Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T78543
(Former ID: TTDI03491)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Protein kinase G1 (PRKG1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
cGMP-dependent protein kinase I; cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1; cGKI; cGK1; cGK 1; PRKGR1B; PRKGR1A; PRKG1B
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PRKG1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
GMP binding activates PRKG1, which phosphorylates serines and threonines on many cellular proteins. Numerous protein targets for PRKG1 phosphorylation are implicated in modulating cellular calcium, but the contribution of each of these targets may vary substantially among cell types. Proteins that are phosphorylated by PRKG1 regulate platelet activation and adhesion, smooth muscle contraction, cardiac function, gene expression, feedback of the NO-signaling pathway, and other processes involved in several aspects of the CNS like axon guidance, hippocampal and cerebellar learning, circadian rhythm and nociception. Smooth muscle relaxation is mediated through lowering of intracellular free calcium, by desensitization of contractile proteins to calcium, and by decrease in the contractile state of smooth muscle or in platelet activation. Regulates intracellular calcium levels via several pathways: phosphorylates MRVI1/IRAG and inhibits IP3-induced Ca(2+) release from intracellular stores, phosphorylation of KCNMA1 (BKCa) channels decreases intracellular Ca(2+) levels, which leads to increased opening of this channel. PRKG1 phosphorylates the canonical transient receptor potential channel (TRPC) family which inactivates the associated inward calcium current. Another mode of action of NO/cGMP/PKGI signaling involves PKGI-mediated inactivation of the Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA). Phosphorylation of RHOA by PRKG1 blocks the action of this protein in myriad processes: regulation of RHOA translocation; decreasing contraction; controlling vesicle trafficking, reduction of myosin light chain phosphorylation resulting in vasorelaxation. Activation of PRKG1 by NO signaling alters also gene expression in a number of tissues. In smooth muscle cells, increased cGMP and PRKG1 activity influence expression of smooth muscle-specific contractile proteins, levels of proteins in the NO/cGMP signaling pathway, down-regulation of the matrix proteins osteopontin and thrombospondin-1 to limit smooth muscle cell migration and phenotype. Regulates vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) functions in platelets and smooth muscle. Serine/threonine protein kinase that acts as key mediator of the nitric oxide (NO)/cGMP signaling pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.12
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSELEEDFAKILMLKEERIKELEKRLSEKEEEIQELKRKLHKCQSVLPVPSTHIGPRTTR
AQGISAEPQTYRSFHDLRQAFRKFTKSERSKDLIKEAILDNDFMKNLELSQIQEIVDCMY PVEYGKDSCIIKEGDVGSLVYVMEDGKVEVTKEGVKLCTMGPGKVFGELAILYNCTRTAT VKTLVNVKLWAIDRQCFQTIMMRTGLIKHTEYMEFLKSVPTFQSLPEEILSKLADVLEET HYENGEYIIRQGARGDTFFIISKGTVNVTREDSPSEDPVFLRTLGKGDWFGEKALQGEDV RTANVIAAEAVTCLVIDRDSFKHLIGGLDDVSNKAYEDAEAKAKYEAEAAFFANLKLSDF NIIDTLGVGGFGRVELVQLKSEESKTFAMKILKKRHIVDTRQQEHIRSEKQIMQGAHSDF IVRLYRTFKDSKYLYMLMEACLGGELWTILRDRGSFEDSTTRFYTACVVEAFAYLHSKGI IYRDLKPENLILDHRGYAKLVDFGFAKKIGFGKKTWTFCGTPEYVAPEIILNKGHDISAD YWSLGILMYELLTGSPPFSGPDPMKTYNIILRGIDMIEFPKKIAKNAANLIKKLCRDNPS ERLGNLKNGVKDIQKHKWFEGFNWEGLRKGTLTPPIIPSVASPTDTSNFDSFPEDNDEPP PDDNSGWDIDF Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T53MV1 | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Ialpha (PKG Ialpha) catalytic domain in AMP-PNP bound state | PDB:6BG2 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.83 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
EDAEAKAKYE
346 AEAAFFANLK356 LSDFNIIDTL366 GVGGFGRVEL376 VQLKSEESKT386 FAMKILKKRH 396 IVDTRQQEHI406 RSEKQIMQGA416 HSDFIVRLYR426 TFKDSKYLYM436 LMEACLGGEL 446 WTILRDRGSF456 EDSTTRFYTA466 CVVEAFAYLH476 SKGIIYRDLK486 PENLILDHRG 496 YAKLVDFGFA506 KKIGFGKKTW516 FCGTPEYVAP527 EIILNKGHDI537 SADYWSLGIL 547 MYELLTGSPP557 FSGPDPMKTY567 NIILRGIDMI577 EFPKKIAKNA587 ANLIKKLCRD 597 NPSERLGNLK607 NGVKDIQKHK617 WFEGFNWEGL627 RKGTLTPPII637 PSVASPTDTS 647 NFDSFPEDND657 EPPPDDNSGW667 DIDF
|
|||||
|
|
LEU366
3.734
GLY367
3.535
VAL368
4.424
GLY369
3.459
GLY370
3.049
PHE371
2.894
GLY372
3.075
VAL374
3.354
ALA388
3.394
LYS390
2.811
GLU409
4.715
VAL422
3.724
MET438
3.673
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Phosphonothreonine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Ialpha (PKG Ialpha) catalytic domain in AMP-PNP bound state | PDB:6BG2 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.83 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
EDAEAKAKYE
346 AEAAFFANLK356 LSDFNIIDTL366 GVGGFGRVEL376 VQLKSEESKT386 FAMKILKKRH 396 IVDTRQQEHI406 RSEKQIMQGA416 HSDFIVRLYR426 TFKDSKYLYM436 LMEACLGGEL 446 WTILRDRGSF456 EDSTTRFYTA466 CVVEAFAYLH476 SKGIIYRDLK486 PENLILDHRG 496 YAKLVDFGFA506 KKIGFGKKTW516 FCGTPEYVAP527 EIILNKGHDI537 SADYWSLGIL 547 MYELLTGSPP557 FSGPDPMKTY567 NIILRGIDMI577 EFPKKIAKNA587 ANLIKKLCRD 597 NPSERLGNLK607 NGVKDIQKHK617 WFEGFNWEGL627 RKGTLTPPII637 PSVASPTDTS 647 NFDSFPEDND657 EPPPDDNSGW667 DIDF
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
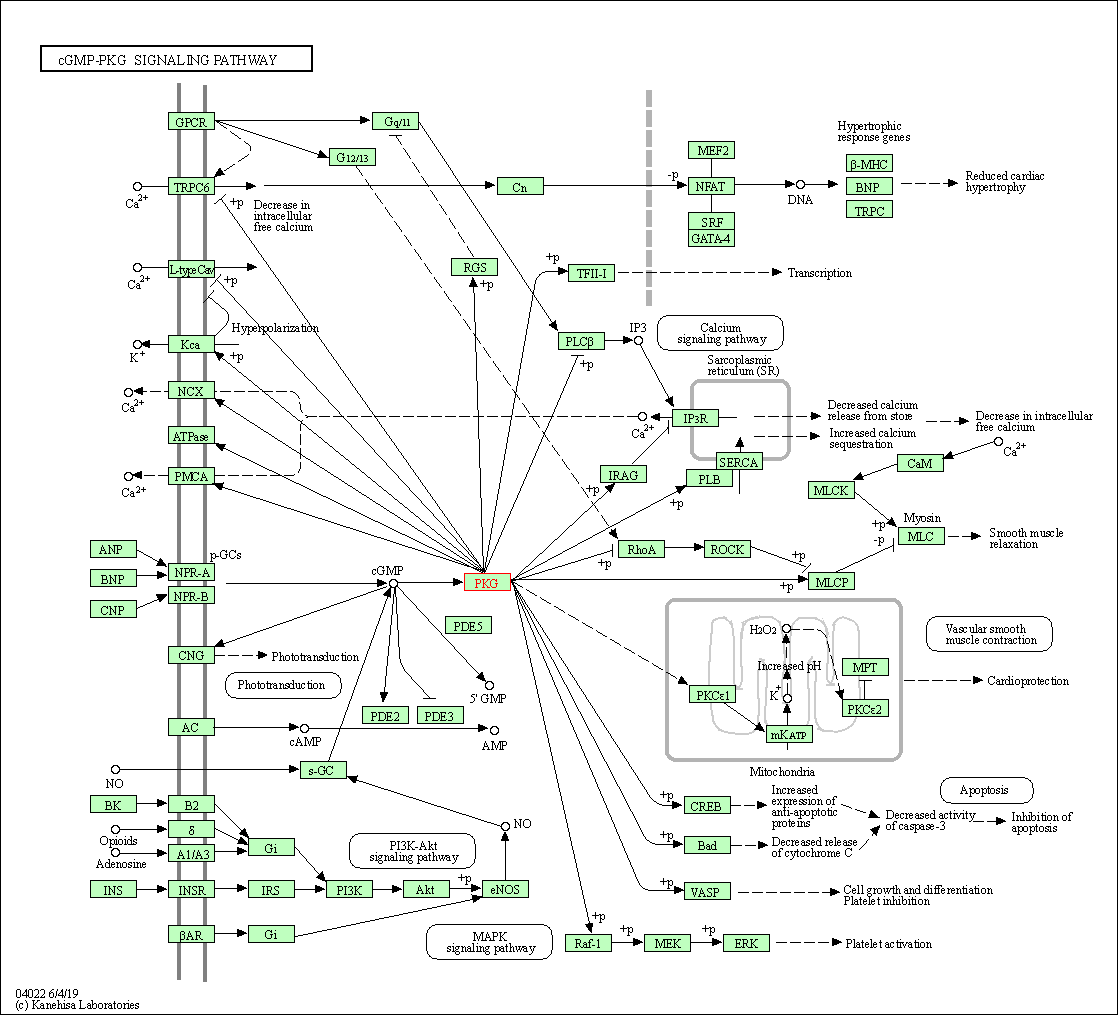
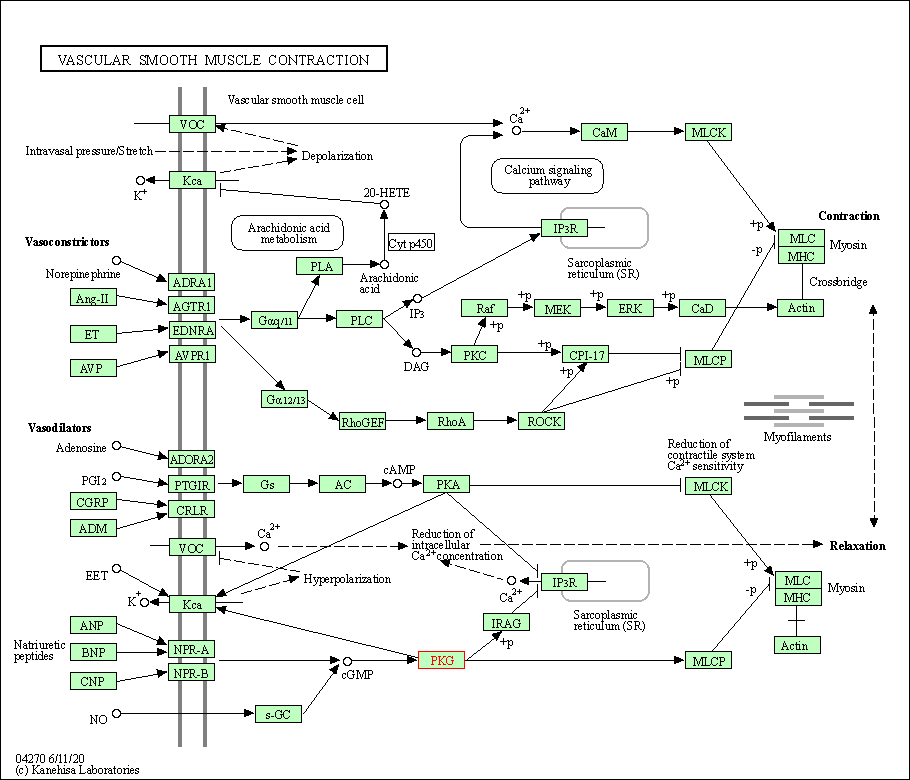
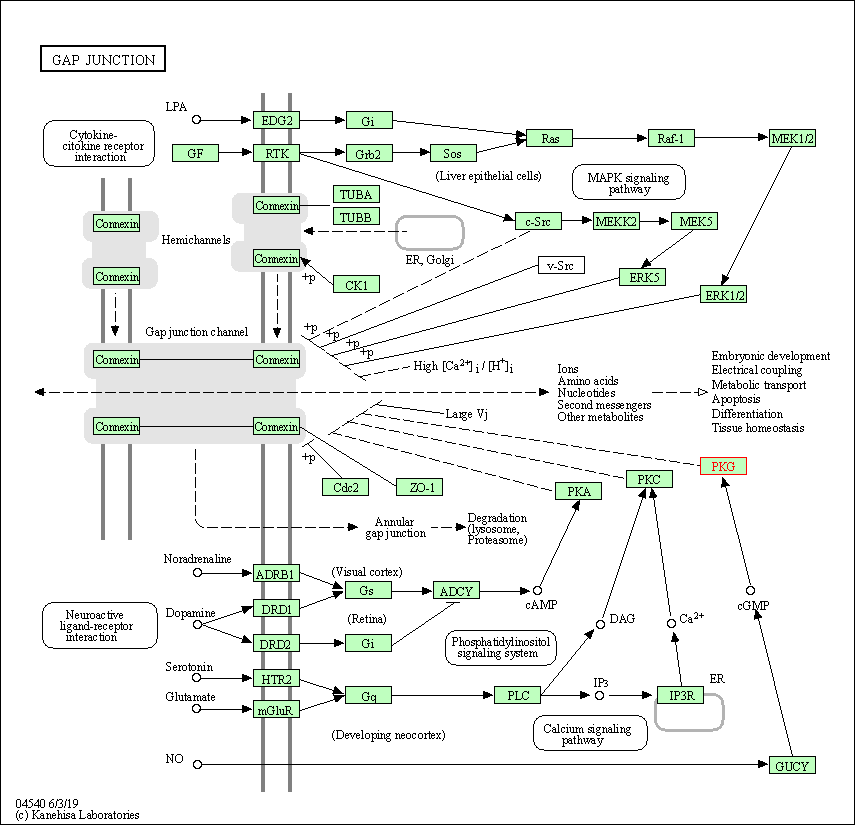
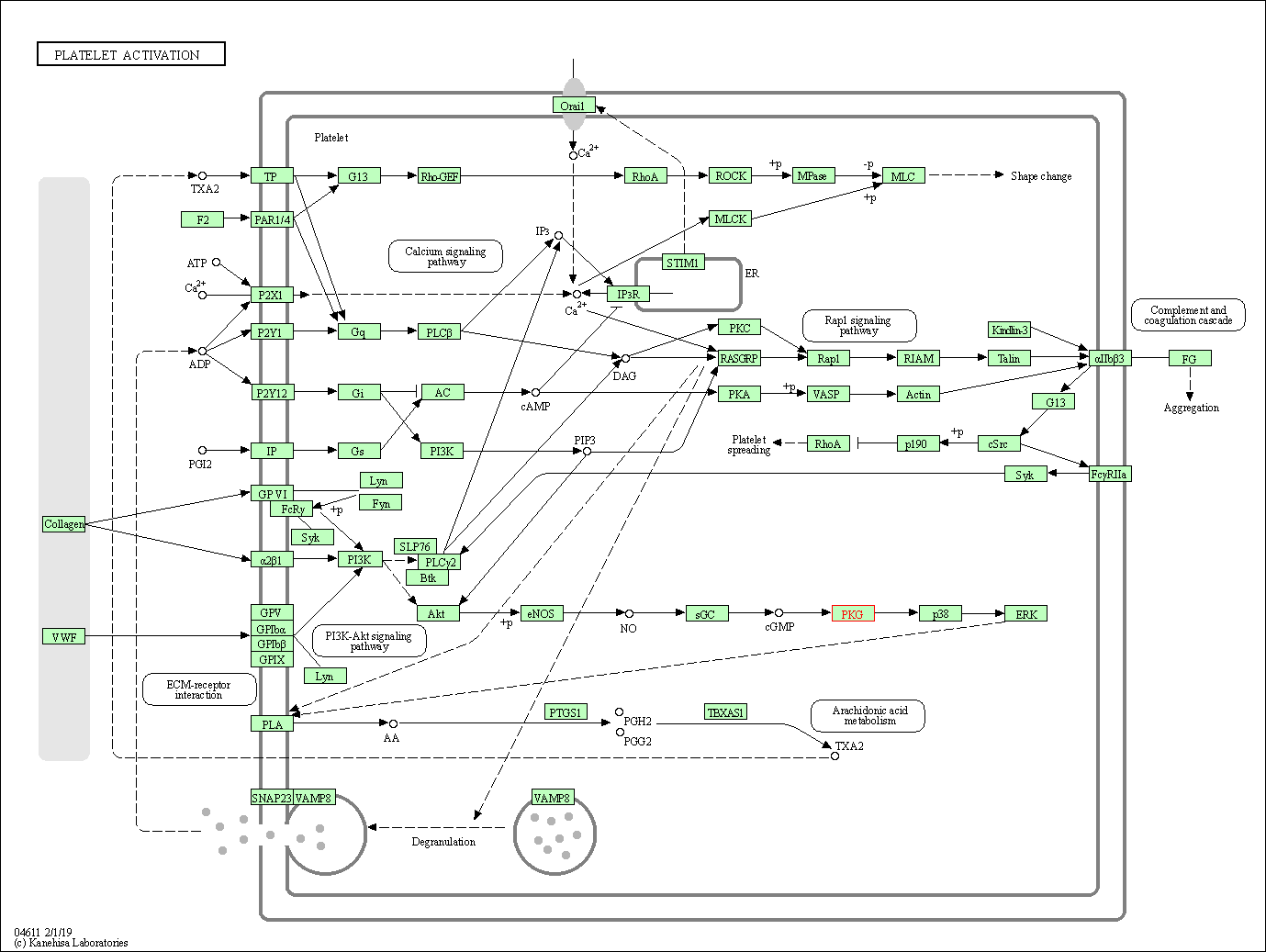
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gap junction | hsa04540 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
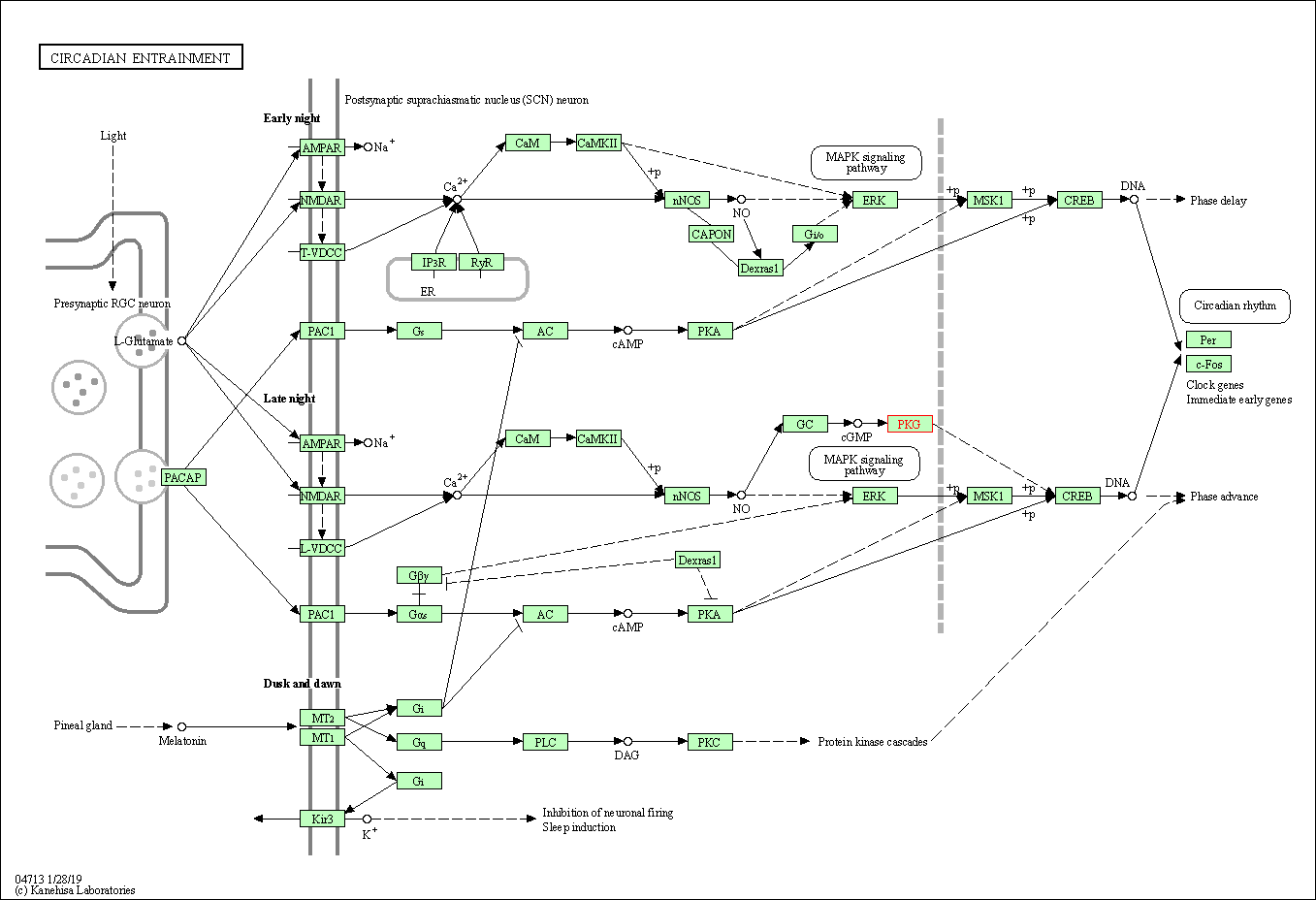
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
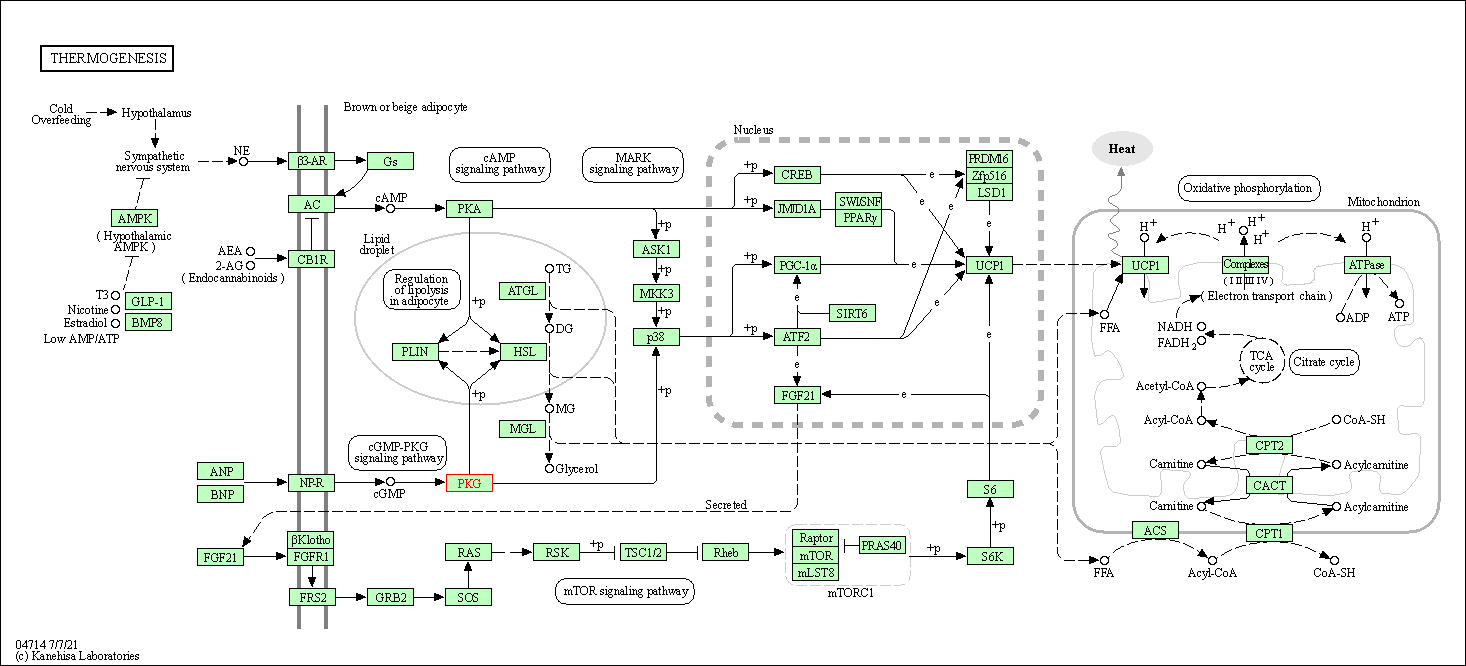
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
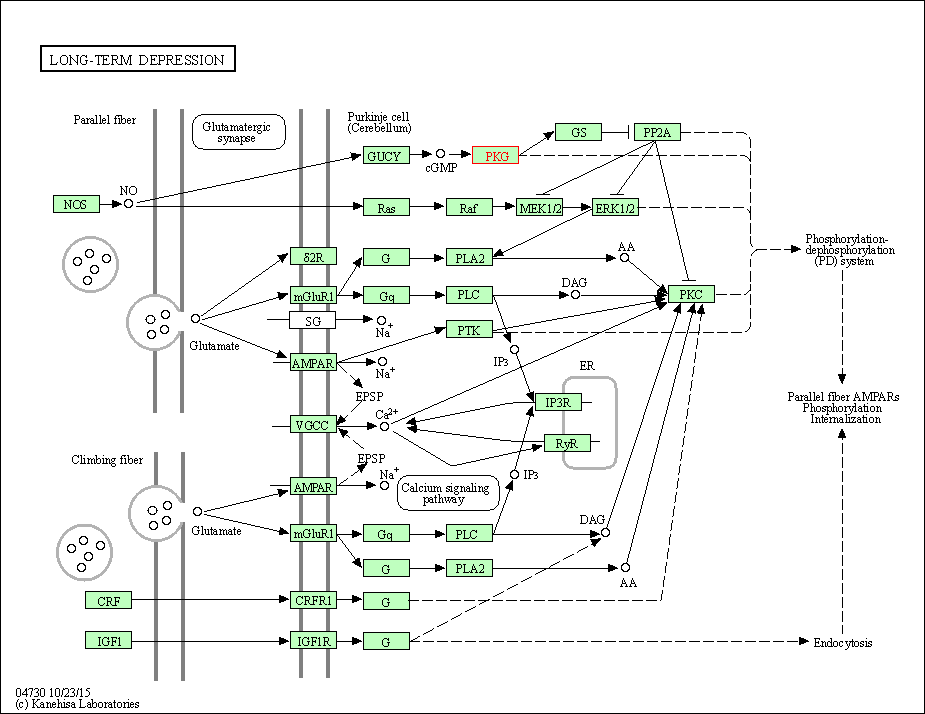
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
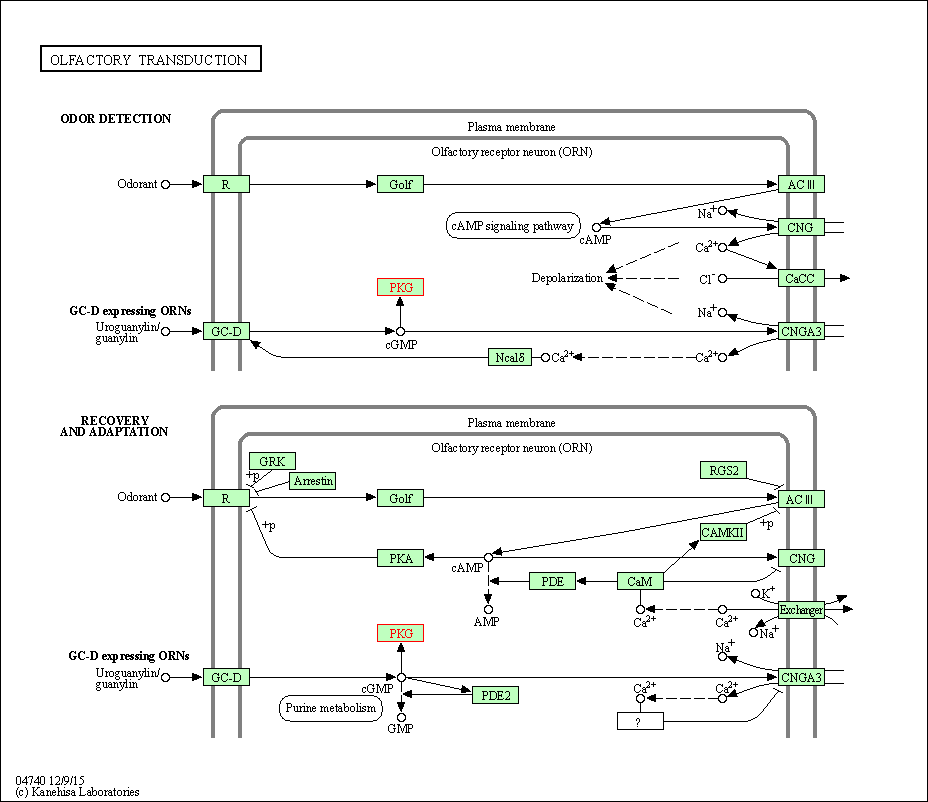
| Olfactory transduction | hsa04740 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | hsa04923 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.31E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.04E-01 | Radiality | 1.35E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.24E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.07E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | (Rp)-8-pCPT-cGMPS, a novel cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 14;269(2):265-8. | |||||
| REF 2 | Crystal structure of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Ialpha (PKG Ialpha) catalytic domain | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

