Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T68163
(Former ID: TTDI02273)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn (JTK8)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
p56Lyn; p53Lyn; V-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral related oncogene homolog; Lck/Yes-related novel protein tyrosine kinase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
LYN
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Musculoskeletal system/connective tissue disease [ICD-11: FC0Z] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Functions primarily as negative regulator, but can also function as activator, depending on the context. Required for the initiation of the B-cell response, but also for its down-regulation and termination. Plays an important role in the regulation of B-cell differentiation, proliferation, survival and apoptosis, and is important for immune self-tolerance. Acts downstream of several immune receptors, including the B-cell receptor, CD79A, CD79B, CD5, CD19, CD22, FCER1, FCGR2, FCGR1A, TLR2 and TLR4. Plays a role in the inflammatory response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Mediates the responses to cytokines and growth factors in hematopoietic progenitors, platelets, erythrocytes, and in mature myeloid cells, such as dendritic cells, neutrophils and eosinophils. Acts downstream of EPOR, KIT, MPL, the chemokine receptor CXCR4, as well as the receptors for IL3, IL5 and CSF2. Plays an important role in integrin signaling. Regulates cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, migration, adhesion, degranulation, and cytokine release. Down-regulates signaling pathways by phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIM), that then serve as binding sites for phosphatases, such as PTPN6/SHP-1, PTPN11/SHP-2 and INPP5D/SHIP-1, that modulate signaling by dephosphorylation of kinases and their substrates. Phosphorylates LIME1 in response to CD22 activation. Phosphorylates BTK, CBL, CD5, CD19, CD72, CD79A, CD79B, CSF2RB, DOK1, HCLS1, LILRB3/PIR-B, MS4A2/FCER1B, SYK and TEC. Promotes phosphorylation of SIRPA, PTPN6/SHP-1, PTPN11/SHP-2 and INPP5D/SHIP-1. Mediates phosphorylation of the BCR-ABL fusion protein. Required for rapid phosphorylation of FER in response to FCER1 activation. Mediates KIT phosphorylation. Acts as an effector of EPOR (erythropoietin receptor) in controlling KIT expression and may play a role in erythroid differentiation during the switch between proliferation and maturation. Depending on the context, activates or inhibits several signaling cascades. Regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and AKT1 activation. Regulates activation of the MAP kinase signaling cascade, including activation of MAP2K1/MEK1, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1, MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK9/JNK2. Mediates activation of STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Phosphorylates LPXN on 'Tyr-72'. Kinase activity facilitates TLR4-TLR6 heterodimerization and signal initiation. Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that transmits signals from cell surface receptors and plays an important role in the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses, hematopoiesis, responses to growth factors and cytokines, integrin signaling, but also responses to DNA damage and genotoxic agents.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MGCIKSKGKDSLSDDGVDLKTQPVRNTERTIYVRDPTSNKQQRPVPESQLLPGQRFQTKD
PEEQGDIVVALYPYDGIHPDDLSFKKGEKMKVLEEHGEWWKAKSLLTKKEGFIPSNYVAK LNTLETEEWFFKDITRKDAERQLLAPGNSAGAFLIRESETLKGSFSLSVRDFDPVHGDVI KHYKIRSLDNGGYYISPRITFPCISDMIKHYQKQADGLCRRLEKACISPKPQKPWDKDAW EIPRESIKLVKRLGAGQFGEVWMGYYNNSTKVAVKTLKPGTMSVQAFLEEANLMKTLQHD KLVRLYAVVTREEPIYIITEYMAKGSLLDFLKSDEGGKVLLPKLIDFSAQIAEGMAYIER KNYIHRDLRAANVLVSESLMCKIADFGLARVIEDNEYTAREGAKFPIKWTAPEAINFGCF TIKSDVWSFGILLYEIVTYGKIPYPGRTNADVMTALSQGYRMPRVENCPDELYDIMKMCW KEKAEERPTFDYLQSVLDDFYTATEGQYQQQP Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T01CL0 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Bafetinib | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Bone disease | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | JNJ-26483327 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Bafetinib | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 4 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | JNJ-26483327 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 2 | Alkynyl-substituted pyrimidinyl-pyrrole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | NG-25 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 4 | PMID17600705C23 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Staurosporine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Lyn kinase domain | PDB:3A4O | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | No | [9] |
| PDB Sequence |
DAWEIPRESI
16 KLVKRLGAGQ26 FGEVWMGYYN36 NSTKVAVKTL46 KPGTMSVQAF56 LEEANLMKTL 66 QHDKLVRLYA76 VVTREEPIYI86 ITEYMAKGSL96 LDFLKSDEGG106 KVLLPKLIDF 116 SAQIAEGMAY126 IERKNYIHRD136 LRAANVLVSE146 SLMCKIADFG156 LARVEGAKFP 175 IKWTAPEAIN185 FGCFTIKSDV195 WSFGILLYEI205 VTYGKIPYPG215 RTNADVMTAL 225 SQGYRMPRVE235 NCPDELYDIM245 KMCWKEKAEE255 RPTFDYLQSV265 LDDFYTATE |
|||||
|
|
LEU22
3.674
GLY23
4.099
ALA24
4.976
VAL30
3.397
ALA42
3.882
LYS44
3.732
VAL72
4.063
THR88
3.536
GLU89
2.672
TYR90
2.997
MET91
2.866
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: N-(1h-Indazol-6-Yl)-8-Piperidin-4-Yloxy-6-Propyl-Quinazolin-2-Amine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of Lyn kinase domain in complex with N-(1H-indazol-6-yl)-8-(piperidin-4-yloxy)-6-propylquinazolin-2-amine | PDB:5XY1 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.70 Å | Mutation | No | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
SAWEIPRESI
247 KLVKRLGAGQ257 FGEVWMGYYN267 NSTKVAVKTL277 KPGTMSVQAF287 LEEANLMKTL 297 QHDKLVRLYA307 VVTREEPIYI317 ITEYMAKGSL327 LDFLKSDEGG337 KVLLPKLIDF 347 SAQIAEGMAY357 IERKNYIHRD367 LRAANVLVSE377 SLMCKIADFG387 LARVKFPIKW 409 TAPEAINFGC419 FTIKSDVWSF429 GILLYEIVTY439 GKIPYPGRTN449 ADVMTALSQG 459 YRMPRVENCP469 DELYDIMKMC479 WKEKAEERPT489 FDYLQSVLDD499 FYT |
|||||
|
|
LEU253
3.753
GLY254
4.502
VAL261
3.519
ALA273
3.386
LYS275
4.587
GLU290
3.228
MET294
3.749
VAL303
4.294
THR319
3.357
GLU320
3.441
TYR321
3.536
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
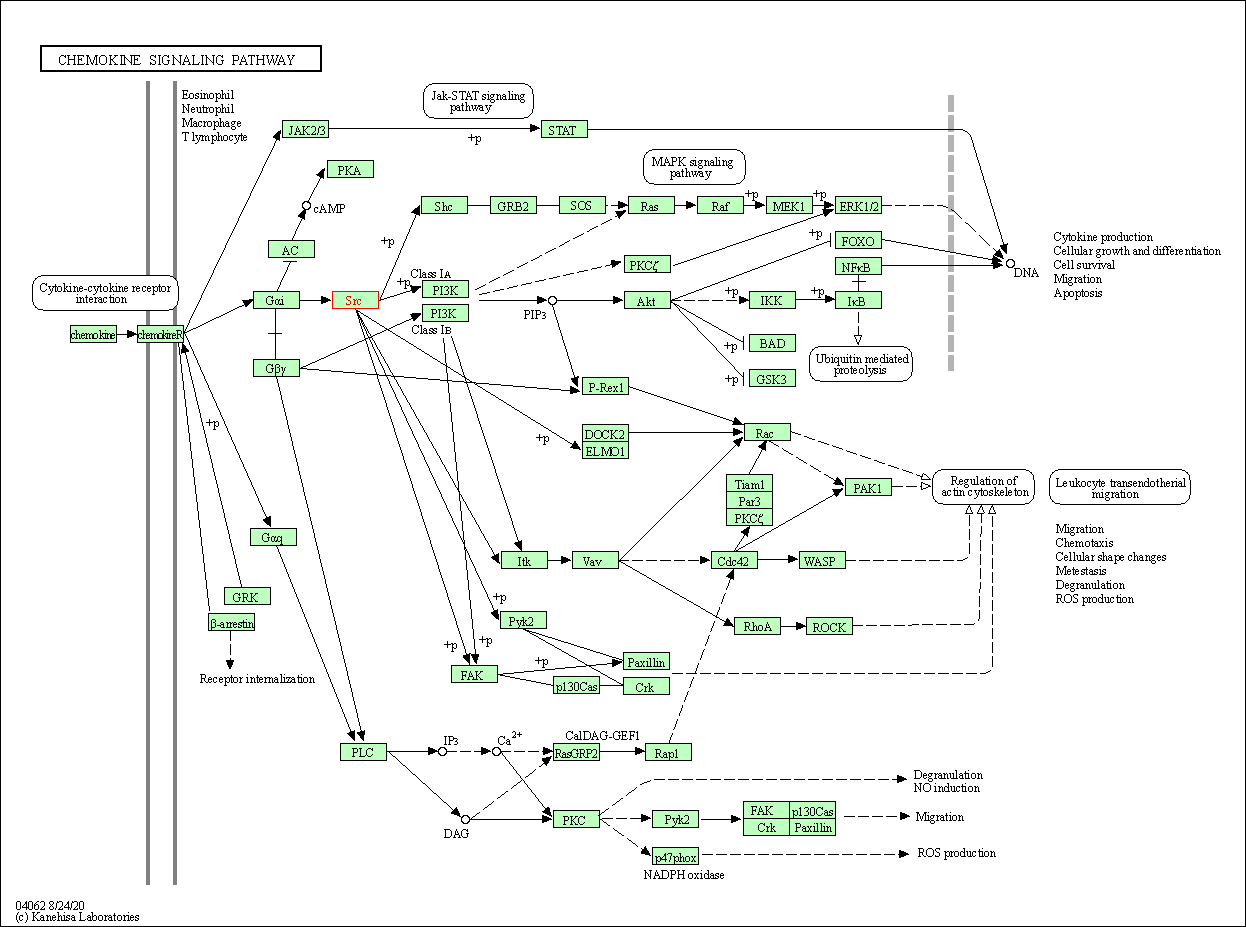


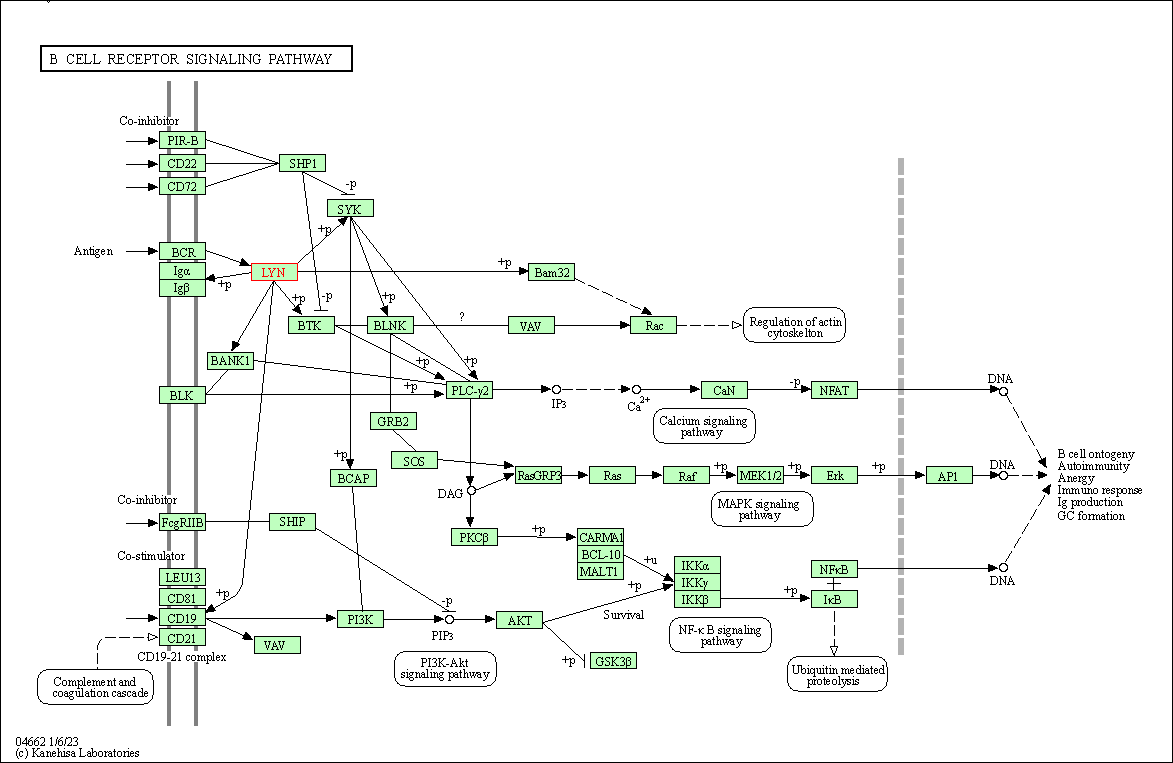
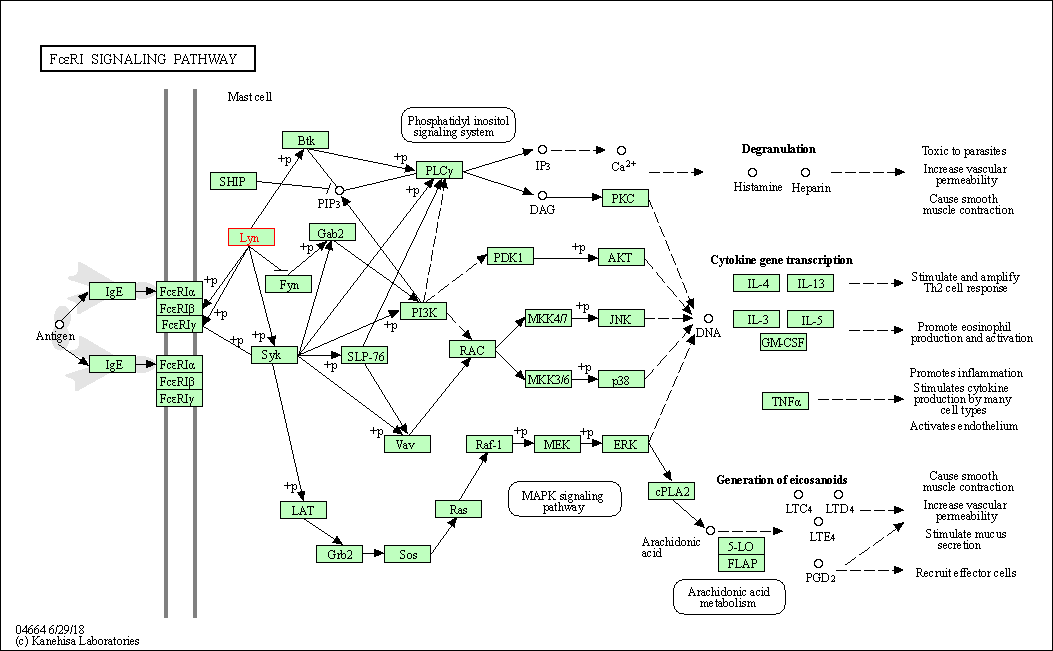

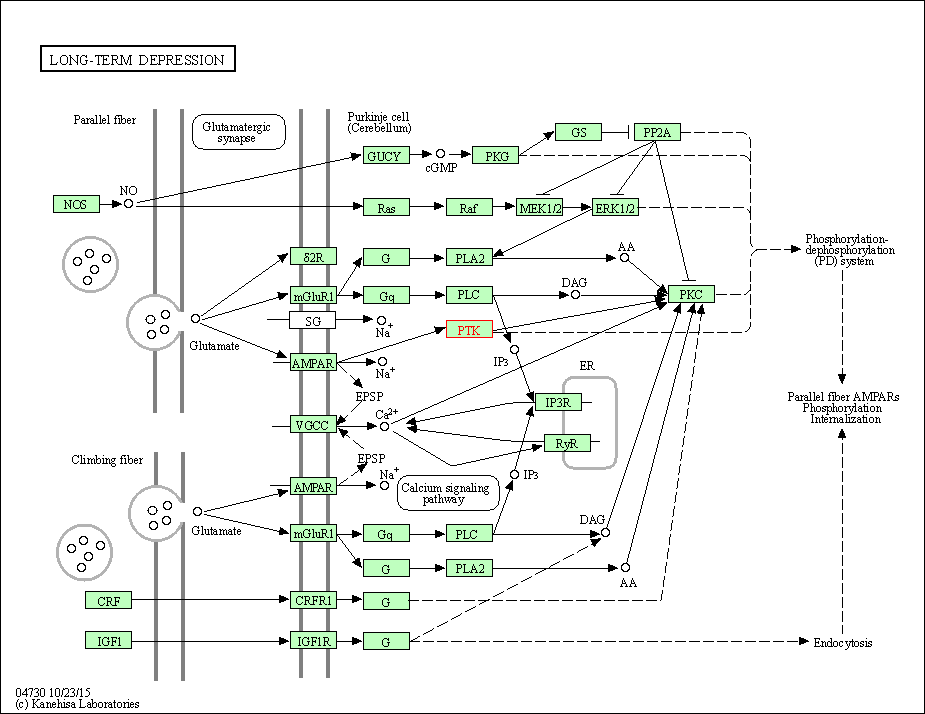
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 48 | Degree centrality | 5.16E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.12E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.53E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.55E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.73E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.37E-02 | Eccentricity | 10 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7906). | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01215799) Study of Bafetinib (INNO-406) as Treatment for Patients With Hormone-Refractory Prostate Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00676299) A Safety and Dose-finding Study of JNJ-26483327, a Drug in Development for Cancer, for Patients With Advanced and/or Refractory Solid Malignancies.. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary (drug id 596693). | |||||
| REF 6 | Inhibitors of JAK-family kinases: an update on the patent literature 2013-2015, part 2.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Feb;27(2):145-161. | |||||
| REF 7 | Discovery of type II inhibitors of TGFbeta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 2 (MAP4K2). J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 8;58(1):183-96. | |||||
| REF 8 | N-4-Pyrimidinyl-1H-indazol-4-amine inhibitors of Lck: indazoles as phenol isosteres with improved pharmacokinetics. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Aug 1;17(15):4363-8. | |||||
| REF 9 | Structural basis for the inhibitor recognition of human Lyn kinase domain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Dec 1;19(23):6557-60. | |||||
| REF 10 | Crystal structure of Lyn kinase domain in complex with N-(1H-indazol-6-yl)-8-(piperidin-4-yloxy)-6-propylquinazolin-2-amine | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

