Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T69619
(Former ID: TTDR00742)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Membrane copper amine oxidase (AOC3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Vascular adhesion protein-1; Vascular adhesion protein 1; VAP1; VAP-1; Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase; SSAO; Membrane primary amine oxidase; HPAO; Copper amine oxidase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
AOC3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00-BA04] | |||||
| Function |
Has semicarbazide-sensitive (SSAO) monoamine oxidase activity. May play a role in adipogenesis. Cell adhesion protein that participates in lymphocyte extravasation and recirculation by mediating the binding of lymphocytes to peripheral lymph node vascular endothelial cells in an L-selectin-independent fashion.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
CH-NH(2) donor oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.4.3.21
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MNQKTILVLLILAVITIFALVCVLLVGRGGDGGEPSQLPHCPSVSPSAQPWTHPGQSQLF
ADLSREELTAVMRFLTQRLGPGLVDAAQARPSDNCVFSVELQLPPKAAALAHLDRGSPPP AREALAIVFFGRQPQPNVSELVVGPLPHPSYMRDVTVERHGGPLPYHRRPVLFQEYLDID QMIFNRELPQASGLLHHCCFYKHRGRNLVTMTTAPRGLQSGDRATWFGLYYNISGAGFFL HHVGLELLVNHKALDPARWTIQKVFYQGRYYDSLAQLEAQFEAGLVNVVLIPDNGTGGSW SLKSPVPPGPAPPLQFYPQGPRFSVQGSRVASSLWTFSFGLGAFSGPRIFDVRFQGERLV YEISLQEALAIYGGNSPAAMTTRYVDGGFGMGKYTTPLTRGVDCPYLATYVDWHFLLESQ APKTIRDAFCVFEQNQGLPLRRHHSDLYSHYFGGLAETVLVVRSMSTLLNYDYVWDTVFH PSGAIEIRFYATGYISSAFLFGATGKYGNQVSEHTLGTVHTHSAHFKVDLDVAGLENWVW AEDMVFVPMAVPWSPEHQLQRLQVTRKLLEMEEQAAFLVGSATPRYLYLASNHSNKWGHP RGYRIQMLSFAGEPLPQNSSMARGFSWERYQLAVTQRKEEEPSSSSVFNQNDPWAPTVDF SDFINNETIAGKDLVAWVTAGFLHIPHAEDIPNTVTVGNGVGFFLRPYNFFDEDPSFYSA DSIYFRGDQDAGACEVNPLACLPQAAACAPDLPAFSHGGFSHN Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Clonidine | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Hydralazine | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [4], [5] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ASP8232 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic macular edema | [6] | |
| 2 | BTT-1023 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Psoriasis vulgaris | [7] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BI 1467335 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Diabetic retinopathy | [8] | |
| 2 | Vapaliximab | Drug Info | Terminated | Inflammation | [9] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 10 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Clonidine | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | ASP8232 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | BI 1467335 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | 6-hydroxydopa quinone | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 5 | FP-1102 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 6 | LJP-1207 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 7 | PSX-4206 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 8 | PXS-4159 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 9 | RTU-1096 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 10 | Vapill | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Hydralazine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: 6-hydroxydopa quinone | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human vascular adhesion protein-1 in complex with pyridazinone inhibitors | PDB:4BTX | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.78 Å | Mutation | No | [15] |
| PDB Sequence |
PGQSQLFADL
63 SREELTAVMR73 FLTQRLGPGL83 VDAAQARPSD93 NCVFSVELQL103 PPKAAALAHL 113 DRGSPPPARE123 ALAIVFFGRQ133 PQPNVSELVV143 GPLPHPSYMR153 DVTVERHGGP 163 LPYHRRPVLF173 QEYLDIDQMI183 FNRELPQASG193 LLHHCCFYKH203 RGRNLVTMTT 213 APRGLQSGDR223 ATWFGLYYNI233 SGAGFFLHHV243 GLELLVNHKA253 LDPARWTIQK 263 VFYQGRYYDS273 LAQLEAQFEA283 GLVNVVLIPD293 NGTGGSWSLK303 SPVPPGPAPP 313 LQFYPQGPRF323 SVQGSRVASS333 LWTFSFGLGA343 FSGPRIFDVR353 FQGERLVYEI 363 SLQEALAIYG373 GNSPAAMTTR383 YVDGGFGMGK393 YTTPLTRGVD403 CPYLATYVDW 413 HFLLESQAPK423 TIRDAFCVFE433 QNQGLPLRRH443 HSDLYSHYFG453 GLAETVLVVR 463 SMSTLLNDYV474 WDTVFHPSGA484 IEIRFYATGY494 ISSAFLFGAT504 GKYGNQVSEH 514 TLGTVHTHSA524 HFKVDLDVAG534 LENWVWAEDM544 VFVPMAVPWS554 PEHQLQRLQV 564 TRKLLEMEEQ574 AAFLVGSATP584 RYLYLASNHS594 NKWGHPRGYR604 IQMLSFAGEP 614 LPQNSSMARG624 FSWERYQLAV634 TQRKEEEPSS644 SSVFNQNDPW654 APTVDFSDFI 664 NNETIAGKDL674 VAWVTAGFLH684 IPHAEDIPNT694 VTVGNGVGFF704 LRPYNFFDED 714 PSFYSADSIY724 FRGDQDAGAC734 EVNPLACLPQ744 AAACAPDLPA754 FSHGGFSH |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: (2S)-2-amino-3-(2,4-dihydroxy-5-imidazol-1-yl-phenyl)propanoic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN SOLUBLE PRIMARY AMINE OXIDASE AOC3 IN THE OFF-COPPER CONFORMATION | PDB:2Y74 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.95 Å | Mutation | No | [16] |
| PDB Sequence |
QLFADLSREE
67 LTAVMRFLTQ77 RLGPGLVDAA87 QARPSDNCVF97 SVELQLPPKA107 AALAHLDRGS 117 PPPAREALAI127 VFFGRQPQPN137 VSELVVGPLP147 HPSYMRDVTV157 ERHGGPLPYH 167 RRPVLFQEYL177 DIDQMIFNRE187 LPQASGLLHH197 CCFYKRNLVT210 MTTAPRGLQS 220 GDRATWFGLY230 YNISGAGFFL240 HHVGLELLVN250 HKALDPARWT260 IQKVFYQGRY 270 YDSLAQLEAQ280 FEAGLVNVVL290 IPDNGTGGSW300 SLKSPVPPGP310 APPLQFYPQG 320 PRFSVQGSRV330 ASSLWTFSFG340 LGAFSGPRIF350 DVRFQGERLV360 YEISLQEALA 370 IYGGNSPAAM380 TTRYVDGGFG390 MGKYTTPLTR400 GVDCPYLATY410 VDWHFLLESQ 420 APKTIRDAFC430 VFEQNQGLPL440 RRHHSDLYSH450 YFGGLAETVL460 VVRSMSTLLN 470 DYVWDTVFHP481 SGAIEIRFYA491 TGYISSAFLF501 GATGKYGNQV511 SEHTLGTVHT 521 HSAHFKVDLD531 VAGLENWVWA541 EDMVFVPMAV551 PWSPEHQLQR561 LQVTRKLLEM 571 EEQAAFLVGS581 ATPRYLYLAS591 NHSNKWGHPR601 GYRIQMLSFA611 GEPLPQNSSM 621 ARGFSWERYQ631 LAVTQRKEEE641 PSSSSVFNQN651 DPWAPTVDFS661 DFINNETIAG 671 KDLVAWVTAG681 FLHIPHAEDI691 PNTVTVGNGV701 GFFLRPYNFF711 DEDPSFYSAD 721 SIYFRGDQDA731 GACEVNPLAC741 LAPDLPAFSH757 GGFS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
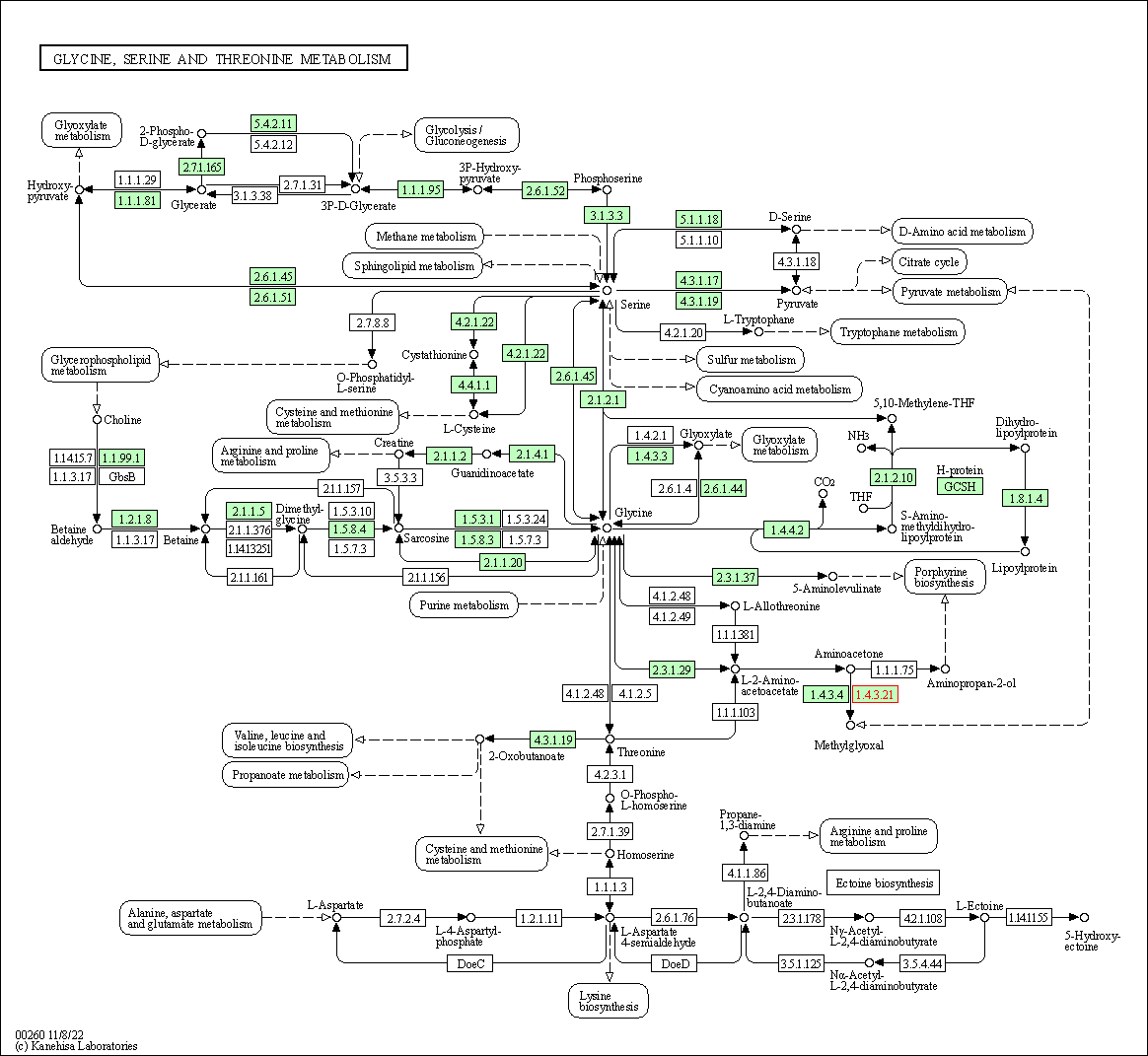
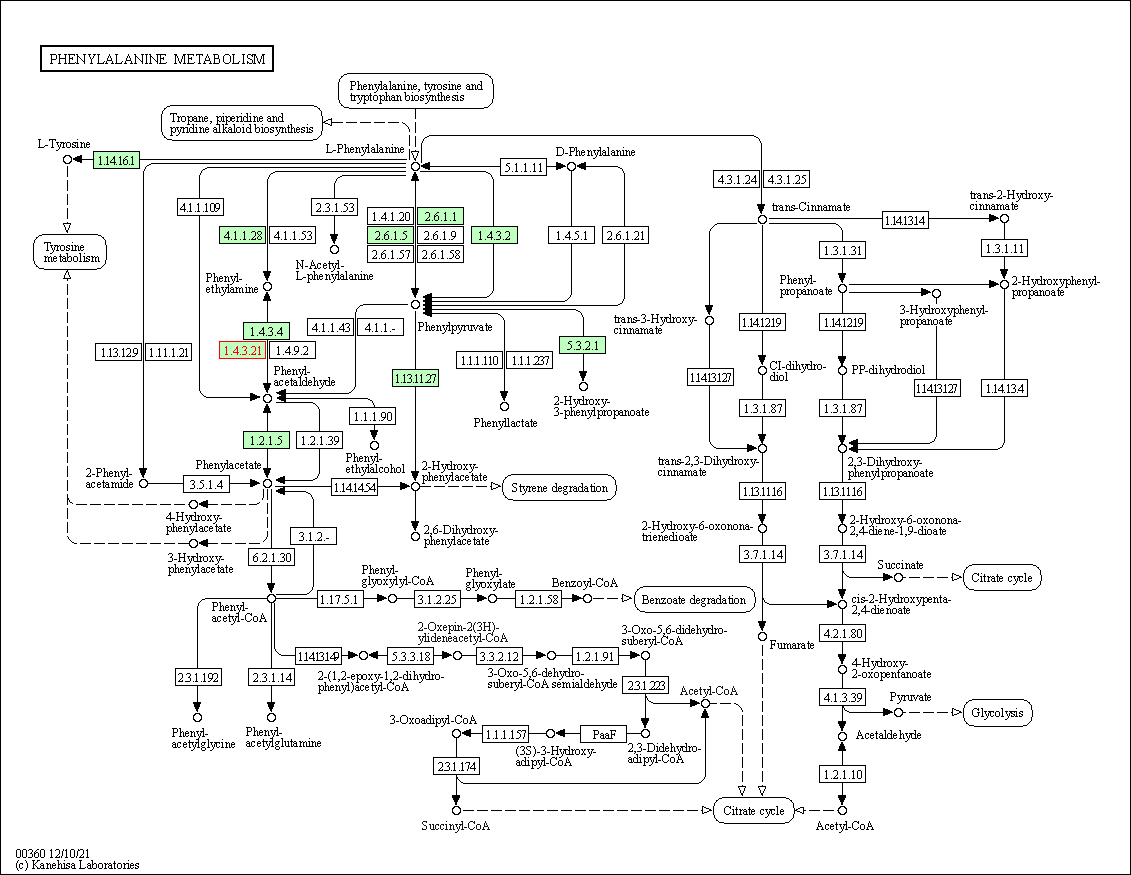
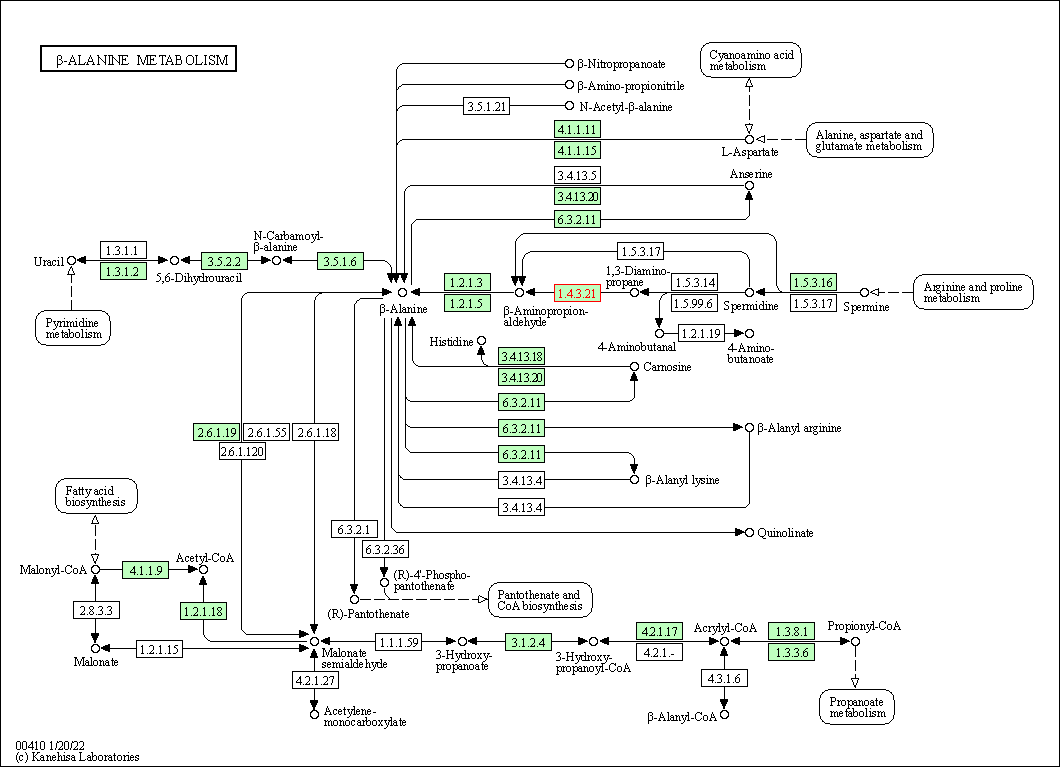
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | hsa00260 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Tyrosine metabolism | hsa00350 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phenylalanine metabolism | hsa00360 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| beta-Alanine metabolism | hsa00410 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of other amino acids | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 2 | Degree centrality | 2.15E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.91E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.61E-01 | Radiality | 1.24E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.00E+00 | Topological coefficient | 5.00E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 2 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phenylethylamine degradation I | |||||
| 2 | Spermine and spermidine degradation I | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Tyrosine metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Phenylalanine metabolism | |||||
| 4 | beta-Alanine metabolism | |||||
| 5 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phenylethylamine degradation | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Beta-Alanine Metabolism | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 516). | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 070315. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7326). | |||||
| REF 5 | Drug information of Hydralazine, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02239211) A Trial of BTT1023 in Patients With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Boehringer Ingelheim. | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800017603) | |||||
| REF 10 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 11 | Preclinical evaluation of a radioiodinated fully human antibody for in vivo imaging of vascular adhesion protein-1-positive vasculature in inflammation. J Nucl Med. 2013 Aug;54(8):1315-9. | |||||
| REF 12 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Huginonline. | |||||
| REF 13 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 14 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2767). | |||||
| REF 15 | Novel pyridazinone inhibitors for vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1): old target-new inhibition mode. J Med Chem. 2013 Dec 27;56(24):9837-48. | |||||
| REF 16 | Identification of two imidazole binding sites and key residues for substrate specificity in human primary amine oxidase AOC3. Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 21;50(24):5507-20. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

