Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T81443
(Former ID: TTDC00209)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
TLR-4; HToll; CD284
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TLR4
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Allergic/hypersensitivity disorder [ICD-11: 4A80-4A8Z] | |||||
| 2 | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||||
| 3 | Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40-1G41] | |||||
| Function |
Acts via MYD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Also involved in LPS-independent inflammatory responses triggered by free fatty acids, such as palmitate, and Ni(2+). Responses triggered by Ni(2+) require non-conserved histidines and are, therefore, species-specific. Both M. tuberculosis HSP70 (dnaK) and HSP65 (groEL-2) act via this protein to stimulate NF-kappa-B expression. In complex with TLR6, promotes sterile inflammation in monocytes/macrophages in response to oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) or amyloid-beta 42. In this context, the initial signal is provided by oxLDL- or amyloid-beta 42-binding to CD36. This event induces the formation of a heterodimer of TLR4 and TLR6, which is rapidly internalized and triggers inflammatory response, leading to the NF-kappa-B-dependent production of CXCL1, CXCL2 and CCL9 cytokines, via MYD88 signaling pathway, and CCL5 cytokine, via TICAM1 signaling pathway, as well as IL1B secretion. Binds electronegative LDL (LDL(-)) and mediates the cytokine release induced by LDL(-). Stimulation of monocytes in vitro with M. tuberculosis PstS1 induces p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation primarily via TLR2, but also partially via this receptor. Cooperates with LY96 and CD14 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Toll-like receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MMSASRLAGTLIPAMAFLSCVRPESWEPCVEVVPNITYQCMELNFYKIPDNLPFSTKNLD
LSFNPLRHLGSYSFFSFPELQVLDLSRCEIQTIEDGAYQSLSHLSTLILTGNPIQSLALG AFSGLSSLQKLVAVETNLASLENFPIGHLKTLKELNVAHNLIQSFKLPEYFSNLTNLEHL DLSSNKIQSIYCTDLRVLHQMPLLNLSLDLSLNPMNFIQPGAFKEIRLHKLTLRNNFDSL NVMKTCIQGLAGLEVHRLVLGEFRNEGNLEKFDKSALEGLCNLTIEEFRLAYLDYYLDDI IDLFNCLTNVSSFSLVSVTIERVKDFSYNFGWQHLELVNCKFGQFPTLKLKSLKRLTFTS NKGGNAFSEVDLPSLEFLDLSRNGLSFKGCCSQSDFGTTSLKYLDLSFNGVITMSSNFLG LEQLEHLDFQHSNLKQMSEFSVFLSLRNLIYLDISHTHTRVAFNGIFNGLSSLEVLKMAG NSFQENFLPDIFTELRNLTFLDLSQCQLEQLSPTAFNSLSSLQVLNMSHNNFFSLDTFPY KCLNSLQVLDYSLNHIMTSKKQELQHFPSSLAFLNLTQNDFACTCEHQSFLQWIKDQRQL LVEVERMECATPSDKQGMPVLSLNITCQMNKTIIGVSVLSVLVVSVVAVLVYKFYFHLML LAGCIKYGRGENIYDAFVIYSSQDEDWVRNELVKNLEEGVPPFQLCLHYRDFIPGVAIAA NIIHEGFHKSRKVIVVVSQHFIQSRWCIFEYEIAQTWQFLSSRAGIIFIVLQKVEKTLLR QQVELYRLLSRNTYLEWEDSVLGRHIFWRRLRKALLDGKSWNPEGTVGTGCNWQEATSI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T11BI7 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 9 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MPL-containing Pollinex allergy desensitization vaccine | Drug Info | Preregistration | Allergy | [2] | |
| 2 | Cadi-05 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Prostate cancer | [3] | |
| 3 | ERITORAN | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Sepsis | [4], [5] | |
| 4 | Resatorvid | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Sepsis | [6] | |
| 5 | G100 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [7] | |
| 6 | CRX-675 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Hepatitis virus infection | [8] | |
| 7 | GSK1795091 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [7] | |
| 8 | NI-0101 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Autoimmune diabetes | [9] | |
| 9 | OM-174 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [10] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CS-4771 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Sepsis | [11] | |
| 2 | LZ-8 | Drug Info | Terminated | Autoimmune diabetes | [12] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 4 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 6 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ERITORAN | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 2 | 3-Hydroxy-Myristic Acid | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 3 | 6-(2-aminophenoxy)benzo[d]isothiazol-3-amine | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 4 | CRX-526 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 5 | Lauric Acid | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 6 | MYRISTIC ACID | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 2 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Resatorvid | Drug Info | [15], [16], [17] | |||
| 2 | G100 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 2 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CRX-675 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 2 | GSK1795091 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 6 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | OM-174 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 2 | CS-4771 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 3 | LZ-8 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 4 | AS04 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 5 | OM-197-MP-AC | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 6 | OM-294-DP | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: ERITORAN | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the TV3 mutant F63W-MD-2-Eritoran complex | PDB:3ULA | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.60 Å | Mutation | Yes | [25] |
| PDB Sequence |
EPCVEVVPNI
36 TYQCMELNFY46 KIPDNLPFST56 KNLDLSWNPL66 RHLGSYSFFS76 FPELQVLDLS 86 RCEIQTIEDG96 AYQSLSHLST106 LILTGNPIQS116 LALGAFSGLS126 SLQKLVAVET 136 NLASLENFPI146 GHLKTLKELN156 VAHNLIQSFK166 LPEYFSNLTN176 LEHLDLSSNK 186 IQSIYCTDLR196 VLHQMPLLNL206 SLDLSLNPMN216 FIQPGAFKEI226 RLKELALDTN 236 QLKSVPDGIF246 DRLTSLQKIW256 LHTNPWDCSC266 PRIDYLSRWL276 NKNSQKEQGS 286 AKCSGSGKPV296 RSIICP
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Myristic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human TLR4 polymorphic variant D299G and T399I in complex with MD-2 and LPS | PDB:4G8A | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | Yes | [26] |
| PDB Sequence |
EPCVEVVPNI
36 TYQCMELNFY46 KIPDNLPFST56 KNLDLSFNPL66 RHLGSYSFFS76 FPELQVLDLS 86 RCEIQTIEDG96 AYQSLSHLST106 LILTGNPIQS116 LALGAFSGLS126 SLQKLVAVET 136 NLASLENFPI146 GHLKTLKELN156 VAHNLIQSFK166 LPEYFSNLTN176 LEHLDLSSNK 186 IQSIYCTDLR196 VLHQMPLLNL206 SLDLSLNPMN216 FIQPGAFKEI226 RLHKLTLRNN 236 FDSLNVMKTC246 IQGLAGLEVH256 RLVLGEFRNE266 GNLEKFDKSA276 LEGLCNLTIE 286 EFRLAYLDYY296 LDGIIDLFNC306 LTNVSSFSLV316 SVTIERVKDF326 SYNFGWQHLE 336 LVNCKFGQFP346 TLKLKSLKRL356 TFTSNKGGNA366 FSEVDLPSLE376 FLDLSRNGLS 386 FKGCCSQSDF396 GTISLKYLDL406 SFNGVITMSS416 NFLGLEQLEH426 LDFQHSNLKQ 436 MSEFSVFLSL446 RNLIYLDISH456 THTRVAFNGI466 FNGLSSLEVL476 KMAGNSFQEN 486 FLPDIFTELR496 NLTFLDLSQC506 QLEQLSPTAF516 NSLSSLQVLN526 MSHNNFFSLD 536 TFPYKCLNSL546 QVLDYSLNHI556 MTSKKQELQH566 FPSSLAFLNL576 TQNDFACTCE 586 HQSFLQWIKD596 QRQLLVEVER606 MECATPSDKQ616 GMPVLSLNIT626 C |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
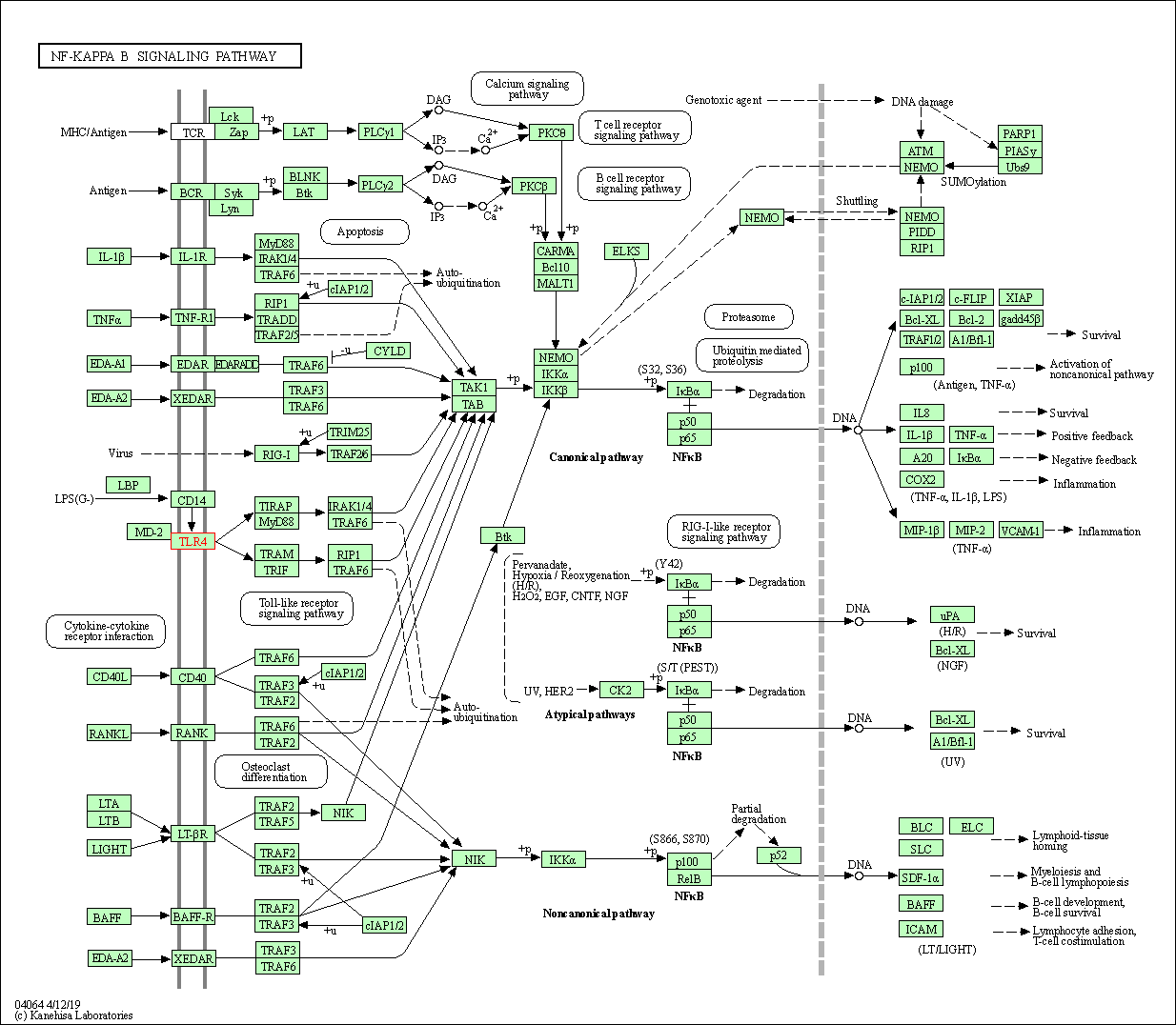
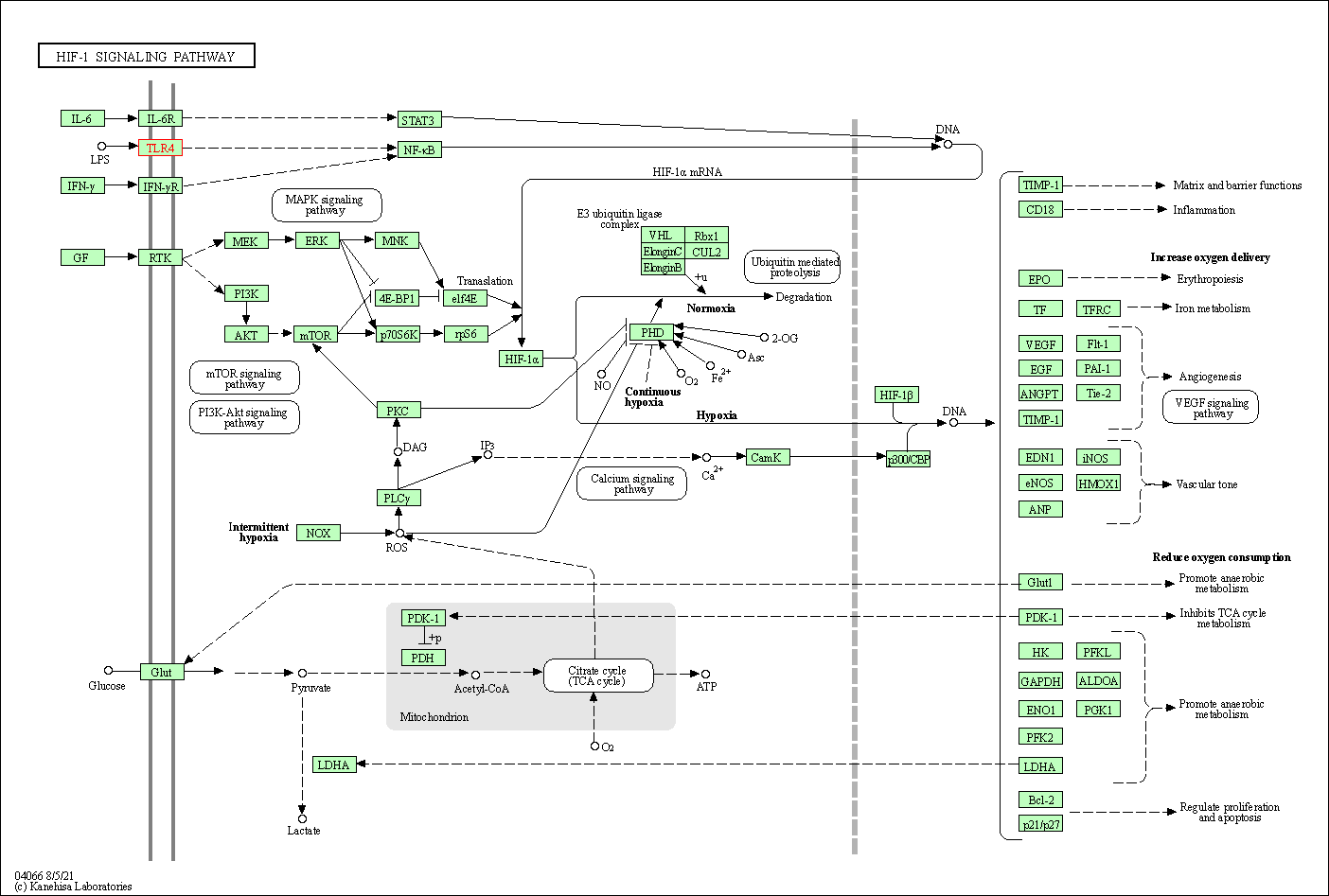
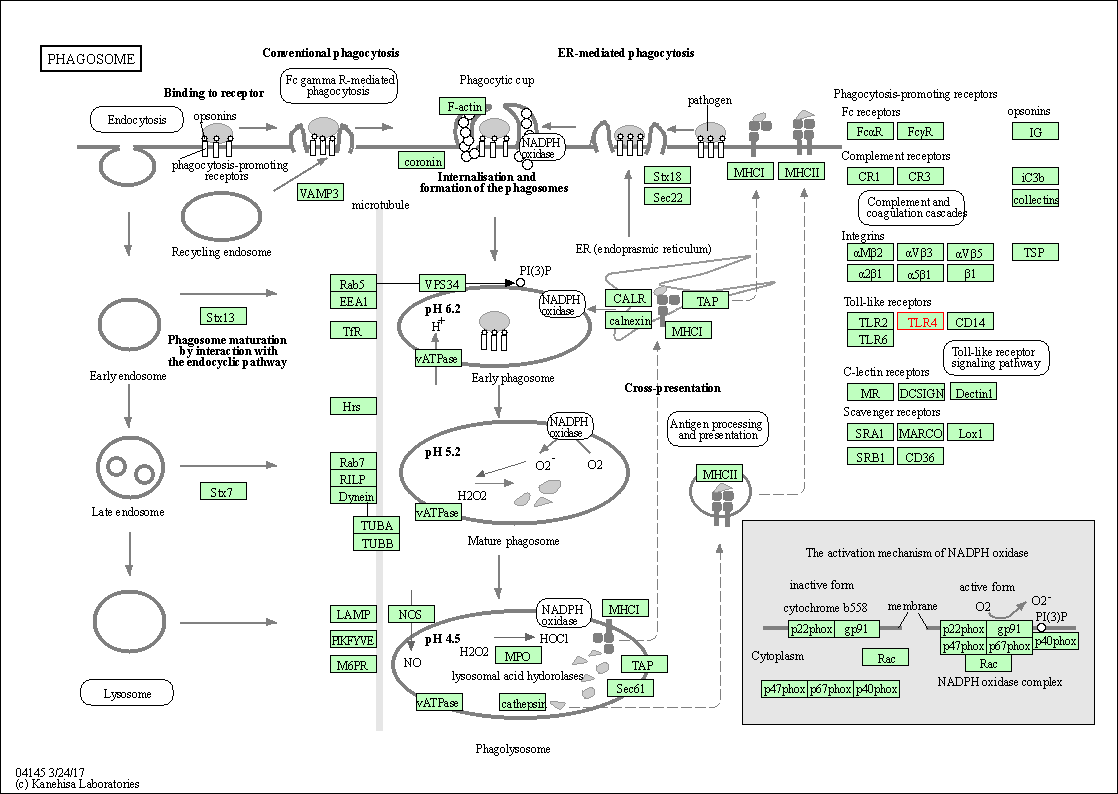
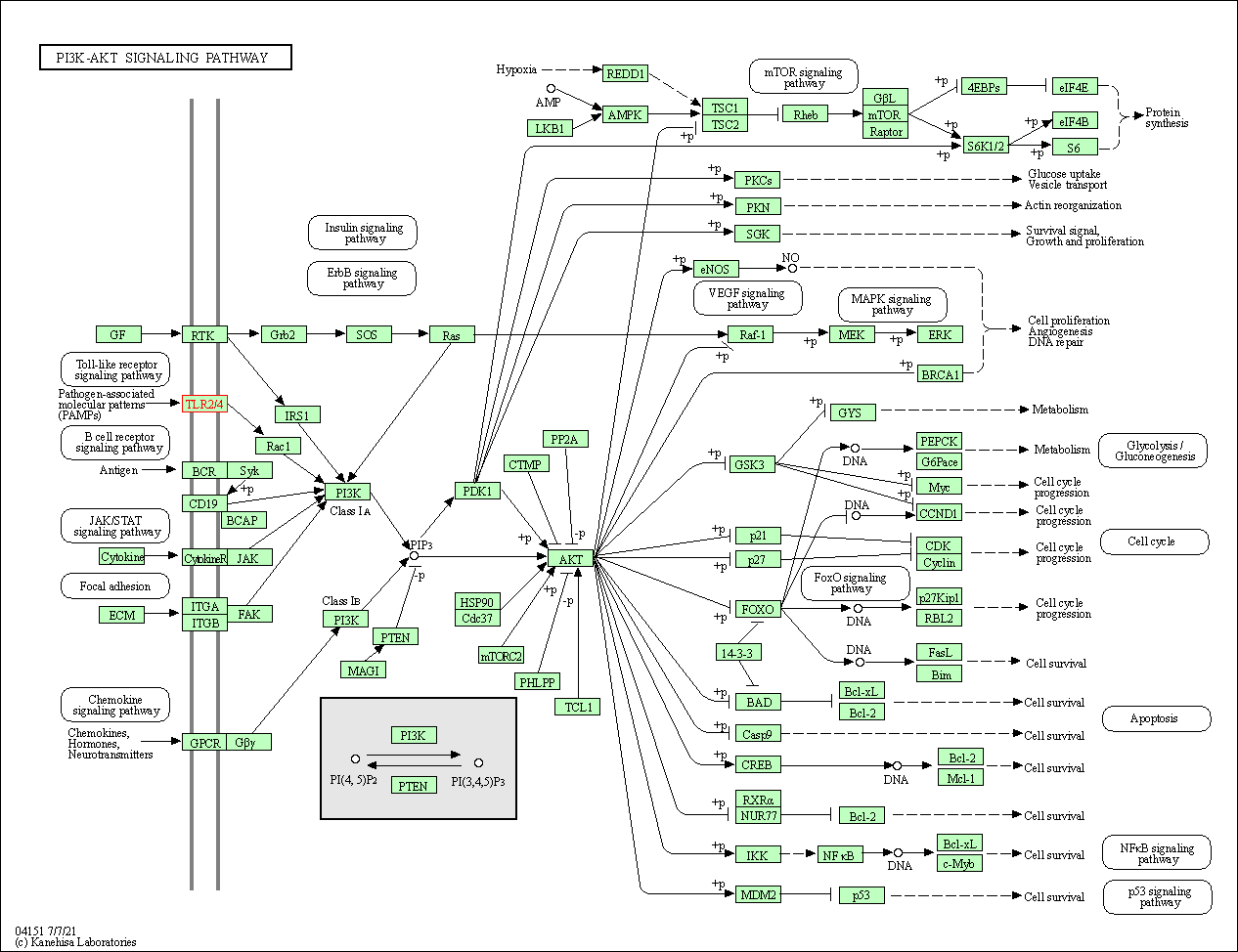


| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phagosome | hsa04145 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
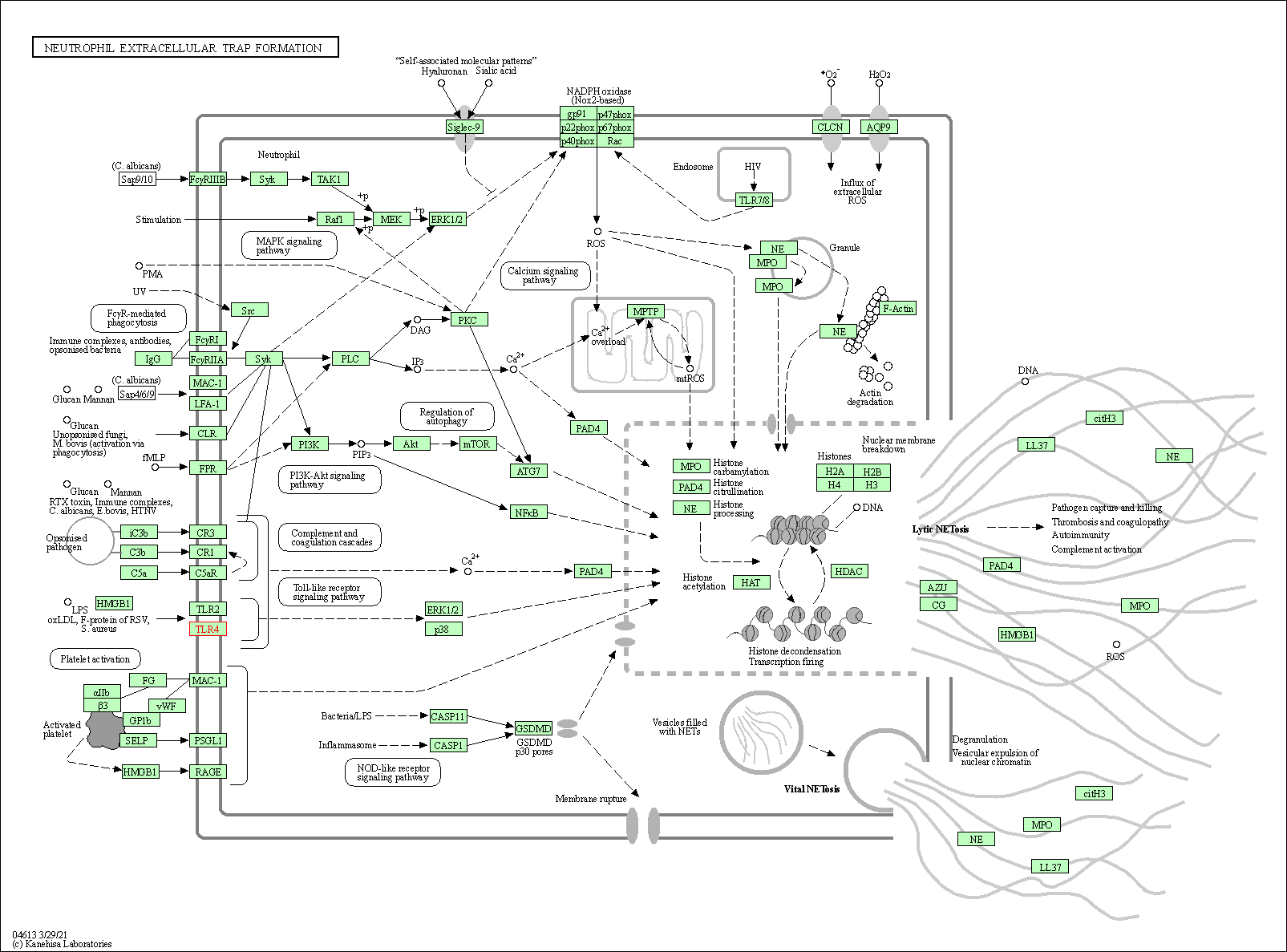
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
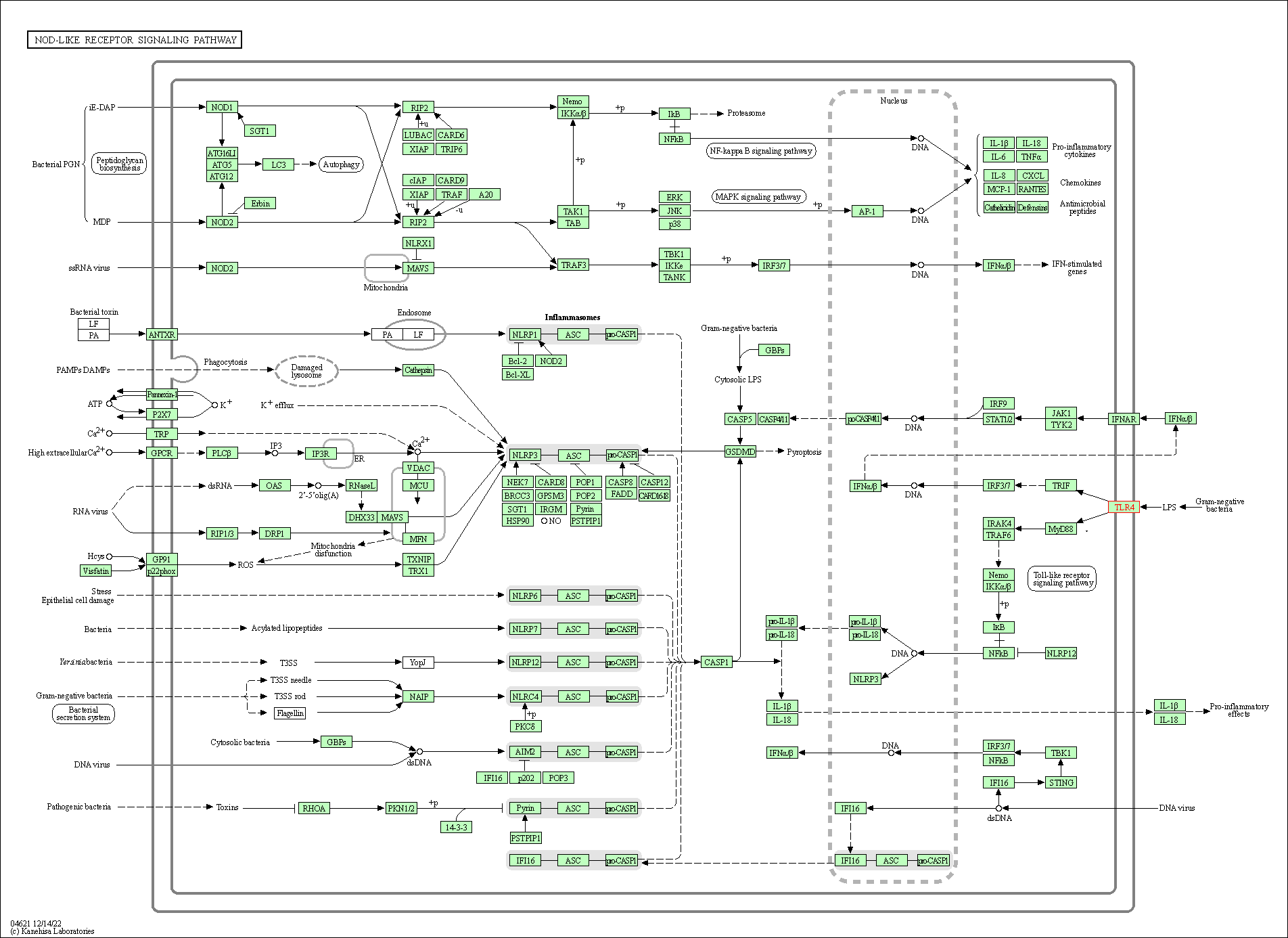
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 41 | Degree centrality | 4.40E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.58E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.50E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.67E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.48E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Allergy Therapeutics PLC. News Announcement. Allergy Therapeutics. Clinical Trials. Allergy Therapeutics PLC. 11 October 2006. | |||||
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800010983) | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00810849) A Trial of Adjunctive Prednisolone and Mycobacterium w Immunotherapy in Tuberculous Pericarditis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4919). | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00334828) ACCESS: A Controlled Comparison of Eritoran Tetrasodium and Placebo in Patients With Severe Sepsis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00633477) Efficacy and Safety of Resatorvid in Patients With Sepsis-induced Cardiovascular and Respiratory Failure. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00076037) Safety of and Immune Response to a New HIV Vaccine: HIV CTL MEP. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01808469) First in Human Study of an Anti-Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Monoclonal Antibody (NI-0101) in Adult Healthy Volunteers. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01800812) Effects of OM-174 in Adult Patients With Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800032166) | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800006001) | |||||
| REF 13 | Trial Watch: Experimental Toll-like receptor agonists for cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology. 2012 August 1; 1(5): 699-716. | |||||
| REF 14 | Small molecule modulators of toll-like receptors. J Med Chem. 2008 Nov 13;51(21):6621-6. | |||||
| REF 15 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Takeda (2009). | |||||
| REF 16 | THE NOVEL SELECTIVE TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR 4 SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION INHIBITOR TAK-242 PREVENTS ENDOTOXAEMIA IN CONSCIOUS GUINEA-PIGS. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology Volume 36, Issue 5-6, pages 589-593, May/June 2009 | |||||
| REF 17 | TAK-242 selectively suppresses Toll-like receptor 4-signaling mediated by the intracellular domain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 14;584(1):40-8. | |||||
| REF 18 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1754). | |||||
| REF 19 | Phase I study of OM-174, a lipid A analogue, with assessment of immunological response, in patients with refractory solid tumors. BMC Cancer. 2013 Apr 2;13:172. | |||||
| REF 20 | Eritoran insight for influenza treatment. SciBX 6(19); doi:10.1038/scibx.2013.453. May 16 2013 | |||||
| REF 21 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 22 | The 'Ethereal' nature of TLR4 agonism and antagonism in the AGP class of lipid A mimetics. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Oct 15;18(20):5350-4. | |||||
| REF 23 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 24 | Characterization of CD8+ T-cell responses in the peripheral blood and skin injection sites of melanoma patients treated with mRNA electroporated autologous dendritic cells (TriMixDC-MEL). Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:976383. | |||||
| REF 25 | Structure-based rational design of a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) decoy receptor with high binding affinity for a target protein. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30929. | |||||
| REF 26 | Structural analyses of human Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms D299G and T399I. J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40611-7. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

