Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T88729
(Former ID: TTDR00082)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
UCP 1; UCP; Thermogenin; Solute carrier family 25 member 7; SLC25A7; Mitochondrial brown fat uncoupling protein 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
UCP1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B80-5B81] | |||||
| Function |
Functions as a long-chain fatty acid/LCFA and proton symporter, simultaneously transporting one LCFA and one proton through the inner mitochondrial membrane. However, LCFAs remaining associated with the transporter via their hydrophobic tails, it results in an apparent transport of protons activated by LCFAs. Thereby, dissipates the mitochondrial proton gradient and converts the energy of substrate oxydation into heat instead of ATP. Regulates the production of reactive oxygen species/ROS by mitochondria. Mitochondrial protein responsible for thermogenic respiration, a specialized capacity of brown adipose tissue and beige fat that participates to non-shivering adaptive thermogenesis to temperature and diet variations and more generally to the regulation of energy balance.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Mitochondrial carrier
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGGLTASDVHPTLGVQLFSAGIAACLADVITFPLDTAKVRLQVQGECPTSSVIRYKGVLG
TITAVVKTEGRMKLYSGLPAGLQRQISSASLRIGLYDTVQEFLTAGKETAPSLGSKILAG LTTGGVAVFIGQPTEVVKVRLQAQSHLHGIKPRYTGTYNAYRIIATTEGLTGLWKGTTPN LMRSVIINCTELVTYDLMKEAFVKNNILADDVPCHLVSALIAGFCATAMSSPVDVVKTRF INSPPGQYKSVPNCAMKVFTNEGPTAFFKGLVPSFLRLGSWNVIMFVCFEQLKRELSKSR QTMDCAT Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T08U92 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CL-316,243 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Obesity | [2], [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inducer | [+] 2 Inducer drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CL-316,243 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | NC-2100 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
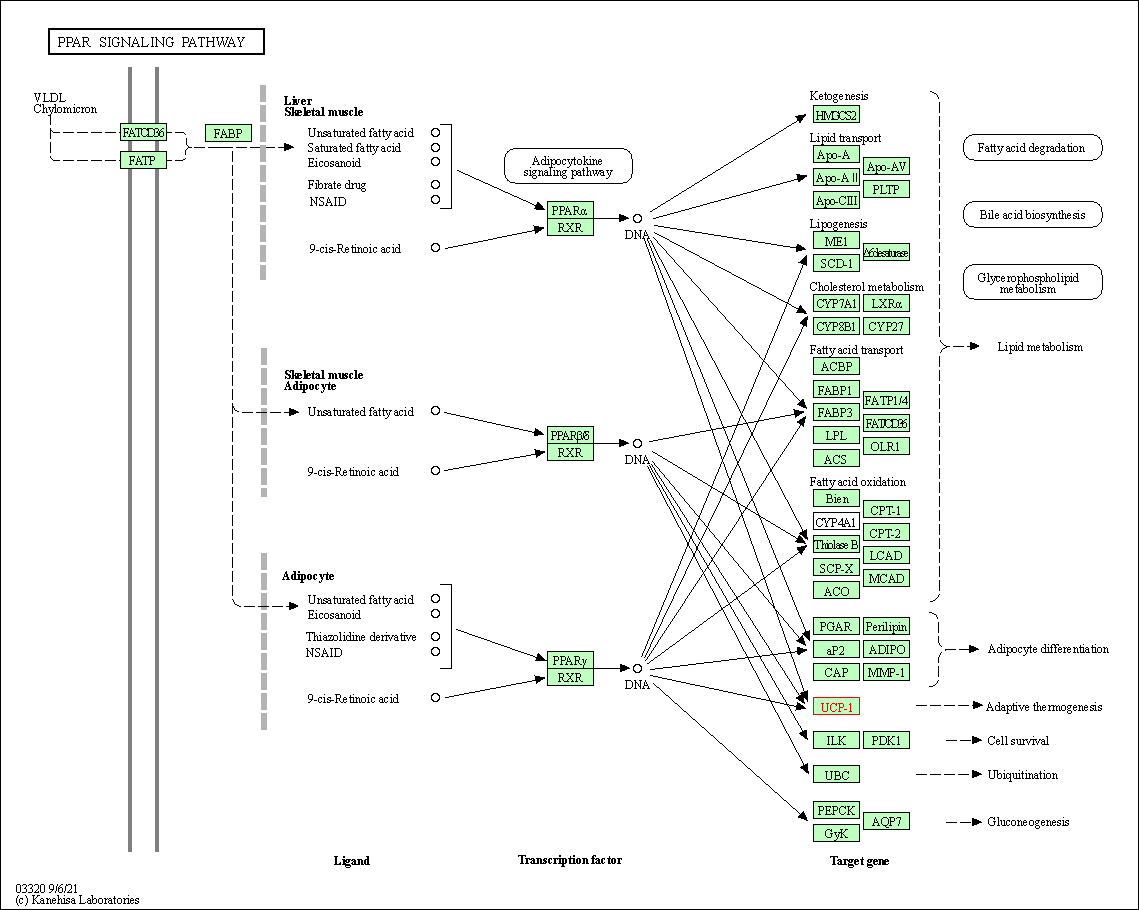
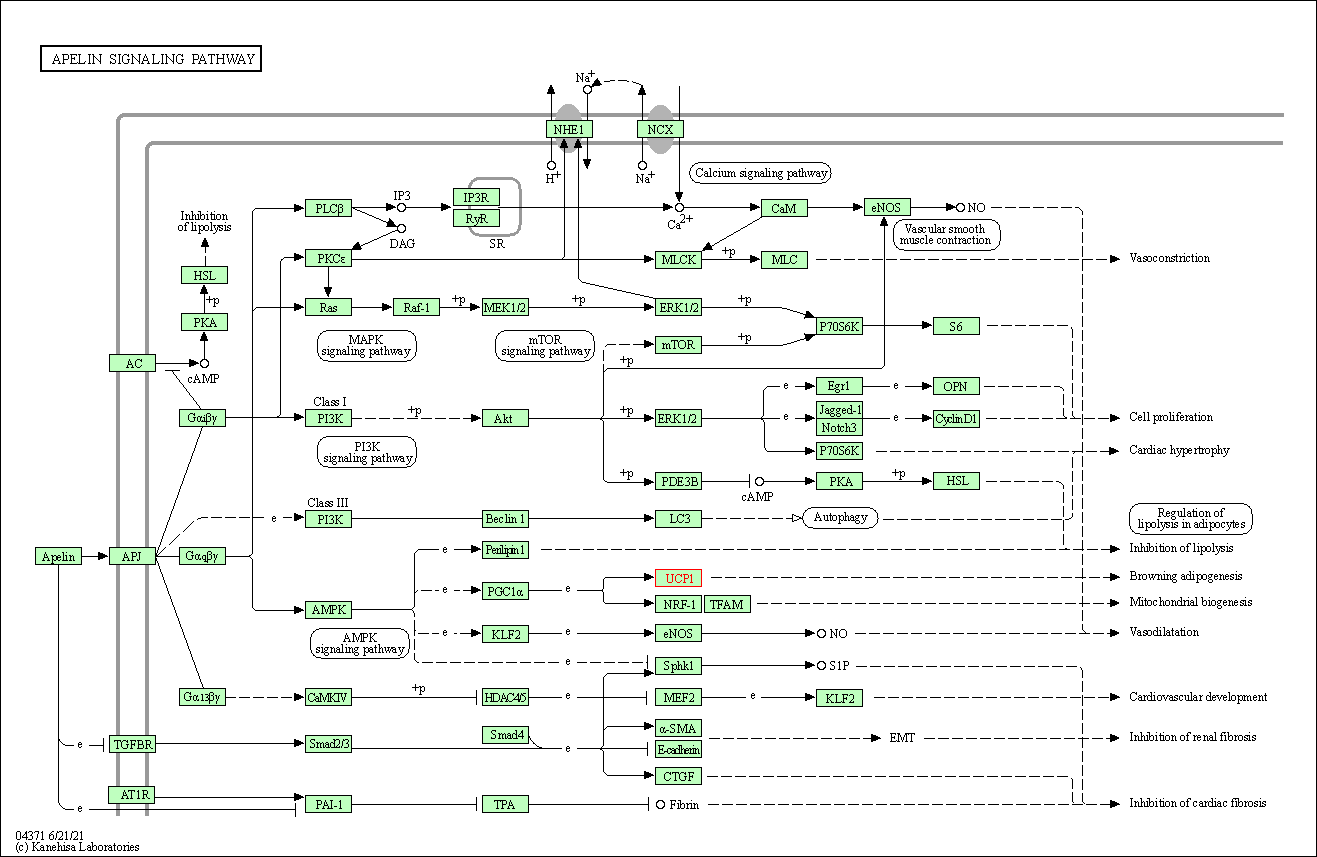
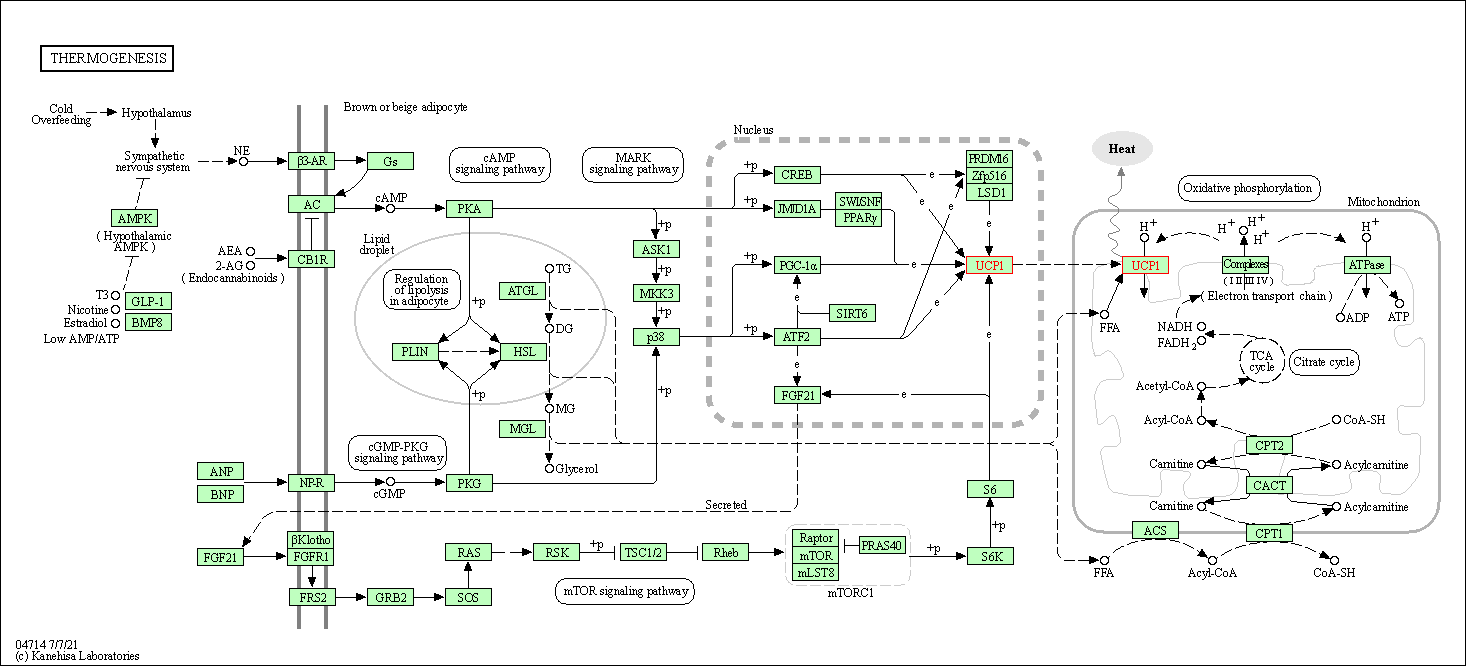
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | PPAR signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Huntington's disease | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Adipogenesis | |||||
| 2 | Respiratory electron transport, ATP synthesis by chemiosmotic coupling, and heat production by uncoupling proteins. | |||||
| 3 | Electron Transport Chain | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of CL316,243, a highly specific beta 3-adrenoceptor agonist, in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats: induction of uncoupling protein and activation of glucose transporter 4 in white fat. Eur J Endocrinol. 1997 Apr;136(4):429-37. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3462). | |||||
| REF 3 | Effect of CL-316,243, a thermogenic beta 3-agonist, on energy balance and brown and white adipose tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):R1371-82. | |||||
| REF 4 | A new thiazolidinedione, NC-2100, which is a weak PPAR-gamma activator, exhibits potent antidiabetic effects and induces uncoupling protein 1 in white adipose tissue of KKAy obese mice. Diabetes. 2000 May;49(5):759-67. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

