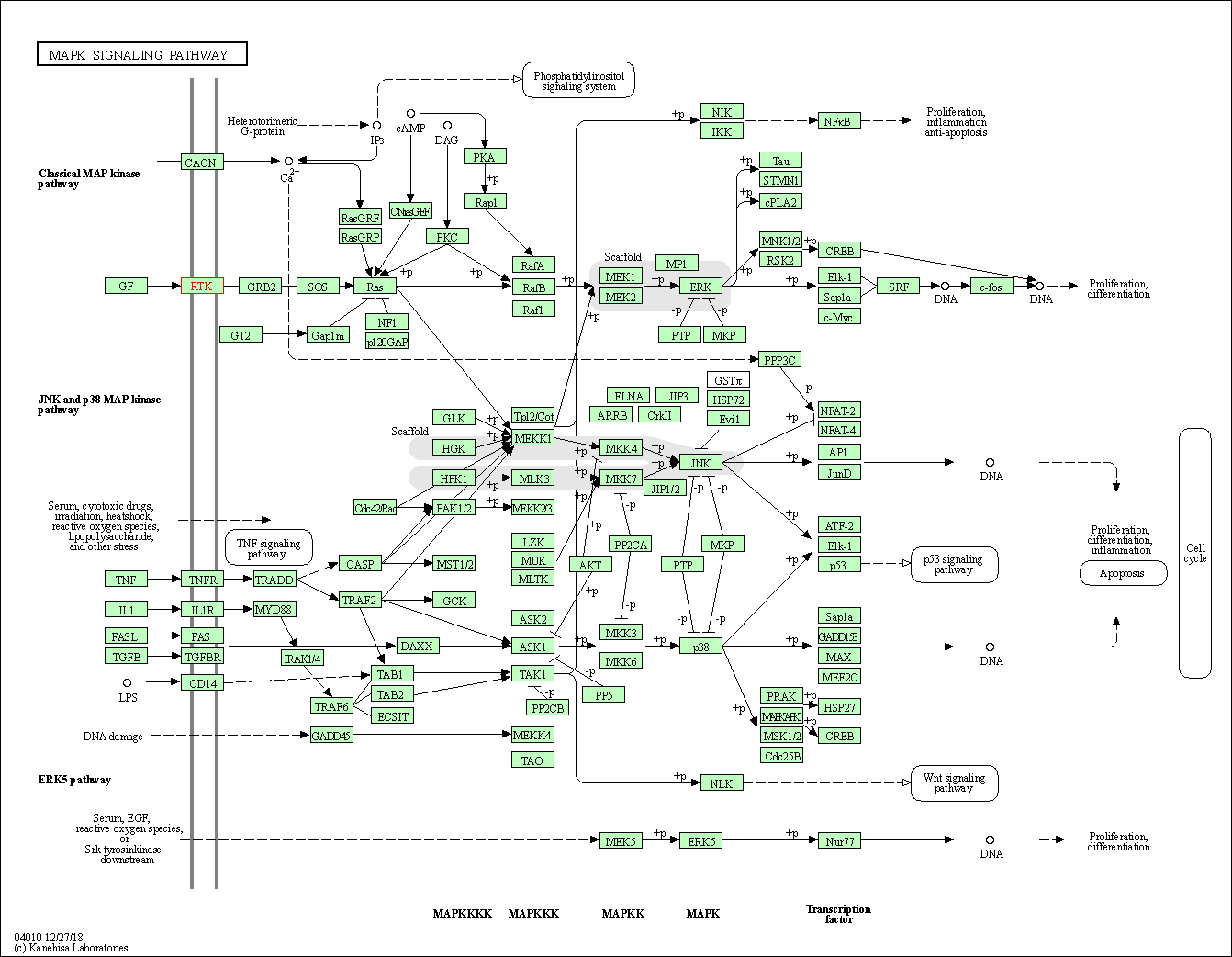
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
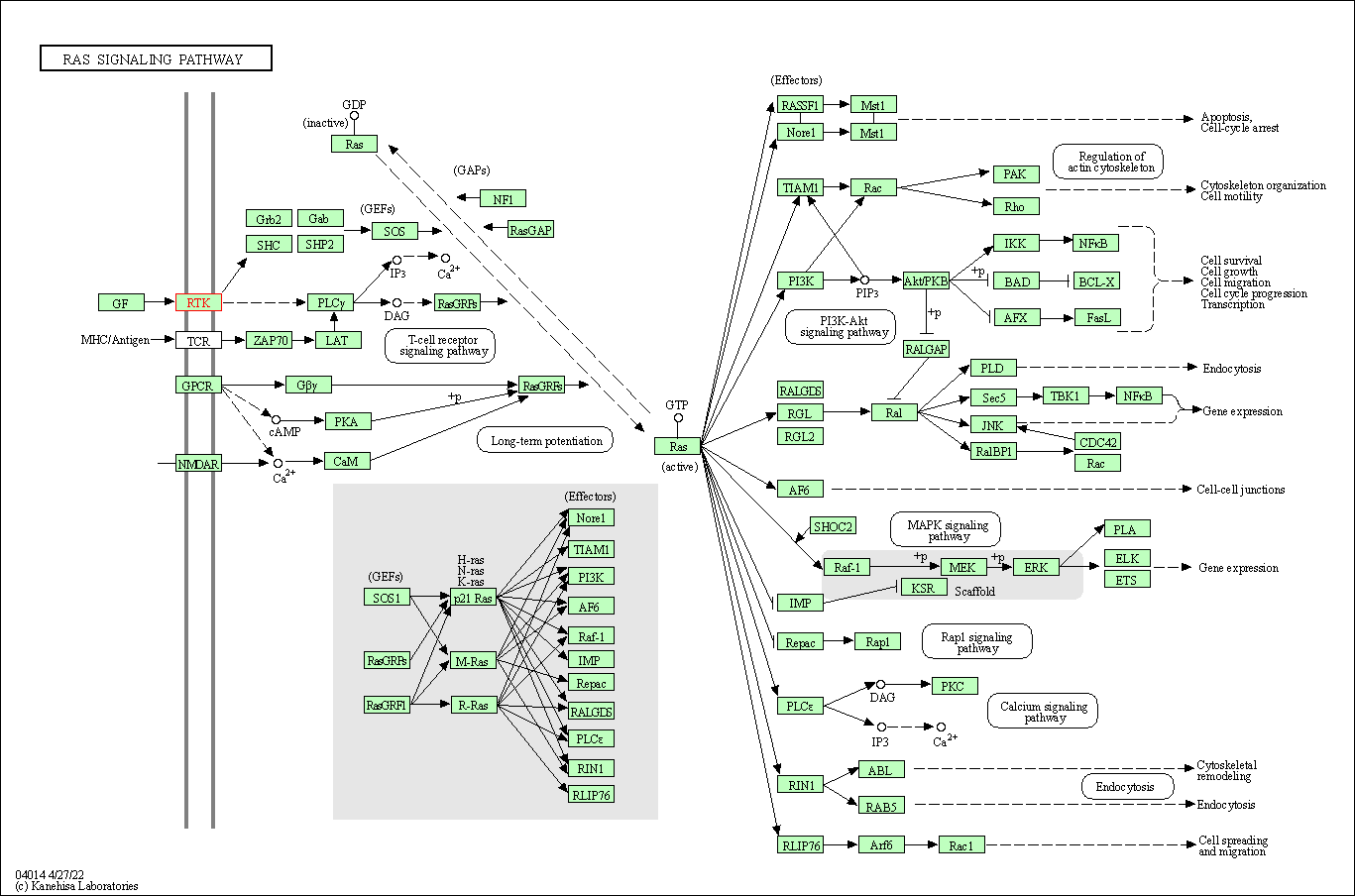
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
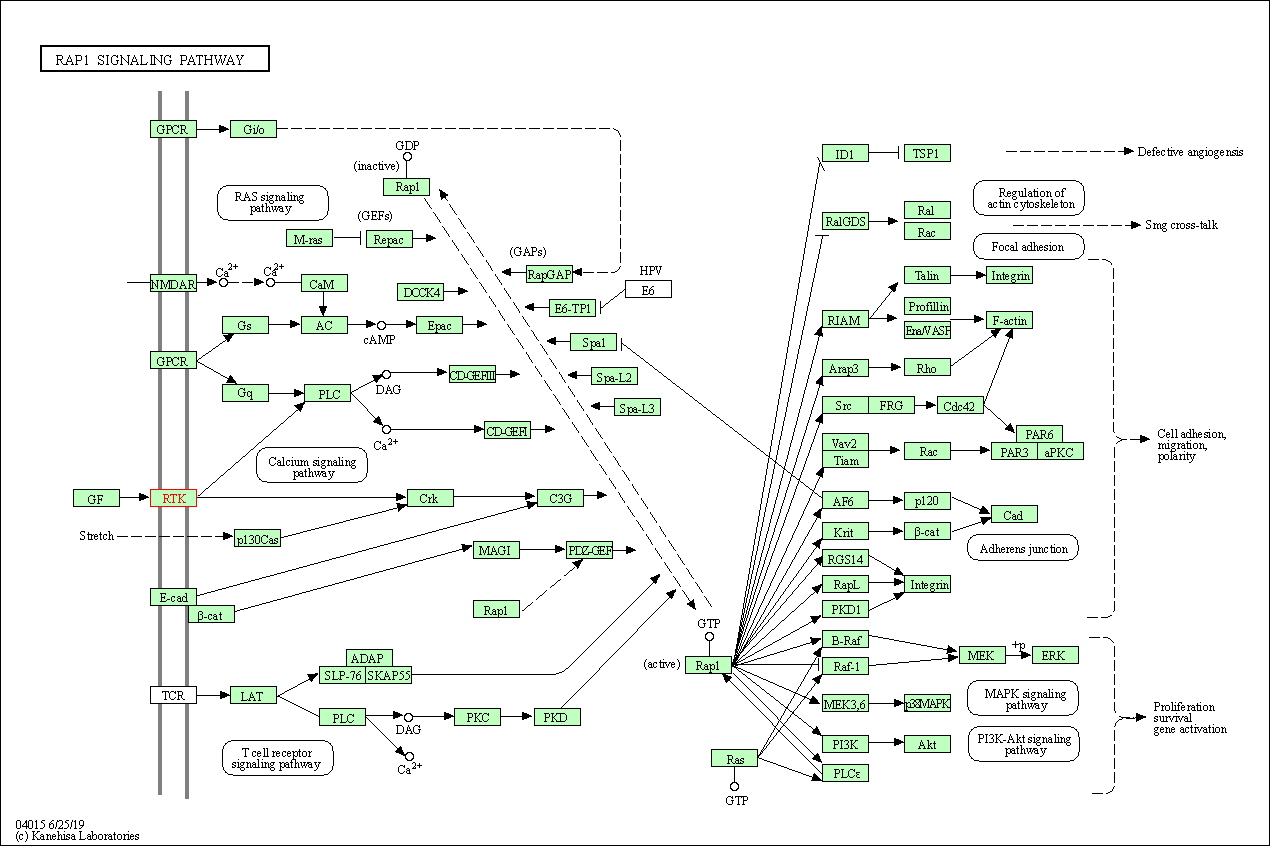
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
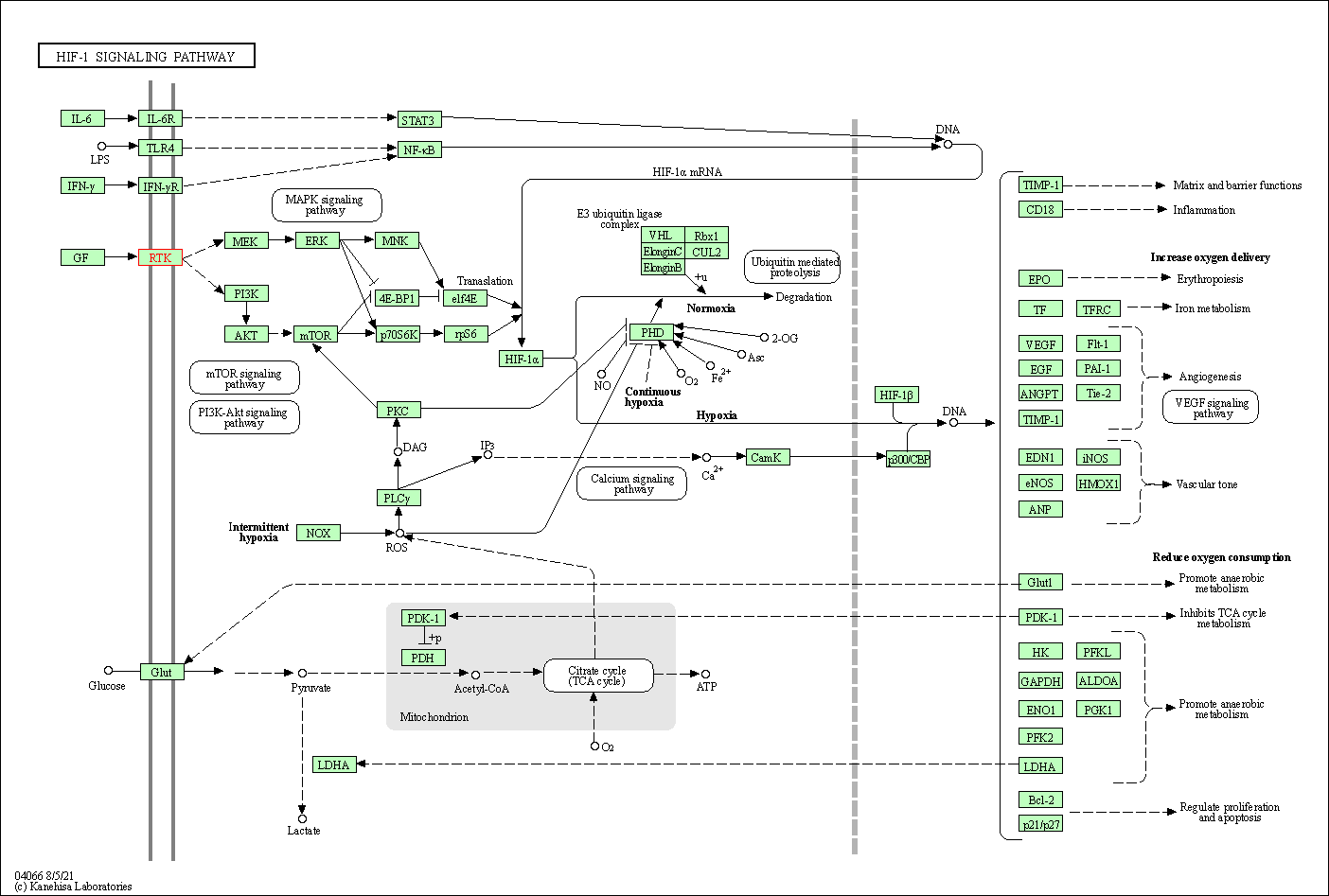
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oocyte meiosis | hsa04114 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Endocytosis | hsa04144 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
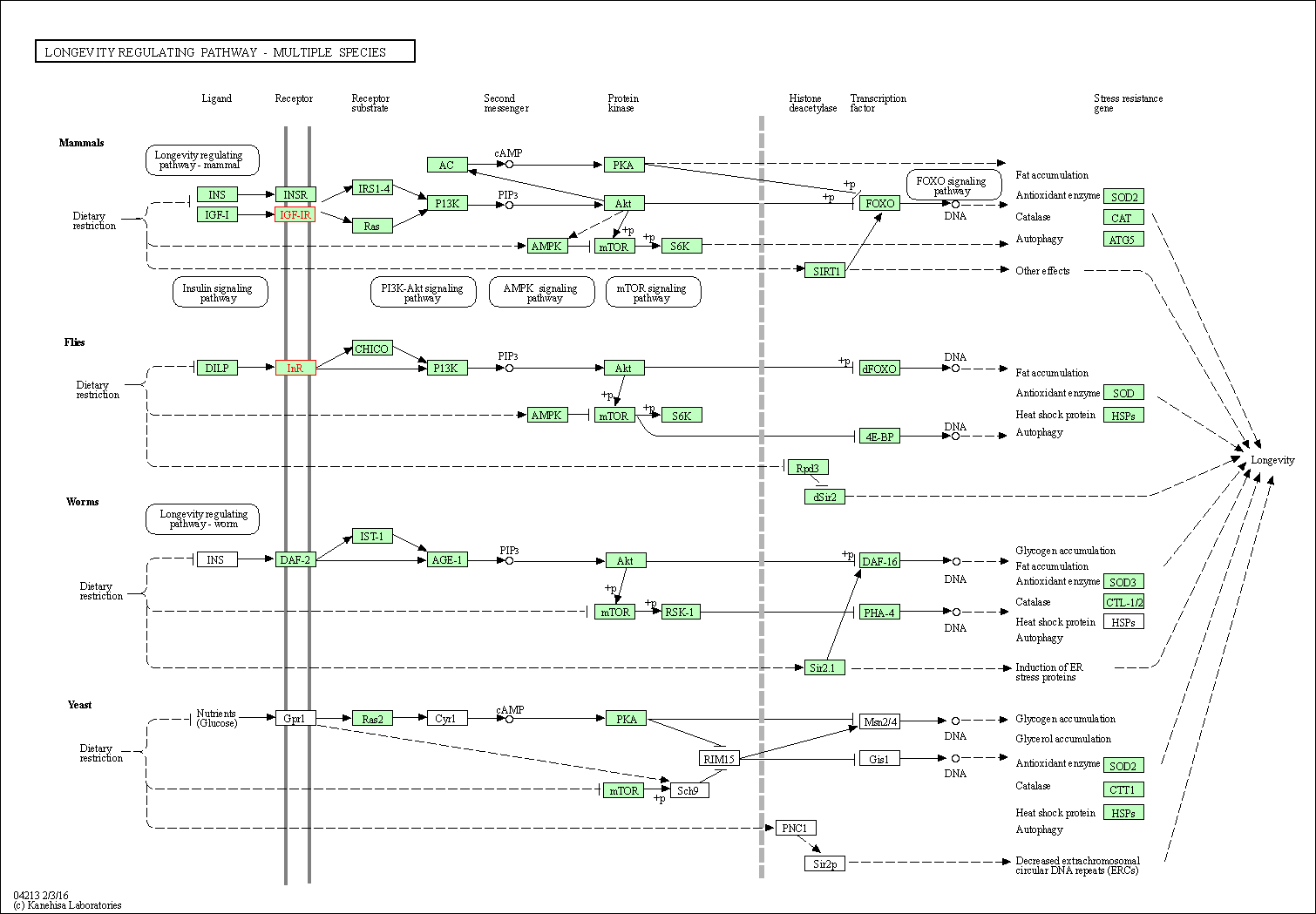
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | hsa04213 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
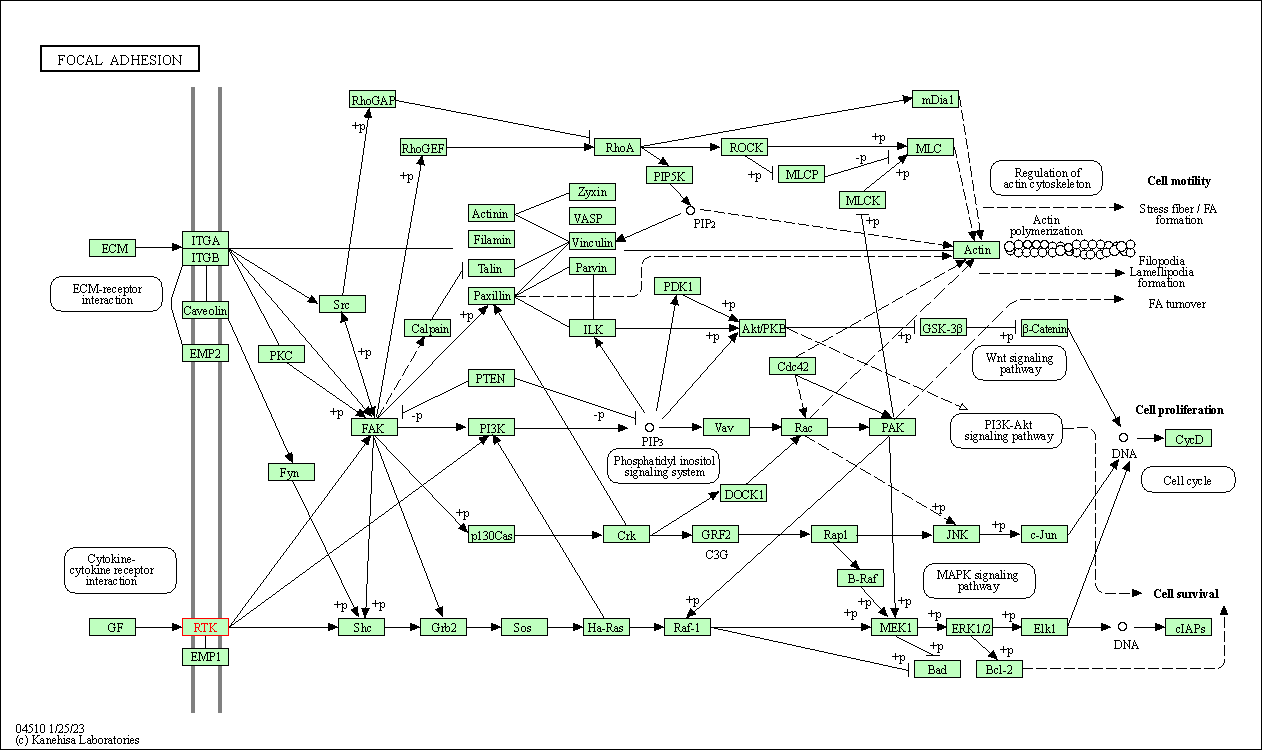
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
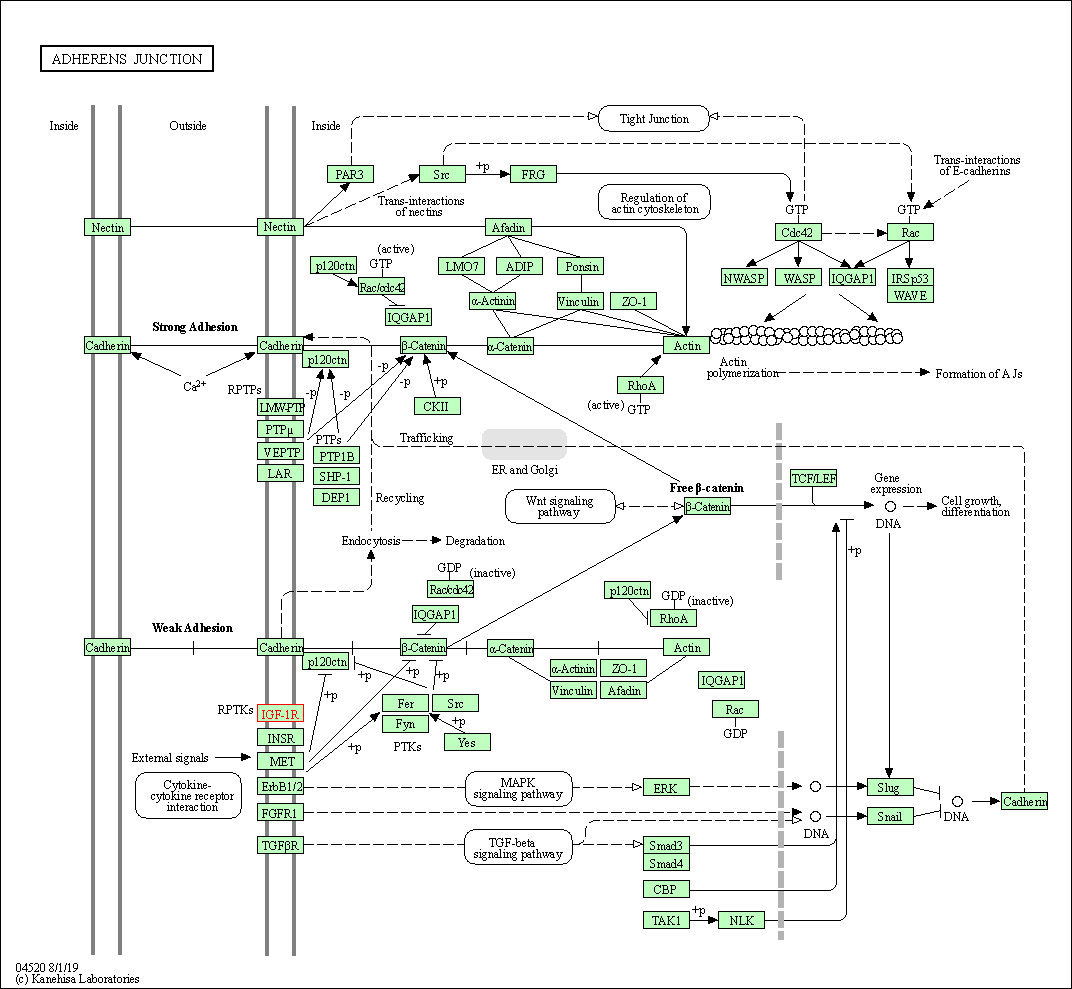
| Adherens junction | hsa04520 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
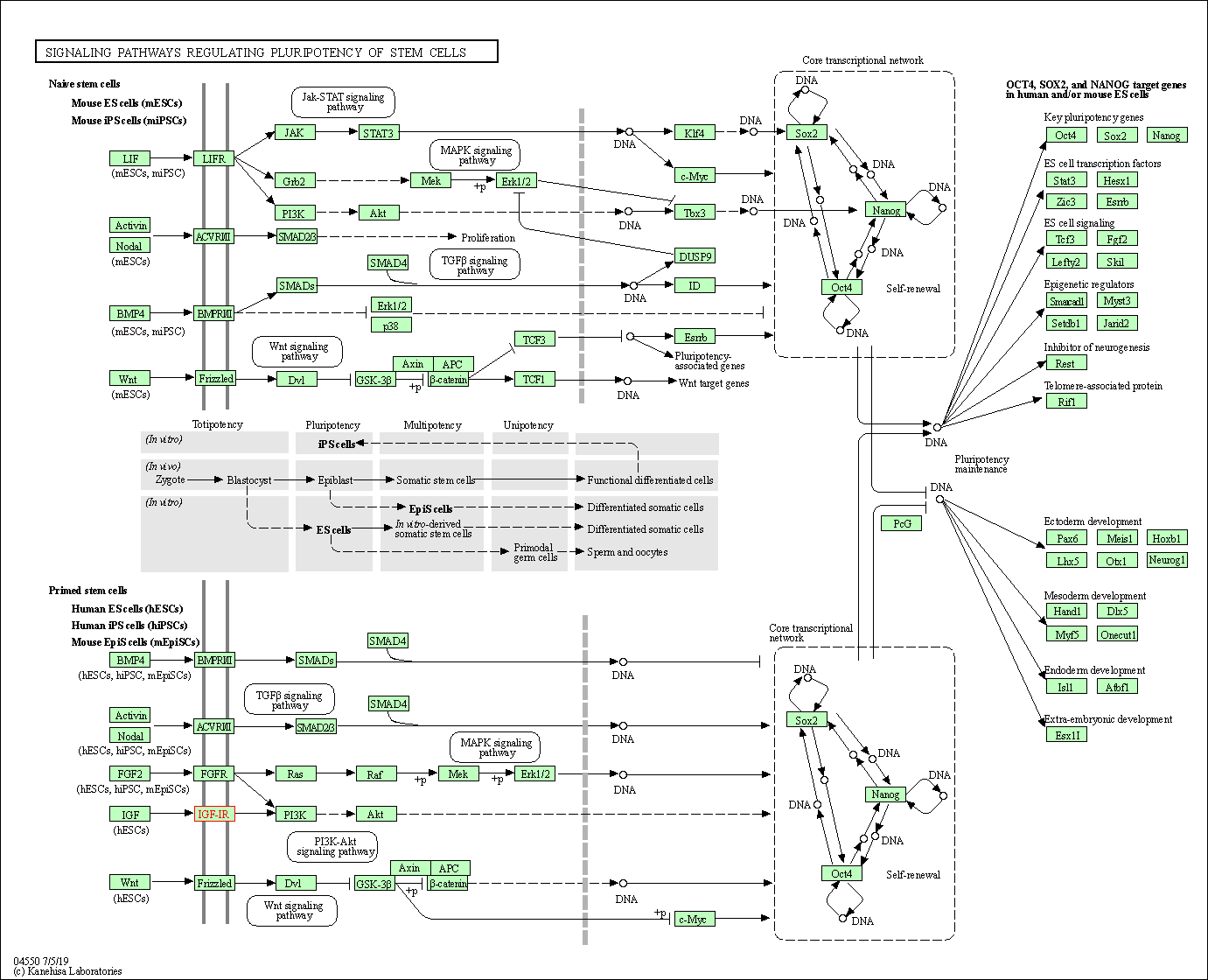
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | hsa04913 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 28 | Degree centrality | 3.01E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.30E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.59E-01 | Radiality | 1.45E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.12E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.31E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.28E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | IGF-1R, IGF-1 and IGF-2 expression as potential prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal-cancer. Virchows Arch. 2003 Aug;443(2):139-45. | |||||
| REF 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 3 | 2005 approvals: Safety first. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 5, 92-93 (February 2006). | |||||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2020 | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7423). | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00924989) A Study of OSI-906 in Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Adrenocortical Carcinoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00368173) IGF-I/IGFBP-3 Therapy in Children and Adolescents With Growth Hormone Insenitivity Syndrome (GHIS) Such as Laron Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800024318) | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7873). | |||||
| REF 11 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01561456) Study of AXL1717 Compared to Docetaxel to Treat Squamous Cell Carcinoma or Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01232452) A Study in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02399137) A Phase 2 Study of MM-141 Plus Nab-paclitaxel and Gemcitabine in Front-line Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800015801) | |||||
| REF 15 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021633) | |||||
| REF 16 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 17 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800019974) | |||||
| REF 18 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800027382) | |||||
| REF 19 | Potent inhibitory effect of the cyclolignan picropodophyllin (PPP) on human adrenocortical carcinoma cells proliferation. Am J Cancer Res. 2011; 1(3): 356-361. | |||||
| REF 20 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03746431) A Phase 1 Study of [225Ac]-FPI-1434 Injection. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 21 | A primary adrenal steroid, 11beta-hydroxyandrostenedione, has an osteotropic effect and little androgenic activity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 15;74(4):203-11. | |||||
| REF 22 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800031207) | |||||
| REF 23 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Sanofi | |||||
| REF 24 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021953) | |||||
| REF 25 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800030562) | |||||
| REF 26 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800020634) | |||||
| REF 27 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800022289) | |||||
| REF 28 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026610) | |||||
| REF 29 | One of two chondrocyte-expressed isoforms of cartilage intermediate-layer protein functions as an insulin-like growth factor 1 antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 May;48(5):1302-14. | |||||
| REF 30 | Analysis of the human type I insulin-like growth factor receptor promoter region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1113-20. | |||||
| REF 31 | Insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene structure. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10759-63. | |||||
| REF 32 | Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazoles: multitargeted inhibitors of both the insulin-like growth factor receptor and members of the epidermal growth factor family... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Apr 15;20(8):2452-5. | |||||
| REF 33 | Mecasermin rinfabate: insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, mecaserimin rinfibate, rhIGF-I/rhIGFBP-3. Drugs R D. 2005;6(2):120-7. | |||||
| REF 34 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Amgen (2009). | |||||
| REF 35 | AMG 479, a fully human anti-insulin-like growth factor receptor type I monoclonal antibody, inhibits the growth and survival of pancreatic carcinom... Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 May;8(5):1095-105. | |||||
| REF 36 | Clinical Phase I study with an Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 receptor inhibitor: experiences in patients with squamous non-small cell lung carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2011 Apr;50(3):441-7. | |||||
| REF 37 | Doxorubicin plus the IGF-1R antibody cixutumumab in soft tissue sarcoma: a phase I study using the TITE-CRM model. Ann Oncol. 2015 Jul;26(7):1459-64. | |||||
| REF 38 | MM-141, an IGF-IR- and ErbB3-directed bispecific antibody, overcomes network adaptations that limit activity of IGF-IR inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb;13(2):410-25. | |||||
| REF 39 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Roche (2009). | |||||
| REF 40 | National Cancer Institute. Dictionary of Cancer Terms. 2009. | |||||
| REF 41 | BiPar Sciences Co-founder Reunites Management Team At TriAct Therapeutics to Advance Clinical Stage Cancer Programs. TriAct Therapeutics. Sept. 10, 2009. | |||||
| REF 42 | A comparison of physicochemical property profiles of marketed oral drugs and orally bioavailable anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors in clinical development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(14):1408-22. | |||||
| REF 43 | Co-targeting the EGFR and IGF-IR with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody ICR62 and the IGF-IR tyrosine kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2008 Nov;33(5):1107-13. | |||||
| REF 44 | FAK and IGF-IR interact to provide survival signals in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 2008 Jun;29(6):1096-107. | |||||
| REF 45 | A phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study of BIIB022 (anti-IGF-1R monoclonal antibody) in subjects with relapsed or refractory solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 2014 Jun;32(3):518-25. | |||||
| REF 46 | The cyclolignan picropodophyllin attenuates intimal hyperplasia after rat carotid balloon injury by blocking insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling. J Vasc Surg. 2007 Jul;46(1):108-15. | |||||
| REF 47 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Fusion Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 48 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800031207) | |||||
| REF 49 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibition induces a resistance mechanism via the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER3/AKT signaling pathway: rational basis for cotargeting insulin-like growthfactor-1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Sep 1;15(17):5445-56. | |||||
| REF 50 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 51 | Pfizer. Product Development Pipeline. March 31 2009. | |||||
| REF 52 | National Cancer Institute. NCI Drug Dictionary. 2009 (CdrID=456793) | |||||
| REF 53 | Discovery and evaluation of 4-(2-(4-chloro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethylamino)-3-(6-(1-(3-fluoropropyl)piperidin-4-yl)-4-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)py... J Med Chem. 2008 Oct 9;51(19):5897-900. | |||||
| REF 54 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Bristol-Myers Squibb. | |||||
| REF 55 | ATP non-competitive IGF-1 receptor kinase inhibitors as lead anti-neoplastic and anti-papilloma agents. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 May 7;562(1-2):1-11. | |||||
| REF 56 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 57 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 58 | SAR of PXR transactivation in benzimidazole-based IGF-1R kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Mar 1;20(5):1744-8. | |||||
| REF 59 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | |||||
| REF 60 | Discovery of a 2,4-disubstituted pyrrolo[1,2-f][1,2,4]triazine inhibitor (BMS-754807) of insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) kinase in cli... J Med Chem. 2009 Dec 10;52(23):7360-3. | |||||
| REF 61 | Identification of a 5-[3-phenyl-(2-cyclic-ether)-methylether]-4-aminopyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine series of IGF-1R inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 15;26(8):2065-7. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

