Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T94444
(Former ID: TTDS00078)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Aldehyde oxidase (AOX1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
AOX1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
AOX1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 2 | Vitamin deficiency [ICD-11: 5B55-5B5F] | |||||
| Function |
Oxidase with broad substrate specificity, oxidizing aromatic azaheterocycles, such as N1-methylnicotinamide and N- methylphthalazinium, as well as aldehydes, such as benzaldehyde, retinal, pyridoxal, and vanillin. Plays a key role in the metabolism of xenobiotics and drugs containing aromatic azaheterocyclic substituents. Participates in the bioactivation of prodrugs such as famciclovir, catalyzing the oxidation step from 6-deoxypenciclovir topenciclovir, which is a potent antiviral agent. Is probably involved in the regulation of reactive oxygen species homeostasis. May be a prominent source of superoxide generation via the one-electron reduction of molecular oxygen. Also may catalyze nitric oxide (NO) production via the reduction of nitrite to NO with NADH or aldehyde as electron donor. May play a role in adipogenesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Aldehyde/oxo donor oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.2.3.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MDRASELLFYVNGRKVIEKNVDPETMLLPYLRKKLRLTGTKYGCGGGGCGACTVMISRYN
PITKRIRHHPANACLIPICSLYGAAVTTVEGIGSTHTRIHPVQERIAKCHGTQCGFCTPG MVMSIYTLLRNHPEPTLDQLTDALGGNLCRCTGYRPIIDACKTFCKTSGCCQSKENGVCC LDQGINGLPEFEEGSKTSPKLFAEEEFLPLDPTQELIFPPELMIMAEKQSQRTRVFGSER MMWFSPVTLKELLEFKFKYPQAPVIMGNTSVGPEVKFKGVFHPVIISPDRIEELSVVNHA YNGLTLGAGLSLAQVKDILADVVQKLPEEKTQMYHALLKHLGTLAGSQIRNMASLGGHII SRHPDSDLNPILAVGNCTLNLLSKEGKRQIPLNEQFLSKCPNADLKPQEILVSVNIPYSR KWEFVSAFRQAQRQENALAIVNSGMRVFFGEGDGIIRELCISYGGVGPATICAKNSCQKL IGRHWNEQMLDIACRLILNEVSLLGSAPGGKVEFKRTLIISFLFKFYLEVSQILKKMDPV HYPSLADKYESALEDLHSKHHCSTLKYQNIGPKQHPEDPIGHPIMHLSGVKHATGEAIYC DDMPLVDQELFLTFVTSSRAHAKIVSIDLSEALSMPGVVDIMTAEHLSDVNSFCFFTEAE KFLATDKVFCVGQLVCAVLADSEVQAKRAAKRVKIVYQDLEPLILTIEESIQHNSSFKPE RKLEYGNVDEAFKVVDQILEGEIHMGGQEHFYMETQSMLVVPKGEDQEMDVYVSTQFPKY IQDIVASTLKLPANKVMCHVRRVGGAFGGKVLKTGIIAAVTAFAANKHGRAVRCVLERGE DMLITGGRHPYLGKYKAGFMNDGRILALDMEHYSNAGASLDESLFVIEMGLLKMDNAYKF PNLRCRGWACRTNLPSNTAFRGFGFPQAALITESCITEVAAKCGLSPEKVRIINMYKEID QTPYKQEINAKNLIQCWRECMAMSSYSLRKVAVEKFNAENYWKKKGLAMVPLKFPVGLGS RAAGQAAALVHIYLDGSVLVTHGGIEMGQGVHTKMIQVVSRELRMPMSNVHLRGTSTETV PNANISGGSVVADLNGLAVKDACQTLLKRLEPIISKNPKGTWKDWAQTAFDESINLSAVG YFRGYESDMNWEKGEGQPFEYFVYGAACSEVEIDCLTGDHKNIRTDIVMDVGCSINPAID IGQIEGAFIQGMGLYTIEELNYSPQGILHTRGPDQYKIPAICDMPTELHIALLPPSQNSN TLYSSKGLGESGVFLGCSVFFAIHDAVSAARQERGLHGPLTLNSPLTPEKIRMACEDKFT KMIPRDEPGSYVPWNVPI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T31ZFD | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Isovanillin | Drug Info | Approved | Solid tumour/cancer | [2] | |
| 2 | Menadione | Drug Info | Approved | Vitamin K deficiency | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Isovanillin | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 2 | Menadione | Drug Info | [1], [4] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Raloxifene | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human Aldehyde Oxidase SNP R1231H in complex with Raloxifene | PDB:7OPN | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | Yes | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
ASELLFYVNG
13 RKVIEKNVDP23 ETMLLPYLRK33 KLRLTGTKYG43 CGGGGCGACT53 VMISRYNPIT 63 KRIRHHPANA73 CLIPICSLYG83 AAVTTVEGIG93 STHTRIHPVQ103 ERIAKCHGTQ 113 CGFCTPGMVM123 SIYTLLRNHP133 EPTLDQLTDA143 LGGNLCRCTG153 YRPIIDACKT 163 FCKPKLFAEE205 EFLPLDPTQE215 LIFPPELMIM225 AEKQSQRTRV235 FGSERMMWFS 245 PVTLKELLEF255 KFKYPQAPVI265 MGNTSVGPEV275 KFKGVFHPVI285 ISPDRIEELS 295 VVNHAYNGLT305 LGAGLSLAQV315 KDILADVVQK325 LPEEKTQMYH335 ALLKHLGTLA 345 GSQIRNMASL355 GGHIISRHPD365 SDLNPILAVG375 NCTLNLLSKE385 GKRQIPLNEQ 395 FLSKCPNADL405 KPQEILVSVN415 IPYSRKWEFV425 SAFRQAQRQE435 NALAIVNSGM 445 RVFFGEGDGI455 IRELCISYGG465 VGPATICAKN475 SCQKLIGRHW485 NEQMLDIACR 495 LILNEVSLLG505 SAPGGKVEFK515 RTLIISFLFK525 FYLEVSQILK535 KMDPVHYPSL 545 ADKYESALED555 LHSKHHCSTL565 KYQNQHPEDP579 IGHPIMHLSG589 VKHATGEAIY 599 CDDMPLVDQE609 LFLTFVTSSR619 AHAKIVSIDL629 SEALSMPGVV639 DIMTAEHLSD 649 VNSFCFFTEA659 EKFLATDKVF669 CVGQLVCAVL679 ADSEVQAKRA689 AKRVKIVYQD 699 LEPLILTIEE709 SIQHNSSFKP719 ERKLEYGNVD729 EAFKVVDQIL739 EGEIHMGGQE 749 HFYMETQSML759 VVPKGEDQEM769 DVYVSTQFPK779 YIQDIVASTL789 KLPANKVMCH 799 VRRVGGAFGG809 KVLKTGIIAA819 VTAFAANKHG829 RAVRCVLERG839 EDMLITGGRH 849 PYLGKYKAGF859 MNDGRILALD869 MEHYSNAGAS879 LDESLFVIEM889 GLLKMDNAYK 899 FPNLRCRGWA909 CRTNLPSNTA919 FRGFGFPQAA929 LITESCITEV939 AAKCGLSPEK 949 VRIINMYKEI959 DQTPYKQEIN969 AKNLIQCWRE979 CMAMSSYSLR989 KVAVEKFNAE 999 NYWKKKGLAM1009 VPLKFPVGLG1019 SRAAGQAAAL1029 VHIYLDGSVL1039 VTHGGIEMGQ 1049 GVHTKMIQVV1059 SRELRMPMSN1069 VHLRGTSTET1079 VPNANISGGS1089 VVADLNGLAV 1099 KDACQTLLKR1109 LEPIISKNPK1119 GTWKDWAQTA1129 FDESINLSAV1139 GYFRGYESDM 1149 NWEKGEGQPF1159 EYFVYGAACS1169 EVEIDCLTGD1179 HKNIRTDIVM1189 DVGCSINPAI 1199 DIGQIEGAFI1209 QGMGLYTIEE1219 LNYSPQGILH1229 THGPDQYKIP1239 AICDMPTELH 1249 IALLPPSQNS1259 NTLYSSKGLG1269 ESGVFLGCSV1279 FFAIHDAVSA1289 ARQERGLHLT 1301 LNSPLTPEKI1311 RMACEDKFTK1321 MIPRDEPGSY1331 VPWNV
|
|||||
|
|
GLY450
4.842
GLU451
3.416
GLY452
3.076
ASP453
3.330
GLY454
3.255
HIS484
3.408
TRP485
4.241
ASN486
2.885
ASP538
3.751
HIS541
3.336
TYR542
3.143
PHE653
3.688
CYS654
4.557
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Flavin-Adenine Dinucleotide | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human aldehyde oxidase | PDB:4UHW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
ASELLFYVNG
13 RKVIEKNVDP23 ETMLLPYLRK33 KLRLTGTKYG43 CGGGGCGACT53 VMISRYNPIT 63 KRIRHHPANA73 CLIPICSLYG83 AAVTTVEGIG93 STHTRIHPVQ103 ERIAKCHGTQ 113 CGFCTPGMVM123 SIYTLLRNHP133 EPTLDQLTDA143 LGGNLCRCTG153 YRPIIDACKT 163 FCKTPKLFAE204 EEFLPLDPTQ214 ELIFPPELMI224 MAEKQSQRTR234 VFGSERMMWF 244 SPVTLKELLE254 FKFKYPQAPV264 IMGNTSVGPE274 VKFKGVFHPV284 IISPDRIEEL 294 SVVNHAYNGL304 TLGAGLSLAQ314 VKDILADVVQ324 KLPEEKTQMY334 HALLKHLGTL 344 AGSQIRNMAS354 LGGHIISRHP364 DSDLNPILAV374 GNCTLNLLSK384 EGKRQIPLNE 394 QFLSKCPNAD404 LKPQEILVSV414 NIPYSRKWEF424 VSAFRQAQRQ434 ENALAIVNSG 444 MRVFFGEGDG454 IIRELCISYG464 GVGPATICAK474 NSCQKLIGRH484 WNEQMLDIAC 494 RLILNEVSLL504 GSAPGGKVEF514 KRTLIISFLF524 KFYLEVSQIL534 KKMDPVHYPS 544 LADKYESALE554 DLHSHHCSTL565 KYQNPKQHPE577 DPIGHPIMHL587 SGVKHATGEA 597 IYCDDMPLVD607 QELFLTFVTS617 SRAHAKIVSI627 DLSEALSMPG637 VVDIMTAEHL 647 SDVNSFCKFL663 ATDKVFCVGQ673 LVCAVLADSE683 VQAKRAAKRV693 KIVYQDLEPL 703 ILTIEESIQS716 FKPERKLEYG726 NVDEAFKVVD736 QILEGEIHMG746 GQEHFYMETQ 756 SMLVVPKGED766 QEMDVYVSTQ776 FPKYIQDIVA786 STLKLPANKV796 MCHVRRVGGA 806 FGGKVLKTGI816 IAAVTAFAAN826 KHGRAVRCVL836 ERGEDMLITG846 GRHPYLGKYK 856 AGFMNDGRIL866 ALDMEHYSNA876 GASLSLFVIE888 MGLLKMDNAY898 KFPNLRCRGW 908 ACRTNLPSNT918 AFRGFGFPQA928 ALITESCITE938 VAAKCGLSPE948 KVRIINMYKE 958 IDQTPYKQEI968 NAKNLIQCWR978 ECMAMSSYSL988 RKVAVEKFNA998 ENYWKKKGLA 1008 MVPLKFPVGL1018 GSRAAGQAAA1028 LVHIYLDGSV1038 LVTHGGIEMG1048 QGVHTKMIQV 1058 VSRELRMPMS1068 NVHLRGTSTE1078 TVPNANISGG1088 SVVADLNGLA1098 VKDACQTLLK 1108 RLEPIISKNP1118 KGTWKDWAQT1128 AFDESINLSA1138 VGYFRGYESD1148 MNWEKGEGQP 1158 FEYFVYGAAC1168 SEVEIDCLTG1178 DHKNIRTDIV1188 MDVGCSINPA1198 IDIGQIEGAF 1208 IQGMGLYTIE1218 ELNYSPQGIL1228 HTRGPDQYKI1238 PAICDMPTEL1248 HIALLPPSQN 1258 SNTLYSSKGL1268 GESGVFLGCS1278 VFFAIHDAVS1288 AARQERGLHG1298 PLTLNSPLTP 1308 EKIRMACEDK1318 FTKMIPRDEP1328 GSYVPWNV
|
|||||
|
|
GLY46
3.355
GLY47
3.557
GLY48
3.867
LEU75
4.282
ALA262
4.918
PRO263
3.341
VAL264
2.846
ILE265
3.730
MET266
2.880
GLY267
2.921
ASN268
3.074
THR269
2.682
SER270
2.901
VAL271
2.940
GLY272
4.819
PRO273
4.201
LEU294
4.761
ALA308
4.179
LEU312
3.952
THR343
4.443
LEU344
3.436
ALA345
3.151
ILE349
3.840
MET352
4.433
ALA353
3.521
SER354
2.963
GLY356
3.967
GLY357
3.511
HIS358
3.280
ILE360
3.694
SER361
3.652
HIS363
3.500
ASP365
4.146
SER366
3.474
ASP367
2.766
LEU368
4.586
LEU405
4.173
GLU409
4.618
ILE410
3.696
LEU411
3.006
ARG429
3.924
ASN436
4.520
ALA437
3.813
LEU438
3.453
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
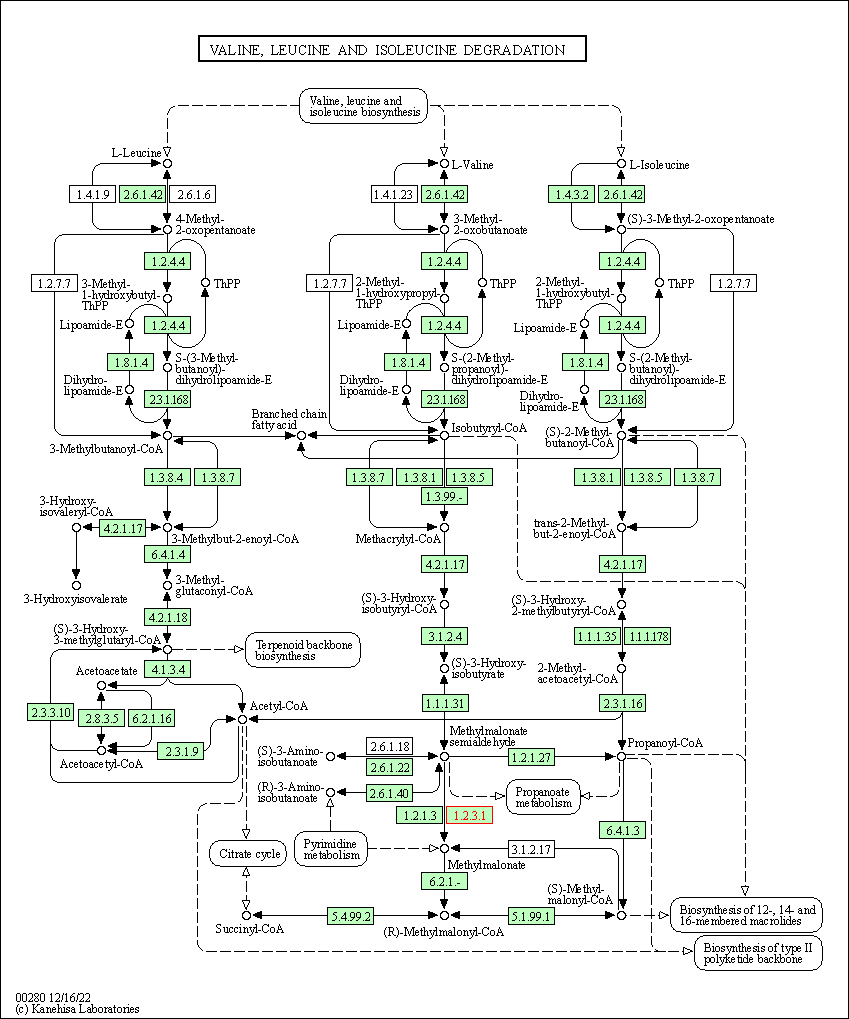
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | hsa00280 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
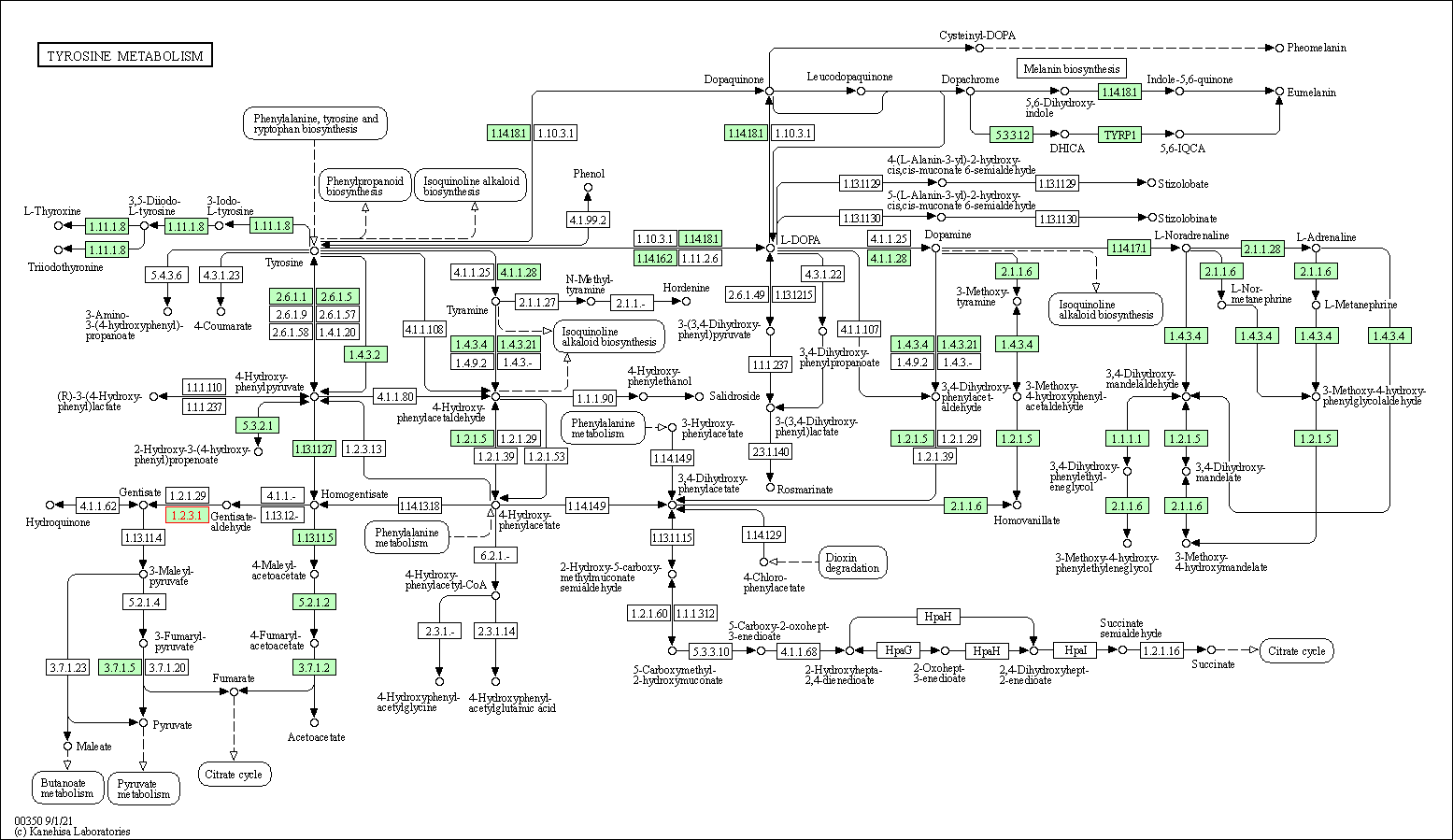
| Tyrosine metabolism | hsa00350 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
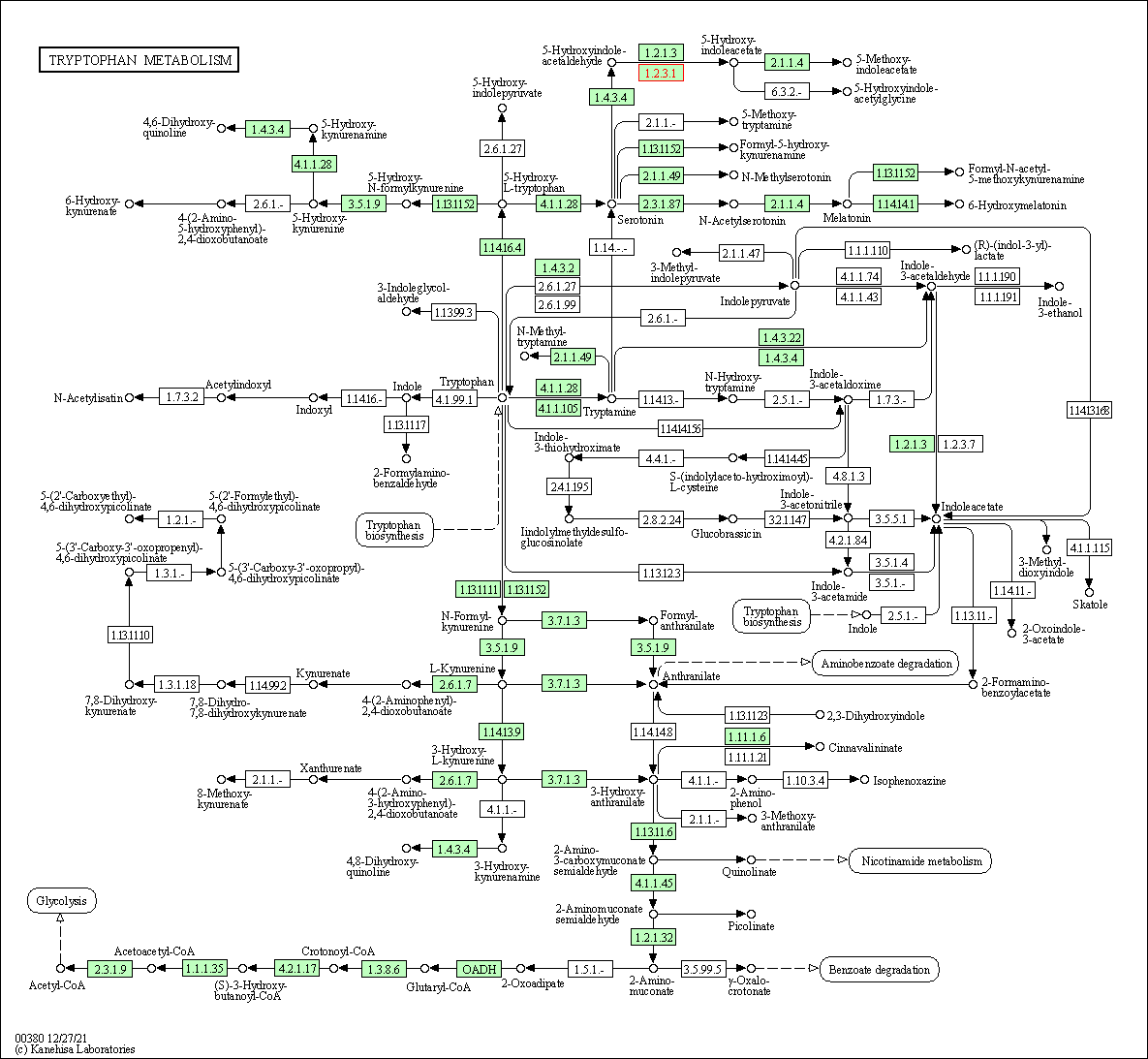
| Tryptophan metabolism | hsa00380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
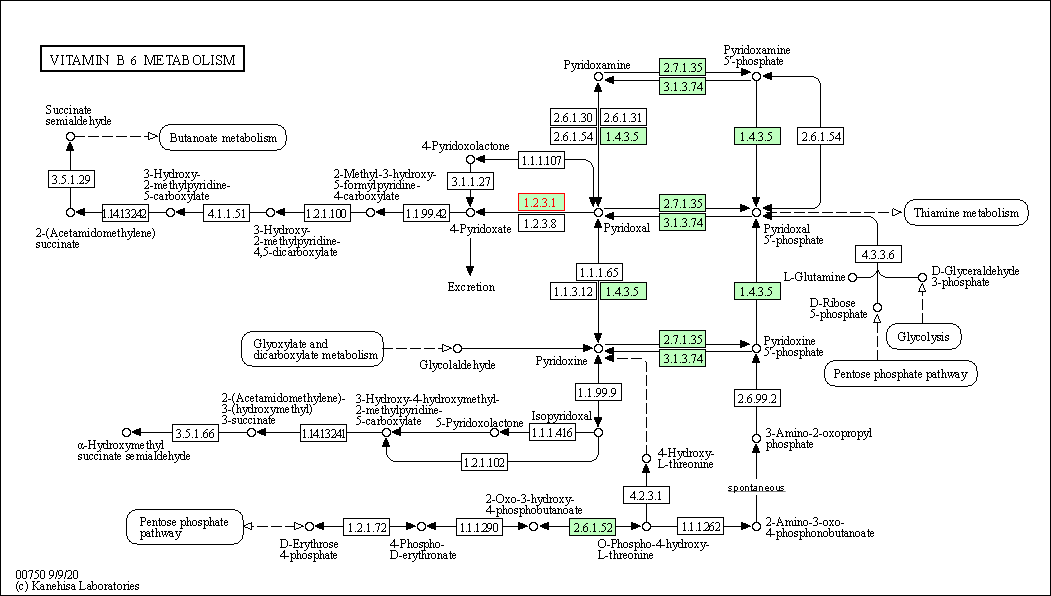
| Vitamin B6 metabolism | hsa00750 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
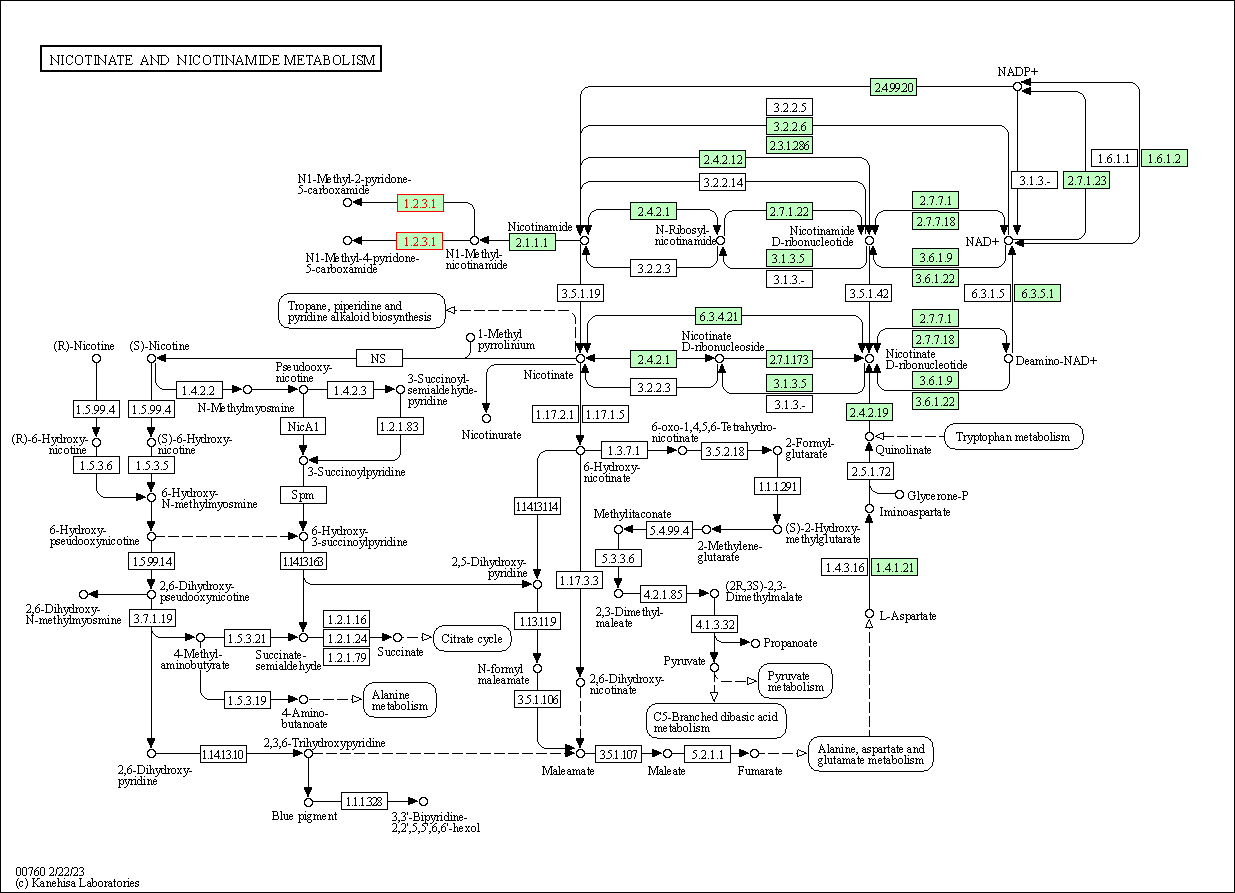
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | hsa00760 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
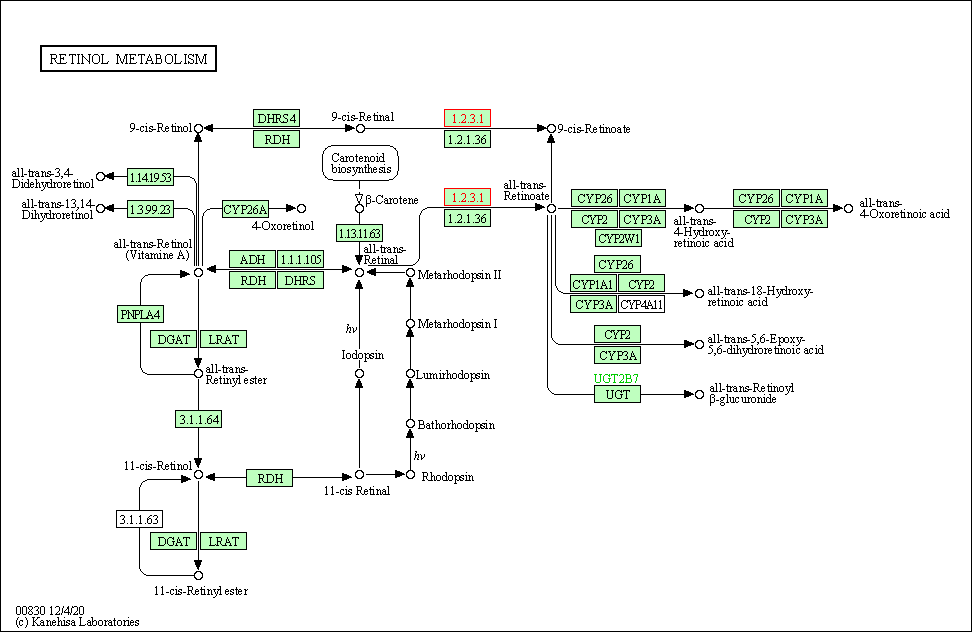
| Retinol metabolism | hsa00830 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
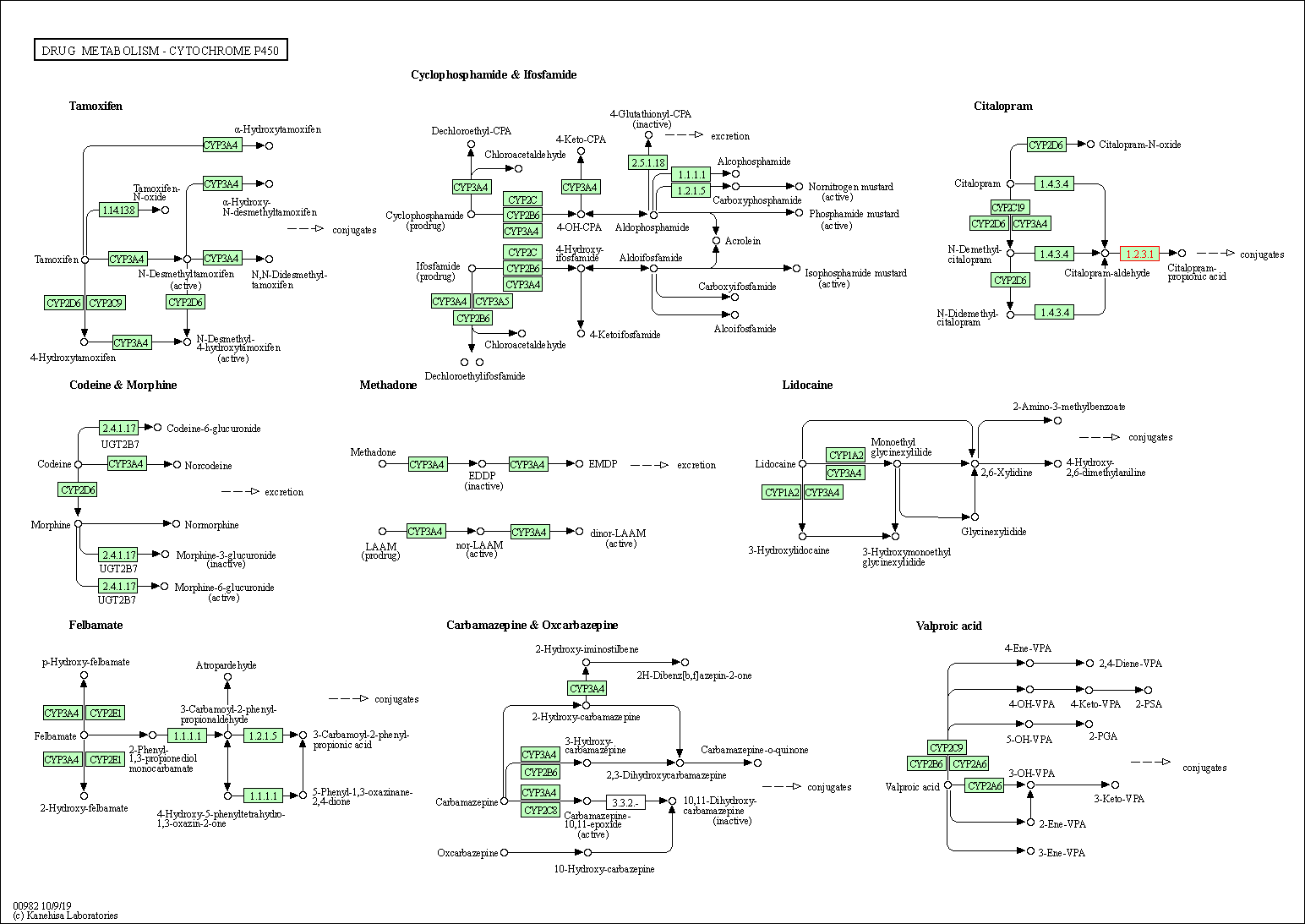
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | hsa00982 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
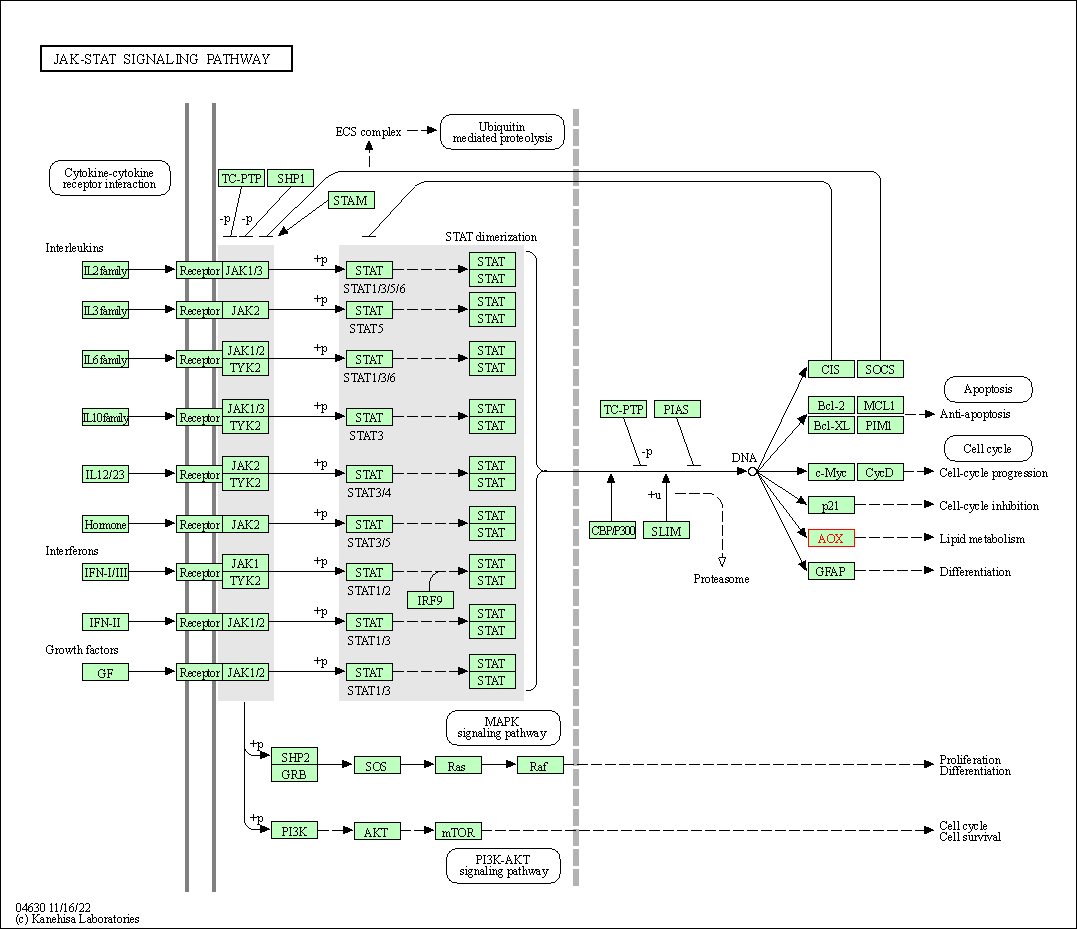
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 2 | Degree centrality | 2.15E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 4.27E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.79E-01 | Radiality | 1.29E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.50E+00 | Topological coefficient | 5.00E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 2 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Nicotine degradation III | |||||
| 2 | Nicotine degradation IV | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 8 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | |||||
| 2 | Tyrosine metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Tryptophan metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Vitamin B6 metabolism | |||||
| 5 | Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | |||||
| 6 | Retinol metabolism | |||||
| 7 | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | |||||
| 8 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 2 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Leptin Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 4 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine Degradation | |||||
| 2 | Vitamin B6 Metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Tryptophan Metabolism | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Tryptophan metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Effects of Nitric Oxide | |||||
| 3 | Metabolism of water-soluble vitamins and cofactors | |||||
| 4 | Nicotine Metabolism | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Inhibition by SKF-525A of the aldehyde oxidase-mediated metabolism of the experimental antitumour agent acridine carboxamide. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 May 25;45(10):2159-62. | |||||
| REF 2 | Contribution of aldehyde oxidizing enzymes on the metabolism of 3,4-dimethoxy-2-phenylethylamine to 3,4-dimethoxyphenylacetic acid by guinea pig li... Cell Physiol Biochem. 2006;17(1-2):47-56. | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 002139. | |||||
| REF 4 | Cytosol mediated metabolism of the experimental antitumor agent acridine carboxamide to the 9-acridone derivative. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 24;42(10):1879-84. | |||||
| REF 5 | Interrogating the Inhibition Mechanisms of Human Aldehyde Oxidase by X-ray Crystallography and NMR Spectroscopy: The Raloxifene Case. J Med Chem. 2021 Sep 9;64(17):13025-13037. | |||||
| REF 6 | Structural insights into xenobiotic and inhibitor binding to human aldehyde oxidase. Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Oct;11(10):779-83. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

