Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T76213
(Former ID: TTDI01963)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Phenylalanine4hydroxylase; Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase; Phe4monooxygenase; Phe-4-monooxygenase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PAH
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Metabolism inborn error [ICD-11: 5C50] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.14.16.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSTAVLENPGLGRKLSDFGQETSYIEDNCNQNGAISLIFSLKEEVGALAKVLRLFEENDV
NLTHIESRPSRLKKDEYEFFTHLDKRSLPALTNIIKILRHDIGATVHELSRDKKKDTVPW FPRTIQELDRFANQILSYGAELDADHPGFKDPVYRARRKQFADIAYNYRHGQPIPRVEYM EEEKKTWGTVFKTLKSLYKTHACYEYNHIFPLLEKYCGFHEDNIPQLEDVSQFLQTCTGF RLRPVAGLLSSRDFLGGLAFRVFHCTQYIRHGSKPMYTPEPDICHELLGHVPLFSDRSFA QFSQEIGLASLGAPDEYIEKLATIYWFTVEFGLCKQGDSIKAYGAGLLSSFGELQYCLSE KPKLLPLELEKTAIQNYTVTEFQPLYYVAESFNDAKEKVRNFAATIPRPFSVRYDPYTQR IEVLDNTQQLKILADSINSEIGILCSALQKIK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pegvaliase | Drug Info | Approved | Phenylketonuria | [2] | |
| 2 | Sapropterin hydrochloride | Drug Info | Approved | Hyperphenylalaninemia | [1] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 4 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | HepaStem | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Liver failure | [3] | |
| 2 | Phenylalanine hydroxylase | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Autoimmune diabetes | [4] | |
| 3 | BMN-307 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Phenylketonuria | [5] | |
| 4 | HMI-102 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Phenylketonuria | [6] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 7 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pegvaliase | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 2 | Sapropterin hydrochloride | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | HepaStem | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 4 | Phenylalanine hydroxylase | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 5 | ALTU-236 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 6 | BH4 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 7 | BMN-168 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | alpha-methylphenylalanine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 2 | fenclonine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Norepinephrine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | HUMAN PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE CATALYTIC DOMAIN DIMER WITH BOUND NOR-ADRENALINE INHIBITOR | PDB:4PAH | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | No | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
TVPWFPRTIQ
126 ELDRFANQIL136 SYGAELDADH146 PGFKDPVYRA156 RRKQFADIAY166 NYRHGQPIPR 176 VEYMEEEKKT186 WGTVFKTLKS196 LYKTHACYEY206 NHIFPLLEKY216 CGFHEDNIPQ 226 LEDVSQFLQT236 CTGFRLRPVA246 GLLSSRDFLG256 GLAFRVFHCT266 QYIRHGSKPM 276 YTPEPDICHE286 LLGHVPLFSD296 RSFAQFSQEI306 GLASLGAPDE316 YIEKLATIYW 326 FTVEFGLCKQ336 GDSIKAYGAG346 LLSSFGELQY356 CLSEKPKLLP366 LELEKTAIQN 376 YTVTEFQPLY386 YVAESFNDAK396 EKVRNFAATI406 PRPFSVRYDP416 YTQRIEVL |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Dopamine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | HUMAN PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE CATALYTIC DOMAIN DIMER WITH BOUND DOPAMINE INHIBITOR | PDB:5PAH | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.10 Å | Mutation | No | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
TVPWFPRTIQ
126 ELDRFANQIL136 SYGAELDADH146 PGFKDPVYRA156 RRKQFADIAY166 NYRHGQPIPR 176 VEYMEEEKKT186 WGTVFKTLKS196 LYKTHACYEY206 NHIFPLLEKY216 CGFHEDNIPQ 226 LEDVSQFLQT236 CTGFRLRPVA246 GLLSSRDFLG256 GLAFRVFHCT266 QYIRHGSKPM 276 YTPEPDICHE286 LLGHVPLFSD296 RSFAQFSQEI306 GLASLGAPDE316 YIEKLATIYW 326 FTVEFGLCKQ336 GDSIKAYGAG346 LLSSFGELQY356 CLSEKPKLLP366 LELEKTAIQN 376 YTVTEFQPLY386 YVAESFNDAK396 EKVRNFAATI406 PRPFSVRYDP416 YTQRIEVL |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
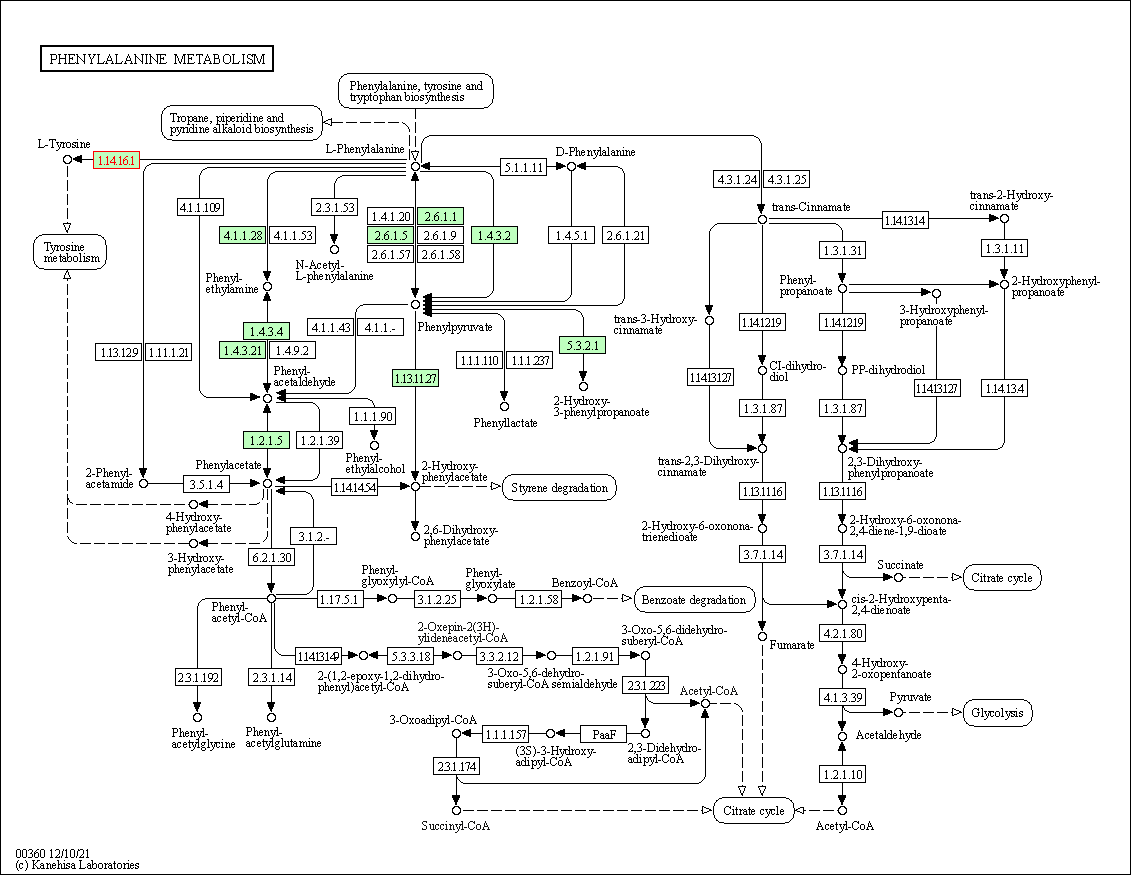
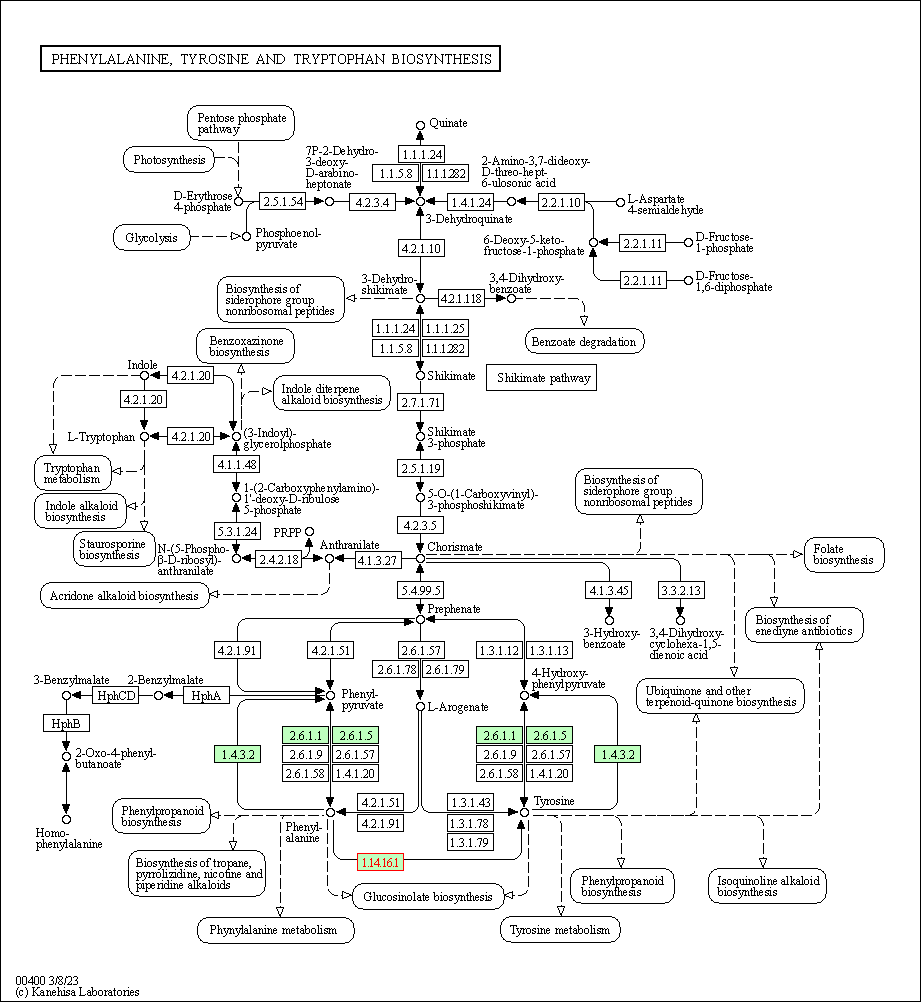
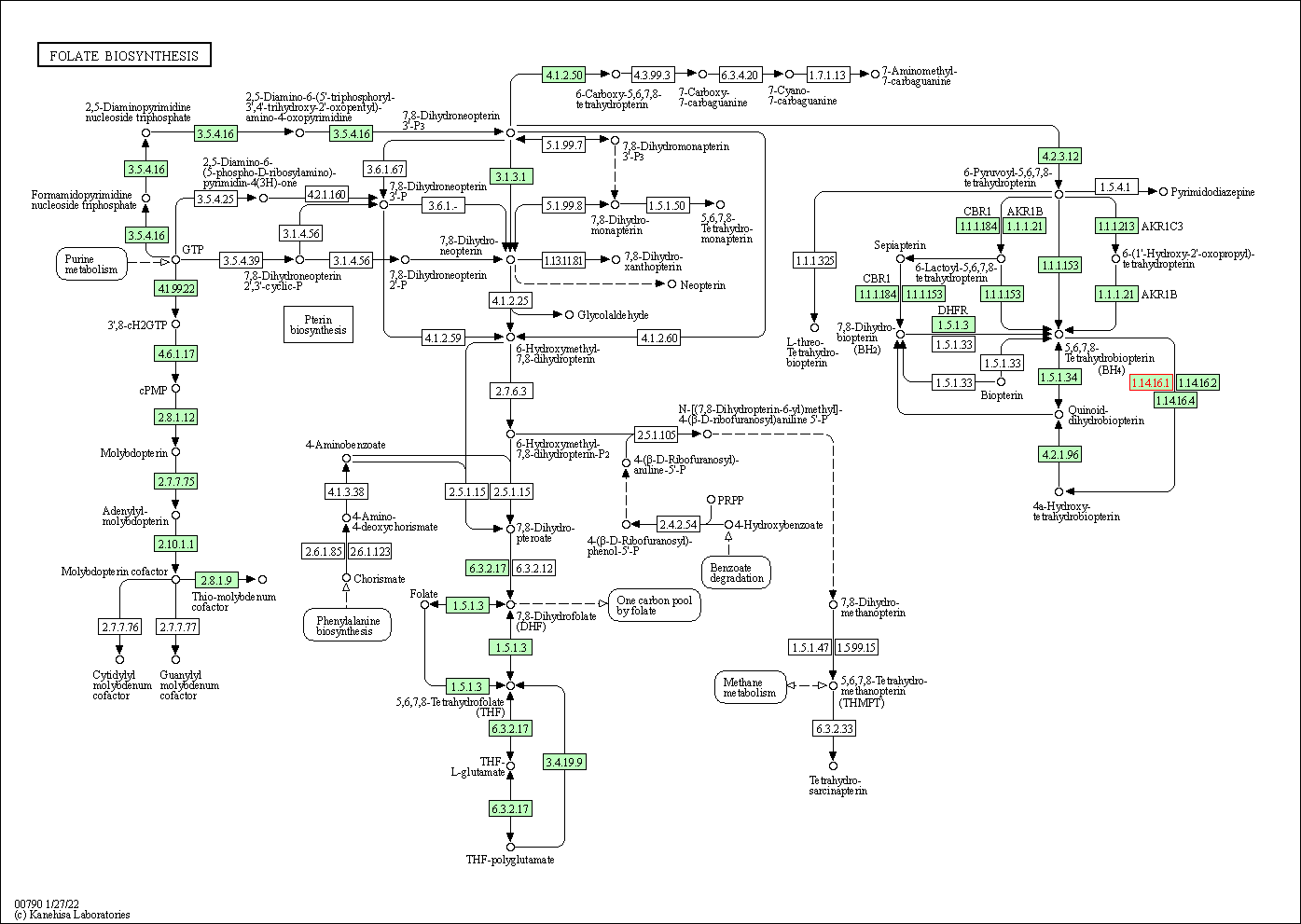
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenylalanine metabolism | hsa00360 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | hsa00400 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Folate biosynthesis | hsa00790 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.23E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.65E-01 | Radiality | 1.25E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.80E+00 | Topological coefficient | 3.05E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 1 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phenylalanine degradation/tyrosine biosynthesis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phenylalanine metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | |||||
| 3 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 4 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | |||||
| 2 | Biogenic Amine Synthesis | |||||
| 3 | Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives | |||||
| 4 | Abnormal metabolism in phenylketonuria | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | 2007 FDA drug approvals: a year of flux. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Feb;7(2):107-9. | |||||
| REF 2 | Induction, titration, and maintenance dosing regimen in a phase 2 study of pegvaliase for control of blood phenylalanine in adults with phenylketonuria.Mol Genet Metab. 2018 Nov;125(3):217-227. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02489292) Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of HepaStem in Urea Cycle Disorders Paediatric Patients (HEP002). | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00925054) Dose-Finding Study to Evaluate the Safety, Efficacy, & Tolerability of Multiple Doses of rAvPAL-PEG in Subjects With PKU. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04480567) A Phase 1/2 Open-Label, Dose Escalation Study to Determine the Safety and Efficacy of BMN 307, an Adeno-Associated Virus Vector-Mediated Gene Transfer of Human Phenylalanine Hydroxylase in Subjects With Phenylketonuria. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03952156) A Phase 1/2 Open-Label, Randomized, Concurrently-Controlled, Dose Escalation Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of HMI-102 in Adult PKU Subjects With PAH Deficiency. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1240). | |||||
| REF 8 | Single-dose, subcutaneous recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase conjugated with polyethylene glycol in adult patients with phenylketonuria: an open-label, multicentre, phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet. 2014 Jul 5;384(9937):37-44. | |||||
| REF 9 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Homology Medicines | |||||
| REF 10 | Alpha-methylphenylalanine, a new inducer of chronic hyperphenylalaninemia in sucling rats. Science. 1976 Jun 4;192(4243):1007-8. | |||||
| REF 11 | Company report of BioMarin | |||||
| REF 12 | Crystallographic analysis of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase catalytic domain with bound catechol inhibitors at 2.0 A resolution. Biochemistry. 1998 Nov 10;37(45):15638-46. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

