Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T78181
(Former ID: TTDI00094)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
MTOR complex 2 (RICTOR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
hAVO3; Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; KIAA1999; AVO3 homolog
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
RICTOR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
mTORC2 is activated by growth factors, but, in contrast to mTORC1, seems to be nutrient-insensitive. mTORC2 seems to function upstream of Rho GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton, probably by activating one or more Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors. mTORC2 promotes the serum-induced formation of stress-fibers or F-actin. mTORC2 plays a critical role in AKT1 'Ser-473' phosphorylation, which may facilitate the phosphorylation of the activation loop of AKT1 on 'Thr-308' by PDK1 which is a prerequisite for full activation. mTORC2 regulates the phosphorylation of SGK1 at 'Ser-422'. mTORC2 also modulates the phosphorylation of PRKCA on 'Ser-657'. Plays an essential role in embryonic growth and development. Subunit of mTORC2, which regulates cell growth and survival in response to hormonal signals.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAAIGRGRSLKNLRVRGRNDSGEENVPLDLTREPSDNLREILQNVARLQGVSNMRKLGHL
NNFTKLLCDIGHSEEKLGFHYEDIIICLRLALLNEAKEVRAAGLRALRYLIQDSSILQKV LKLKVDYLIARCIDIQQSNEVERTQALRLVRKMITVNASLFPSSVTNSLIAVGNDGLQER DRMVRACIAIICELALQNPEVVALRGGLNTILKNVIDCQLSRINEALITTILHLLNHPKT RQYVRADVELERILAPYTDFHYRHSPDTAEGQLKEDREARFLASKMGIIATFRSWAGIIN LCKPGNSGIQSLIGVLCIPNMEIRRGLLEVLYDIFRLPLPVVTEEFIEALLSVDPGRFQD SWRLSDGFVAAEAKTILPHRARSRPDLMDNYLALILSAFIRNGLLEGLVEVITNSDDHIS VRATILLGELLHMANTILPHSHSHHLHCLPTLMNMAASFDIPKEKRLRASAALNCLKRFH EMKKRGPKPYSLHLDHIIQKAIATHQKRDQYLRVQKDIFILKDTEEALLINLRDSQVLQH KENLEWNWNLIGTILKWPNVNLRNYKDEQLHRFVRRLLYFYKPSSKLYANLDLDFAKAKQ LTVVGCQFTEFLLESEEDGQGYLEDLVKDIVQWLNASSGMKPERSLQNNGLLTTLSQHYF LFIGTLSCHPHGVKMLEKCSVFQCLLNLCSLKNQDHLLKLTVSSLDYSRDGLARVILSKI LTAATDACRLYATKHLRVLLRANVEFFNNWGIELLVTQLHDKNKTISSEALDILDEACED KANLHALIQMKPALSHLGDKGLLLLLRFLSIPKGFSYLNERGYVAKQLEKWHREYNSKYV DLIEEQLNEALTTYRKPVDGDNYVRRSNQRLQRPHVYLPIHLYGQLVHHKTGCHLLEVQN IITELCRNVRTPDLDKWEEIKKLKASLWALGNIGSSNWGLNLLQEENVIPDILKLAKQCE VLSIRGTCVYVLGLIAKTKQGCDILKCHNWDAVRHSRKHLWPVVPDDVEQLCNELSSIPS TLSLNSESTSSRHNSESESVPSSMFILEDDRFGSSSTSTFFLDINEDTEPTFYDRSGPIK DKNSFPFFASSKLVKNRILNSLTLPNKKHRSSSDPKGGKLSSESKTSNRRIRTLTEPSVD FNHSDDFTPISTVQKTLQLETSFMGNKHIEDTGSTPSIGENDLKFTKNFGTENHRENTSR ERLVVESSTSSHMKIRSQSFNTDTTTSGISSMSSSPSRETVGVDATTMDTDCGSMSTVVS TKTIKTSHYLTPQSNHLSLSKSNSVSLVPPGSSHTLPRRAQSLKAPSIATIKSLADCNFS YTSSRDAFGYATLKRLQQQRMHPSLSHSEALASPAKDVLFTDTITMKANSFESRLTPSRF MKALSYASLDKEDLLSPINQNTLQRSSSVRSMVSSATYGGSDDYIGLALPVDINDIFQVK DIPYFQTKNIPPHDDRGARAFAHDAGGLPSGTGGLVKNSFHLLRQQMSLTEIMNSIHSDA SLFLESTEDTGLQEHTDDNCLYCVCIEILGFQPSNQLSAICSHSDFQDIPYSDWCEQTIH NPLEVVPSKFSGISGCSDGVSQEGSASSTKSTELLLGVKTIPDDTPMCRILLRKEVLRLV INLSSSVSTKCHETGLLTIKEKYPQTFDDICLYSEVSHLLSHCTFRLPCRRFIQELFQDV QFLQMHEEAEAVLATPPKQPIVDTSAES Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Phosphothiophosphoric acid-adenylate ester | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | cryo-EM structure of human mTOR complex 2, focused on one half | PDB:6ZWO | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
NVPLDLTREP
34 SDNLREILQN44 VARLQGVSNM54 RKLGHLNNFT64 KLLCDIGHSE74 EKLGFHYEDI 84 IICLRLALLN94 EAKEVRAAGL104 RALRYLIQDS114 SILQKVLKLK124 VDYLIARCID 134 IQQSNEVERT144 QALRLVRKMI154 TVNASLFPSS164 VTNSLIAVGN174 DGLQERDRMV 184 RACIAIICEL194 ALQNPEVVAL204 RGGLNTILKN214 VIDCQLSRIN224 EALITTILHL 234 LNHPKTRQYV244 RADVELERIL254 APYTDFHYRH264 SPDTAEGQLK274 EDREARFLAS 284 KMGIIATFRS294 WAGIINLCKP304 GNSGIQSLIG314 VLCIPNMEIR324 RGLLEVLYDI 334 FRLPLPVVTE344 EFIEALLSVD354 PGRFQDSWRL364 SDGFVAAEAK374 TILPHRARSR 384 PDLMDNYLAL394 ILSAFIRNGL404 LEGLVEVITN414 SDDHISVRAT424 ILLGELLHMA 434 NTILPHSHSH444 HLHCLPTLMN454 MAASFDIPKE464 KRLRASAALN474 CLKRFHEMKK 484 RGPKPYSLHL494 DHIIQKAIAT504 HQKRDQILKD523 TEEALLINLR533 DSQVLQHKEN 543 LEWNWNLIGT553 ILKWPNVNLR563 NYKDEQLHRF573 VRRLLYFYKP583 SSKLYANLDL 593 DFAKAKQLTV603 VGCQFTEFLL613 ESEEDGQGYL623 EDLVKDIVQW633 LNASSGMKPE 643 RSLQNNGLLT653 TLSQHYFLFI663 GTLSCHPHGV673 KMLEKCSVFQ683 CLLNLCSLKN 693 QDHLLKLTVS703 SLDYSRDGLA713 RVILSKILTA723 ATDACRLYAT733 KHLRVLLRAN 743 VEFFNNWGIE753 LLVTQLHDKN763 KTISSEALDI773 LDEACEDKAN783 LHALIQMKPA 793 LSHLGDKGLL803 LLLRFLSIPK813 GFSYLNERGY823 VAKQLEKWHR833 EYNSKYVDLI 843 EEQLNEALTT853 YRKPQRPHVY877 LPIHLYGQLV887 HHKTGCHLLE897 VQNIITELCR 907 NVRTPDLDKW917 EEIKKLKASL927 WALGNIGSSN937 WGLNLLQEEN947 VIPDILKLAK 957 QCEVLSIRGT967 CVYVLGLIAK977 TKQGCDILKC987 HNWDAVRHSR997 KHLWPVVPDY 1424 IGLALPVDIN1434 DIFQVKDIPY1444 FQTKSFHLLR1484 QQMSLTEIMN1494 TGLQEHTDDN 1519 CLYCVCIEIL1529 GFQPSNQLSM1607 CRILLRKEVL1617 RLVINLSSSV1627 STKCHETGLL 1637 TIKEKYPQTF1647 DDICLYSEVS1657 HLLSHCTFRL1667 PCRRFIQELF1677 QDVQFLQMHE 1687 EAEAVLA
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
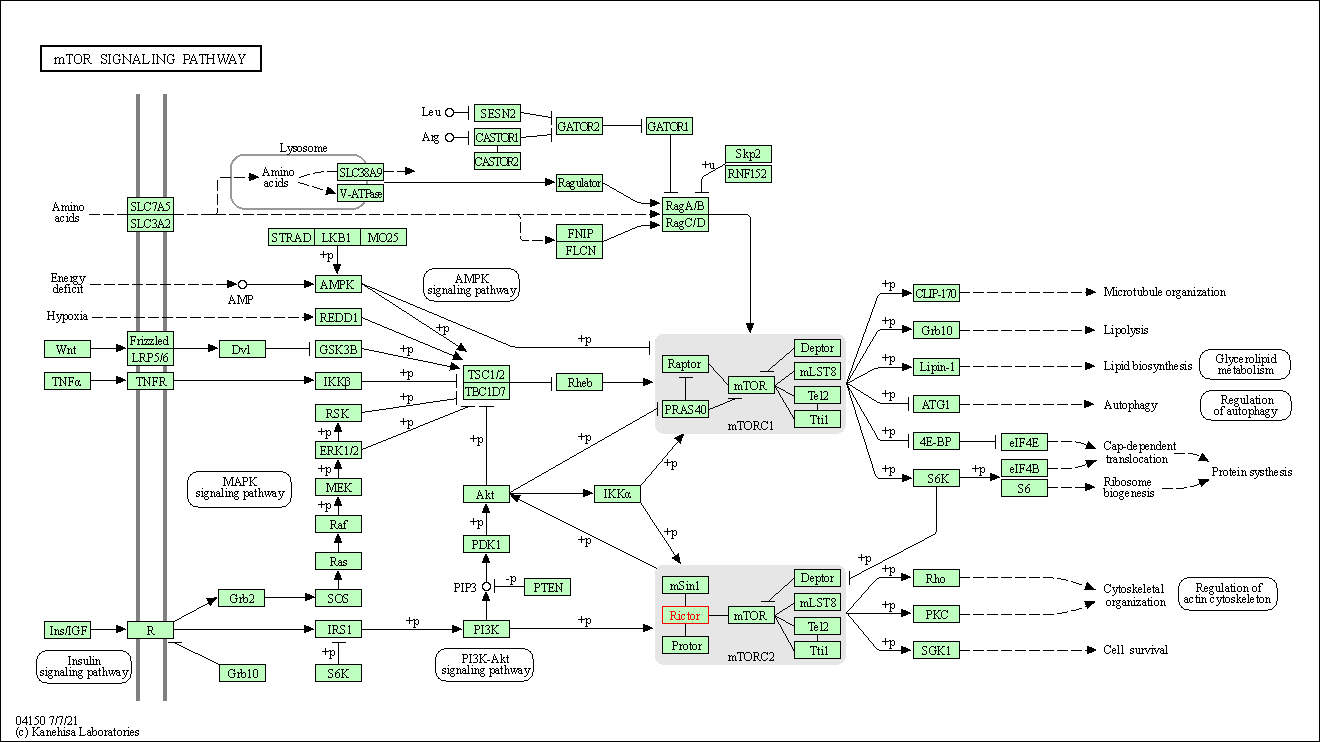
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.57E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.37E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.92E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.29E+01 | Topological coefficient | 9.82E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Chronic Repression of mTOR Complex 2 Induces Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 29;6:30887. | |||||
| REF 2 | The 3.2-? resolution structure of human mTORC2. Sci Adv. 2020 Nov 6;6(45):eabc1251. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

